Novel Thin Film Nanocomposite Membranes Based on Chitosan Succinate Modified with Fe-BTC for Enhanced Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
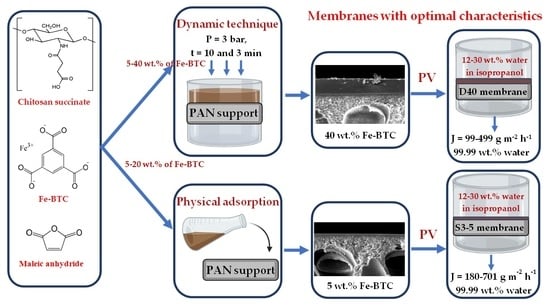
2.2. Preparation of Thin Film Composite (TFC) and Thin Film Nanocomposite (TFN) Membranes
2.2.1. Preparation of ChS-MA Solutions and ChS-MA-Fe-BTC Dispersions
2.2.2. Formation of ChS Selective Layer via Dynamic Technique
2.2.3. Formation of ChS Selective Layer by Physical Adsorption
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.3.4. Contact Angle
2.3.5. Pervaporation Experiments
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Membrane Structure and Physicochemical Studies
3.1.1. Studies of the Selective Layer Composition
3.1.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Studies
3.1.3. Atomic Force Microscopy Studies of the Selective Layer Surface
3.1.4. Contact Angle
3.2. Membrane Pervaporation Performance
3.2.1. Performance of Thin Film Composite Membranes Prepared via Dynamic Technique
3.2.2. Performance of Membranes Prepared by Physical Adsorption
3.3. Comparison of D40 and P3-5 TFN Membranes
3.4. Comparison of the Performance of the Developed TFN Membranes with Chitosan-Based Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdin, A.Y.; Yeboah, P.; Jacob, C. Chemical Impurities: An Epistemological Riddle with Serious Side Effects. IJERPH Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atlaskin, A.A.; Trubyanov, M.M.; Yanbikov, N.R.; Bukovsky, M.V.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Total Reflux Operating Mode of Apparatuses of a Membrane Column Type during High Purification of Gases to Remove a Highly Permeable Impurity. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlaskin, A.A.; Trubyanov, M.M.; Yanbikov, N.R.; Vorotyntsev, A.V.; Drozdov, P.N.; Vorotyntsev, V.M.; Vorotyntsev, I.V. Comprehensive Experimental Study of Membrane Cascades Type of “Continuous Membrane Column” for Gases High-Purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davletbaeva, I.; Zaripov, I.; Mazilnikov, A.; Davletbaev, R.; Sharifullin, R.; Atlaskin, A.; Sazanova, T.; Vorotyntsev, I. Synthesis and Study of Gas Transport Properties of Polymers Based on Macroinitiators and 2,4-Toluene Diisocyanate. Membranes 2019, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besha, A.T.; Tsehaye, M.T.; Tiruye, G.A.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Awoke, A.; Tufa, R.A. Deployable Membrane-Based Energy Technologies: The Ethiopian Prospect. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Mai, Z.; Fu, J.; Wei, Y.; Wan, J. Transport Models of Ammonium Nitrogen in Wastewater from Rare Earth Smelteries by Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkin, A.A.; Golubev, G.S.; Podtynnikov, I.A.; Borisov, I.L.; Volkov, V.V.; Volkov, A.V. Separation of Mixtures of Polar and Nonpolar Organic Liquids by Pervaporation and Nanofiltration (Review). Pet. Chem. 2020, 60, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, P.Y.; Bobreshova, O.V.; Volkov, A.V.; Volkov, V.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Stenina, I.A.; Filippov, A.N.; Yampolskii, Y.P.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Prospects of Membrane Science Development. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Liamin, V.; Kuzminova, A.; Mazur, A.; Lahderanta, E.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Novel Mixed Matrix Sodium Alginate–Fullerenol Membranes: Development, Characterization, and Study in Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol. Polymers 2020, 12, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, M.S.; Reddy, K.R.; Soontarapa, K.; Naveen, S.; Raghu, A.V.; Kulkarni, R.V.; Suhas, D.P.; Shetti, N.P.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Membranes for Dehydration of Alcohols via Pervaporation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.E.; Penkova, A.V.; Kuzminova, A.I.; Morshed, M.; Larionov, M.I.; Alem, H.; Zolotarev, A.A.; Ermakov, S.S.; Roizard, D. Investigation of New Modification Strategies for PVA Membranes to Improve Their Dehydration Properties by Pervaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 450, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogorodnikov, S.K.; Lesteva, T.; Kogan, V. Azeotropnye Smesi: Spravochnik (Azeotropic Mixtures: A Handbook); Zvukov, D., Ed.; Khimiya: Moscow, Russia, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Benzaqui, M.; Semino, R.; Carn, F.; Tavares, S.R.; Menguy, N.; Giménez-Marqués, M.; Bellido, E.; Horcajada, P.; Berthelot, T.; Kuzminova, A.I.; et al. Covalent and Selective Grafting of Polyethylene Glycol Brushes at the Surface of ZIF-8 for the Processing of Membranes for Pervaporation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6629–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toti, U.