Establishment of Non-Destructive Methods for the Detection of Amylose and Fat Content in Single Rice Kernels Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
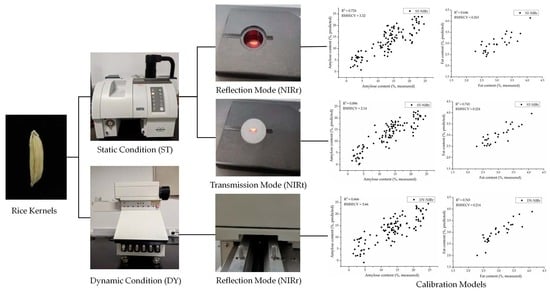
2.2.1. Spectral Acquisition of Single Rice Kernels under Static Conditions
2.2.2. Spectral Acquisition of Single Rice Kernels under Dynamic Conditions
2.3. Trace Detection of Single Rice Kernels
2.3.1. Trace Detection of AC in Rice
2.3.2. Trace Detection of FC in Rice
2.4. Multivariate Data Analysis
2.4.1. NIRS-Based Method for Detecting AC and FC in Single Rice Kernels
2.4.2. Multivariate Calibration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of AC and FC Trace Detection Methods with the Traditional Method
3.2. Trace Detection Results of AC and FC in Single Rice Kernels
3.3. Spectra of Single Rice Kernels under Different Measurement Conditions
3.4. Calibration and Validation Results of the Optimized Models
3.5. Characteristic Bands of Single Rice Kernel AC and FC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Wu, K.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Zeng, R.; Zhu, H.; Dong, G.; Qian, Q. Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Xia, D.; He, Y. Rice grain quality—Traditional traits for high quality rice and health-plus substances. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xia, D.; Li, P.; Ao, Y.; Xu, X.; Wan, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.; Shi, H.; Wang, K. Genetic architecture and key genes controlling the diversity of oil composition in rice grains. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, W.R.; Milligan, T.P.; Azudin, M. A relationship between the amylose and lipid contents of starches from diploid cereals. J. Cereal Sci. 1984, 2, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, A.; Waters, D.L.; Liu, L. The impact of rice protein on in vitro rice starch digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Fang, C.; Qian, Z.; Guo, B.; Huo, Z. Differences in starch structure, physicochemical properties and texture characteristics in superior and inferior grains of rice varieties with different amylose contents. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agelet, L.E.; Hurburgh, C.R., Jr. Limitations and current applications of Near Infrared Spectroscopy for single seed analysis. Talanta 2014, 121, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve Agelet, L.; Armstrong, P.R.; Romagosa Clariana, I.; Hurburgh, C.R. Measurement of single soybean seed attributes by near-infrared technologies. A comparative study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8314–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6647–2:2015; Rice—Determination of Amylose Content—Part 2: Routine Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Thiex, N.J.; Anderson, S.; Gildemeister, B. Crude fat, diethyl ether extraction, in feed, cereal grain, and forage (Randall/Soxtec/submersion method): Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Fan, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Tao, L.; Wu, J.; Hu, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y. A calibration transfer optimized single kernel near-infrared spectroscopic method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 220, 117098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Study on test methodology of amylose content of single (half) seed of rice. Crop Var. Res. 1992, 1, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Shi, C. Prediction of grain weight, brown rice weight and amylose content in single rice grains using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Field Crops Res. 2004, 87, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, H. A high–throughput method for determination of apparent amylase content in rice. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2014, 26, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Janni, J.; Weinstock, B.R.; Hagen, L.; Wright, S. Novel near-infrared sampling apparatus for single kernel analysis of oil content in maize. Appl. Spectrosc. 2008, 62, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, P.R.; Tallada, J.G.; Hurburgh, C.; Hildebrand, D.F.; Specht, J.E. Development of single-seed near-infrared spectroscopic predictions of corn and soybean constituents using bulk reference values and mean spectra. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Walczak, B.; Massart, D.; Heuerding, S.; Erni, F.; Last, I.; Prebble, K. Artificial neural networks in classification of NIR spectral data: Design of the training set. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1996, 33, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, G.; Mei, C.; Yu, S.; Xiao, X.; Ding, Y. Measurement of process variables in solid-state fermentation of wheat straw using FT-NIR spectroscopy and synergy interval PLS algorithm. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 97, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, W.F.; Stanfield, D.L. Near-infrared spectroscopy of biomaterials. In Handbook of Vibrational Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wan, X.; Bi, J.; Wang, J.K.; Jiang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhai, H.; Wan, J. Quantitative Analysis of Fat Content in Rice by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Technique. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, P.S.; Soares, A.; Castanho, A.; Almeida, A.S.; Oliveira, J.; Brites, C. Optimization of rice amylose determination by NIR-spectroscopy using PLS chemometrics algorithms. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Woltering, E.J. Identifying key wavenumbers that improve prediction of amylose in rice samples utilizing advanced wavenumber selection techniques. Talanta 2021, 224, 121908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimonsiri, L.; Ritthiruangdej, P.; Kasemsumran, S.; Therdthai, N.; Chanput, W.; Ozaki, Y. Rapid analysis of chemical composition in intact and milled rice cookies using near infrared spectroscopy. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2017, 25, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Fan, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Q. Data fusion of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra and transmittance spectra for the accurate determination of rice flour constituents. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1193, 339384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Analytes | Calibration Samples | Validation Samples | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Range | Mean | SE | SD | N | Range | Mean | SE | SD | |
| AC% | 107 | 1.35–24.61 | 13.20 | 0.615 | 6.36 | 45 | 1.63–24.45 | 13.15 | 1.051 | 7.05 |
| FC% | 28 | 2.29–4.10 | 3.00 | 0.085 | 0.45 | 11 | 2.44–3.82 | 3.07 | 0.142 | 0.47 |
| Group | Movement Condition | Measurement Mode | R2cv | RMSECV (%) | R2p | RMSEP (%) | Pretreatment Method | LV | Spectral Ranges (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | ST | NIRt | 0.886 | 2.14 | 0.832 | 2.86 | 1 der + MSC | 12 | 845.6–954.6, 1018.3–1401.5 |
| ST | NIRr | 0.724 | 3.32 | 0.737 | 3.57 | ECO | 8 | 963.1–1043.7, 1138.1–2502.5 | |
| DY | NIRr | 0.666 | 3.66 | 0.724 | 3.66 | MSC | 10 | 1100–1220, 1340–1460, 1580–2060 | |
| ACc | ST | NIRt | 0.834 | 2.58 | 0.818 | 3.02 | 1 der + MSC | 9 | 1099.5–1300.2 |
| ST | NIRt | 0.804 | 2.8 | 0.651 | 3.4 | 1 der + MSC | 11 | 1099.5–1500.3 | |
| ST | NIRr | 0.66 | 3.69 | 0.685 | 4.02 | None | 8 | 1099.5–1500.3, 1797.9–2200.8 | |
| ST | NIRr | 0.638 | 3.81 | 0.673 | 4.04 | ECO | 8 | 1099.5–1500.3, 1797.9–2400.6 | |
| DY | NIRr | 0.644 | 3.78 | 0.718 | 3.76 | MSC | 8 | 1100–1500, 1800–2000 | |
| DY | NIRr | 0.567 | 4.16 | 0.656 | 4.1 | 1der + MSC | 8 | 1100–1500, 1800–2200 | |
| FC | ST | NIRt | 0.743 | 0.224 | 0.644 | 0.266 | 1 der + SNV | 2 | 953.9–1019.9, 1179.5–1282.2 |
| ST | NIRr | 0.646 | 0.263 | 0.624 | 0.283 | 1 der + SNV | 11 | 1137.1–1251.2, 1389.4–2087.4 | |
| DY | NIRr | 0.765 | 0.214 | 0.655 | 0.262 | MSC | 8 | 1220–1340, 1700–1820 | |
| FCc | ST | NIRt | 0.546 | 0.298 | 0.624 | 0.274 | 1der + MSC | 6 | 1099.5–1500.3 |
| ST | NIRt | 0.43 | 0.334 | 0.595 | 0.284 | 1der + MSC | 5 | 1099.5–1300.2, 1498.6–1726.1 | |
| ST | NIRr | 0.572 | 0.289 | 0.43 | 0.435 | None | 10 | 1099.5–1500.3, 1698.9–1900.7 | |
| ST | NIRr | 0.524 | 0.305 | 0.529 | 0.365 | SNV | 9 | 1099.5–1500.3, 1698.9–1900.7, 2298.4–2521.4 | |
| DY | NIRr | 0.536 | 0.301 | 0.632 | 0.271 | 1der + SNV | 6 | 1100–1300, 1700–1900 | |
| DY | NIRr | 0.497 | 0.313 | 0.596 | 0.283 | ECO | 6 | 1100–1300 |
| Instrument | Content | Sample | Motion State | Resolution | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPA–reflection | amylose content | rice kernels | static conditions | 16 cm−1 | RMSECV (%) = 3.32, RMSEP (%) = 3.57 | This study |
| fat content | RMSECV (%) = 0.263, RMSEP (%) = 0.283 | This study | ||||
| MPA–transmission | amylose content | rice kernels | static conditions | 16 cm−1 | RMSECV (%) = 2.14, RMSEP (%) = 2.86 | This study |
| fat content | RMSECV (%) = 0.224, RMSEP (%) = 0.266 | This study | ||||
| AOTF | amylose content | rice kernels | dynamic conditions | 1 nm | RMSECV (%) = 3.66, RMSEP (%) = 3.66 | This study |
| fat content | RMSECV (%) = 0.214, RMSEP (%) = 0.262 | This study | ||||
| MPA–reflection | amylose content | rice flour | static conditions | 16 cm−1 | RMSECV (%) = 1.92, RMSEP (%) = 1.938 | [21] |
| MPA–reflection & transmission | fat content | rice flour | static conditions | 16 cm−1 | RMSECV (%) = 0.12, RMSEP (%) = 0.165 | [24] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, S.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Y. Establishment of Non-Destructive Methods for the Detection of Amylose and Fat Content in Single Rice Kernels Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081258
Fan S, Xu Z, Cheng W, Wang Q, Yang Y, Guo J, Zhang P, Wu Y. Establishment of Non-Destructive Methods for the Detection of Amylose and Fat Content in Single Rice Kernels Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Agriculture. 2022; 12(8):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081258
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Shuang, Zhuopin Xu, Weimin Cheng, Qi Wang, Yang Yang, Junyao Guo, Pengfei Zhang, and Yuejin Wu. 2022. "Establishment of Non-Destructive Methods for the Detection of Amylose and Fat Content in Single Rice Kernels Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy" Agriculture 12, no. 8: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081258
APA StyleFan, S., Xu, Z., Cheng, W., Wang, Q., Yang, Y., Guo, J., Zhang, P., & Wu, Y. (2022). Establishment of Non-Destructive Methods for the Detection of Amylose and Fat Content in Single Rice Kernels Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Agriculture, 12(8), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081258