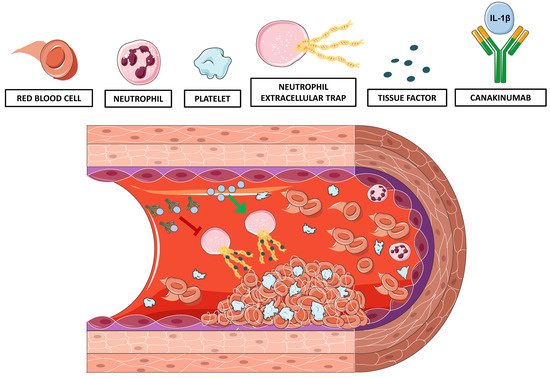
Interleukin-1β Mediates Arterial Thrombus Formation via NET-Associated Tissue Factor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Patient Enrollment and Blood Sampling
2.2. IL-1β Quantification in Human Plasma
2.3. NETosis Assessment in Human and Murine Plasma
2.4. Tissue Factor-DNA Complexes Quantification in Human and Murine Plasma
2.5. Animals
2.6. Monoclonal anti IL-1β Antibody
2.7. Treatments and Arterial Thrombosis
2.8. Artery and Plasma Sampling for Tissue Factor Assessment
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. IL-1β levels, NETosis and TF–DNA Complexes Increase in STEMI Patients with High Systemic Inflammation
3.2. IL-1β Neutralization Delays Arterial Thrombotic Occlusion In Vivo in LPS-Treated Mice
3.3. Treatment with Canakinumab-Surrogate Anti-Mouse IL-1β Antibody Reduces Plasma Levels of Tissue Factor
3.4. Anti-IL-1β Treatment Reduces NETosis and NET-Associated Tissue Factor Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Franchini, M.; Targher, G. Arterial thrombus formation in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecucco, F.; Liberale, L.; Bonaventura, A.; Vecchie, A.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F. The Role of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Outcome. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.K.; Libby, P.; Tabas, I. Inflammation and plaque vulnerability. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Simon, D.I. Inflammation and thrombosis: The clot thickens. Circulation 2001, 103, 1718–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P.; Darbousset, R.; Schoenwaelder, S.M. Thromboinflammation: Challenges of therapeutically targeting coagulation and other host defense mechanisms. Blood 2019, 133, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, M.; Montecucco, F.; Bonaventura, A.; Liberale, L.; Vecchié, A.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F. Update on the role of Pentraxin 3 in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2017, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Bonaventura, A.; Liberale, L.; Paolino, S.; Torre, F.; Dallegri, F.; Montecucco, F.; Cutolo, M. Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Promoters and Opponents. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambas, K.; Mitroulis, I.; Ritis, K. The emerging role of neutrophils in thrombosis-the journey of TF through NETs. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinod, K.; Wagner, D.D. Thrombosis: Tangled up in NETs. Blood 2014, 123, 2768–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stakos, D.A.; Kambas, K.; Konstantinidis, T.; Mitroulis, I.; Apostolidou, E.; Arelaki, S.; Tsironidou, V.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Skendros, P.; Konstantinides, S.; et al. Expression of functional tissue factor by neutrophil extracellular traps in culprit artery of acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart. J. 2015, 36, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventura, A.; Montecucco, F.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F.; Lüscher, T.F.; Camici, G.G.; Liberale, L. Novel findings in neutrophil biology and their impact on cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1266–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventura, A.; Liberale, L.; Carbone, F.; Vecchié, A.; Díaz-Cañestro, C.; Camici, G.; Montecucco, F.; Dallegri, F. The Pathophysiological Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Inflammatory Diseases. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 6–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, L.; Obeid, S.; Mach, F.; Shahin, M.; Yousif, N.; Denegri, A.; Muller, O.; Räber, L.; Matter, C.M.; Lüscher, T.F. Pre-existing treatment with aspirin or statins influences clinical presentation, infarct size and inflammation in patients with de novo acute coronary syndromes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 275, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Nakazawa, D.; Shida, H.; Miyoshi, A.; Kusunoki, Y.; Tomaru, U.; Ishizu, A. NETosis markers: Quest for specific, objective, and quantitative markers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 459, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Krumbholz, M.; Schönermarck, U.; Back, W.; Gross, W.L.; Werb, Z.; Gröne, H.