Biomarkers Predict In-Hospital Major Adverse Cardiac Events in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicenter International Study
Abstract
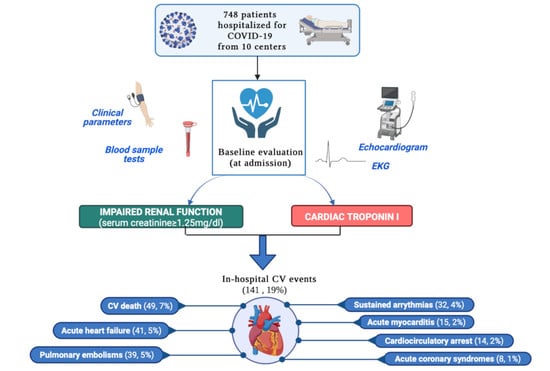
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Follow-Up
3.2. Clinical and Biohumoral Characteristics
3.3. Biomarkers Associated with In-Hospital Cardiovascular Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Renal Disease in COVID-19
4.2. The Use of Cardiac Troponin in COVID-19
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Luton Hospital, United Kingdom | 213 patients |
| San Donato Hospital, Milan, Italy | 200 patients |
| Guglielmo da Saliceto Hospital, Piacenza, Italy | 78 patients |
| San Giovanni di Dio e Ruggi d’Aragona University Hospital, Salerno, Italy | 73 patients |
| Santa Maria alle Scotte University Hospital, Siena, Italy | 71 patients |
| S.Elia Hospital, Caltanissetta, Italy | 27 patients |
| Westmead Hospital, Sydney, Australia | 25 patients |
| Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden | 21 patients |
| Federico II University Hospital, Naples Italy | 20 patients |
| Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron, Barcelona, Spain | 20 patients |
References
- Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 13 November 2021).
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. The coagulopathy, endotheliopathy, and vasculitis of COVID-19. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhmerov, A.; Marbán, E. COVID-19 and the Heart. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cameli, M.; Pastore, M.C.; Mandoli, G.E.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Focardi, M.; Biagioni, G.; Cameli, P.; Patti, G.; Franchi, F.; Mondillo, S.; et al. COVID-19 and Acute Coronary Syndromes: Current Data and Future Implications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 7, 593496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, V.M.; McCoy, T.H.; Perlis, R.H. Laboratory Findings Associated With Severe Illness and Mortality Among Hospitalized Individuals With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Eastern Massachusetts. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2023934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böger, B.; Fachi, M.M.; Vilhena, R.O.; Cobre, A.F.; Tonin, F.S.; Pontarolo, R. Systematic review with meta-analysis of the accuracy of diagnostic tests for COVID-19. Am. J. Infect. Control 2021, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Ang, L.W.; Leo, Y.S.; Young, B.E. Risk Factors for Severe Disease and Efficacy of Treatment in Patients Infected With COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBane, R.D., 2nd; Torres Roldan, V.D.; Niven, A.S.; Pruthi, R.K.; Franco, P.M.; Linderbaum, J.A.; Casanegra, A.I.; Oyen, L.J.; Houghton, D.E.; Marshall, A.L.; et al. Anticoagulation in COVID-19: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Rapid Guidance From Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 2467–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.A.; Kane, A.D.; Cook, T.M. Outcomes from intensive care in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.P.; Pritam, M.; Pandey, B.; Yadav, T.P. Microstructure, pathophysiology, and potential therapeutics of COVID-19: A comprehensive review. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.P.; Sweitzer, N.K.; Indik, J.H.; Acharya, D.; William, P. SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cardiovascular Disease: COVID-19 Heart. Heart Lung Circ. 2020, 29, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermali, M.; Khalsa, R.K.; Pillai, K.; Ismail, Z.; Harky, A. The role of biomarkers in diagnosis of COVID-19—A systematic review. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, Y.