Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Portal Hypertension and HIV Infection: Comparative Characteristics and Prognostic Predictors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Assessment
2.3. Statistics
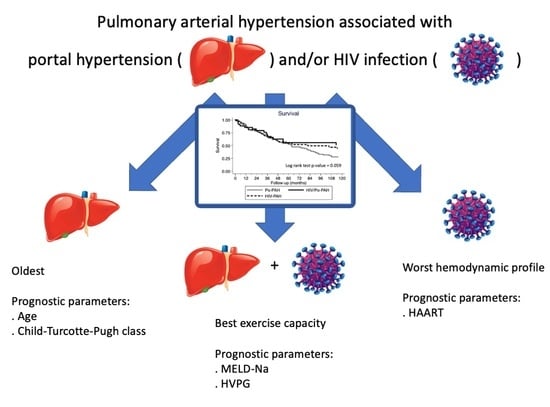
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Po-PAH
3.3. HIV-PAH
3.4. HIV/Po-PAH
3.5. Survival
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension: Developed by the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Endorsed by the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) and the European Reference Network on Rare Respiratory Diseases (ERN-LUNG). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krowka, M.J.; Miller, D.P.; Barst, R.J.; Taichman, D.; Dweik, R.A.; Badesch, D.B.; McGoon, M.D. Portopulmonary Hypertension: A Report from the US-Based REVEAL Registry. Chest 2012, 141, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krowka, M.J.; Plevak, D.J.; Findlay, J.Y.; Rosen, C.B.; Wiesner, R.H.; Krom, R.A. Pulmonary Hemodynamics and Perioperative Cardiopulmonary-Related Mortality in Patients with Portopulmonary Hypertension Undergoing Liver Transplantation. Liver Transplant. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Study Liver Dis. Int. Liver Transplant. Soc. 2000, 6, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.L.; Wiesner, R.H.; Nyberg, S.L.; Rosen, C.B.; Krowka, M.J. Survival in Portopulmonary Hypertension: Mayo Clinic Experience Categorized by Treatment Subgroups. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2008, 8, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitbon, O.; Bosch, J.; Cottreel, E.; Csonka, D.; de Groote, P.; Hoeper, M.M.; Kim, N.H.; Martin, N.; Savale, L.; Krowka, M. Macitentan for the Treatment of Portopulmonary Hypertension (PORTICO): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 4 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, H.-A.; Galiè, N.; Grimminger, F.; Grünig, E.; Humbert, M.; Jing, Z.-C.; Keogh, A.M.; Langleben, D.; Kilama, M.O.; Fritsch, A.; et al. Riociguat for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Seyfarth, H.J.; Hoeffken, G.; Wirtz, H.; Spiekerkoetter, E.; Pletz, M.W.; Welte, T.; Halank, M. Experience with Inhaled Iloprost and Bosentan in Portopulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halank, M.; Knudsen, L.; Seyfarth, H.-J.; Ewert, R.; Wiedemann, B.; Kolditz, M.; Höffken, G.; Hoeper, M.M. Ambrisentan Improves Exercise Capacity and Symptoms in Patients with Portopulmonary Hypertension. Z. Gastroenterol. 2011, 49, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenberger, F.; Voswinckel, R.; Steveling, E.; Enke, B.; Kreckel, A.; Olschewski, H.; Grimminger, F.; Seeger, W.; Ghofrani, H.A. Sildenafil Treatment for Portopulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.C.; Johnson, L.B.; Plotkin, J.S.; Howell, C.D.; Bartlett, S.T.; Rubin, L.J. Continuous Intravenous Infusion of Epoprostenol for the Treatment of Portopulmonary Hypertension. Transplantation 1997, 63, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Planinsic, R.M.; Mathier, M.A.; de Vera, M.E.; Venkataramanan, R. Initial Experience Using Continuous Intravenous Treprostinil to Manage Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Patients with End-Stage Liver Disease. Transpl. Int. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Organ Transplant. 2009, 22, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savale, L.; Magnier, R.; Pavec, J.L.; Jaïs, X.; Montani, D.; O’Callaghan, D.S.; Humbert, M.; Dingemanse, J.; Simonneau, G.; Sitbon, O. Efficacy, Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Bosentan in Portopulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losay, J.; Piot, D.; Bougaran, J.; Ozier, Y.; Devictor, D.; Houssin, D.; Bernard, O. Early Liver Transplantation Is Crucial in Children with Liver Disease and Pulmonary Artery Hypertension. J. Hepatol. 