Incidence of Escherichia coli in Vegetable Crops and Soil Profile Drip Irrigated with Primarily Treated Municipal Wastewater in a Semi-Arid Peri Urban Area
Abstract
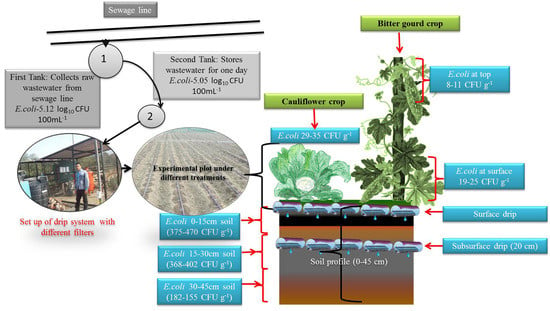
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location of Experimental Field
2.2. Climatic Condition
2.3. Soil Properties
2.4. Nursery Raising, Transplanting and Harvesting
2.5. Crop Water Requirement
2.6. Experimental Treatment and Setup
2.7. Operational Procedure
2.8. Water, Vegetable and Soil sampling
2.8.1. Water sampling
2.8.2. Vegetable sampling
2.8.3. Soil Sampling
2.9. Analysis of Water, Soil and Crop Samples
2.9.1. Water Analysis
2.9.2. Soil Analysis
2.9.3. Crop Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of Laterals in Reducing E.coli in Irrigation Water
3.2. Yield of Vegetable Crops
3.3. E. coli Incident in Cauliflower Curd and Bitter Gourd Fruit
3.4. Variation of E. coli Incident with Respect to Plant Height in Bitter Gourd Fruit
3.5. E. coli Incident in Soil Profile
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheltona, D.R.; Kiefer, L.A.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Martineza, G.; McCarty, G.W.; Dao, T.H. Comparison of microbial quality of irrigation water delivered in aluminum and PVC pipes. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.M.; Mazumder, A. Health and environmental policy issues in Canada: The role of watershed management in sustaining clean drinking water quality at surface sources. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 68, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, T.A.; El-Shaarawi, A.; Gannon, V.; Jokinen, C.; Kent, R.; Khan, I.U.; Koning, W.; Lapen, D.; Miller, J.; Neumann, N.; et al. Investigation of an Escherichia coli environmental benchmark for waterborne pathogens in agricultural watersheds in Canada. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, E.-M.; Shelton, D.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Nam, W.-H.; Coppock, C.; Muirhead, R. Modeling the inter-annual variability of microbial quality metrics of irrigation water in a Pennsylvania stream. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Shelton, D.R.; McLain, J.E.T.; Patel, J.; Mandrell, R.E. Irrigation waters as a source of pathogenic microorganisms in produce. A Rev. Adv. Agron. 2011, 113, 73–138. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Health Guidelines for the Use of Wastewater in Agriculture and Aquaculture. Report of a WHO Scientific Group; Technical Report Series No. 778; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, J.D.; Bezanson, G.S.; Gordon, R.J.; Jamieson, R. Population dynamics of Escherichia coli inoculated by irrigation into the phyllosphere of spinach grown under commercial production conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 143, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Wichelns, D.; Raschid-Sally, L.; McCornick, P.G.; Drechsel, P.; Bahri, A.; Minhas, P.S. The challenges of wastewater irrigation in developing countries. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toze, S. Reuse of effluent water-benefits and risks. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, M.R.; Abdullahi, U.S. Reuse of wastewater in urban farming and urban planning implications in Katsina metropolis, Nigeria. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lonigro, A.; Rubino, P.; Lacasella, V.; Montemurro, N. Faecal pollution on vegetables and soil drip irrigated with treated municipal wastewaters. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 174, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceuppens, S.; Hessel, C.T.; de Quadros, R.R.; Bartz, S.; Tondo, E.C.; Uyttendaele, M. Microbiological quality and safety assessment of lettuce production in Brazil. Int. J. Food Microb. 2014, 181, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelting, R.J.; Baloch, M.A.; Zarate-Bermudez, M.A.; Selman, C. Irrigation water issues potentially related to the 2006 multistate E. coli O157:H7 outbreak associated with spinach. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Morrow, J.; Guber, A.; Shelton, D.; Rowland, R.; Davies, G. Effect of biofilm in irrigation pipes on microbial quality of irrigation water. Appl. Microb. 2012, 54, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Navratil, S.; Gregory, A.; Bauer, A.; Srinath, I.; Jun, M.; Szonyi, B.; Nightingale, K.; Anciso, J.; Ivanek, R. Generic Escherichia coli contamination of spinach at the preharvest level: The role of farm management and environmental factors. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2013, 79, 4347–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CPCB. Status of Water Supply, Wastewater Generation and Treatment in Class-I Cities & Class-II Towns of India; Control of urban pollution series, CUPS/70/2009-10; Central Pollution Control Board, Ministry of Environment and Forest, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2016.