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Jaffe, A.S. Cardiac Troponin for Assessment of Myocardial Injury in COVID-19: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1244–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulstad, H.; Cosyns, B.; Popescu, B.A.; Galderisi, M.; Salvo, G.D.; Donal, E.; Petersen, S.; Gimelli, A.; Haugaa, K.H.; Muraru, D.; et al. COVID-19 pandemic and cardiac imaging: EACVI recommendations on precautions, indications, prioritization, and protection for patients and healthcare personnel. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameli, M.; Pastore, M.C.; Henein, M.; Aboumarie, H.S.; Mandoli, G.E.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Cameli, P.; Franchi, F.; Mondillo, S.; Valente, S. Safe performance of echocardiography during the COVID-19 pandemic: A practical guide. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 21, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 1–39.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedrich, M.G.; Sechtem, U.; Schulz-Menger, J.; Holmvang, G.; Alakija, P.; Cooper, L.T.; White, J.A.; Abdel-Aty, H.; Gutberlet, M.; Prasad, S.; et al. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Myocarditis: A JACC White Paper. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dirim, A.B.; Demir, E.; Yadigar, S.; Garayeva, N.; Parmaksiz, E.; Safak, S.; Bahat, K.A.; Ucar, A.R.; Oruc, M.; Oto, O.A.; et al. COVID-19 in chronic kidney disease: A retrospective, propensity score-matched cohort study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akchurin, O.; Meza, K.; Biswas, S.; Greenbaum, M.; Licona-Freudenstein, A.P.; Goyal, P.; Choi, J.J.; Choi, M.E. COVID-19 in Patients with CKD in New York City. Kidney360 2021, 2, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirjalili, H.; Dastgheib, S.A.; Shaker, S.H.; Bahrami, R.; Mazaheri, M.; Sadr-Bafghi, S.M.H.; Sadeghizadeh-Yazdi, J.; Neamatzadeh, H. Proportion and mortality of Iranian diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, hypertension and cardiovascular disease patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2021, 20, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon-Abarca, J.A.; Memon, R.S.; Rehan, B.; Iftikhar, M.; Chatterjee, A. The impact of COVID-19 in diabetic kidney disease and chronic kidney disease: A population-based study. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakhchanian, H.; Raiker, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Khan, A.; Singh, S.; Chatterjee, A. Outcomes of COVID-19 in CKD Patients: A Multicenter Electronic Medical Record Cohort Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Xu, W.; Huang, C.L.; Fei, L.; Xie, X.D.; Li, Q.; Chen, L. Acute cardiac injury and acute kidney injury associated with severity and mortality in patients with COVID-19. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakhshoori, M.; Heidarpour, M.; Shafie, D.; Taheri, M.; Rezaei, N.; Sarrafzadegan, N. Acute Cardiac Injury in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arch. Iran. Med. 2020, 23, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.C.; Liu, W.F.; Lei, S.H.; Zhou, B.W.; Yang, X.; Huang, T.Y.; Deng, Q.W.; Xu, M.; Li, C.; Liu, K.X. Prevalence and prognostic value of elevated troponins in patients hospitalised for coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Intensive Care 2020, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, G.; Pallisgaard, J.; Schjerning Olsen, A.M.; McGettigan, P.; Andersen, M.; Krogager, M.; Kragholm, K.; Køber, L.; Gislason, G.H.