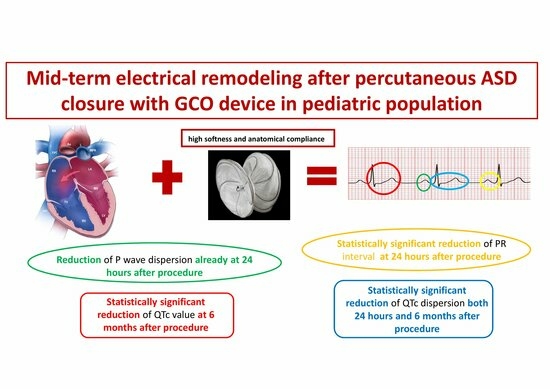
Mid-Term Electrical Remodeling after Percutaneous Atrial Septal Defect Closure with GCO Device in a Pediatric Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. ASD Closure
2.3. Electrocardiographic Findings
2.4. Echocardiographic Findings
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoffman, J.I.; Kaplan, S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol 2002, 39, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, H.; Bonhoeffer, P.; De Groot, N.M.; de Haan, F.; Deanfield, J.E.; Galie, N.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Gohlke-Baerwolf, C.; Kaemmerer, H. ESC guidelines for the management of grown-up congenital heart disease (new version 2010). Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2915–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraisse, A.; Latchman, M.; Sharma, S.R.; Bayburt, S.; Amedro, P.; di Salvo, G.; Baruteau, A.E. Atrial septal defect closure: Indications and contra-indications. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10 (Suppl. S24), S2874–S2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, M.L.; Levi, D.S. State-of-the-art atrial septal defect closure devices for congenital heart. Interv. Cardiol. Clin. 2019, 8, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, C.J.; Feldt, R.H.; Edward, W.D. Atrial septal defects. In Heart Disease in Infants, Children and Adolescents, Including the Fetus and Young Adults, 5th ed.; Emmanouilides, G.C., Riemenschneider, T.A., Allen, H.D., Gutgessel, H.P., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1995; pp. 687–703. [Google Scholar]
- Saton, T.; Zipes, D.P. Unequal atrial stretch in dogs increases dispersion of refractoriness conductive to developing atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1996, 7, 833–842. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, J.B.; Sanders, P.; Vohra, J.K.; Sparks, P.B.; Morgan, J.G.; Spence, S.J.; Grigg, L.E.; Kalman, J.M. Effect of chronic right atrial stretch on atrial electrical remodeling in patients with an atrial septal defect. Circulation 2003, 107, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilaveris, P.E.; Gialafos, E.J.; Sideris, S.K.; Theopistou, A.M.; Andrikopoulos, G.K.; Kyriakidis, M.; Gialafos, J.E.; Toutouzas, P.K. Simple electrocardiographic markers for the prediction of paroxysmal idio-pathic atrial fibrillation. Am. Heart J. 1998, 135, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytemir, K.; Ozer, N.; Atalar, E.; Sade, E.; Aksoyek, S.; Ovunc, K.; Oto, A.; Ozmen, F.; Kes, S. P-wave dispersion on 12-lead electrocardiography in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Pacing Electrophysiol. 2000, 23, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, C.S.; Naas, A.; Freeman, M.; Land, C.C.; Struthers, A.D. QT dispersion and sudden unexpected death in chronic heart failure. Lancet 1994, 343, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulzaite, I.; Brazdzionyte, J.; Zaliunas, R.; Rickli, H.; Ammann, P. QT dispersion and heart rate variability in sudden death risk stratification in patients with ischemic heart disease. Med. Kaunas 2006, 42, 450–454. [Google Scholar]
- Pye, M.; Quinn, A.C.; Cobbe, S.M. QT interval dispersion: A noninvasive marker of susceptibility to arrhythmia in patients with sustained ventricular arrhythmias? Br. Heart J. 1994, 71, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.G.; Baykan, A.; Dogan, A.; Inanc, T.; Gunebakmaz, O.; Dogdu, O.; Uzum, K.; Eryol, N.K.; Narin, N. Intermediate-Term Effects of Transcatheter Secundum Atrial Septal Defect Closure on Cardiac Remodeling in Children and Adults. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2010, 31, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, G.; Pascotto, M.; Sarubbi, B.; Bigazzi, M.C.; Calvanese, R.; Iacono, C.; Pisacane, C.; Palladino, M.T.; Pacileo, G.; Russo, M.G.; et al. Early electrical and geometric changes after percutaneous closure of large atrial septal defect. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 93, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roushdy, A.M.; Attia, H.; Nossir, H. Immediate and short term effects of percutaneous atrial septal defect device closure on cardiac electrical remodeling in children. Egypt. Heart J. 2018, 70, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, G.; Pascotto, M.; Caputo, S.; Gaio, G.; Iacono, C.; Caso, I.; Sarubbi, B.; Carrozza, M.; Russo, M.G.; Calabrò, R. Short-term electro-geometric atrial remodeling after percutaneous atrial septal defect closure. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 9, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamphuis, V.P.; Nassif, M.; Man, S.