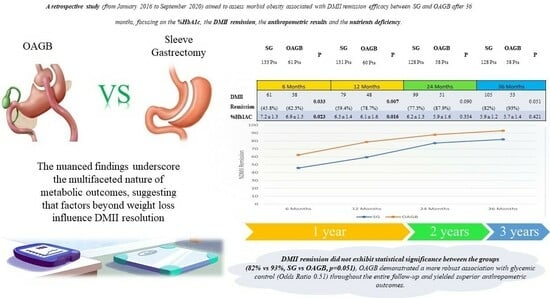
One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass vs. Sleeve Gastrectomy in the Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Analysis on 3 Years of Follow-Up
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Setting and Study Population
2.3. Surgical Technique
2.3.1. One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass
2.3.2. Sleeve Gastrectomy
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Study Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Primary Outcome
3.3. Secondary Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghusn, W.; Hage, K.; Vierkant, R.A. Type-2 diabetes mellitus remission prediction models after Roux-En-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy based on disease severity scores. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 13, 111091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, M.; Yumuk, V.; Oppert, J.M.; Scopinaro, N.; Torres, A.J.; Weiner, R.; Yashkov, Y.; Frühbeck, G. European Association for the Study of Obesity, International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity—European Chapter: Interdisciplinary European guidelines on metabolic and bariatric surgery. Obes. Facts 2013, 6, 449–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Toplak, H.; Woodward, E.; Yumuk, V.; Maislos, M.; Oppert, J.M. Executive Committee of the European Association for the Study of Obesity: Obesity: The gateway to ill health—An EASO position statement on a rising public health, clinical and scientific challenge in Europe. Obes. Facts 2013, 6, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affinati, A.H.; Esfandiari, N.H.; Oral, E.A.; Kraftson, A.T. Bariatric Surgery in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Moore, M. The Role of Lifestyle Modification with Second-Generation Anti-obesity Medications: Comparisons, Questions, and Clinical Opportunities. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Vetrani, C.; Caprio, M. Nutritional management of type 2 diabetes in subjects with obesity: An international guideline for clinical practice. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, P.; Kawar, B.; El Nahas, M. Obesity and diabetes in the developing world—A growing challenge. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruze, R.; Liu, T.; Zou, X.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Yin, X.; Xu, Q. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1161521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arterburn, D.E.; Telem, D.A.; Kushner, R.F.; Courcoulas, A.P. Benefits and Risks of Bariatric Surgery in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.E.; Rubino, F. Metabolic surgery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in obese individuals. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M.; Zappa, M.A.; Zese, M. Development of the Italian Clinical Practice Guidelines on Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery: Design and Methodological Aspects. Nutrients 2022, 15, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghusn, W.; Ikemiya, K.; Al Annan, K. Diabetes Mellitus Remission in Patients with BMI > 50 kg/m2 after Bariatric Surgeries: A Real-World Multi-Centered Study. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, S.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; Small, P.K.; Woodcock, S.A.; Pucci, A.; Aribasala, B.; Al-Mrabeh, A.; Batterham, R.L.; Taylor, R. Calorie restriction and not glucagon-like peptide-1 explains the acute improvement in glucose control after gastric bypass in Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Med. 2016, 33, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubaramaniam, V.; Pouwels, S. Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) after Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG), One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB), and Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB): A Systematic Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumakova-Orin, M.; Vanetta, C.; Moris, D.P.; Guerron, A.D. Diabetes remission after bariatric surgery. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Abeid, A.; Lessing, Y.; Pencovich, N.; Dayan, D.; Klausner, J.M.; Abu-Abeid, S. Diabetes resolution after one anastomosis gastric bypass. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2018, 14, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterli, R.; Wölnerhanssen, B.K.; Peters, T.; Vetter, D.; Kröll, D.; Borbély, Y.; Schultes, B.; Beglinger, C.; Drewe, J.; Schiesser, M.; et al. Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Weight Loss in Patients With Morbid Obesity: The SM-BOSS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2018, 319, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizza, F.; Lucido, F.S.; D’Antonio, D. Biliopancreatic Limb Length in One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass: Which Is the Best? Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 3685–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizza, F.; D’antonio, D.; Lucido, F.S.; Tolone, S.; Del Genio, G.; Dell’isola, C.; Docimo, L.; Gambardella, C. The Role of Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCA) in Cholelithiasis Management After One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) for Morbid Obesity: Results of a Monocentric Randomized Controlled Trial. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 4315–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanevik, M.; Lorentzen, J.; Borgeraas, H. Patient-reported outcomes, weight loss, and remission of type 2 diabetes 3 years after gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy (Oseberg); a single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingrone, G.; Panunzi, S.; De Gaetano, A.; Guidone, C.; Iaconelli, A.; Capristo, E.; Chamseddine, G.; Bornstein, S.R.; Rubino, F. Metabolic surgery versus conventional medical therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: 10-year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagner, M. For whom the bell tolls? It is time to retire the classic BPD (bilio-pancreatic diversion) operation. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angrisani, L.; Santonicola, A.; Iovino, P.; Formisano, G.; Buchwald, H.; Scopinaro, N. Bariatric surgery worldwide 2013. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, A.; Tantia, O.; Goyal, G.; Chaudhuri, T.; Khanna, S.; Poddar, A.; Gupta, S.; Majumdar, K. MGB-OAGB: Effect of Biliopancreatic Limb Length on Nutritional Deficiency, Weight Loss, and Comorbidity Resolution. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M.; Tie, T.; Ooi, G.; Higa, K.; Himpens, J.; Carbajo, M.-A.; Mahawar, K.; Shikora, S.; Brown, W.A. Mini Gastric Bypass-One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (MGB-OAGB)-IFSO Position Statement. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 1188–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musella, M.; Apers, J.; Rheinwalt, K.; Ribeiro, R.; Manno, E.; Greco, F.; Čierny, M.; Milone, M.; Di Stefano, C.; Guler, S.; et al. Efficacy of Bariatric Surgery in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Remission: The Role of Mini Gastric Bypass/One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy at 1 Year of Follow-up. A European survey. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrakopoulou, G.Z.; Theodoropoulos, C.; Kalles, V.; Zografos, G.; Almpanopoulos, K. Type 2 diabetes mellitus status in obese patients following sleeve gastrectomy or one anastomosis gastric bypass. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Jin, L.; Song, Y.; Feng, C.; Shen, P.; Li, H. Comparison of single-anastomosis gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy on type 2 diabetes mellitus remission for obese patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Asian J. Surg. 2023, 46, 4152–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumar, S.; Tantia, O.; Goyal, G.; Chaudhuri, T.; Khanna, S.; Ahuja, A.; Poddar, A.; Majumdar, K. LSG vs. MGB-OAGB3 year follow-up data: A randomised control trial. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2820–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kular, K.S.; Manchanda, N.; Rutledge, R. Analysis of the five-year outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy and mini gastric bypass: A report from the indian sub-continent. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 1724–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musella, M.; Berardi, G.; Vitiello, A.; Dayan, D.; Schiavone, V.; Franzese, A.; Abu-Abeid, A. Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients with Morbid Obesity before and after Metabolic Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.-J.; Jimenez, J.-M.; Carbajo, M.-A.; Lopez, M.; Cao, M.-J.; Garcia, S.; Ruiz-Tovar, J. Long-Term Weight Loss Results, Remission of Comorbidities and Nutritional Deficiencies of Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG), Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) on Type 2 Diabetic (T2D) Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group A (SG) 137 pts | Group B (OAGB) 64 pts | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (Male/Female) | 76/61 (55.5%/44.5%) | 35/29 (55%/45%) | 0.196 ** |
| Age (Years) ° | 38.9 ± 4.6 | 40.1 ± 5.1 | 0.518 * |
| ASA I–II/III–IV | 58/79 (42.4–57.6%) | 24/40 (37.5–62.5%) | 0.515 ** |
| BMI (kg/m2) ° | 46.2 ± 3.6 | 47.1 ± 2.3 | 0.438 * |
| Weight (kg) ° | 135.6 ± 20.7 | 137.1 ± 21.4 | 0.078 * |
| EBW (kg) ° | 66.5 ± 21.3 | 68.1 ± 28.7 | 0.364 * |
| Hypertension | 59 (43.1%) | 31 (48.4%) | 0.475 ** |
| Dyslipidemia | 79 (57.6%) | 38 (59.7%) | 0.818 ** |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 21 (15.3%) | 11 (17.2%) | 0.737 ** |
| Cerebrovascular Disease | 10 (7.4%) | 5 (8%) | 0.897 ** |
| Smoking | 59 (43.1%) | 26 (41.3%) | 0.744 ** |
