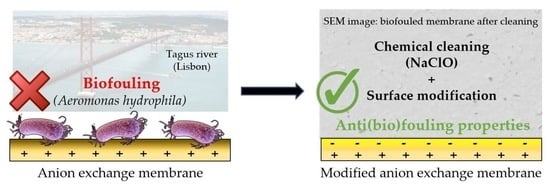
A Study on Biofouling and Cleaning of Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Membranes
2.2. Surface Membrane Modification
2.3. Membrane Surface Characterization
2.3.1. Contact Angle
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Static Assays
2.4.1. Fouling Experiments
Water Sampling and Characterization
Aeromonas Isolation and Identification
Membrane Biofouling
2.4.2. Effect of Chemical Cleaning on Membrane Surface
2.5. Ion Exchange Capacity
2.6. Electrochemical Measurements and Sulfate Mass Transport Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Static Assays
3.1.1. (Bio)fouling Experiments
3.1.2. Effect of the Type of Cleaning Solution
3.2. Experiments Using Model Saline Solutions
3.2.1. Hydrophilicity
3.2.2. Ion Exchange Capacity
3.2.3. ATR-FTIR Measurements
3.2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3.2.5. SEM Analyses
4. Conclusions
- The presence of poly (acrylic acid) on the membrane surface decreases the water contact angle value of the membranes (improved hydrophilicity). The presence of organic foulants (SDS and SDBS) increased the membrane surface hydrophobicity, while for the Aeromonas, this effect was negligible.
- The PAA-modified membranes exhibit a significantly improved anti-adhesion behavior, since a much lower number of total bacteria counts (in the assays with the real water matrices) and Aeromonas (in the assays with the fortified bacteria) were attached on its surface.
- A chemical cleaning method using sodium hypochlorite as the cleaning agent demonstrated an effective recovery of the initial membrane properties after (bio)fouling employing natural feedwaters, without compromising the main properties and structure of the samples. As a result, this chemical cleaning strategy can be applied to recover membrane properties and characteristics, such as ion exchange capacity, water contact angle, and membrane conductivity.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gielen, D.; Gorini, R.; Wagner, N.; Leme, R.; Gutierrez, L.; Prakash, G.; Asmelash, E.; Janeiro, L.; Gallina, G.; Vale, G. Global Energy Transformation: A Roadmap to 2050; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kempener, R.; Neumann, F. Salinity Gradient Energy Technology Brief; IRENA and IMIEU: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, K.E.; Thomas, J.T.; Johnson, J.X.; DeCarolis, J.F.; Call, D.F. Life cycle assessment of salinity gradient energy recovery using reverse electrodialysis. J. Ind. Ecol. 2021, 25, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besha, A.T.; Tsehaye, M.T.; Aili, D.; Zhang, W.; Tufa, R.A. Design of Monovalent Ion Selective Membranes for Reducing the Impacts of Multivalent Ions in Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes 2019, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Coma, L.; Abarca, J.A.; Fallanza, M.; Ortiz, A.; Ibáñez, R.; Ortiz, I. Optimum recovery of saline gradient power using reversal electrodialysis: Influence of the stack components. J. Wat. Proc. Eng. 2022, 48, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martínez, V.M.; Gómez-Coma, L.; Tristán, C.; Pérez, G.; Fallanza, M.; Ortiz, A.; Ibáñez, R.; Ortiz, I. A comprehensive study on the effects of operation variables on reverse electrodialysis performance. Desalination 2020, 482, 114389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, S.; Huertas, R.M.; Galinha, C.F.; Crespo, J.G.; Velizarov, S. On Operation of Reverse Electrodialysis (RED) and Membrane Capacitive Deionisation (MCDI) with Natural Saline Streams: A Critical Review. Desalination 2020, 476, 114183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansima, M.A.C.K.; Makehelwala, M.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Wei, Y.; Nanayakkara, K.G.N.; Herath, A.C.; Weerasooriya, R. Fouling of Ion Exchange Membranes used in the Electrodialysis Reversal Advanced Water Treatment: A Review. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 127951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoka, F.; Merino-Garcia, I.; Velizarov, S. Surface Modifications of Anion Exchange Membranes for an Improved Reverse Electrodialysis Process Performance: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Zhang, Y.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Tailor-made anion-exchange membranes for salinity gradient power generation using reverse electrodialysis. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintossi, D.; Saakes, M.; Borneman, Z.; Nijmeijer, K. Tailoring the Surface Chemistry of Anion Exchange Membranes with Zwitterions: Toward Antifouling RED Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 18348–18357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; van Baak, W.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Monovalent-ion-selective membranes for reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Park, T.W. Electrochemical characterizations and reverse electrodialysis performance of hybrid anion exchange membranes for salinity gradient energy. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 817, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarale, R.K.; Shahi, V.K.; Schubert, R.; Rangarajan, R.; Mehnert, R. Development of urethane acrylate composite ion-exchange membranes and their electrochemical characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 270, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedem, O.; Schechtmann, L.; Mirsky, Y.; Saveliev, G.; Daltrophe, N. Low-polarisation electrodialysis membranes. Desalination 1998, 118, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Liu, L.; Meng, Q.; Cao, B. Preparation and characterization of cross-linked quaternised polyvinyl alcohol membrane/activated carbon composite electrode for membrane capacitive deionization. Desalination 2014, 354, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, B.; Tong, X.; Chen, Y. Monovalent-anion selective and antifouling polyelectrolytes multilayer anion exchange membrane for reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 567, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Garcia, I.; Kotoka, F.; Portugal, C.A.M.; Crespo, G.; Velizarov, S. Characterization of Poly (Acrylic) Acid-Modified Heterogenous Anion Exchange Membranes with Improved Monovalent Permselectivity for RED. Membranes 2020, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, B.; Torres, E.V.; Sleutels, T.; Gagliano, M.C.; Saakes, M.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Fouling fractionation in reverse electrodialysis with natural feed waters demonstrates dual media rapid filtration as an effective pre-treatment for fresh water. Desalination 2021, 518, 115277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koók, L.; Bakonyi, P.; Harnisch, F.; Kretzschmar, J.; Chae, K.-J.; Zhen, G.; Kumar, G.; Rózsenberszki, T.; Tóth, G.; Nemestóthy, N.; et al. Biofouling of membranes in microbial electrochemical technologies: Causes, characterization methods and mitigation strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tesfai, M.; Ma, G.; Jiang, W.; Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, P. Polydopamine-Assisted Modification of Anion-Exchange Membranes with Nanomaterials for Improved Biofouling Resistance and Electrodialysis Performance. ACS EST Eng. 2021, 1, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.S.; Dudley, L.Y. Biofouling in Membrane Systems—A Review. Desalination 1998, 118, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzberg, M.; Pandit, S.; Mauter, M.S.; Oren, Y. Bacterial Biofilm Formation on Ion Exchange Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 596, 117564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talagrand-Reboul, E.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Lamy, B. The Social Life of Aeromonas through Biofilm and Quorum Sensing Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianetti, A.; Falcioni, T.; Bruscolini, F.; Sabatini, L.; Sisti, E.; Papa, S. Determination of the Viability of Aeromonas Hydrophila in Different Types of Water by Flow Cytometry, and Comparison with Classical Methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7948–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency; Office of Science and Technology Washington, D.C.; EPA Office of Water. Aeromonas: Human Health Criteria Document. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/901Q0C00.PDF?Dockey=901Q0C00.PDF (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The Genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, Pathogenicity, and Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S. Inactivation Kinetics of Various Chemical Disinfectants on Aeromonas Hydrophila Planktonic Cells and Biofilms. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percival, S.L.; Williams, D.W. Chapter Three-Aeromonas. In Microbiology of Waterborne Diseases, 2nd ed.; Percival, S.L., Yates, M.V., Williams, D.W., Chalmers, R., Gray, N., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Bernagozzi, M.; Bianucci, F.; Sacchetti, R. Prevalence of Aeromonas spp. in Surface Waters. Water Environ. Res. 1995, 67, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Garcia, I.; Velizarov, S. New insights into the definition of membrane cleaning strategies to diminish the fouling impact in ion exchange membrane separation processes. Sep. Pur. Technol. 2021, 277, 119445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, K.S.; Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Espinosa, D.C.R. A three-stage chemical cleaning of ion-exchange membranes used in the treatment by electrodialysis of wastewaters generated in brass electroplating industries. Desalination 2020, 492, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; You, F.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, D. Mechanisms of chemical cleaning of ion exchange membranes: A case study of plant-scale electrodialysis for oily wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 496, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Dammak, L.; Chaabane, L.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Cleaning of cation-exchange membranes used in electrodialysis for food industry by chemical solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Porozhnyy, M.; Nevakshenova, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Nikonenko, V. Characterization and cleaning of anion-exchange membranes used in electrodialysis of polyphenol-containing food industry solutions; comparison with cation-exchange membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Guo, H.; Ye, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R. Study on the fouling mechanism and cleaning method in the treatment of polymer flooding produced water with ion exchange membranes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29947–29957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, S.; Cao, H.; Li, Y. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and surface properties characterization of anion exchange membrane fouled by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Vasquez, W.; Ghalloussi, R.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Nikonenko, V.; Grande, D. Structure and properties of heterogeneous and homogeneous ion-exchange membranes subjected to ageing in sodium hypochlorite. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Yao, Z.; Ji, L.; Toy, P.H.; Tang, C.Y. Effects of hypochlorite exposure on the structure and electrochemical performance of ion exchange membranes in reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.R.; Sanches, S.; Huertas, R.M.; Crespo, M.T.B.; Pereira, V.J. Treatment of a Real Water Matrix Inoculated with Aspergillus Fumigatus Using a Photocatalytic Membrane Reactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.J.; Marques, R.; Marques, M.; Benoliel, M.J.; Crespo, M.T.B. Free Chlorine Inactivation of Fungi in Drinking Water Sources. Water Res. 2012, 47, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzl, G.; Paulik, C.; Hild, S.; Guggenbichler, J.P.; Lackner, M. Antimicrobial Activity of Poly(acrylic acid) Block Copolymers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 38, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, S.; Cao, H.; Yujiao Li, Y.; Van der Bruggen, B. Layer-by-layer assembly of anion exchange membrane by electrodeposition of polyelectrolytes for improved antifouling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 558, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Hu, B.; Deng, H. Super-hydrophilic TiO2-based coating of anion exchange membranes with improved antifouling performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 614, 126136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Hong, M.-K.; Han, S.-D.; Cho, S.-H.; Moon, S.-H. Fouling of an anion exchange membrane in the electrodialysis desalination process in the presence of organic foulants. Desalination 2009, 238, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akberova, E.M.; Vasil’eva, V.I.; Zabolotsky, V.I.; Novak, L. A Study of Ralex Membrane Morphology by SEM. Membranes 2019, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| pH | Total Solids (g/L) | Total Suspended Solids (mg/L) | COD (mg/L O2) | Total Bacteria Count (CFU */mL) | Total Coliforms (MPN **/100 mL) | E. coli (MPN **/100 mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface water | 7.8 | 46.5 | 50.2 | 220.5 | 830 | 750 | 140 |
| Seawater | 8.0 | 46.8 | 44.8 | 60.0 | 700 | 270 | 39 |
| Unmodified Membrane | Modified Membrane | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Bacteria Count (CFU/cm2) | Total Coliforms (MPN/cm2) | E. coli (MPN/ cm2) | Total Bacteria Count (CFU/cm2) | Total Coliforms (MPN/ cm2) | E. coli (MPN/ cm2) | |
| Surface water | 1050 | <2.5 | <2.5 | 800 | <2.5 | <2.5 |
| Seawater | 275 | <2.5 | <2.5 | 38 | <2.5 | <2.5 |
| Unmodified Membrane | Modified Membrane | |
|---|---|---|
| Aeromonas cell suspension | 5.30 × 105 CFU/cm2 | 1.75 × 105 CFU/cm2 |
| Membrane Type | Presence/Absence of Foulants | Current (mA) |
|---|---|---|
| Unmodified | No fouling | 2.687 ± 0.006 |
| SDS (25 ppm) | 2.556 ± 0.018 | |
| SDS (250 ppm) | 2.596 ± 0.076 | |
| SDBS (25 ppm) | 2.586 ± 0.025 | |
| Aeromonas (batch 1) | 2.361 ± 0.073 | |
| Aeromonas (batch 1) + NaClO cleaning | 2.486 ± 0.032 | |
| Aeromonas (batch 2) | 2.291 ± 0.021 | |
| Aeromonas (batch 2) + NaClO cleaning | 2.694 ± 0.021 | |
| Modified | No fouling | 2.946 ± 0.028 |
| SDS (25 ppm) | 2.531 ± 0.028 | |
| SDBS (25 ppm) | 2.431 ± 0.040 | |
| Aeromonas (batch 1) | 2.730 ± 0.031 | |
| Aeromonas (batch 1) + NaClO cleaning | 2.759 ± 0.031 | |
| Aeromonas (batch 2) | 2.322 ± 0.045 | |
| Aeromonas (batch 2) + NaClO cleaning | 2.659 ± 0.042 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiago, G.; Cristóvão, M.B.; Marques, A.P.; Huertas, R.; Merino-Garcia, I.; Pereira, V.J.; Crespo, J.G.; Velizarov, S. A Study on Biofouling and Cleaning of Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070697
Tiago G, Cristóvão MB, Marques AP, Huertas R, Merino-Garcia I, Pereira VJ, Crespo JG, Velizarov S. A Study on Biofouling and Cleaning of Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes. 2022; 12(7):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070697
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiago, Gonçalo, Maria Beatriz Cristóvão, Ana Paula Marques, Rosa Huertas, Ivan Merino-Garcia, Vanessa Jorge Pereira, João Goulão Crespo, and Svetlozar Velizarov. 2022. "A Study on Biofouling and Cleaning of Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis" Membranes 12, no. 7: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070697
APA StyleTiago, G., Cristóvão, M. B., Marques, A. P., Huertas, R., Merino-Garcia, I., Pereira, V. J., Crespo, J. G., & Velizarov, S. (2022). A Study on Biofouling and Cleaning of Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes, 12(7), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070697