-C.; Swenne, C.A.; Kors, J.A.; Vink, A.S.; Harkel, A.D.T.; Maan, A.C.; Mulder, B.J.; de Winter, R.J.; et al. Electrical remodeling after percutaneous atrial septal defect closure in pediatric and adult patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 285, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, G.; Castaldi, B.; Cuman, M.; Di Candia, A.; Pizzuto, A.; Sirico, D.; Cantinotti, M.; Garibaldi, S.; Pak, V.; Di Salvo, G. Transcatheter atrial Septal defect closure with the new GORE® cardioform ASD occluder: First European experience. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 327, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, G.; Cuman, M.; Pizzuto, A.; Haxhiademi, D.; Lunardini, A.; Franchi, E.; Marrone, C.; Pak, V.; Assanta, N.; Cantinotti, M. GORE® Cardioform ASD Occluder experience in transcatheter closure of “complex” atrial septal defects. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 99, E22–E30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, G.; Pizzuto, A.; Cuman, M.; Haxhiademi, D.; Marchese, P.; Franchi, E.; Marrone, C.; Pak, V.; Assanta, N.; Cantinotti, M. Transcatheter closure of “Surgical” ostium secundum atrial septal defects with GORE® Cardioform ASD Occluder. J. Card. Surg. 2022, 37, 3200–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Premarket Approval (PMA): Gore CARDIOFORM ASD, Occluder. 2019. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpma/pma.cfm?id=P050006S078 (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- GORE®, CARDIOFORM ASD Occluder IFU. 2019. Available online: https://www.goremedical.com/news/gore-cardioform-asd-occluder-ce-mark-2019-10-02 (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- de Hemptinne, Q.; Horlick, E.M.; Osten, M.D.; Millán, X.; Tadros, V.-X.; Pighi, M.; Barlatey, F.G.; Alnasser, S.M.; Miró, J.; Asgar, A.W.; et al. Initial clinical experience with the GORE® CARDIOFORM ASD occluder for transcatheter atrial septal defect closure. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 90, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, P.S.; Carabello, B.A.; Lang, R.M.; Lopez, L.; Pellikka, P.A.; Picard, M.H.; Thomas, J.D.; Varghese, P.; Wang, T.Y.; Weissman, N.J.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA/ASE Key Data Elements and Definitions for Transthoracic Echocardiography: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Data Standards (Writing Committee to Develop Cardiovascular Endpoints Data Standards) and the American Society of Echocardiography. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfredi, O.; Luckie, M.; Mirjafari, H.; Willard, T.; Buckley, H.; Griffiths, L.; Clarke, B.; Mahadevan, V.S. Percutaneous device closure of atrial septal defect results in very early and sustained changes of right and left heart function. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignani, R.T.; Tolentino, K.M.; Rajgor, D.D.; Quek, S.C. Longitudinal evaluation of P- wave dispersion and P-wave maximum in children after transcatheter device closure of secundum atrial septal defect. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2015, 36, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilen, U.; Carlson, J.; Platonov, P.G.; Olsson, S.B. Atrial myocardial pathoelectrophysiology in adults with a secundum atrial septal defect is unaffected by closure of the defect. A study using high resolution signal-averaged orthogonal P-wave technique. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 132, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; Shabana, A.; El Amrousy, D.; Zoair, A. Predictive value of P-wave and QT interval dispersion in children with congenital heart disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension for the occurrence of arrhythmias. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2019, 31, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucklova, K.; Koubsky, K.; Tomek, V.; Kubus, P.; Janousek, J. Prolonged repolarization in atrial septal defect: An example of mechanoelectrical feedback due to right ventricular volume overload. Heart Rhythm. 2016, 13, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, R.J.; Love, B.A.; Paolillo, J.A.; Gray, R.G.; Goldstein, B.H.; Morgan, G.J.; Gillespie, M.J.; ASSURED Investigators. ASSURED clinical study: New GORE® CARDIOFORM ASD occluder for transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect, Cathe-ter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 95, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyak, Z.; de Groot, J.R.; Bouma, B.J.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Silversides, C.K.; Oechslin, E.N.; Budts, W.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Mulder, B.J.; Harris, L. Sudden cardiac death in adult congenital heart disease: Can the unpredictable be foreseen? Europace 2017, 19, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyak, Z.; Harris, L.; de Groot, J.R.; Silversides, C.K.; Oechslin, E.N.; Bouma, B.J.; Budts, W.