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation Separation of Water-Isopropyl Alcohol Mixtures with Blend Membranes of Sodium Alginate and Poly(Acrylamide)-Grafted Guar Gum. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 2014–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjan, A.M.; Jeevan Kumar, B.K.; Kittur, A.A.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Novel Approach for the Development of Pervaporation Membranes Using Sodium Alginate and Chitosan-Wrapped Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for the Dehydration of Isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 425–426, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Liamin, V.; Lahderanta, E.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Mixed Matrix Membranes Based on Sodium Alginate Modified by Fullerene Derivatives with L-Amino Acids for Pervaporation Isopropanol Dehydration. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 7765–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzminova, A.I.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Poloneeva, D.Y.; Selyutin, A.A.; Mazur, A.S.; Emeline, A.V.; Mikhailovskii, V.Y.; Solovyev, N.D.; Ermakov, S.S.; Penkova, A.V. Sustainable Composite Pervaporation Membranes Based on Sodium Alginate Modified by Metal Organic Frameworks for Dehydration of Isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 626, 119194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Baek, M.; Kwon, Y.; Shon, M.; Nam, S.; Park, Y. Surface-Modified Halloysite Nanotube-Embedded Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyvinyl Amine Blended Membranes for Pervaporation Dehydration of Water/Isopropanol Mixtures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.V.K.; Subha, M.C.S.; Sairam, M.; Mallikarjuna, N.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Blend Membranes of Chitosan and Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) in Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol and Tetrahydrofuran. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 1918–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X. Maleic Anhydride Surface-Modification of Crosslinked Chitosan Membrane and Its Pervaporation Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 295, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Cui, Y.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, W. The Effect of Structure on Pervaporation of Chitosan Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Q. A Poly(Ionic Liquid) Complex Membrane for Pervaporation Dehydration of Acidic Water-Isopropanol Mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 576, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedula, S.S.; Yadav, G.D. Chitosan-Based Membranes Preparation and Applications: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; González-Valdez, J. New Trends in Biopolymer-Based Membranes for Pervaporation. Molecules 2019, 24, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zielińska, K.; Kujawski, W.; Chostenko, A.G. Chitosan Hydrogel Membranes for Pervaporative Dehydration of Alcohols. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 83, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Zolotarev, A.; Plisko, T.; Burts, K.; Liamin, V.; Bildyukevich, A.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Effect of the Formation of Ultrathin Selective Layers on the Structure and Performance of Thin-Film Composite Chitosan/PAN Membranes for Pervaporation Dehydration. Membranes 2020, 10, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zou, Y.; Wei, T.; Mu, C.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Pervaporation Dehydration of Binary and Ternary Mixtures of N-Butyl Acetate, n-Butanol and Water Using PVA-CS Blended Membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Shi, Y.; Chen, G. Properties and Pervaporation Characteristics of Chitosan-Poly(N-Vinyl-2-Pyrrolidone) Blend Membranes for MeOH-MTBE. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, L.; Chen, X. Chitosan/TiO2 Nanocomposite Pervaporation Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3130–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Liu, Q.L.; Fang, J.; Zhu, A.M.; Zhang, Q.G. Composite Hybrid Membrane of Chitosan–Silica in Pervaporation Separation of MeOH/DMC Mixtures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.