-J.; Brinkmann, V.E.; Jenne, D. Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Farahvash, A.; Douda, D.N.; Licht, J.-C.; Grasemann, H.; Sweezey, N.; Palaniyar, N. JNK Activation Turns on LPS- and Gram-Negative Bacteria-Induced NADPH Oxidase-Dependent Suicidal NETosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA). CHMP Assessment Report for Ilaris. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/001109/WC500031679.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Osborn, O.; Brownell, S.E.; Sanchez-Alavez, M.; Salomon, D.; Gram, H.; Bartfai, T. Treatment with an Interleukin 1 beta antibody improves glycemic control in diet-induced obesity. Cytokine 2008, 44, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaul, D.S.; Weber, J.; Van Tits, L.J.; Sluka, S.; Pasterk, L.; Reiner, M.F.; Calatayud, N.; Lohmann, C.; Klingenberg, R.; Pahla, J.; et al. Loss of Sirt3 accelerates arterial thrombosis by increasing formation of neutrophil extracellular traps and plasma tissue factor activity. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, Z.; Denis, M.; Roubtsova, A.; Essalmani, R.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Awan, A.; Gram, H.; Seidah, N.G.; Genest, J. Reducing Vascular Calcification by Anti-IL-1beta Monoclonal Antibody in a Mouse Model of Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Angiology 2016, 67, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberale, L.; Diaz-Cañestro, C.; Bonetti, N.R.; Paneni, F.; Akhmedov, A.; Beer, J.H.; Montecucco, F.; Lüscher, T.F.; Camici, G.G. Post-ischaemic administration of the murine Canakinumab-surrogate antibody improves outcome in experimental stroke. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3511–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Tannenbaum, S.; Rordorf, C.; Lowe, P.J.; Floch, D.; Gram, H.; Roy, S. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of canakinumab, a human anti-interleukin-1beta monoclonal antibody. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, e1–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Canestro, C.; Reiner, M.F.; Bonetti, N.R.; Liberale, L.; Merlini, M.; Wüst, P.; Amstalden, H.; Briand-Schumacher, S.; Semerano, A.; Sessa, M.; et al. AP-1 (Activated Protein-1) Transcription Factor JunD Regulates Ischemia/Reperfusion Brain Damage via IL-1beta (Interleukin-1beta). Stroke 2019, 50, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holy, E.W.; Akhmedov, A.; Speer, T.; Camici, G.G.; Zewinger, S.; Bonetti, N.; Tanner, F.C.; Beer, J.H.; Lüscher, T.F. Carbamylated Low-Density Lipoproteins Induce a Prothrombotic State Via LOX-1: Impact on Arterial Thrombus Formation In Vivo. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1664–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenstein, A.; Stämpfli, S.F.; Reiner, M.F.; Shi, Y.; Keller, S.; Akhmedov, A.; Clerigué, A.S.; Spescha, R.D.; Beer, H.-J.; Lüscher, T.F.; et al. The MAP kinase JNK2 mediates cigarette smoke-induced arterial thrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Stampfli, S.F.; Akhmedov, A.; Gebhard, C.; Lohmann, C.; Holy, E.W.; Rozenberg, I.; Spescha, R.; Shi, Y.; Luscher, T.F.; Tanner, F.C.; et al. Aging induces endothelial dysfunction while sparing arterial thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1960–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization, W.H. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Liberale, L.; Camici, G.G. The Role of Vascular Aging in Atherosclerotic Plaque Development and Vulnerability. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 3098–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Liberale, L.; Bonaventura, A.; Cea, M.; Montecucco, F. Targeting Inflammation in Primary Cardiovascular Prevention. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5662–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borissoff, J.I.; Joosen, I.A.; Versteylen, M.O.; Brill, A.; Fuchs, T.A.; Savchenko, A.S.; Gallant, M.; Martinod, K.; Cate, H.T.; Hofstra, L.; et al. Elevated levels of circulating DNA and chromatin are independently associated with severe coronary atherosclerosis and a prothrombotic state. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Interleukin-1 Beta as a Target for Atherosclerosis Therapy: Biological Basis of CANTOS and Beyond. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, W.F.; Fearon, D.T. Inflammation and cardiovascular disease: Role of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Circulation 2008, 117, 2577–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bevilacqua, M.P.; Pober, J.S.; Majeau, G.R.; Cotran, R.S.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr. Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bevilacqua, M.P.; Pober, J.S.; Wheeler, M.E.; Cotran, R.S.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr. Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J. Clin. Investig. 1985, 76, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, J.; Armstrong, J.; Gadsdon, P.; Holden, H.; Francis, S.E.; Holt, C.M. Interleukin-1 beta in coronary arteries of patients with ischemic heart disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1996, 16, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirii, H.; Niwa, T.; Yamada, Y.; Wada, H.; Saito, K.; Iwakura, Y.; Asano, M.; Moriwaki, H.; Seishima, M. Lack of interleukin-1beta decreases the severity of atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breitenstein, A.; Tanner, F.C.; Luscher, T.F. Tissue factor and cardiovascular disease: Quo vadis? Circ. J. 2010, 74, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, H.S.; Blann, A.D.; Lip, G.Y. Soluble CD40 ligand, soluble P-selectin, interleukin-6, and tissue factor in diabetes mellitus: Relationships to cardiovascular disease and risk factor intervention. Circulation 2004, 109, 2524–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambola, A.; Osende, J.; Hathcock, J.; Degen, M.; Nemerson, Y.; Fuster, V.; Crandall, J.; Badimon, J.J. Role of risk factors in the modulation of tissue factor activity and blood thrombogenicity. Circulation 2003, 107, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suefuji, H.; Ogawa, H.; Yasue, H.; Kaikita, K.; Soejima, H.; Motoyama, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Oshima, S.; Saito, T.; Tsuji, I.; et al. Increased plasma tissue factor levels in acute myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 1997, 134, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhlmann, M.; Weinreich, D.M.; Farma, J.M.; Carroll, N.M.; Turner, E.M.; Alexander, H.R., Jr. Interleukin-1beta induced vascular permeability is dependent on induction of endothelial tissue factor (TF) activity. J. Transl. Med. 2005, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osnes, L.T.; Westvik, A.B.; Joo, G.B.; Okkenhaug, C.; Kierulf, P. Inhibition of IL-1 induced tissue factor (TF) synthesis and procoagulant activity (PCA) in purified human monocytes by IL-4, IL-10 and IL-13. Cytokine 1996, 8, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schecter, A.D.; Spirn, B.; Rossikhina, M.; Giesen, P.L.A.; Bogdanov, V.; Fallon, J.T.; Fisher, E.A.; Schnapp, L.M.; Nemerson, Y.; Taubman, M.B. Release of active tissue factor by human arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darbousset, R.; Thomas, G.M.; Mezouar, S.; Frere, C.; Bonier, R.; Mackman, N.; Renné, T.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Tissue factor-positive neutrophils bind to injured endothelial wall and initiate thrombus formation. Blood 2012, 120, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kambas, K.; Mitroulis, I.; Apostolidou, E.; Girod, A.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Pneumatikos, I.; Skendros, P.; Kourtzelis, I.; Koffa, M.; Kotsianidis, I.; et al. Autophagy mediates the delivery of thrombogenic tissue factor to neutrophil extracellular traps in human sepsis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshari, R.S.; Jyoti, A.; Dubey, M.; Kothari, N.; Kohli, M.; Bogra, J.; Barthwal, M.K.; Dikshit, M. Cytokines induced neutrophil extracellular traps formation: Implication for the inflammatory disease condition. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitroulis, I.; Kambas, K.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Skendros, P.; Apostolidou, E.; Kourtzelis, I.; Drosos, G.I.; Boumpas, D.T.; Ritis, K. Neutrophil extracellular trap formation is associated with IL-1beta and autophagy-related signaling in gout. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, A.K.; Spinosa, M.; Davis, J.P.; Pope, N.; Laubach, V.E.; Su, G.; Serbulea, V.; Leitinger, M.; Ailawadi, N.; Upchurch, G.R., Jr. Novel Role of IL (Interleukin)-1beta in Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folco, E.J.; Mawson, T.L.; Vromman, A.; Bernardes-Souza, B.; Franck, G.; Persson, O.; Nakamura, M.; Newton, G.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Libby, P. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induce Endothelial Cell Activation and Tissue Factor Production through Interleukin-1α and Cathepsin G. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.T.; Narayanan, P.; Li, W.; Silverstein, R.L.; McIntyre, T.M. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates platelets through an IL-1beta autocrine loop. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5196–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepys, M.B.; Baltz, M.; Gomer, K.; Davies, A.J.; Doenhoff, M. Serum amyloid P-component is an acute-phase reactant in the mouse. Nature 1979, 278, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Whole Cohort (n = 66) | Low CRP * (n = 33) | High CRP (n = 33) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | ||||
| Age, years | 66 ± 12 | 66 ± 12 | 65 ± 12 | NS |
| Gender, m/f | 46/20 | 23/10 | 23/10 | NS |
| Clinical and biochemical | ||||
| Systolic BP †, mmHg | 130 ± 23 | 130 ± 26 | 123 ± 20 | NS |
| Diastolic BP, mmHg | 78±15 | 81±16 | 75±12 | NS |
| BMI ‡, Kg/m2 | 25.5±3.6 | 25.2±3.6 | 25.8±3.6 | NS |
| Hypertension | 33 (50.0%) | 17 (51.5%) | 16 (48.5%) | NS |
| Diabetes | 9 (13.6%) | 5 (15.2%) | 4 (12.1%) | NS |
| Active smokers | 43 (65.2%) | 10 (30.0%) | 18 (54.5%) | NS |
| Total-c §, mmol/L | 4.93±1.12 | 5.15±1.26 | 4.70±0.93 | NS |
| HDL-c ∥, mmol/L | 1.22±0.31 | 1.24±0.27 | 1.21±0.34 | NS |
| LDL-c #, mmol/L | 3.31±1.13 | 3.57±1.23 | 3.07±0.97 | NS |
| Dyslipidaemia | 33 (50.0%) | 17 (51.5%) | 16 (48.5%) | NS |
| Medications | ||||
| Aspirin | 17 (25.8%) | 9 (27.3%) | 8 (24.2%) | NS |
| Clopidogrel | 2 (3.0%) | 1 (3.0%) | 1 (3.0%) | NS |
| ACE-I ** or ARBs †† | 17 (26.2%) | 11 (33.3%) | 6 (18.8%) | NS |
| β-blockers | 10 (15.2%) | 7 (21.2%) | 3 (9.1%) | NS |
| Diuretics | 6 (9.1%) | 4 (12.1%) | 2 (6.1%) | NS |
| Statins | 12 (18.2%) | 4 (12.1%) | 8 (24.2%) | NS |
| Vehicle | Anti IL *-1β | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total WBC ‡ (103/mm3) | 1.37 ± 0.13 | 1.38 ± 0.18 | NS |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 43.1 ± 5.2 | 32.3 ± 4.2 | NS |
| Neutrophils (%) | 51.4 ± 5.0 | 62.7 ± 4.2 | NS |
| Monocytes (%) | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 5.0 ± 0.7 | NS |
| NLR † | 1.5 ± 0.3 | 2.7 ± 0.7 | NS |
| Platelets (103/mm3) | 297.6 ± 44.2 | 312.8 ± 28.8 | NS |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liberale, L.; Holy, E.W.; Akhmedov, A.; Bonetti, N.R.; Nietlispach, F.; Matter, C.M.; Mach, F.; Montecucco, F.; Beer, J.H.; Paneni, F.; et al. Interleukin-1β Mediates Arterial Thrombus Formation via NET-Associated Tissue Factor. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122072
Liberale L, Holy EW, Akhmedov A, Bonetti NR, Nietlispach F, Matter CM, Mach F, Montecucco F, Beer JH, Paneni F, et al. Interleukin-1β Mediates Arterial Thrombus Formation via NET-Associated Tissue Factor. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(12):2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122072
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiberale, Luca, Erik W. Holy, Alexander Akhmedov, Nicole R. Bonetti, Fabian Nietlispach, Christian M. Matter, François Mach, Fabrizio Montecucco, Jürg H. Beer, Francesco Paneni, and et al. 2019. "Interleukin-1β Mediates Arterial Thrombus Formation via NET-Associated Tissue Factor" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 12: 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122072
APA StyleLiberale, L., Holy, E. W., Akhmedov, A., Bonetti, N. R., Nietlispach, F., Matter, C. M., Mach, F., Montecucco, F., Beer, J. H., Paneni, F., Ruschitzka, F., Libby, P., Lüscher, T. F., & Camici, G. G. (2019). Interleukin-1β Mediates Arterial Thrombus Formation via NET-Associated Tissue Factor. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(12), 2072. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122072