- Hussain, I.; Raschid, M.A.; Hanjra, F.; Marikar, W.; Hoek, V. Wastewater Use in Agriculture: Review of Impacts and Methodological Issues in Valuing Impacts. (With an Extended List of Bibliographical References); Working Paper 37; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos, I. Wastewater Management for Agriculture Protection in the Near East Region; FAO Regional Office for the Near East: Cairo, Egypt, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, M.J.; Mazahreh, N. Changes in soil fertility parameter in response to irrigation of forage crops with secondary treated wastewater. Comm. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2003, 34, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, A.; Brissaud, F. Wastewater reuse in Tunisia: Assessing a national policy. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Avnimelech, Y.; Juanico, M. Salt enrichment of municipal sewage: New prevention approaches in Israel. Environ. Manage. 1996, 20, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Bank. World Development Report 2008: Agriculture for Development; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 365. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jamal, M.S.; Sammis, T.W.; Mexal, J.G.; Picchioni, G.A.; Zachritz, W.H. A growth-irrigation scheduling model for wastewater use in forest production. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 56, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shreideh, B. Reuse of treated wastewater in irrigation and agriculture as a non-conventional resource. In Advanced Short Course on Water Saving and Increasing Water Productivity: Challenges and Options; Faculty of Agriculture, University of Jordan: Amman, Jordan, 2001; pp. 18.1–18.30. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Marecos, D.; Monte, M.H.F.; Bontoux, L.; Asano, T. The status of wastewater reuse practice in the Mediterranean basin: Need for guidelines. Water Res. 1999, 10, 2201–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, A.; Scicolone, B. Emitter and filter test for wastewater reuse by drip irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 68, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, H.T.L.; Allender, E.; Sandell, P.; Kube, P. Irrigation of tree plantations with recycled water in Australia: Research developments and care studies. In The Forest Alternative for Treatment and Utilization of Municipal and Industrial Wastes; Cole, D.H., Henry, C.L., Nutter, W.L., Eds.; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1986; pp. 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; FAO Irrigation and Drainage paper 29; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, K.K.; Hossain, A.; Murad, K.F.I.; Biswas, S.K.; Akter, F.; Rannu, R.P.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Karim, N.N.; Timsina, J. Development and Evaluation of an Emitter with a Low-Pressure Drip-Irrigation System for Sustainable Eggplant Production. AgriEngineering 2019, 1, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capra, A.; Scicolone, B. Recycling of poor quality urban wastewater by drip irrigation systems. J. Clean Prod. 2007, 15, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cararo, D.C.; Botrel, T.A.; Hills, D.J.; Leverenz, H.L. Analysis of clogging in drip emitters during wastewater irrigation. Appl Eng. Agric. 2006, 22, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, G. Laboratory experiment on drip emitter clogging with fresh water and treated sewage effluent. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.R.; Lau, L.S.; Wu, I.P.; Gee, H.K.; Young, S.C.H. Improved Emitter and Network System Design for Reuse of Wastewater in Drip Irrigation; Technical Report No. 163; Water Resources Research Centre, University of Hawaii at Manoa: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Oron, G.; Shelef, G.; Turzynski, B. Trickle irrigation using treated wastewaters. J. Irrig Drain. Div. 1979, 105, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, M.; Mancl, K.; Tuovinen, O.H. Clogging incidence of drip irrigation emitters distributing effluents of different levels of treatments. In On-Site Wastewater Treatment X : Proceedings of the Tenth National Symposium on Individual and Small Community Sewage Systems, Sacramento, CA, USA, 21–24 March 2004; Mankin, K.R., Ed.; American Society of Agricultural Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2004; pp. 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Tajrishy, M.A.; Hills, D.J.; Tchobanoglous, G. Pretreatment of secondary effluent for drip irrigation. J. Irrig Drain. Eng. 1994, 120, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, V.K.; Rajput, T.B.S.; Patel, N. Performance of different filter combinations with surface and subsurface drip irrigation systems for utilizing municipal wastewater. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Patel, N.; Rajput, T.B.S.; Lata Varghese, C. Study of soil water dynamics under bioline and inline drip laterals using groundwater and wastewater. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 12, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Hamilton, M.J.; Ping, W.; Staley, C.; Matteson, S.; Birr, A.; Michael, J.S. Geographic isolation of Escherichia coli genotypes in sediments and water of the Seven Mile Creek—A constructed riverine watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Ibanez, I.; Gil, M.I.; Tudela, J.A.; Ivanek, R.; Allende, A. Assessment of microbial risk factors and impact of meteorological conditions during production of baby spinach in the Southeast of Spain. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ling, C.; Lin-Yan, H.; Xia-Fang, S. Increased biomass and reduced heavy metal accumulation of edible tissues of vegetable crops in the presence of plant growth-promoting Neorhizobium huautlense T1-17 and biochar. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 228, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, H.L.S. Methods of Analysis of Soils, Plants, Waters, Fertilizers and Organic Manures; Fertilizer Development and Consultation Organization: New Delhi, India, 2005; p. 204. [Google Scholar]
- Brandy, N.C. The Nature and Properties of Soil, 8th ed.; MacMillan Publishing Co., Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Muhr, G.R.; Datta, P.; Sankarasubramoney, H.; Dever, F.; Laley, V.K.; Donahue, L. Critical test values for available N, P and K in different soil. In Soil Testing in India, 2nd ed.; U.S. Agency for International Development: New Delhi, India, 1965; p. 120. [Google Scholar]
- Subbiah, B.V.; Asija, G.L. A rapid procedure for the determination of available nitrogen in soil. Curr. Sci. 1956, 25, 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, R.E.; Smettem, K.R.J.; Broadbridge, P.; Woolhiser, D.A. Infiltration Theory for Hydrologic Applications; Water Resources Monograph–15; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), Water NEWS: Climate Change & Water. 2016. Available online: http://www.fao.org/nr/water/news/climchange.html (accessed on 29 March 2018).
- Jeong, H.; Kim, H.; Jang, T. Irrigation Water Quality Standards for Indirect Wastewater Reuse in Agriculture: A Contribution toward Sustainable Wastewater Reuse in South Korea. Water 2016, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, W.W.; Ma, X.Y.; Li, J.; Parkes, M. Simulation of point source wetting pattern of subsurface drip irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2011, 29, 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Scarpare, F.V.; Hernandes, T.A.D.; Ruiz-Correa, S.T.; Kolln, O.T.; Gava, G.J.C.; Silva dosSantos, L.N.; Victoria, R.L. Sugarcane water footprint under different management practices in Brazil: Tietê/Jacaré watershed assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4576–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, I.Z.; Barbosa, E.A.A.; Santos, L.N.S.; Nazário, A.A.; Feitosa, D.R.C.; Tuta, N.F.; Matsura, E.E. Water relations and productivity of sugarcane irrigated with domestic wastewater by subsurface drip. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 185, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, M.; Bernstein, N. Utilization of reclaimed wastewater for irrigation off-field-grown melons by surface and subsurface drip irrigation. Isr. J. Plant. Sci. 2011, 59, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shock, C.C.; Reitz, S.R.; Roncarati, R.A.; Kreeft, H.; Shock, B.M.; Klauzer, J. Drip vs. furrow irrigation in the delivery of Escherichia coli to onions. Appl. Eng.Agric. 2016, 32, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Song, I.; Stine, S.; Choi, C.; Gerba, C. Comparison of crop contamination by microorganisms during subsurface drip and furrow irrigation. J. Environ. Eng. 2006, 132, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende, A.; Monaghan, J. Irrigation Water Quality for Leafy Crops: A Perspective of Risks and Potential Solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7457–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA., Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Scientific opinion on the risk posed by pathogens in food of non-animal origin. Part 2 (Salmonella and Norovirus in leafy greens eaten raw as salads). EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3600. [Google Scholar]
- Cools, D.; Merckx, R.; Vlassak, K.; Verhaegen, J. Survival of E. coli and Enterococcus spp. derived from pig slurry in soils of different texture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2001, 17, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorber, C.A.; Moore, B.E. Survival and transport of pathogens in sludge amended soil: A critical literature review; Report no. EPA/600/2-97/028; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1987.