-S.; Chang, S.-M.; Lecaros, R.L.G.; Ji, Y.-L.; An, Q.-F.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Fabrication of Hydrothermally Reduced Graphene Oxide/Chitosan Composite Membranes with a Lamellar Structure on Methanol Dehydration. Carbon 2017, 117, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wu, L.; Shi, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Preparation and Pervaporation Property of Chitosan Membrane with Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11667–11675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, M.; Senthil Raja, D.; Jiang, Y.-C.; Liu, T.-Y.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Lin, Y.-F.; Yang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Alshehri, S.M.; Ahamad, T.; et al. Effects of Structural Crystallinity and Defects in Microporous Al-MOF Filled Chitosan Mixed Matrix Membranes for Pervaporation of Water/Ethanol Mixtures. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 83, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harutyunyan, L.R.; Harutyunyan, R.S.; Gabrielyan, G.A.; Lasareva, E.V. Modification of Chitosan and Chitosan Succinate by Surfactants and Investigation of Their Properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 578, 123622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusiana, R.A.; Sangkota, V.D.A.; Santosa, S.J. Chitosan Succinate/PVA-PEG Membrane: Preparation, Characterization and Permeation Ability Test on Creatinine. J. Kim. Sains Appl. 2018, 21, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kochan, J.; Wintgens, T.; Wong, J.E.; Melin, T. Properties of Polyethersulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes Modified by Polyelectrolytes. Desalination 2010, 250, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lu, T.-D.; Yan, X.-Y.; Zhao, L.-L.; Yin, H.; Xiong, X.-X.; Zhou, R.; Sun, S.-P. Designing Nanofiltration Hollow Fiber Membranes Based on Dynamic Deposition Technology. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 610, 118336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, A.; Chun, Y.; Hua, T.; Chew, J.W.; Wang, R. Pre-Deposited Dynamic Membrane Filtration—A Review. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prihatiningtyas, I.; Van der Bruggen, B. Nanocomposite Pervaporation Membrane for Desalination. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 164, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.E.; Penkova, A.V.; Kuzminova, A.I.; Atta, R.R.; Zolotarev, A.A.; Mazur, A.S.; Vezo, O.S.; Lahderanta, E.; Markelov, D.A.; Ermakov, S.S. Development and Investigation of Novel Polyphenylene Isophthalamide Pervaporation Membranes Modified with Various Fullerene Derivatives. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 226, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tong, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, B. Polyamide Composite Membranes Sandwiched with Modified Carbon Nanotubes for High Throughput Pervaporation Desalination of Hypersaline Solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msahel, A.; Galiano, F.; Pilloni, M.; Russo, F.; Hafiane, A.; Castro-Muñoz, R.; Kumar, V.B.; Gedanken, A.; Ennas, G.; Porat, Z.; et al. Exploring the Effect of Iron Metal-Organic Framework Particles in Polylactic Acid Membranes for the Azeotropic Separation of Organic/Organic Mixtures by Pervaporation. Membranes 2021, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudek, G.; Turczyn, R.; Gnus, M.; Konieczny, K. Pervaporative Dehydration of Ethanol/Water Mixture through Hybrid Alginate Membranes with Ferroferic Oxide Nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Krasowska, M.; Turczyn, R.; Strzelewicz, A.; Djurado, D.; Pouget, S. Clustering Analysis for Pervaporation Performance Assessment of Alginate Hybrid Membranes in Dehydration of Ethanol. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 144, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Shi, M.; Shan, C.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X.; Lv, L.; Hua, M.; et al. MIL-PVDF Blend Ultrafiltration Membranes with Ultrahigh MOF Loading for Simultaneous Adsorption and Catalytic Oxidation of Methylene Blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, N.; Rahman, M.A.; Dzarfan Othman, M.H.; Jaafar, J.; Aziz, A.A. Preparation, Characterizations and Performance Evaluations of Alumina Hollow Fiber Membrane Incorporated with UiO-66 Particles for Humic Acid Removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burts, K.S.; Plisko, T.V.; Prozorovich, V.G.; Melnikova, G.B.; Ivanets, A.I.; Bildyukevich, A.V. Development and Study of PVA–SiO2/Poly(AN-Co-MA) Dynamic Nanocomposite Membranes for Ethanol Dehydration via Pervaporation. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2022, 4, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzminova, A.; Dmitrenko, M.; Zolotarev, A.; Korniak, A.; Poloneeva, D.; Selyutin, A.; Emeline, A.; Yushkin, A.; Foster, A.; Budd, P.; et al. Novel Mixed Matrix Membranes Based on Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity PIM-1 Modified with Metal-Organic Frameworks for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions and Food Dyes by Nanofiltration. Membranes 2021, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascón, V.; Jiménez, M.B.; Blanco, R.M.; Sanchez-Sanchez, M. Semi-Crystalline Fe-BTC MOF Material as an Efficient Support for Enzyme Immobilization. Catal. Today 2018, 304, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Hei, S.; Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, W. Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) at Low Temperature and Atmospheric Pressure. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 792827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.-Y.; Yang, C.-X.; Yan, X.-P. Metal-Organic Framework MIL-100(Fe) as the Stationary Phase for Both Normal-Phase and Reverse-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1274, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzminova, A.; Dmitrenko, M.; Mazur, A.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Novel Pervaporation Membranes Based on Biopolymer Sodium Alginate Modified by FeBTC for Isopropanol Dehydration. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lou, X.; Li, C.; Ning, Y.; Liao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Mananga, E.S.; Shen, M.; Hu, B. Facile Synthesis of the Basolite F300-like Nanoscale Fe-BTC Framework and Its Lithium Storage Properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 114483–114490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawski, J.; Rozicka, A.; Bryjak, M.; Kujawski, W. Pervaporative Removal of Acetone, Butanol and Ethanol from Binary and Multicomponent Aqueous Mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, M.Ş.A.; Arslanoğlu, H.; Çiftçi, H. Production of Microporous Cu-Doped BTC (Cu-BTC) Metal-Organic Framework Composite Materials, Superior Adsorbents for the Removal of Methylene Blue (Basic Blue 9). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Karimi-Sabet, J.; Ghoreishi, S.M. Intensification of Helium Separation from CH4 and N2 by Size-Reduced Cu-BTC Particles in Matrimid Matrix. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burts, K.S.; Plisko, T.V.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Li, G.; Kujawa, J.; Kujawski, W. Development of Dynamic PVA/PAN Membranes for Pervaporation: Correlation between Kinetics of Gel Layer Formation, Preparation Conditions, and Separation Performance. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 182, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.S.; Sajjan, A.M.; Khan, T.M.Y.; Badruddin, I.A.; Kamangar, S.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Ayachit, N.H.; Ashwini, M.; Sharanappa, A. Development and Characterization of Biocompatible Membranes from Natural Chitosan and Gelatin for Pervaporative Separation of Water–Isopropanol Mixture. Polymers 2021, 13, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achari, D.; Rachipudi, P.; Naik, S.; Karuppannan, R.; Kariduraganavar, M. Polyelectrolyte Complex Membranes Made of Chitosan—PSSAMA for Pervaporation Separation of Industrially Important Azeotropic Mixtures. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 78, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.-X.; Ding, H.; Yang, H.; Ma, X.-H.; Xu, X.-R.; Xu, Z.-L.; Tang, C.Y. Double-Crosslinked GO Interlayer Framework as a Pervaporation Hybrid Membrane with High Performance. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15043–15050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanachai, A.; Jiraratananon, R.; Uttapap, D.; Moon, G.Y.; Anderson, W.A.; Huang, R.Y.M. Pervaporation with Chitosan/Hydroxyethylcellulose (CS/HEC) Blended Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 166, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.A.; Chen, H.C.; Chou, W.L.; Lee, K.R.; Yang, M.C.; Lai, J.Y. Pervaporation of Water/Alcohol Mixtures through Chitosan/Cellulose Acetate Composite Hollow-Fiber Membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittur, A.A.