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; et al. Association between biomarkers and COVID-19 severity and mortality: A nationwide Danish cohort study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e041295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyılmaz, S.; Ergün Alış, E.; Ermiş, E.; Allahverdiyev, S.; Uçar, H. Assessment of the Relationship between Mortality and Troponin I Levels in Hospitalized Patients with the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19). Medicina 2020, 56, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.A.; Spolaore, F.; Ammirabile, M.; Romeo, F.; Caciagli, P.; Ceriotti, F.; Bernardini, S. The assessment of high sensitivity cardiac troponin in patients with COVID-19: A multicenter study. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2021, 32, 100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeanu, E.M.; Duthil, N.; Severac, F.; Lambach, H.; Tousch, J.; Jambert, L.; Mirea, C.; Delatte, A.; Younes, W.; Frantz, A.S.; et al. Prognostic Value of Troponin Elevation in COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Michieli, L.; Babuin, L.; Vigolo, S.; Berti De Marinis, G.; Lunardon, A.; Favretto, F.; Lobo, R.; Sandoval, Y.; Bryant, S.C.; Donato, D.; et al. Using high sensitivity cardiac troponin values in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19): The Padova experience. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 90, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García de Guadiana-Romualdo, L.; Morell-García, D.; Rodríguez-Fraga, O.; Morales-Indiano, C.; María Lourdes Padilla Jiménez, A.; Gutiérrez Revilla, J.I.; Urrechaga, E.; Álamo, J.M.; Hernando Holgado, A.M.; Lorenzo-Lozano, M.D.C.; et al. Cardiac troponin and COVID-19 severity: Results from BIOCOVID study. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 56, e13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Abbasi, B.; Torres, P.; Ramos-Tuarez, F.; Dewaswala, N.; Abdallah, A.; Chen, K.; Abdul Qader, M.; Job, R.; Aboulenain, S.; Dziadkowiec, K.; et al. Cardiac Troponin-I and COVID-19: A Prognostic Tool for In-Hospital Mortality. Cardiol. Res. 2020, 11, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M.; Pastore, M.C.; Soliman Aboumarie, H.; Mandoli, G.E.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Cameli, P.; Bigio, E.; Franchi, F.; Mondillo, S.; Valente, S. Usefulness of echocardiography to detect cardiac involvement in COVID-19 patients. Echocardiography 2020, 37, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, C.; Giannitsis, E.; Jaffe, A.S.; Huber, K.; Mair, J.; Cullen, L.; Hammarsten, O.; Mills, N.L.; Möckel, M.; Krychtiuk, K.; et al. Cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with COVID-19. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2021, 10, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Whole Population (n = 748) | No CV Events (n = 607) | CV Events (n = 141) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Features | ||||
| Age (years) | 67 ± 16 | 65 ± 17 | 72 ± 15 | 0.008 |
| Sex (female) | 274 (37) | 226 (37) | 48 (34) | 0.604 |
| Hypertension n, (%) | 402 (54) | 312 (50) | 90 (64) | 0.008 |
| Diabetes | 198 (26) | 155 (24) | 43 (30) | 0.187 |
| Dyslipidemia | 155 (20) | 124 (19) | 31 (21) | 0.704 |
| Renal failure | 243 (30) | 184 (28) | 59 (39) | 0.024 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 105 (13) | 77 (11) | 28 (19) | 0.013 |
| History of AF | 81 (11) | 57 (9) | 24 (17) | 0.013 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 127 ± 22 | 127 ± 21 | 128 ± 22 | 0.385 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 87 ± 18 | 87 ± 17 | 128 ± 22 | 0.849 |
| Temperature (°C) | 37.4 ± 1.0 | 37.4 ± 1.0 | 37.6 ± 1.1 | 0.042 |
| Saturation (%) | 84 ± 29 | 84 ± 29 | 84 ± 28 | 0.942 |
| Length of follow up (days) | 18 ± 17 | 18 ± 16 | 21 ± 20 | 0.041 |
| Laboratory findings | ||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.0 ± 2.1 | 13.0 ± 2.1 | 13.0 ± 2.3 | 0.133 |
| White blood cells (cells/mmc) | 1234 ± 3286 | 1085 ± 2837 | 1990 ± 4934 | <0.001 |
| Platelets (cells/mmc) | 228408 ± 102893 | 226385 ± 98926 | 239968 ± 123121 | 0.007 |
