Clinical Presentations and Multimodal Imaging Diagnosis in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
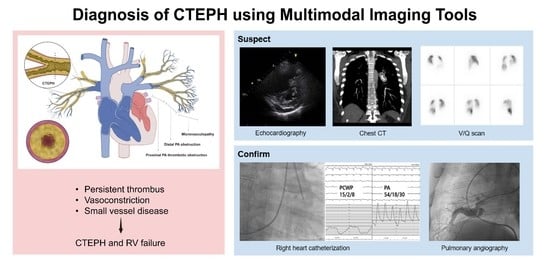
:1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation: Learning from a Case
3. Diagnosis (Using Multimodal Imaging)
3.1. Echocardiography
3.2. CT Scan
3.2.1. CT Findings Suggestive of PH
3.2.2. CT Findings for Chronic Thrombus: Morphology and Location
3.3. V/Q Scan
3.4. RHC and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galie, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 2200879. ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, M.P.; Schernthaner, G.H.; Lang, I.M. Chronic complications of venous thromboembolism. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papamatheakis, D.G.; Poch, D.S.; Fernandes, T.M.; Kerr, K.M.; Kim, N.H.; Fedullo, P.F. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2155–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; Boyer-Neumann, C.; Parent, F.; Eschwege, V.; Jaillet, H.; Meyer, D.; Simonneau, G. Thrombotic risk factors in pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, I.M.; Pesavento, R.; Bonderman, D.; Yuan, J.X. Risk factors and basic mechanisms of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A current understanding. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonderman, D.; Jakowitsch, J.; Adlbrecht, C.; Schemper, M.; Kyrle, P.A.; Schönauer, V.; Exner, M.; Klepetko, W.; Kneussl, M.P.; Maurer, G.; et al. Medical conditions increasing the risk of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Delcroix, M.; Bogaard, H.J. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension from the perspective of patients with pulmonary embolism. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delcroix, M.; Lang, I.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Jansa, P.; D’Armini, A.M.; Snijder, R.; Bresser, P.; Torbicki, A.; Mellemkjaer, S.; Lewczuk, J.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Results from an International Prospective Registry. Circulation 2016, 133, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Shin, J.W.; Choi, B.W.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.S.; Do Lee, S.; Park, S.S.; Moon, H.S.; Park, Y.B. Epidemiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension in Korea: Results from the Korean registry. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Ahn, J.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, H.W.; Oh, J.H.; Lee, H.C.; Cha, K.S.; Hong, T.J. The predictive value of echocardiography for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after acute pulmonary embolism in Korea. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfmüller, P.; Günther, S.; Ghigna, M.R.; de Montpréville, V.T.; Boulate, D.; Paul, J.F.; Jaïs, X.; Decante, B.; Simonneau, G.; Dartevelle, P.; et al. Microvascular disease in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A role for pulmonary veins and systemic vasculature. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonneau, G.; Torbicki, A.; Dorfmüller, P.; Kim, N. The pathophysiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietra, G.G.; Capron, F.; Stewart, S.; Leone, O.; Humbert, M.; Robbins, I.M.; Reid, L.M.; Tuder, R.M. Pathologic assessment of vasculopathies in pulmonary hypertension. J. Am. Coll Cardiol. 2004, 43 (Suppl. S12), 25S–32S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remy-Jardin, M.; Ryerson, C.J.; Schiebler, M.L.; Leung, A.N.; Wild, J.M.; Hoeper, M.M.; Alderson, P.O.; Goodman, L.R.; Mayo, J.; Haramati, L.B.; et al. Imaging of pulmonary hypertension in adults: A position paper from the Fleischner Society. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2004455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisinghani, A.; Ben-Yehuda, O. Echocardiography in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2006, 18, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Hu, K.; Pelzer, H.T.; Störk, S.; Weidemann, F. Journey of a patient with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2015, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahay, S.; Tonelli, A.R. Pericardial effusion in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 1–39.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badano, L.P.; Ginghina, C.; Easaw, J.; Muraru, D.; Grillo, M.T.; Lancellotti, P.; Pinamonti, B.; Coghlan, G.; Marra, M.P.; Popescu, B.A.; et al. Right ventricle in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Haemodynamics, structural changes, imaging, and proposal of a study protocol aimed to assess remodelling and treatment effects. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2010, 11, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, J.H. Strain Analysis of the Right Ventricle Using Two-dimensional Echocardiography. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 26, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H. Two-dimensional Echocardiographic Assessment of Myocardial Strain: Important Echocardiographic Parameter Readily Useful in Clinical Field. Korean Circ. J. 2019, 49, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraru, D.; Badano, L.P.; Nagata, Y.; Surkova, E.; Nabeshima, Y.; Genovese, D.; Otsuji, Y.; Guida, V.; Azzolina, D.; Palermo, C.; et al. Development and prognostic validation of partition values to grade right ventricular dysfunction severity using 3D echocardiography. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugu, T.; Kawakami, T.; Kataoka, M.; Endo, J.; Kohno, T.; Itabashi, Y.; Fukuda, K.; Murata, M. Preoperative right ventricular strain predicts sustained right ventricular dysfunction after balloon pulmonary angioplasty in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Echocardiography 2020, 37, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanar, B.G.; Mutlu, B.; Atas, H.; Akaslan, D.; Yıldızeli, B. Improvements of right ventricular function and hemodynamics after balloon pulmonary angioplasty in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Echocardiography 2019, 36, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascha, M.; Renapurkar, R.D.; Tonelli, A.R. A review of imaging modalities in pulmonary hypertension. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2017, 12, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, A.J.; Dwivedi, K.; Johns, C.; Garg, P.; Chin, M.; Currie, B.J.; Rothman, A.M.; Capener, D.; Shahin, Y.; Elliot, C.A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of CT pulmonary angiography in suspected pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4918–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.; Hoey, E.T.; Reynolds, J.H.; Ganeshan, A.; Ment, J. Multi-detector CT assessment in pulmonary hypertension: Techniques, systematic approach to interpretation and key findings. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2015, 5, 423–432. [Google Scholar]
