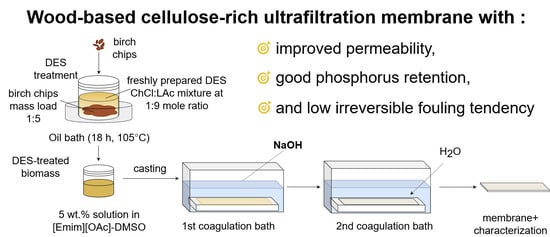
Wood-Based Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membranes: Alkaline Coagulation Bath Introduction and Investigation of Its Effect over Membranes’ Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. DES Treatment
2.2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.2.3. Membrane Permeability and Retention Measurements
2.2.4. Membrane Characterisation
Examination of the Zeta Potential of the Membranes
Examination of the Chemical Structure of the Membranes
Examination of the Hydrophilicity of the Membranes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Membrane Characteristics Due to the Alkaline Treatment
3.2. Membrane Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dang, H.T.; Narbaitz, R.M.; Matsuura, T.; Khulbe, K.C. A Comparison of Commercial and Experimental Ultrafiltration Membranes via Surface Property Analysis and Fouling Tests. Water Qual. Res. J. 2006, 41, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Abd. Mutalib, M.; Jamil, S.M. Feasibility of Recycled Newspaper as Cellulose Source for Regenerated Cellulose Membrane Fabrication. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopakumar, D.A.; Arumughan, V.; Pasquini, D.; Leu, S.Y.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Thomas, S. Nanocellulose-Based Membranes for Water Purification. In Nanoscale Materials in Water Purification; Thomas, S., Pasquini, D., Leu, S.-Y., Gopakumar, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 59–85. ISBN 978-0-12-813926-4. [Google Scholar]
- Nancy, L.; Jackie, Z.; Hadi, P.; Yang, M.; Huang, X.; Ma, H.; Walke, H.W.; Hsiao, B.S. Synthesis and Characterization of a High Flux Nanocellulose–Cellulose Acetate Nanocomposite Membrane. Membranes 2019, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acharya, S.; Liyanage, S.; Abidi, N.; Parajuli, P.; Rumi, S.S.; Shamshina, J.L. Utilization of Cellulose to Its Full Potential: A Review on Cellulose Dissolution, Regeneration, and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medronho, B.; Lindman, B. Competing Forces during Cellulose Dissolution: From Solvents to Mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.C.H. Cellulose Solutions: Dissolution, Regeneration, Solution Structure and Molecular Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, L.; Medronho, B.; Antunes, F.E.; Topgaard, D.; Lindman, B. Dissolution State of Cellulose in Aqueous Systems. 1. Alkaline Solvents. Cellulose 2016, 23, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Medronho, B.; Eivazi, A.; Svanedal, I. Lignin Enhances Cellulose Dissolution in Cold Alkali. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallioinen, M.; Mänttäri, M.; Nyström, M.; Nuortila-Jokinen, J.; Nurminen, P.; Sutela, T. Membrane Evaluation for the Treatment of Acidic Clear Filtrate. Desalination 2010, 250, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Razak, N.H.; Chew, Y.M.J.; Bird, M.R. Membrane Fouling during the Fractionation of Phytosterols Isolated from Orange Juice. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 113, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, N.S.N.; Zakaria, S.; Gan, S.; Hua, C.C.; Baharin, K.W. Comparison of Regenerated Cellulose Membrane Coagulated in Sulphate Based Coagulant. Cerne 2019, 25, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, D.; Nunes, S.P.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Figoli, A.; Lee, Y.M. Recent Advances in Polymer Membranes Employing Non-Toxic Solvents and Materials. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 9815–9843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livazovic, S.; Li, Z.; Behzad, A.R.; Peinemann, K.V.; Nunes, S.P. Cellulose Multilayer Membranes Manufacture with Ionic Liquid. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anokhina, T.S.; Pleshivtseva, T.S.; Ignatenko, V.Y.; Antonov, S.V.; Volkov, A.V. Fabrication of Composite Nanofiltration Membranes from Cellulose Solutions in an [Emim]OAc–DMSO Mixture. Pet. Chem. 2017, 57, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, E.N.; Çulfaz-Emecen, P.Z. Cellulose-Based Membranes via Phase Inversion Using [EMIM]OAc-DMSO Mixtures as Solvent. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 178, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Meireles, C.; Filho, G.R.; Fernandes Ferreira, M.; Cerqueira, D.A.; Assunção, R.M.N.; Ribeiro, E.A.M.; Poletto, P.; Zeni, M. Characterization of Asymmetric Membranes of Cellulose Acetate from Biomass: Newspaper and Mango Seed. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopatina, A.; Anugwom, I.; Esmaeili, M.; Puro, L.; Virtanen, T.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen, M. Preparation of Cellulose-Rich Membranes from Wood: Effect of Wood Pretreatment Process on Membrane Performance. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9505–9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kai, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Z. Facile Fabrication of Cellulose Membrane Containing Polyiodides and Its Antibacterial Properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 500, 144046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of Cellulose with Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhi, A.; Le, K.A.; Ries, M.E.; Budtova, T. Macroscopic and Microscopic Study of 1-Ethyl-3-Methyl-Imidazolium Acetate-DMSO Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. Eco-Fabrication of Antibacterial Nanofibrous Membrane with High Moisture Permeability from Wasted Wool Fabrics. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J. Processing and Valorization of Cellulose, Lignin and Lignocellulose Using Ionic Liquids. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.A.; Rudaz, C.; Budtova, T. Phase Diagram, Solubility Limit and Hydrodynamic Properties of Cellulose in Binary Solvents with Ionic Liquid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, H.; Yumei, Z.; Huaping, W. Physical Properties and Solubility Parameters of 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Based Ionic Liquids/DMSO Mixtures at 298.15 K. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 2015, 89, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmar, A.S.M.; Koch, D.; Prymak, O.; Ulbricht, M. Factors Affecting the Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation of Cellulose from Ionic Liquid-Based Solutions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27314–27322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Nunes, S.P. Green Solvents for Membrane Manufacture: Recent Trends and Perspectives. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 28, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevstrueva, D.; Pihlajamäki, A.; Nikkola, J.; Mänttäri, M. Effect of Precipitation Temperature on the Properties of Cellulose Ultrafiltration Membranes Prepared via Immersion Precipitation with Ionic Liquid as Solvent. Membranes 2018, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, H.; Wu, C.; Hu, X. Formation and Characterization of Cellulose Membranes from N-Methylmorpholine-N-Oxide Solution. Macromol. Biosci. 2001, 1, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duolikun, T.; Ghazali, N.; Leo, B.F.; Lee, H.V.; Lai, C.W.; Bin Johan, M.R. Asymmetric Cellulosic Membranes: Current and Future Aspects. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frollini, E.; Ass, B.A.P. Linters Cellulose: Characterization and Acetylation in N, n-Dimethylacetamide/Lithium Chloride. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Natural Polymers and Composites, 8th Brazilian Symposium on the Chemistry of Lignins and Other Wood Component. pp. 25–28. Available online: https://www.eucalyptus.com.br/artigos/2004_Eigth+Symposium+Lignins+Wood+Components_Arquivo+78.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Sescousse, R.; Smacchia, A.; Budtova, T. Influence of Lignin on Cellulose-NaOH-Water Mixtures Properties and on Aerocellulose Morphology. Cellulose 2010, 17, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melro, E.; Alves, L.; Antunes, F.E.; Medronho, B. A Brief Overview on Lignin Dissolution. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 265, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensson, B.; Larsson, A.; Hasani, M. Dissolution of Cellulose Using a Combination of Hydroxide Bases in Aqueous Solution. Cellulose 2020, 27, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Yang, Q.; Cai, J.; Kuga, S.; Matsumoto, Y. Effects of Lignin and Hemicellulose Contents on Dissolution of Wood Pulp in Aqueous NaOH/Urea Solution. Cellulose 2014, 21, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribitsch, V.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Kreze, T.; Strnad, S. The Significance of Surface Charge and Structure on the Accessibility of Cellulose Fibres. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciacco, G.T.; Morgado, D.L.; Frollini, E.; Possidonio, S.; El Seoud, O.A. Some Aspects of Acetylation of Untreated and Mercerized Sisal Cellulose. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindman, B.; Medronho, B.; Alves, L.; Costa, C.; Edlund, H.; Norgren, M. The Relevance of Structural Features of Cellulose and Its Interactions to Dissolution, Regeneration, Gelation and Plasticization Phenomena. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 23704–23718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, M.L.; O’Connor, R.T. Relation of Certain Infrared Bands to Cellulose Crystallinity and Crystal Lattice Type. Part II. A New Infrared Ratio for Estimation of Crystallinity in Celluloses I and II. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1964, 8, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.L.; O’Connor, R.T. Relation of Certain Infrared Bands to Cellulose Crystallinity and Crystal Latticed Type. Part I. Spectra of Lattice Types I, II, III and of Amorphous Cellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1964, 8, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hallström, B. Membrane Characterization Using the Contact Angle Technique I. Methodology of the Captive Bubble Technique. Desalination 1990, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatzos, S.K.; Edye, L.A.; Wellard, R.M. The Undesirable Acetylation of Cellulose by the Acetate Ion of 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Acetate. Cellulose 2012, 19, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciolacu, D.; Ciolacu, F.; Popa, V.I. Amorphous Cellulose—Structure and Characterization. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2011, 45, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.L.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhu, B.K.; Xu, Y.Y. High-Flux and Anti-Fouling Cellulose Nanofiltration Membranes Prepared via Phase Inversion with Ionic Liquid as Solvent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 83, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljun, A.; Benians, T.A.S.; Goubet, F.; Meulewaeter, F.; Knox, J.P.; Blackburn, R.S. Comparative Analysis of Crystallinity Changes in Cellulose i Polymers Using ATR-FTIR, X-Ray Diffraction, and Carbohydrate-Binding Module Probes. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 4121–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyraz, B.; Tozluoğlu, A.; Candan, Z.; Demir, A.; Yavuz, M.; Büyuksarı, Ü.; Ünal, H.İ.; Fidan, H.; Saka, R.C. TEMPO-Treated CNF Composites: Pulp and Matrix Effect. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Qiao, X.; Hou, X.; He, C. Fabrication of Cellulose Membrane with “Imprinted Morphology” and Low Crystallinity from Spherulitic [Bmim]Cl. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Recent Progress in Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy Study of Compositional, Structural and Physical Attributes of Developmental Cotton Fibers. Materials 2013, 6, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabov, K.; Oja, T.; Deguchi, T.; Fallarero, A.; Fardim, P. Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Application of Hybrid Cellulose-Lignin Beads. Cellulose 2017, 24, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Winestrand, S.; Gillgren, T.; Jönsson, L.J. Chemical and Structural Factors Influencing Enzymatic Saccharification of Wood from Aspen, Birch and Spruce. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 109, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, S.; Shobana, K.H.; Anitharaj, S.; Mohan, D.R. Preparation, Morphology, Performance, and Hydrophilicity Studies of Poly(Amide-Imide) Incorporated Cellulose Acetate Ultrafiltration Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 5550–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Plume, S.; Ernst, M.; Croué, J.P.; Jekel, M. In-Line Coagulation Prior to UF of Treated Domestic Wastewater—Foulants Removal, Fouling Control and Phosphorus Removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 403–404, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.P. Improvement of Ultrafiltration for Treatment of Phosphorus-Containing Water by a Lanthanum-Modified Aminated Polyacrylonitrile Membrane. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7170–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyvän Pilotointi on Meneillään Toikansuolla Lappeenrannan Energia. Available online: https://www.lappeenrannanenergia.fi/hyva-blogi/hyvan-pilotointi-meneillaan-toikansuolla (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Warsinger, D.M.; Chakraborty, S.; Tow, E.W.; Plumlee, M.H.; Bellona, C.; Loutatidou, S.; Karimi, L.; Mikelonis, A.M.; Achilli, A.; Ghassemi, A.; et al. A Review of Polymeric Membranes and Processes for Potable Water Reuse. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Hadi, P.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, X.; Ma, H.; Walker, H.; Hsiao, B.S. Antifouling Nanocellulose Membranes: How Subtle Adjustment of Surface Charge Lead to Self-Cleaning Property. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| NaOH Concentration, wt.% | Time Spent in NaOH Coagulation Bath, Min | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 30 | 60 | |
| 0 | 0/0 | - | - |
| 5 | - | 5/30 | 5/60 |
| 10 | - | 10/30 | 10/60 |
| FTIR | Zeta Potential | Amicon (Dead-End) | Cross-Flow | Contact Angle | P Tubes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWP | PEG Retention | CaCO3 | WW Flux | PWP | WW Flux | |||||
| 0/0 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||||
| 5/30 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||||
| 5/60 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||||
| 10/30 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
| 10/60 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| 10/60 | 10/30 | RC70PP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure water flux before wastewater filtration at 2 bar, L/(m2h) | 460 | 440 | 150 |
| Wastewater flux at the beginning (8 min), L/(m2h) | 106 | 105 | 64 |
| Wastewater flux at VRF ~3 (11 days), L/(m2h) | 69 | 68 | 42 |
| Phosphorous removal, % | 67 | 69 | 68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopatina, A.; Liukkonen, A.; Bec, S.; Anugwom, I.; Nieminen, J.; Mänttäri, M.; Kallioinen-Mänttäri, M. Wood-Based Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membranes: Alkaline Coagulation Bath Introduction and Investigation of Its Effect over Membranes’ Performance. Membranes 2022, 12, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060581
Lopatina A, Liukkonen A, Bec S, Anugwom I, Nieminen J, Mänttäri M, Kallioinen-Mänttäri M. Wood-Based Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membranes: Alkaline Coagulation Bath Introduction and Investigation of Its Effect over Membranes’ Performance. Membranes. 2022; 12(6):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060581
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopatina, Anastasiia, Alma Liukkonen, Sabina Bec, Ikenna Anugwom, Joona Nieminen, Mika Mänttäri, and Mari Kallioinen-Mänttäri. 2022. "Wood-Based Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membranes: Alkaline Coagulation Bath Introduction and Investigation of Its Effect over Membranes’ Performance" Membranes 12, no. 6: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060581
APA StyleLopatina, A., Liukkonen, A., Bec, S., Anugwom, I., Nieminen, J., Mänttäri, M., & Kallioinen-Mänttäri, M. (2022). Wood-Based Cellulose-Rich Ultrafiltration Membranes: Alkaline Coagulation Bath Introduction and Investigation of Its Effect over Membranes’ Performance. Membranes, 12(6), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060581