| C reactive protein (mg/dL) | 15.10 (5.60–53.50) | 16.00 (6.02–56.00) | 11.84 (4.75–38.83) | 0.713 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.16 ± 0.91 | 1.14 ± 0.93 | 2 ± 0.83 | <0.001 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 138 ± 6 | 138 ± 5 | 138 ± 7 | 0.24 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 4.1 ± 0.5 | 4.1 ± 0.5 | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 0.146 |
| Troponin (ng/L) | 16 (7–40) | 12 (6–29) | 31 (17–94) | <0.001 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 35 ± 34 | 37 ± 35 | 30 ± 23 | 0.225 |
| Electrocardiographic findings | ||||
| Supraventricular arrhythmias | 91 (12) | 69 (11) | 22 (16) | 0.214 |
| Therapy | ||||
| ACE inhibitors/ARB | 252 (34) | 192 (32) | 60 (42) | 0.046 |
| Beta blockers | 153 (21) | 122 (20) | 31 (22) | 0.701 |
| MRA | 24 (3) | 21 (4) | 3 (2) | 0.587 |
| CCB | 110 (15) | 84 (14) | 26 (18) | 0.208 |
| Diuretics | 115 (15) | 80 (13) | 25 (18) | 0.001 |
| Antiarrhythmics | 48 (6) | 39 (7) | 9 (6) | 0.418 |
| Antiplatelet drugs | 110 (15) | 84 (14) | 26 (18) | 0.208 |
| Anticoagulants | 71 (10) | 47 (8) | 24 (17) | 0.001 |
| Corticosteroids | 67 (9) | 51 (8) | 16 (11) | 0.427 |
| Unadjusted HR (CI (95%)) | Unadjusted p-Value | Adjusted HR (CI (95%)) | Adjusted p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.025 [1.012–1.038] | <0.001 | 0.991 [0.968–1.016] | 0.481 |
| Renal failure | 1.605 [1.407–1.890] | 0.013 | 1.314 [1.139–1.706] | 0.005 |
| Chronic obstructive disease | 0.628 [0.401–0.982] | 0.041 | 0.746 [0.275–2.021] | 0.621 |
| Oxygen saturation | 0.992 [0.985–0.999] | 0.027 | 0.998 [0.976–1.021] | 0.805 |
| History of AF | 0.579 [0.371–0.902] | 0.016 | 4.737 [0.314–7.134] | 0.311 |
| Troponin | 1.607 [1.346–1.918] | <0.001 | 1.396 [1.122–1.737] | 0.003 |
| Diuretics | 0.55 [0.372–0.813] | 0.003 | 0.523 [0.194–1.413] | 0.201 |
| Anticoagulants | 0.490 [0.314–0.764] | 0.002 | 0.489 [0.031–7.741] | 0.611 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henein, M.Y.; Mandoli, G.E.; Pastore, M.C.; Ghionzoli, N.; Hasson, F.; Nisar, M.K.; Islam, M.; Bandera, F.; Marrocco-Trischitta, M.M.; Baroni, I.; et al. Biomarkers Predict In-Hospital Major Adverse Cardiac Events in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicenter International Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245863
Henein MY, Mandoli GE, Pastore MC, Ghionzoli N, Hasson F, Nisar MK, Islam M, Bandera F, Marrocco-Trischitta MM, Baroni I, et al. Biomarkers Predict In-Hospital Major Adverse Cardiac Events in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicenter International Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(24):5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245863
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenein, Michael Y., Giulia Elena Mandoli, Maria Concetta Pastore, Nicolò Ghionzoli, Fouhad Hasson, Muhammad K. Nisar, Mohammed Islam, Francesco Bandera, Massimiliano M. Marrocco-Trischitta, Irene Baroni, and et al. 2021. "Biomarkers Predict In-Hospital Major Adverse Cardiac Events in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicenter International Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 24: 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245863
APA StyleHenein, M. Y., Mandoli, G. E., Pastore, M. C., Ghionzoli, N., Hasson, F., Nisar, M. K., Islam, M., Bandera, F., Marrocco-Trischitta, M. M., Baroni, I., Malagoli, A., Rossi, L., Biagi, A., Citro, R., Ciccarelli, M., Silverio, A., Biagioni, G., Moutiris, J. A., Vancheri, F., ... Cameli, M. (2021). Biomarkers Predict In-Hospital Major Adverse Cardiac Events in COVID-19 Patients: A Multicenter International Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(24), 5863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10245863