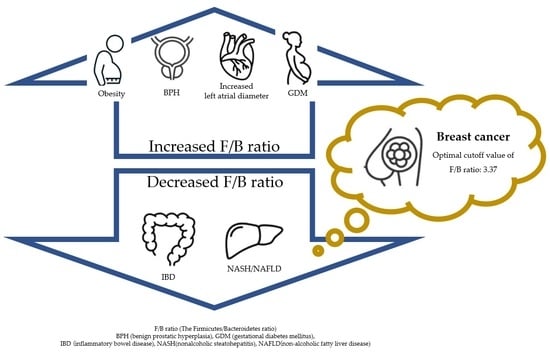
The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio as a Risk Factor of Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients Recruitment and Ethics Statement
2.2. EV Isolation and DNA Extraction from Blood
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing and Microbiome Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Firmicutes/Bateroidetes Ratio in Patients with Breast Cancer
3. Results
3.1. Patients Characteristics
3.2. Characteristics of Phyla Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes
3.3. Analysis of F/B Ratio in Patients with Breast Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, M.; George, R.; Sharma, A.; Graham, D.Y. Changing trends in stomach cancer throughout the world. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 19, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gao, K.; Gu, S.; You, L.; Qian, S.; Tang, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Jin, M. Worldwide trends in cervical cancer incidence and mortality, with predictions for the next 15 years. Cancer 2021, 127, 4030–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.J.; Thomassen, M.; Gerdes, A.M.; Kruse, T.A. Hereditary breast cancer: Clinical, pathological and molecular characteristics. Breast Cancer 2014, 8, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taha, Z.; Eltom, S.E. The Role of diet and lifestyle in women with breast cancer: An update review of related research in the middle east. BioRes. Open Access 2018, 7, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mili, N.; Paschou, S.A.; Goulis, D.G.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Lambrinoudaki, I.; Psaltopoulou, T. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cancer: Pathophysiological and therapeutic associations. Endocrine 2021, 74, 478–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijová, E. Synbiotic supplements in the prevention of obesity and obesity-related diseases. Metabolites 2022, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The influence of probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman, A.; Romanenko, M.; Piven, L.; Moseiko, V.; Lushchak, O.; Kryzhanovska, N.; Guryanov, V.; Koliada, A. Differences in the gut Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio across age groups in healthy Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliada, A.; Moseiko, V.; Romanenko, M.; Lushchak, O.; Kryzhanovska, N.; Guryanov, V.; Vaiserman, A. Sex differences in the phylum-level human gut microbiota composition. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, K.; Fujita, K.; Matsushita, M.; Motooka, D.; Hatano, K.; Banno, E.; Shimizu, N.; Takao, T.; Takada, S.; Okada, K.; et al. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio of the human gut microbiota is associated with prostate enlargement. Prostate 2021, 81, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Karampela, I.; Tsilingiris, D.; Magkos, F.; Stratigou, T.; Kounatidis, D.; Dalamaga, M. Understanding the role of the gut microbiome and microbial metabolites in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Current evidence and perspectives. Biomolecules 2021, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.J.; Tsai, W.C.; Hung, W.C.; Hung, W.W.; Chang, C.C.; Dai, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.C. Gut microbiota and subclinical cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sililas, P.; Huang, L.; Thonusin, C.; Luewan, S.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.; Tongsong, T. Association between gut microbiota and development of gestational diabetes mellitus. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Jobin, C. The microbiome and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zitvogel, L.; Daillère, R.; Roberti, M.P.; Routy, B.; Kroemer, G. Anticancer effects of the microbiome and its products. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, L.; Nanan, R.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E.; Grau, G.E. Host- and microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles, immune function, and disease development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ñahui Palomino, R.A.; Vanpouille, C.; Costantini, P.E.; Margolis, L. Microbiota-host communications: Bacterial extracellular vesicles as a common language. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Kwon, H.; Lim, W.; Moon, B.I. Staphylococcus aureus-derived extracellular vesicles enhance the efficacy of endocrine therapy in breast cancer cells. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Kim, J.B.; Yang, E.Y.; Kim, H.O.; Lee, W.H.; Yang, J.; Kwon, H.; Paik, N.S.; Lim, W.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Bacterial extracellular vesicles affect endocrine therapy in MCF7 cells. Medicine 2021, 100, e25835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliada, A.; Syzenko, G.; Moseiko, V.; Budovska, L.; Puchkov, K.; Perederiy, V.; Gavalko, Y.; Dorofeyev, A.; Romanenko, M.; Tkach, S.; et al. Association between body mass index and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in an adult Ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.Y.; Chen, J.S.; Hsu, B.M.; Hussain, B.; Rathod, J.; Lee, K.H. Colorectal cancer stage-specific fecal bacterial community fingerprinting of the Taiwanese population and underpinning of potential taxonomic biomarkers. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeler, M.; Caesar, R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Figueroa-Magalhães, M.C.; Jelovac, D.; Connolly, R.; Wolff, A.C. Treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. Breast 2014, 23, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukumar, J.; Gast, K.; Quiroga, D.; Lustberg, M.; Williams, N. Triple-negative breast cancer: Promising prognostic biomarkers currently in development. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2021, 21, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Qin, Y.C.; Tang, L.Y.; Liao, Y.H.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.M.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Ren, Z.F. Patient and care delays of breast cancer in China. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.A.; Jian, J.W.; Hung, C.F.; Peng, H.P.; Yang, C.F.; Cheng, H.S.; Yang, A.S. Germline breast cancer susceptibility gene mutations and breast cancer outcomes. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.L.; Chen, C.; Yuan, J.P.; Li, J.J.; Sun, S.R. Family history of cancer other than breast or ovarian cancer in first-degree relatives is associated with poor breast cancer prognosis. Breast 2017, 32, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muti, P.; Quattrin, T.; Grant, B.J.; Krogh, V.; Micheli, A.; Schünemann, H.J.; Ram, M.; Freudenheim, J.L.; Sieri, S.; Trevisan, M.; et al. Fasting glucose is a risk factor for breast cancer: A prospective study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2002, 11, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Rios-Covian, D.; Sánchez, B.; Salazar, N.; Martínez, N.; Redruello, B.; Gueimonde, M.; de Los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G. Different metabolic features of Bacteroides fragilis growing in the presence of glucose and exopolysaccharides of Bifidobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.T.; Kantilal, H.K.; Davamani, F. The mechanism of Bacteroides fragilis toxin contributes to colon cancer formation. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 27, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; LeRoith, D.; Gallagher, E.J. Diabetes, obesity, and breast cancer. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 3801–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Guo, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, Y.F. prausnitzii and its supernatant increase SCFAs-producing bacteria to restore gut dysbiosis in TNBS-induced colitis. AMB Express 2021, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, P.V.; Wong, S.S.; Tang, M.L.; Karagiannis, T.C. Epigenome targeting by probiotic metabolites. Gut Pathog. 2010, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marks, P.A.; Richon, V.M.; Rifkind, R.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Inducers of differentiation or apoptosis of transformed cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2000, 92, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giuffrè, M.; Campigotto, M.; Campisciano, G.; Comar, M.; Crocè, L.S. A story of liver and gut microbes: How does the intestinal flora affect liver disease? A review of the literature. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G889–G906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrè, M.; Moretti, R.; Campisciano, G.; da Silveira, A.B.M.; Monda, V.M.; Comar, M.; Di Bella, S.; Antonello, R.M.; Luzzati, R.; Crocè, L.S. You talking to me? Says the enteric nervous system (ENS) to the microbe. How intestinal microbes interact with the ENS. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3705. [Google Scholar]






| Characteristics | Healthy Controls | Patients with Breast Cancer |
|---|---|---|
| Number of female patients (N) | 190 | 95 |
| Age (years) | 51.4 ± 9.7 | 51.0 ± 10.4 |
| Characteristics | Patients with Breast Cancer |
|---|---|
| Subtype | |
| Luminal A | 30 (31.5%) |
| Luminal B | 38 (40%) |
| HER2 | 12 (12.6%) |
| TNBC | 15 (15.7%) |
| Stage | |
| 0 | 3 (3.1%) |
| I | 44 (46.3%) |
| II | 35 (36.8%) |
| III | 13 (13.6%) |
| Family history | |
| Yes Cancer: Breast, Ovary | 15 (15.7%) |
| Others | 21 (22.1%) |
| no | 59 (62.1%) |
| Hemoglobin | 13 ± 1.1 (g/dL) |
| Glucose | 100.1 ± 14.7 (mg/dL) |
| LDL cholesterol | 113.0 ± 34.3 (mg/dL) |
| BMI | |
| ~19 | 18 (18.9%) |
| 20~24 | 50 (52.6%) |
| 25~29 | 21 (22.1%) |
| 30~ | 6 (6.3%) |
| Eating habits | |
| omnivorous | 64 (67.3%) |
| vegetarian | 18 (18.9%) |
| meat based diet | 5 (5.2%) |
| nonresponse | 8 (8.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, J.; Kwon, H.; Kim, Y.J. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio as a Risk Factor of Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062216
An J, Kwon H, Kim YJ. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio as a Risk Factor of Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(6):2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062216
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Jeongshin, Hyungju Kwon, and Young Ju Kim. 2023. "The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio as a Risk Factor of Breast Cancer" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 6: 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062216
APA StyleAn, J., Kwon, H., & Kim, Y. J. (2023). The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio as a Risk Factor of Breast Cancer. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(6), 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062216