1998, 28, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schott, R.; Chaouat, A.; Launoy, A.; Pottecher, T.; Weitzenblum, E. Improvement of Pulmonary Hypertension after Liver Transplantation. Chest 1999, 115, 1748–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savale, L.; Guimas, M.; Ebstein, N.; Fertin, M.; Jevnikar, M.; Renard, S.; Horeau-Langlard, D.; Tromeur, C.; Chabanne, C.; Prevot, G.; et al. Portopulmonary Hypertension in the Current Era of Pulmonary Hypertension Management. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opravil, M.; Pechère, M.; Speich, R.; Joller-Jemelka, H.I.; Jenni, R.; Russi, E.W.; Hirschel, B.; Lüthy, R. HIV-Associated Primary Pulmonary Hypertension. A Case Control Study. Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Leong, S.; Lee, K.A.; Patel, A.; Chua, J.M.E.; Venkatanarasimha, N.; Lo, R.H.; Irani, F.G.; Zhuang, K.D.; Gogna, A.; et al. Hepatic Venous-Portal Gradient (HVPG) Measurement: Pearls and Pitfalls. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardi, F.; Manes, A.; Guarino, D.; Zuffa, E.; De Lorenzis, A.; Magnani, I.; Rotunno, M.; Ballerini, A.; Lo Russo, G.V.; Nardi, E.; et al. A Pragmatic Approach to Risk Assessment in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Using the 2015 European Society of Cardiology/European Respiratory Society Guidelines. Open Heart 2021, 8, e001725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardi, F.; Manes, A.; Palazzini, M.; Bachetti, C.; Mazzanti, G.; Rinaldi, A.; Albini, A.; Gotti, E.; Monti, E.; Bacchi Reggiani, M.L.; et al. Combining Bosentan and Sildenafil in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Patients Failing Monotherapy: Real-World Insights. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Kramer, T.; Pan, Z.; Eichstaedt, C.A.; Spiesshoefer, J.; Benjamin, N.; Olsson, K.M.; Meyer, K.; Vizza, C.D.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A.; et al. Mortality in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Prediction by the 2015 European Pulmonary Hypertension Guidelines Risk Stratification Model. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucly, A.; Weatherald, J.; Savale, L.; Jaïs, X.; Cottin, V.; Prevot, G.; Picard, F.; de Groote, P.; Jevnikar, M.; Bergot, E.; et al. Risk Assessment, Prognosis and Guideline Implementation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benza, R.L.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; Elliott, C.G.; Farber, H.W.; Foreman, A.J.; Frost, A.E.; McGoon, M.D.; Pasta, D.J.; Selej, M.; Burger, C.D.; et al. Predicting Survival in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: The REVEAL Risk Score Calculator 2.0 and Comparison With ESC/ERS-Based Risk Assessment Strategies. Chest 2019, 156, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androutsakos, T.; Schina, M.; Pouliakis, A.; Kontos, A.; Sipsas, N.; Hatzis, G. Causative Factors of Liver Fibrosis in HIV-Infected Patients. A Single Center Study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellares, C.; Barreiro, P.; Martín-Carbonero, L.; Labarga, P.; Vispo, M.E.; Casado, R.; Galindo, L.; García-Gascó, P.; García-Samaniego, J.; Soriano, V. Liver Cirrhosis in HIV-Infected Patients: Prevalence, Aetiology and Clinical Outcome. J. Viral Hepat. 2008, 15, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBrock, H.M.; Cartin-Ceba, R.; Channick, R.N.; Kawut, S.M.; Krowka, M.J. Sex Differences in Portopulmonary Hypertension. Chest 2021, 159, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaitis, N.A.; Lammi, M.; Mazimba, S.; Feldman, J.; McConnell, W.; Sager, J.S.; Raval, A.A.; Simon, M.A.; De Marco, T. HIV-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Report from the Pulmonary Hypertension Association Registry. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, M.L.; Rodríguez-Padial, L.; Soto Abánades, C.; Cruz Utrilla, A.; Barberá Mir, J.A.; López-Meseguer, M.; Segovia Cubero, J.; Samper, G.J.; Blanco Vich, I.; Escribano-Subías, P.; et al. Management and Prognosis of HIV-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: 20 Years of Evidence from the REHAP Registry. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degano, B.; Guillaume, M.; Savale, L.; Montani, D.; Jaïs, X.; Yaici, A.; Le Pavec, J.; Humbert, M.; Simonneau, G.; Sitbon, O. HIV-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Survival and Prognostic Factors in the Modern Therapeutic Era. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2010, 24, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories ATS Statement: Guidelines for the Six-Minute Walk Test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [CrossRef]
- Sahay, S.; Al Abdi, S.; Melillo, C.; Newman, J.; Dweik, R.A.; Heresi, G.A.; Tonelli, A.R. Causes and Circumstances of Death in Portopulmonary Hypertension. Transplant. Direct 2021, 7, e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, M.; Li, M.; Bhardwaj, A.; Wallace, W.D.; Wang, X.; Carey, W.D.; Dweik, R.A.; Heresi, G.A.; Tonelli, A.R. Predictors of Survival in Portopulmonary Hypertension: A 20-Year Experience. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 34, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigna, J.J.R.; Sime, P.S.D.; Koulla-Shiro, S. HIV Related Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Epidemiology in Africa, Physiopathology, and Role of Antiretroviral Treatment. AIDS Res. Ther. 2015, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, M.; Martin-Carbonero, L.; Soriano, V.; Vispo, E.; Valencia, E.; Moreno, V.; de Isla, L.P.; Lennie, V.; Almería, C.; Zamorano, J.L. Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated with Pulmonary Hypertension in HIV-Infected Patients on Regular Follow-Up. AIDS Lond. Engl. 2012, 26, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, J.; Sen, K.; Sarkar, G.; Mandal, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Deb, A. Effect of Antiretroviral Therapy on Pulmonary Hypertension in HIV Patients. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 2013, 111, 845–845, 849. [Google Scholar]
- Zuber, J.-P.; Calmy, A.; Evison, J.M.; Hasse, B.; Schiffer, V.; Wagels, T.; Nuesch, R.; Magenta, L.; Ledergerber, B.; Jenni, R.; et al. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Related to HIV Infection: Improved Hemodynamics and Survival Associated with Antiretroviral Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2004, 38, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, A.; Isnardi, D.; Saini, A.; Scarabelli, T.; Raddino, R.; Torre, D. Impact of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in HIV-Positive Patients with Cardiac Involvement. J. Infect. 2000, 40, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Hassan, F.F.; Bou Hamdan, M.A.; El Asmar, K.; Mokhbat, J.E.; Melhem, N.M. Trends & Predictors of Non-AIDS Comorbidities among People Living with HIV and Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy in Lebanon. Medicine 2022, 101, e29162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, A.; Shah, S.A.; Anwar, N.; Jones, C.R.; Sherman, K.E.; Elwing, J.M. Pulmonary Vascular Resistance Predicts Mortality and Graft Failure in Transplantation Patients with Portopulmonary Hypertension. Liver Transplant. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Study Liver Dis. Int. Liver Transplant. Soc. 2021, 27, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certain, M.C.; Baron, A.; Turpin, M.; Ebstein, N.; Boucly, A.; Beurnier, A.; Jevnikar, M.; Roche, A.; Keddache, S.; Bulifon, S.; et al. Outcomes of Cirrhotic Patients with Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Vascular Resistance between 2 and 3 Wood Units. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2200107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Po-PAH | HIV/Po-PAH | HIV-PAH | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 128 | 35 | 41 | / |