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Aralaguppi, M.I.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Preparation and Characterization of Novel Pervaporation Membranes for the Separation of Water–Isopropanol Mixtures Using Chitosan and NaY Zeolite. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 247, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegal, J.; Lee, K.-H. Chitosan Membranes Crosslinked with Sulfosuccinic Acid for the Pervaporation Separation of Water/Alcohol Mixtures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 71, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjali Devi, D.; Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation Separation of Isopropanol/Water Mixtures through Crosslinked Chitosan Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 262, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Nawawi, M.G.M.; So, L.K. Development of Novel NH 4 Y Zeolite--Filled Chitosan Membranes for the Dehydration of Water--Isopropanol Mixture Using Pervaporation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 3071–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svang-Ariyaskul, A.; Huang, R.Y.M.; Douglas, P.L.; Pal, R.; Feng, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, L. Blended Chitosan and Polyvinyl Alcohol Membranes for the Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-H.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Chitosan/Poly(Tetrafluoroethylene) Composite Membranes Using in Pervaporation Dehydration Processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, S.; Kittur, A.; Kulkarni, S.; Kariduraganavar, M. Development of Novel Blocked Diisocyanate Crosslinked Chitosan Membranes for Pervaporation Separation of Water–Isopropanol Mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 302, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerapur, R.S.; Gudasi, K.B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol Using Blend Membranes of Chitosan and Hydroxypropyl Cellulose. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-H.; Ma, L.-C.; Lin, G.-C.; Tsai, H.-A.; Lai, J.-Y. The Effects of Surface Modifications on Preparation and Pervaporation Dehydration Performance of Chitosan/Polysulfone Composite Hollow-Fiber Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, S.K.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Development of Novel Composite Membranes Using Quaternized Chitosan and Na+-MMT Clay for the Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachipudi, P.S.; Kittur, A.A.; Choudhari, S.K.; Varghese, J.G.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Development of Polyelectrolyte Complexes of Chitosan and Phosphotungstic Acid as Pervaporation Membranes for Dehydration of Isopropanol. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.G.; Kittur, A.A.; Rachipudi, P.S.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Synthesis, Characterization and Pervaporation Performance of Chitosan-g-Polyaniline Membranes for the Dehydration of Isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Abbreviation | ChS Concentration in Aqueous Solution [wt.%] | Fe-BTC Concentration in ChS Solution [wt.%, Ratio to ChS] | Method of the Selective Layer Formation |
|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | 1.0 | 0 | dynamic technique |
| D5 | 5 | ||
| D10 | 10 | ||
| D15 | 15 | ||
| D20 | 20 | ||
| D30 | 30 | ||
| D40 | 40 | ||
| P2 | 2 | 0 | physical adsorption |
| P3 | 3 | 0 | |
| P3-5 | 5 | ||
| P3-10 | 10 | ||
| P3-20 | 20 |
| Membrane Abbreviation | Selective Layer Thickness [μm] |
|---|---|
| D0 | 0.44 |
| D5 | 0.50 |
| D10 | 0.92 |
| D15 | 2.02 |
| D20 | 2.85 |
| D30 | 4.53 |
| D40 | 4.65 |
| Membrane Abbreviation | Selective Layer Thickness [μm] |
|---|---|
| P3 | 0.32 |
| P3-5 | 0.43 |
| P3-10 | 0.62 |
| P3-20 | 0.71 |
| Membrane Abbreviation | Roughness Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Ra [nm] | Rq [nm] | |
| D0 | 3.44 | 5.07 |
| D5 | 4.46 | 5.97 |
| D10 | 4.61 | 6.07 |
| D15 | 4.63 | 6.39 |
| D20 | 8.25 | 10.87 |
| D30 | 8.95 | 11.74 |
| D40 | 10.39 | 14.88 |
| Membrane Abbreviation | Roughness Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Ra [nm] | Rq [nm] | |
| P3 | 2.31 | 3.20 |
| P3-5 | 3.40 | 4.48 |
| P3-10 | 3.58 | 5.13 |
| P3-20 | 7.73 | 13.16 |
| Membrane Abbreviation | D40 | P3-5 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||
| Selective Layer Thickness [µm] | 4.65 | 0.43 | |
| Roughness parameters | Ra [nm] | 10.39 | 3.40 |
| Rq [nm] | 14.88 | 4.48 | |
| Contact angle [°] | 41 | 44 | |