| Antiplatelets/Anticoagulation | 19 (13.9%) | 9 (13.7%) | 0.970 ** |
| Coronary artery disease | 24 (17.5%) | 12 (19.5%) | 0.832 ** |
| DMII-positive familial history | 92 (67.1%) | 41 (64.2%) | 0.519 ** |
| Age at diagnosis (Years) ° | 40.2 ± 6.7 | 41.4 ± 7.1 | 0.478 * |
| Diabetes history (Months) ° | 64.9 ± 50.3 | 66.1 ± 43.3 | 0.312 * |
| IDDM | 34 (24.6%) | 12 (19.6%) | 0.340 ** |
| 1 Antidiabetic agent | 87 (63.5%) | 36 (56.2%) | 0.325 ** |
| 2 Antidiabetic agents | 39 (28.4%) | 20 (31.3%) | 0.686 ** |
| 3 Antidiabetic agents | 11 (8.1%) | 8 (12.5%) | 0.312 ** |
| Preoperative %Hb1AC ° | 7.7 ± 1.6 | 7.9 ± 1.8 | 0.163 * |
| Group A 133 pts | Group B 61 pts | p | GroupA 131 pts | Group B 60 pts | p | Group A 128 pts | Group B 58 pts | p | Group A 128 pts | Group B 57 pts | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 Months | 12 Months | 24 Months | 36 Months | |||||||||
| Number of ADAs ° | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.012 * | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.012 * | 0.8 ± 0.5 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.064 * | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.059 * |
| Diabetes’ Remission | 61 (45.8%) | 38 (62.3%) | 0.033 ** | 79 (59.4%) | 48 (78.7%) | 0.007 ** | 99 (77.3%) | 51 (87.9%) | 0.090 ** | 105 (82%) | 53 (93%) | 0.051 ** |
| 1 ADA | 43 | 11 | 0.039 ** | 41 | 8 | 0.008 ** | 21 | 4 | 0.078 ** | 18 (14%) | 3 (5.3%) | 0.081 ** |
| 2 ADAs | 27 | 9 | 0.356 ** | 10 | 3 | 0.502 ** | 7 | 3 | 0.933 ** | 4 (3.2%) | 1 (1.7%) | 0.595 ** |
| 3 ADAs | 2 | 3 | 0.163 ** | 1 | 1 | 0.569 ** | 1 | - | 0.499 ** | 1 (0.8%) | - | 0.503 ** |
| %Hb1AC ° | 7.2 ± 1.3 | 6.9 ± 1.5 | 0.023 * | 6.5 ± 1.4 | 6.1 ± 1.6 | 0.016 * | 6.2 ± 1.3 | 5.9 ± 1.6 | 0.354 * | 5.9 ± 1.2 | 5.7 ± 1.4 | 0.421 * |
| Group A (SG) 128 pts | Group B (OAGB) 57 pts | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 88.3 ± 8.4 | 83.5 ± 6.2 | 0.023 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31.9 ± 5.3 | 29.2 ± 6.9 | 0.016 * |
| %EWL | 74.3 ± 13.8 | 83.6 ± 18.1 | 0.003 * |
| %TWL | 37.9 ± 14.5 | 41.57 ± 12.8 | 0.002 * |
| Group A (SG) 128 pts | Group B (OAGB) 57 pts | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cholecalciferol (Vit. D3) | 5 (3.9%) | 7 (12.3%) | 0.03 ** |
| Iron | 12 (9.3%) | 9 (15.7%) | <0.001 ** |
| Cyanocobalamin (Vit. B12) | 4 (3.1%) | 4 (7.0%) | 0.229 ** |
| Total Protein | 6 (4.7%) | 5 (8.7%) | 0.278 ** |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 3 (2.3%) | 3 (5.2%) | 0.300 ** |
| Folic Acid (Vit. B11) | 5 (3.9%) | 4 (7.0%) | 0.363 ** |
| Thiamine (Vit. B1) | 6 (4.7%) | 4 (7.0%) | 0.517 ** |
| Riboflavin (Vit. B2) | 3 (2.3%) | 5 (8.7%) | 0.043 ** |
| Niacin (Vit. B3) | 4 (3.1%) | 4 (7.0%) | 0.229 ** |
| Acid pantotenic (Vit. B5) | 6 (4.7%) | 5 (8.7%) | 0.278 ** |
| Pyridoxine (Vit. B6) | 3 (2.3%) | 4 (7.0%) | 0.124 ** |
| Biotina (Vit. B8) | 4 (3.1%) | 4 (7.0%) | 0.229 ** |
| Iodine | 3 (2.3%) | 2 (3.5%) | 0.651 ** |
| Zinco | 3 (2.3%) | 3 (5.2%) | 0.300 ** |
| Manganese | 5 (3.9%) | 6 (10.5%) | 0.078 ** |
| Calcium citrate | 6 (4.7%) | 7 (12.3%) | 0.062 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gambardella, C.; Mongardini, F.M.; Paolicelli, M.; Lucido, F.S.; Tolone, S.; Brusciano, L.; Parisi, S.; Esposito, R.; Iovino, F.; Nazzaro, L.; et al. One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass vs. Sleeve Gastrectomy in the Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Analysis on 3 Years of Follow-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030899
Gambardella C, Mongardini FM, Paolicelli M, Lucido FS, Tolone S, Brusciano L, Parisi S, Esposito R, Iovino F, Nazzaro L, et al. One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass vs. Sleeve Gastrectomy in the Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Analysis on 3 Years of Follow-Up. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(3):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030899
Chicago/Turabian StyleGambardella, Claudio, Federico Maria Mongardini, Maddalena Paolicelli, Francesco Saverio Lucido, Salvatore Tolone, Luigi Brusciano, Simona Parisi, Rosetta Esposito, Francesco Iovino, Luca Nazzaro, and et al. 2024. "One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass vs. Sleeve Gastrectomy in the Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Analysis on 3 Years of Follow-Up" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 3: 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030899
APA StyleGambardella, C., Mongardini, F. M., Paolicelli, M., Lucido, F. S., Tolone, S., Brusciano, L., Parisi, S., Esposito, R., Iovino, F., Nazzaro, L., Pizza, F., & Docimo, L. (2024). One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass vs. Sleeve Gastrectomy in the Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Analysis on 3 Years of Follow-Up. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(3), 899. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030899