- Haramati, A.; Haramati, L.B. Imaging of Chronic Thromboembolic Disease. Lung 2020, 198, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, D.; Gore, I.; Blenke, A.; Collins, D.P. Pulmonary arterial bands and webs: An unrecognized manifestation of organized pulmonary emboli. Am. J. Pathol. 1962, 40, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Auger, W.R.; Kerr, K.M.; Kim, N.H.; Fedullo, P.F. Evaluation of patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension for pulmonary endarterectomy. Pulm. Circ. 2012, 2, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remy-Jardin, M.; Duhamel, A.; Deken, V.; Bouaziz, N.; Dumont, P.; Remy, J. Systemic collateral supply in patients with chronic thromboembolic and primary pulmonary hypertension: Assessment with multi-detector row helical CT angiography. Radiology 2005, 235, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhou, M.; Liu, D.; Long, X.; Guo, T.; Kong, X. Diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, D.; Delcroix, M.; Held, M. Diagnosis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagspiel, K.D.; Flors, L.; Housseini, A.M.; Phull, A.; Ahmad, E.A.; Bozlar, U.; Norton, P.T.; Bonatti, H.J. Pulmonary blood volume imaging with dual-energy computed tomography: Spectrum of findings. Clin. Radiol. 2012, 67, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunariu, N.; Gibbs, S.J.; Win, Z.; Gin-Sing, W.; Graham, A.; Gishen, P.; Adil, A.N. Ventilation-perfusion scintigraphy is more sensitive than multidetector CTPA in detecting chronic thromboembolic pulmonary disease as a treatable cause of pulmonary hypertension. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar]
- Sirajuddin, A.; Donnelly, E.F.; Crabtree, T.P.; Henry, T.S.; Iannettoni, M.D.; Johnson, G.B.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Maldonado, F.; Olsen, K.M.; Expert Panel on Thoracic Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Suspected Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2017, 14, S350–S361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worsley, D.F.; Palevsky, H.I.; Alavi, A. Ventilation-perfusion lung scanning in the evaluation of pulmonary hypertension. J. Nucl. Med. 1994, 35, 793–796. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, F.; Morris, T.A.; Hoh, C.K. Perfusion Scintigraphy in Diagnosis and Management of Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Radiographics 2019, 39, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Fang, W.; Lv, B.; He, J.G.; Xiong, C.M.; Liu, Z.H.; He, Z.X. Diagnosis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Comparison of ventilation/perfusion scanning and multidetector computed tomography pulmonary angiography with pulmonary angiography. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2012, 33, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, X.; Kerr, K.M.; Marsh, J.J.; Renner, J.W.; Hoh, C.K.; Test, V.J.; Morris, T.A. Pilot study comparing SPECT perfusion scintigraphy with CT pulmonary angiography in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Respirology 2012, 17, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Variable | Echocardiography | CT Scan | V/Q Scan |
|---|---|---|---|
| PH detection | ++ | + | − |
| Assessment of PH etiology | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| Evaluated anatomic region | |||
| Lung parenchyma | − | +++ | − |
| Cardiac chambers | ++ | ++ (especially on ECG-gated CT) | − |
| Pulmonary vessels | + | +++ | + |
| Strengths | Good for initial screening and follow-up for PH; readily available; safe for repeated testing | Excellent evaluation for etiologies of PH | Good for initial screening of thromboembolic disease (acute PE, CTEPH) |
| Weaknesses | Limited role for the assessment of etiology (lung parenchyma, pulmonary vessels); cannot confirm PH and requires RHC | Radiation risks; limited assessment of hemodynamic assessment; needs experienced radiologists; cannot confirm PH and requires RHC | Findings often nonspecific; needs additional testing to assess etiology; cannot confirm PH and requires RHC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, M.-H.; Jung, H.O.; Kwon, S.J.; Chang, S. Clinical Presentations and Multimodal Imaging Diagnosis in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6678. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226678
Jung M-H, Jung HO, Kwon SJ, Chang S. Clinical Presentations and Multimodal Imaging Diagnosis in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(22):6678. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226678
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Mi-Hyang, Hae Ok Jung, Soo Jin Kwon, and Suyon Chang. 2022. "Clinical Presentations and Multimodal Imaging Diagnosis in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 22: 6678. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226678
APA StyleJung, M. -H., Jung, H. O., Kwon, S. J., & Chang, S. (2022). Clinical Presentations and Multimodal Imaging Diagnosis in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(22), 6678. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11226678