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Van Gelder, I.C.; Mulder, B.J. Sudden cardiac death in adult congenital heart disease. Circulation 2012, 126, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyilmaz, I.; Ozyilmaz, S.; Tola, H.T.; Saygi, M.; Kiplapinar, N.; Tanıdır, C.; Ergul, Y.; Guzeltas, A.; Odemis, E. Holter electrocardiography findings and P-wave dispersion in pediatric patients with transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2014, 19, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.M.; Gallego, P.; González, A.; Benito, F.; Mesa, J.M.; Sobrino, J.A. Predisposing conditions for atrial fibrillation in atrial septal defect with and without operative closure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2002, 89, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guray, U.; Guray, Y.; Yýlmaz, M.; Mecit, B.; Sasmaz, H.; Korknaz, S.; Kutuk, E. Evaluation of P wave duration and P wave dispersion in adult patients with secundum atrial septal defect during normal sinus rhythm. Int. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.F.; Chia, E.L.; Yip, W.C.; Chan, K.Y. Analysis of P wave and P dispersion in children with secundum atrial septal defect. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2001, 6, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duong, P.; Ferguson, L.P.; Lord, S.; Murray, S.; Shepherd, E.; Bourke, J.P.; Crossland, D.; O’Sullivan, J. Atrial arrhythmia after transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects in patients ≥ 40 years of age. EP Europace 2017, 19, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, B.; Cui, X.; Luo, G.; Pan, S. Prediction of arrhythmia after intervention in children with atrial septal defect based on random forest. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Baseline Characteristics | Findings |
|---|---|
| Median age (yrs) | 8.2 ± 4.2 (median 7) |
| Mean of BSA (m2) | 1.0 ± 0.3 (median 0.9) |
| ASD**stretched diameter (mm) | 16.3 ± 4.5 |
| Balloon sizing (yes/no) | 39 (all) |
| QP/QS | 1.7 ± 0.6 (median 1.5) |
| Baseline | 24 h | 6 Months | p (24 h) | p (6 Mo) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR [bpm] | 88.6 ± 12.6 | 87.3 ± 14.2 | 81.0 ± 12.7 | p = 0.9 | p = 0.009 |
| P Wave Dispersion [ms] | 40 ± 15 | 30 ± 13 | 30 ± 13 | p < 0.002 | p < 0.002 |
| PR Conduction [ms] | 175.0 ± 20.8 | 144.0 ± 22.7 | 164.0 ± 19.5 | p = 0.018 | N.S. |
| QTc Dispersion [ms] | 40.9 ± 13.3 | 31.7 ± 20.3 | 28.0 ± 18.1 | p < 0.02 | p < 0.002 |
| QTc value [ms] | 405.9 ± 19.95 | 403.6 ± 17.28 | 398.2 ± 15.5 | p = 0.5 | p = 0.03 |
| Baseline | 6 Months | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IVSd (mm) | 6.5 ± 1.2 | 6.6 ± 1.2 | |
| LVd (mm) | 34.8 ± 8.0 | 40.5 ± 5.6 | <0.0001 |
| LVPWd (mm) | 6.1 ± 1.1 | 6.4 ± 1.2 | |
| LVs (mm) | 22.3 ± 3.7 | 25.6 ± 4.6 | 0.0001 |
| LVEF (%) | 67.3 ± 6.2 | 67.5 ± 5.6 | |
| RVd (mm) | 27.4 ± 5.1 | 18.3 ± 3.3 | <0.0001 |
| RVd/LVd ratio | 0.78 ± 0.09 | 0.45 ± 0.7 | <0.0001 |
| LAVI (ml/mq) | 17.1 ± 4.7 | 19.2 ± 5.8 | 0.007 |
| RAVI (ml/mq) | 27.4 ± 7.9 | 17.2 ± 5.0 | <0.0001 |
| E/A | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 0.0017 |
| E/E’ | 6.2 ± 1.7 | 6.6 ± 2.4 | |
| TAPSE (mm) | 24.4 ± 4.4 | 22.5 ± 4.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fumanelli, J.; Garibaldi, S.; Castaldi, B.; Di Candia, A.; Pizzuto, A.; Sirico, D.; Cuman, M.; Mirizzi, G.; Marchese, P.; Cantinotti, M.; et al. Mid-Term Electrical Remodeling after Percutaneous Atrial Septal Defect Closure with GCO Device in a Pediatric Population. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6334. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196334
Fumanelli J, Garibaldi S, Castaldi B, Di Candia A, Pizzuto A, Sirico D, Cuman M, Mirizzi G, Marchese P, Cantinotti M, et al. Mid-Term Electrical Remodeling after Percutaneous Atrial Septal Defect Closure with GCO Device in a Pediatric Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6334. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196334
Chicago/Turabian StyleFumanelli, Jennifer, Silvia Garibaldi, Biagio Castaldi, Angela Di Candia, Alessandra Pizzuto, Domenico Sirico, Magdalena Cuman, Gianluca Mirizzi, Pietro Marchese, Massimiliano Cantinotti, and et al. 2023. "Mid-Term Electrical Remodeling after Percutaneous Atrial Septal Defect Closure with GCO Device in a Pediatric Population" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6334. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196334
APA StyleFumanelli, J., Garibaldi, S., Castaldi, B., Di Candia, A., Pizzuto, A., Sirico, D., Cuman, M., Mirizzi, G., Marchese, P., Cantinotti, M., Piacenti, M., Assanta, N., Viacava, C., Di Salvo, G., & Santoro, G. (2023). Mid-Term Electrical Remodeling after Percutaneous Atrial Septal Defect Closure with GCO Device in a Pediatric Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6334. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196334