| Male gender, n (%) | 70 (55) | 19 (54) | 19 (46) | 0.638 |
| Age, years | 53 (44–61) *,∬ | 44 (39–48) * | 40 (37–44) ∬ | <0.001 |
| WHO-FC III-IV, n (%) | 62 (48.4)–3 (2.3) | 12 (34.3)–0 | 19 (46.3)–0 | 0.222 |
| 6MWD, m | 426 (366–504) * | 516 (432–571) *,∔ | 448 (370–510) ∔ | 0.001 |
| Baseline risk, n (%) | 0.063 | |||
| 48 (37.5) | 19 (54.3) | 10 (24.4) | |
| 70 (54.7) | 15 (42.9) | 25 (61.0) | |
| 10 (7.8) | 1 (2.9) | 6 (14.6) | |
| BNP/NT-proBNP, n (%) | 0.488 | |||
| 34 (46.0) | 10 (62.5) | 3 (37.5) | |
| 26 (35.1) | 3 (18.75) | 2 (25.0) | |
| 14 (18.9) | 3 (18.75) | 3 (37.5) | |
| (n tot = 74) | (n tot = 16) | (n tot = 8) | ||
| PAH-specific therapy at baseline, n (%) | 0.222 | |||
| 116 (90.6) | 34 (97.1) | 37 (90.3) | |
| 3 (2.3) | 0 | 3 (7.3) | |
| 9 (7.1) | 1 (2.9) | 1 (2.4) | |
| PAH-specific therapy at the end of follow-up, n (%) | 0.795 | |||
| 19 (14.8) | 5 (14.3) | 6 (14.6) | |
| 77 (60.2) | 25 (71.4) | 26 (63.4) | |
| 28 (21.9) | 5 (14.3) | 7 (17.1) | |
| 4 (3.1) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (4.9) | |
| Etiology of portal hypertension, n (%) | 0.069 | |||
| 112 (87.5) | 34 (97.1) | / | |
| 15 (11.7) | / | / | |
| 1 (0.8) | 1 (2.9) | / | |
| MELD-Na | 14 (11–18) | 13 (10–15) | / | 0.13 |
| CTP, n (%) | ||||
| 68 (53.1) | 21 (60.0) | / | 0.768 |
| 56 (43.8) | 13 (37.1) | / | |
| 4 (3.1) | 1 (2.9) | / | |
| HAART at baseline, n (%) | / | 23 (66) | 23 (56) | 0.393 |
| HAART at follow-up, n (%) | / | 27 (77) | 32 (78) | 0.925 |
| CD4, n/mmc | / | 371 (200–530) | 410 (294–535) | 0.272 |
| RAP, mmHg | 6 (4–9) | 6 (4–8) | 8 (5–11) | 0.105 |
| mPAP, mmHg | 45 (40–53) | 45 (38–55) | 48 (41–56) | 0.272 |
| PAWP, mmHg | 8 (6–10) | 7 (6–11) | 7 (6–9) | 0.147 |
| mBP, mmHg | 90 (80–98) | 89 (83–104) | 88 (78–97) | 0.614 |
| CI, L/min/m2 | 3.1 (2.6–3.8) ∬ | 3.0 (2.7–3.7) ∔ | 2.6 (2.2–2.9) ∬,∔ | <0.001 |
| PVR, WU | 6.2 (4.9–8.8) ∬ | 7.0 (5.5–11.2) ∔ | 8.9 (7.5–12.2)∬,∔ | <0.001 |
| SVR, WU | 14.0 (11.5–17.2) ∬ | 15.6 (12.8–18.9) | 18.1 (15.7–21.6) ∬ | <0.001 |
| Syst O2 Sat, % | 96 (95–97) ∬ | 97 (95–98) ∔ | 95 (94–96) ∬,∔ | 0.011 |
| SvO2, % | 70 (65–75) ∬ | 67 (62–71) ∔ | 61 (55–66) ∬,∔ | <0.001 |
| HVPG, mmHg | 12 (8–16) | 11 (8–17) | / | 0.702 |
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Male gender | 1.193 (0.777–1.830) | 0.420 |
| Age, years | 1.039 (1.019–1.059) | <0.001 |
| Etiology of portal hypertension | ||
| 2.234 (1.029–4.848) | 0.042 |
| 12.386 (1.460–105.059) | 0.021 |
| MELD-Na | 1.055 (1.013–1.098) | 0.010 |
| CTP, A/B/C | 1.752 (1.216–2.524) | 0.003 |
| Baseline Risk, low/interm/high | 1.367 (0.997–1.875) | 0.052 |
| WHO-FC III-IV | 1.268 (0.831–1.935) | 0.270 |
| BNP/NT-proBNP, low/interm/high (n = 74) | 1.235 (0.847–1.800) | 0.272 |
| 6MWD, m | 0.997 (0.995–0.999) | 0.011 |
| RAP, mmHg | 1.005 (0.968–1.044) | 0.787 |
| mPAP, mmHg | 0.982 (0.962–1.001) | 0.068 |
| PAWP, mmHg | 0.974 (0.902–1.051) | 0.500 |
| mBP, mmHg | 0.991 (0.975–1.007) | 0.250 |
| CI, L/min/m2 | 0.889 (0.685–1.154) | 0.378 |
| PVR, WU | 1.000 (0.948–1.056) | 0.987 |
| SVR, WU | 1.003 (0.965–1.042) | 0.896 |
| Syst O2 Sat, % | 0.931 (0.861–1.007) | 0.075 |
| SvO2, % | 0.994 (0.967–1.023) | 0.685 |
| HVPG, mmHg | 1.042 (1.002–1.084) | 0.039 |
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 1.039 (1.018–1.060) | <0.001 |
| Child–Turcotte–Pugh, A/B/C | 1.665 (1.153–2.403) | 0.007 |
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Male gender | 1.366 (0.622–2.998) | 0.437 |
