Gastrointestinal Disorders and Atopic Dermatitis in Infants in the First Year of Life According to ROME IV Criteria—A Possible Association with the Mode of Delivery and Early Life Nutrition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Objectives
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
3.2. Atopic Dermatitis
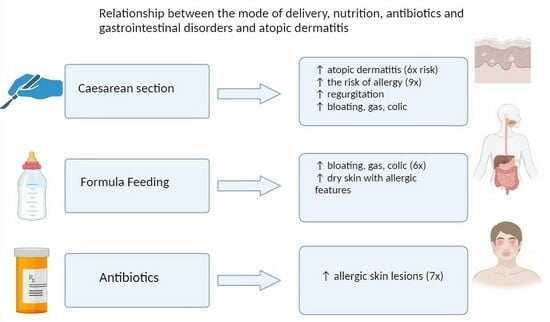
3.3. Mode of Delivery
3.4. Nutrition
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellù, R.; Condò, M. Functional gastrointestinal disorders in newborns: Nutritional perspectives. Pediatr. Med. Chir. 2018, 40, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiori, N.; Serra, M.; Cenni, S.; Pacella, D.; Martinelli, M.; Miele, E.; Staiano, A.; Tolone, C.; Auricchio, R.; Strisciuglio, C. Prevalence of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children with celiac disease on different types of gluten-free diets. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 6589–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnayake, C.; Kamm, M.; Stanley, A.; Wilson-O’brien, A.; Burrell, K.; Lees-Trinca, I.; Khera, A.; Kantidakis, J.; Wong, O.; Fox, K.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of Multidisciplinary Versus Standard Gastroenterologist Care for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Randomized Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2022, 20, 2102–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeevenhooven, J.; Koppen, I.J.; Benninga, M.A. The New Rome IV Criteria for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infants and Toddlers. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2017, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Gupta, A.; Bhatt, R.; Brawer, J.; Gao, K.; Tillisch, K.; Lagishetty, V.; Firth, R.; Gudleski, G.D.; Ellingson, B.M.; et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for irritable bowel syndrome induces bidirectional alterations in the brain-gut-microbiome axis associated with gastrointestinal symptom improvement. Microbiome 2021, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wauters, L.; Li, H.; Talley, N. Disruption of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Functional Dyspepsia and Gastroparesis: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 941810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labanski, A.; Langhorst, J.; Engler, H.; Elsenbruch, S. Stress and the brain-gut axis in functional and chronic-inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases: A transdisciplinary challenge. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 111, 104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kułaga, Z.; Różdżyńska-Świątkowska, A.; Grajda, A. Percentile charts for growth and nutritional status assessment in Polish children and adolescents from birth to 18 year of age. Stand. Med. Pediatr. 2015, 12, 119–135. [Google Scholar]
- Słabuszewska-Jóźwiak, A.; Szymański, J.K.; Ciebiera, M.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Jakiel, G. Pediatrics Consequences of Caesarean Section-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Berkel, A.C.; den Dekker, H.T.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Reiss, I.K.; Gaillard, R.; Hofman, A.; de Jongste, J.C.; Duijts, L. Mode of delivery and childhood fractional exhaled nitric oxide, interrupter resistance and asthma: The Generation R study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 26, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.T.; Zhou, Y.B.; Liu, J.M. The impact of cesarean section on offspring overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pärtty, A.; Rautava, S.; Kalliomäki, M. Probiotics on Pediatric Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiequn, B.; Guanqun, C.; Shuo, Z. Therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus in treating irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaiche, M.; Ategbo, S.; Krumholz, F.; Ludwig, T.; Miqdady, M.; Abkari, A.; Vandenplas, Y. A large-scale study to describe the prevalence, characteristics and management of functional gastrointestinal disorders in African infants. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chogle, A.; Velasco-Benitez, C.A.; Koppen, I.J.; Moreno, J.E.; Hernández, C.R.R.; Saps, M. A Population-Based Study on the Epidemiology of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Young Children. J. Pediatr. 2016, 179, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Benninga, M.; Broekaert, I.; Falconer, J.; Gottrand, F.; Guarino, A.; Lifschitz, C.; Lionetti, P.; Orel, R.; Papadopoulou, A.; et al. Functional gastro-intestinal disorder algorithms focus on early recognition, parental reassurance and nutritional strategies. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 244–252, Erratum in Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.E.; Di Mauro, A.; Salvatore, S.; Tafuri, S.; Bianchi, F.P.; Dattoli, E.; Morando, L.; Pensabene, L.; Meneghin, F.; Dilillo, D.; et al. Birth Weight and the Development of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infants. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2020, 23, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campeotto, F.; Barbaza, M.O.; Hospital, V. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Outpatients Aged up to 12 Months: A French Non-Interventional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, S.G.; Keller, C.; Zwiener, R.; Hyman, P.E.; Nurko, S.; Saps, M.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Shulman, R.J.; Hyams, J.S.; Palsson, O.; et al. Prevalence of Pediatric Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Utilizing the Rome IV Criteria. J. Pediatr. 2018, 195, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Abkari, A.; Bellaiche, M.; Benninga, M.; Chouraqui, J.P.; Çokura, F.; Harb, T.; Hegar, B.; Lifschitz, C.; Ludwig, T.; et al. Prevalence and health outcomes of functional gastrointestinal symptoms in infants from birth to 12 months of age. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, K.S.; Em, J.M.; Koay, Z.L.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Ng, R.T.; Lum, L.C.S.; Lee, W.S. Low prevalence of infantile functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) in a multi-ethnic Asian population. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisgaard, H.; Halkjaer, L.B.; Hinge, R.; Giwercman, C.; Palmer, C.; Silveira, L.; Strand, M. Risk analysis of early childhood eczema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woon, F.C.; Chin, Y.S.; Ismail, I.H.; Chan, Y.M.; Batterham, M.; Latiff, A.H.A.; Gan, W.Y.; Appannah, G. Contribution of early nutrition on the development of malnutrition and allergic diseases in the first year of life: A study protocol for the Mother and Infant Cohort Study (MICOS). BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, S.; Barberi, S.; Borrelli, O.; Castellazzi, A.; Di Mauro, D.; Di Mauro, G.; Doria, M.; Francavilla, R.; Landi, M.; Miniello, V.L.; et al. Pharmacological interventions on early functional gastrointestinal disorders. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2016, 42, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojsak, I. Probiotics in Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1125, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, F.R.; Sicherer, S.H.; Burks, A.W.; Committee On Nutrition; Section on Allergy and Immunology. The Effects of Early Nutritional Interventions on the Development of Atopic Disease in Infants and Children: The Role of Maternal Dietary Restriction, Breastfeeding, Hydrolyzed Formulas, and Timing of Introduction of Allergenic Complementary Foods. Pediatrics 2019, 143, e20190281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, C.J.; Tan, D.J.; Lau, M.X.; Dai, X.; Tham, R.; Lowe, A.J.; Bowatte, G.; Allen, K.J.; Dharmage, S.C. Breastfeeding and asthma and allergies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, G.; Carta, M.; Montante, C.; Notarbartolo, V.; Corsello, G.; Giuffrè, M. Current Insights on Early Life Nutrition and Prevention of Allergy. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 6, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifschitz, C.; Szajewska, H. Cow’s milk allergy: Evidence-based diagnosis and management for the practitioner. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Iwasa, H.; Kyozuka, H.; Go, H.; Sato, A.; Ogata, Y.; Murata, T.; Fujimori, K.; Shinoki, K.; et al. Association of cesarean section and allergic outcomes among infants at 1 year of age: Logistics regression analysis using data of 104,065 fetal and children’s records from the Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Authorea 2021, 118, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selma-Royo, M.; Calatayud Arroyo, M.; García-Mantrana, I.; Parra-Llorca, A.; Escuriet, R.; Martínez-Costa, C.; Collado, M.C. Perinatal environment shapes microbiota colonization and infant growth: Impact on host response and intestinal function. Mikrobiom 2020, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Abrahamsson, T.R.; Jenmalm, M.C.; Harris, K.; Quince, C.; Jernberg, C.; Björkstén, B.; Engstrand, L.; Andersson, A.F. Decreased gut microbiota diversity, delayed Bacteroidetes colonisation and reduced Th1 responses in infants delivered by Caesarean section. Gut 2014, 63, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: History, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features and Rome IV. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1262–1279.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gestation/Delivery (n = 82) | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 31.22 | 4.49 |
| Body weight before pregnancy (kg) | 68.28 | 17.59 |
| Birth weight during delivery (kg) | 82.20 | 16.55 |
| BMI before pregnancy | 24.56 | 6.05 |
| BMI during delivery | 29.57 | 5.62 |
| Weight gain (kg) | 14.24 | 7.01 |
| Week of gestation completion | 38.44 | 1.30 |
| Natural childbirth n (%) | 35 (42.7) | - |
| Cesarean section n (%) | 47 (57.3) | - |
| Parameters | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Male n (%) | 38 (46.3) | - |
| Female n (%) | 44 (53.7) | |
| Neonatal birth weight (g) | 3286 | 395 |
| Neonatal birth weight (g) at 3 MOA (n = 82) | 6340 | 651 |
| Neonatal weight (g) at 6 MOA (n = 82) | 8020 | 900 |
| Neonatal weight (g) at 12 MOA (n = 42) | 10,560 | 1040 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziętek, M.; Szczuko, M.; Machałowski, T. Gastrointestinal Disorders and Atopic Dermatitis in Infants in the First Year of Life According to ROME IV Criteria—A Possible Association with the Mode of Delivery and Early Life Nutrition. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13040927
Ziętek M, Szczuko M, Machałowski T. Gastrointestinal Disorders and Atopic Dermatitis in Infants in the First Year of Life According to ROME IV Criteria—A Possible Association with the Mode of Delivery and Early Life Nutrition. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(4):927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13040927
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiętek, Maciej, Małgorzata Szczuko, and Tomasz Machałowski. 2024. "Gastrointestinal Disorders and Atopic Dermatitis in Infants in the First Year of Life According to ROME IV Criteria—A Possible Association with the Mode of Delivery and Early Life Nutrition" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 4: 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13040927
APA StyleZiętek, M., Szczuko, M., & Machałowski, T. (2024). Gastrointestinal Disorders and Atopic Dermatitis in Infants in the First Year of Life According to ROME IV Criteria—A Possible Association with the Mode of Delivery and Early Life Nutrition. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(4), 927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13040927