- Semenov, A.V.; van Bruggen, A.H.C.; van Overbeek, L.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; Semenov, A.M. Influence of temperature fluctuations on Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in cow manure. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamieson, R.C.; Gordon, R.J.; Sharples, K.E.; Stratton, G.W.; Madani, A. Movement and persistence of fecal bacteria in agricultural soils and subsurface drainage water: A review. Can. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Balkhair, K.S. Microbial contamination of vegetable crop and soil profile in arid regions under controlled application of domestic wastewater. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, S83–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wen, J. Effects of water managements on transport of E. coli in soil-plant system for drip irrigation applying secondary sewage effluent. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Wetting patterns and bacterial distributions in different soils from a surface point source applying effluents with varying Escherichia coli concentrations. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Soil Depth (m) | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Soil Texture | *Ks (cm h˗1) | Bulk Density (g cm˗3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–0.15 | 70.3 ± 5.12a | 12.5 ± 1.04a | 17.2 ± 2.01a | Sandy loam | 1.23 ± 0.14a | 1.53 ± 0.2a |
| 0.15–0.3 | 68.1 ± 7.02a | 11.7 ± 1.12a | 20.2 ± 2.14a | Sandy loam | 1.19 ± 0.13a | 1.57 ± 0.21b |
| 0.30–0.45 | 55.2 ± 8.51b | 21.2 ± 2.2b | 23.7 ± 3.15a | Loam | 0.75 ± 0.18b | 1.59 ± 0.18b |
| Soil Depth (m) | pH | EC (dS m˗1) | Available Nutrients (kg ha˗1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | |||
| 0–0.15 | 8.24 ± 0.69a | 0.19 ± 0.02a | 286.0 ± 15.17a | 36.4 ± 3.1a | 281.1 ± 23.41a |
| 0.15–0.3 | 8.37 ± 0.87a | 0.21 ± 0.02ab | 275.9 ± 09.14a | 34.2 ± 2.91a | 275.2 ± 29.18a |
| 0.30–0.45 | 8.46 ± 0.97a | 0.24 ± 0.02b | 194.4 ± 16.53b | 30.6 ± 1.48b | 260.2 ± 18.79a |
| Type of irrigation | E. coli (CFU 100 mL˗1) (Mean) |
|---|---|
| Unrestricted 1 | |
| Root crops (a) | ≤103 |
| Leaf crops (b) | ≤104 |
| Drip irrigation, low-growing crops | ≤103 |
| Drip irrigation, high-growing crops (c) | ≤105 |
| Restricted 2 | |
| Labor-intensive, high-contact agriculture | ≤104 |
| Highly mechanized agriculture | ≤105 |
| Pathogen removal in a septic tank | ≤106 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, D.; Patel, N.; Gadedjisso-Tossou, A.; Patra, S.; Singh, N.; Singh, P.K. Incidence of Escherichia coli in Vegetable Crops and Soil Profile Drip Irrigated with Primarily Treated Municipal Wastewater in a Semi-Arid Peri Urban Area. Agriculture 2020, 10, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10070291
Singh D, Patel N, Gadedjisso-Tossou A, Patra S, Singh N, Singh PK. Incidence of Escherichia coli in Vegetable Crops and Soil Profile Drip Irrigated with Primarily Treated Municipal Wastewater in a Semi-Arid Peri Urban Area. Agriculture. 2020; 10(7):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10070291
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Deepak, Neelam Patel, Agossou Gadedjisso-Tossou, Sridhar Patra, Nisha Singh, and Pushpendra Kumar Singh. 2020. "Incidence of Escherichia coli in Vegetable Crops and Soil Profile Drip Irrigated with Primarily Treated Municipal Wastewater in a Semi-Arid Peri Urban Area" Agriculture 10, no. 7: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10070291
APA StyleSingh, D., Patel, N., Gadedjisso-Tossou, A., Patra, S., Singh, N., & Singh, P. K. (2020). Incidence of Escherichia coli in Vegetable Crops and Soil Profile Drip Irrigated with Primarily Treated Municipal Wastewater in a Semi-Arid Peri Urban Area. Agriculture, 10(7), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10070291