| Age, years | 0.973 (0.908–1.043) | 0.439 |
| HAART at baseline | 0.866 (0.394–1.904) | 0.721 |
| HAART during follow-up | 0.283 (0.119–0.675) | 0.004 |
| CD4, n/mmc | 0.999 (0.997–1.000) | 0.155 |
| Baseline risk, low/interm/high | 1.864 (0.906–3.837) | 0.091 |
| WHO-FC III-IV | 1.833 (0.829–4.051) | 0.135 |
| BNP/NT-proBNP, low/interm/high (n = 8) | 1.878 (0.571–6.177) | 0.299 |
| 6MWD, m | 0.995 (0.991–0.999) | 0.006 |
| RAP, mmHg | 1.069 (0.967–1.181) | 0.192 |
| mPAP, mmHg | 1.019 (0.987–1.051) | 0.253 |
| PAWP, mmHg | 1.035 (0.866–1.237) | 0.706 |
| mBP, mmHg | 1.010 (0.976–1.046) | 0.558 |
| CI, L/min/m2 | 0.980 (0.583–1.647) | 0.939 |
| PVR, WU | 1.081 (0.971–1.204) | 0.154 |
| SVR, WU | 1.017 (0.920–1.123) | 0.746 |
| Syst O2 Sat, % | 0.887 (0.793–0.992) | 0.036 |
| SvO2, % | 0.983 (0.943–1.025) | 0.422 |
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Male gender | 1.072 (0.408–2.822) | 0.887 |
| Age, years | 1.009 (0.942–1.082) | 0.794 |
| Etiology of portal hypertension | ||
| 7.931 (0.886–70.996) | 0.064 |
| MELD-Na | 1.199 (1.044–1.376) | 0.010 |
| CTP, A/B/C | 3.010 (1.203–7.532) | 0.019 |
| HAART at baseline | 0.879 (0.334–2.317) | 0.795 |
| HAART during follow-up | 0.433 (0.158–1.188) | 0.104 |
| CD4, n/mmc | 0.999 (0.997–1.001) | 0.253 |
| Baseline risk, low/interm/high | 0.485 (0.189–1.242) | 0.131 |
| WHO-FC III-IV | 0.697 (0.245–1.985) | 0.499 |
| BNP/NT-proBNP low/interm/high (n = 16) | 0.465 (0.155–1.395) | 0.172 |
| 6MWD, m | 1.000 (0.995–1.004) | 0.827 |
| RAP, mmHg | 0.936 (0.811–1.080) | 0.366 |
| mPAP, mmHg | 0.983 (0.941–1.028) | 0.450 |
| PAWP, mmHg | 1.019 (0.868–1.196) | 0.818 |
| mBP, mmHg | 0.948 (0.899–1.000) | 0.051 |
| CI, L/min/m2 | 2.032 (1.119–3.690) | 0.020 |
| PVR, WU | 0.825 (0.689–0.988) | 0.037 |
| SVR, WU | 0.826 (0.721–0.947) | 0.006 |
| Syst O2 Sat, % | 1.117 (0.886–1.407) | 0.350 |
| SvO2, % | 1.061 (0.985–1.142) | 0.117 |
| HVPG, mmHg | 1.107 (1.011–1.213) | 0.029 |
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| MELD-Na | 1.224 (1.064–1.408) | 0.005 |
| HVPG, mmHg | 1.125 (1.026–1.235) | 0.013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dardi, F.; Guarino, D.; Cennerazzo, F.; Ballerini, A.; Magnani, I.; Bertozzi, R.; Donato, F.; Martini, G.; Manes, A.; Galiè, N.; et al. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Portal Hypertension and HIV Infection: Comparative Characteristics and Prognostic Predictors. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103425
Dardi F, Guarino D, Cennerazzo F, Ballerini A, Magnani I, Bertozzi R, Donato F, Martini G, Manes A, Galiè N, et al. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Portal Hypertension and HIV Infection: Comparative Characteristics and Prognostic Predictors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(10):3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103425
Chicago/Turabian StyleDardi, Fabio, Daniele Guarino, Francesco Cennerazzo, Alberto Ballerini, Ilenia Magnani, Riccardo Bertozzi, Federico Donato, Giulia Martini, Alessandra Manes, Nazzareno Galiè, and et al. 2023. "Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Portal Hypertension and HIV Infection: Comparative Characteristics and Prognostic Predictors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 10: 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103425
APA StyleDardi, F., Guarino, D., Cennerazzo, F., Ballerini, A., Magnani, I., Bertozzi, R., Donato, F., Martini, G., Manes, A., Galiè, N., & Palazzini, M. (2023). Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Portal Hypertension and HIV Infection: Comparative Characteristics and Prognostic Predictors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(10), 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103425