| Permeation flux (g m−2 h−1) | 88% isopropanol/12% water | 99 | 180 |
| 80% isopropanol/20% water | 296 | 405 | |
| 70% isopropanol/30% water | 499 | 701 | |
| Normalized flux (g µm m−2 h−1) | 88% isopropanol/12% water | 460 | 77 |
| 80% isopropanol/20% water | 1376 | 174 | |
| 70% isopropanol/30% water | 2320 | 301 | |
| Water content in permeate (wt.%) | 88% isopropanol/12% water | 99.99 | 99.99 |
| 80% isopropanol/20% water | 99.99 | 99.99 | |
| 70% isopropanol/30% water | 99.99 | 99.99 | |
| PSI (kg m−2 h−1) | 88% isopropanol/12% water | 7,259 | 13,050 |
| 80% isopropanol/20% water | 19,502 | 29,362 | |
| 70% isopropanol/30% water | 36,589 | 50,822 | |
| Normalized PSI (kg µm m−2 h−1) | 88% isopropanol/12% water | 33,754 | 5,612 |
| 80% isopropanol/20% water | 90,684 | 12,626 | |
| 70% isopropanol/30% water | 170,139 | 21,853 | |
| Membranes | Thickness (µm) | Water Content in Feed (wt.%) | Temperature (°C) | Permeation Flux (g m−2 h−1) | Separation Factor (β) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D40 | 4.65 | 12 | 25 | 99 | 73,326 | This study |
| P3-5 | 0.43 | 12 | 25 | 180 | 73,326 | This study |
| PERVAPTM 1201 | - | 12 | 22 | 28 | 73,326 | [9] |
| Chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol (20 wt.%) | 35-40 | 15 | 30 | 130 | 1625 | [19] |
| Chitosan/gelatin (15 wt.%) | - | 10 | 30 | 42 | 6330 | [58] |
| Polyelectrolyte complex membranes from chitosan and polystyrene sulfonic acid-co-maleic acid (9 wt.%) | 40 | ~12 | 30 | 29 | 2898 | [59] |
| Supported chitosan membrane | ~0.6–0.7 | 12 | 28 | 130 | ~200 | [26] |
| Chitosan (1 wt.%)–Graphene oxide (0.1 wt.%)/trimesoyl chloride/3 cycles | 0.432 | 10 | 60 | 4391 | 1491 | [60] |
| Chitosan (1 wt.%)–Graphene oxide (0.2 wt.%)/trimesoyl chloride/3 cycles | 0.682 | 10 | 60 | 2835 | 2991 | [60] |
| Chitosan/hydroxy-ethyl-cellulose (CS/HEC) | 30–35 | 10 | 60 | 175 | 26,091 | [61] |
| Chitosan/Cellulose Acetate composite hollow fiber membranes | - | 10 | 25 | 166 | ~809 | [62] |
| Chitosan/NaY zeolite (30 wt.%) | 40 | 5 | 30 | 115 | 2620 | [63] |
| Chitosan cross-linked with sulfo-succinic acid | 20 | 20 | 40 | 105 | ∞ | [64] |
| Chitosan cross-linked with toluene-2,4-diisocyanate | 50 | 8.4 | 30 | 79 | 472 | [65] |
| Chitosan/NH4Y zeolite (0.2 wt.%) | 30 | 10 | 30 | 39 | ~38 | [66] |
| Chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol (75/25) | 18–25 | 10 | 60 | 644 | ∞ | [67] |
| Supported chitosan membrane | ~1.26 | 10 | 25 | 409 | 1490 | [68] |
| Chitosan/blocked diisocyanate (40 wt.%) | 40 | 10 | 30 | 34 | 2423 | [69] |
| Chitosan/hydroxy-propyl cellulose (40 wt.%) | 50 | 12.5 | 30 | 263 | 320 | [70] |
| Chitosan (1.5 wt.%)/poly-sulfone composite hollow fiber membranes | ~0.7 | 30 | 25 | 128 | 78 | [71] |
| Chitosan/Na+-MMT clay (10 wt.%) | 40 | 10 | 30 | 14.23 | 14,992 | [72] |
| Polyelectrolyte complex membranes from chitosan and phospho-tungstic acid (0.045 M) | 40 | 10 | 30 | 1170 | 7490 | [73] |
| Chitosan-g-polyaniline | 40 | 10 | 30 | 19 | 502 | [74] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burts, K.; Plisko, T.; Dmitrenko, M.; Zolotarev, A.; Kuzminova, A.; Bildyukevich, A.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Novel Thin Film Nanocomposite Membranes Based on Chitosan Succinate Modified with Fe-BTC for Enhanced Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol. Membranes 2022, 12, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070653
Burts K, Plisko T, Dmitrenko M, Zolotarev A, Kuzminova A, Bildyukevich A, Ermakov S, Penkova A. Novel Thin Film Nanocomposite Membranes Based on Chitosan Succinate Modified with Fe-BTC for Enhanced Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol. Membranes. 2022; 12(7):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070653
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurts, Katsiaryna, Tatiana Plisko, Mariia Dmitrenko, Andrey Zolotarev, Anna Kuzminova, Alexandr Bildyukevich, Sergey Ermakov, and Anastasia Penkova. 2022. "Novel Thin Film Nanocomposite Membranes Based on Chitosan Succinate Modified with Fe-BTC for Enhanced Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol" Membranes 12, no. 7: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070653
APA StyleBurts, K., Plisko, T., Dmitrenko, M., Zolotarev, A., Kuzminova, A., Bildyukevich, A., Ermakov, S., & Penkova, A. (2022). Novel Thin Film Nanocomposite Membranes Based on Chitosan Succinate Modified with Fe-BTC for Enhanced Pervaporation Dehydration of Isopropanol. Membranes, 12(7), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070653