Modelling Vineyard Spraying by Precisely Assessing the Duty Cycles of a Blast Sprayer Controlled by Pulse-Width-Modulated Nozzles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
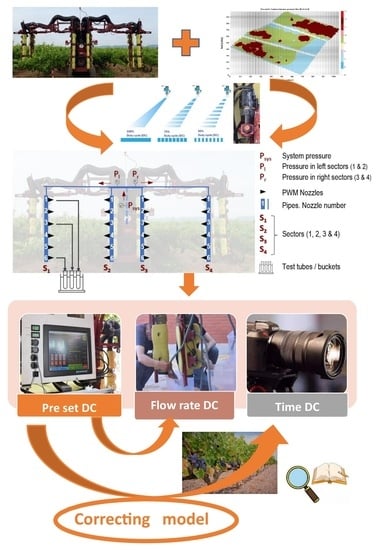
2. Materials and Methods
- Preset DC: The duty cycle selected by the user and manually commanded through the computer for each experiment;
- Theoretical R: The ratio between the measured (actual) flowrate and the theoretical flowrate calculated from the nozzle manufacture’s catalogue for the pressure registered in the experiments;
- Flow-based R: The ratio between the measured flowrate (actual) of a selected nozzle at a certain DC and the maximum average flowrate measured (actual) in the tests for 100% DC;
- Time-based DC: The DC calculated as the proportion of the signal cycle in which the solenoid remains activated as determined from the analysis of high-speed video frames.
3. Results
3.1. Measured Flowrate
3.2. DC Corrected According to the Maximum Flowrate
(For DC between 0% and 100%)
(For DC between 0% and 100%)
3.3. Time-Based DC According to Video Frame Timestamps
(For DC between 0% and 100%)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Further Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verycruysse, F.; Steurbaut, W. POCER—The pesticide occupational and environmental riskindicator. Crop Prot. 2002, 21, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaro, C.M.; Smith, M.N.; Workman, T.; Grieth, W.C. Characterization of organophosphate pesticides in urine and home environment dust in an agricultural community. Biomarkers 2018, 23, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, S.; Rasool, T.; Gani, K.M. A review of interactions of pesticides within various interfaces of intrinsic and organic residue amended soil environment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Selvinsimpson, S. Fate and Assessment of Pesticide in Aquatic Ecosystem. In Pesticides in the Natural Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, J.; Jia, J.; Liu, A.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, Z. Pollution levels of banned and non-banned pesticides in surface sediments from the East China Sea. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2019, 139, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teysseire, R.; Manangama, G.; Baldi, I.; Carles, C.; Brochard, P.; Bedos, C.; Delva, F. Assessment of residential exposures to agricultural pesticides. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenberger, S.; Bach, B.; Skitschak, A.; Frede, H.G. Mitigation strategies to reduce pesticide inputs into ground- and surface water and their effectiveness; A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, A.P.; Khot, L.R.; Hoheisel, G.A.; Thistle, H.W.; Teske, M.E.; Willett, M.J. Downwind spray drift assessment for airblast sprayer applications in a modern apple orchard system. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.C.B.; Lane, A.G.; O’Sullivan, C.M.; Jones, S. Wind tunnel investigation of the ability of drift-reducing nozzles to provide mitigation measures for bystander exposure to pesticides. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 202, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walklate, P.J.; Cross, J.V. Regulated dose adjustment of commercial orchard spraying products. Crop Prot. 2013, 54, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Huang, J.; Liang, X.; Yang, S.X.; Hu, W.; Tang, D. An Intelligent Multi-Sensor Variable Spray System with Chaotic Optimization and Adaptive Fuzzy Control. Sensors 2020, 20, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahn, R.A.; Yehya, A.A.K.; Zurayk, R. Digitalization for Sustainable Agri-Food Systems: Potential, Status, and Risks for the MENA Region. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Hayat, R.; Ahmad, M.; Kheir, A.M.S.; ul-Hassan, F.; ur-Renhman, M.H.; Shaheen, F.A.; Raza, M.A.; Ahmad, A. Impact of Climate Change on Dryland Agricultural Systems: A Review of Current Status, Potentials, and Further Work Need. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2022, 16, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanin, A.R.A.; Neves, D.C.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; Da Silva, C.A.; Da Silva, S.P.; Teodoro, P.E.; Rojo-Bajo, F. Reduction of pesticide application via real-time precision spraying. Scientific Report. Sci. Rep. 2021, 12, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandkar, S.V.; Bhatt, Y.C.; Jain, H.K.; Nalawade, S.M.; Pawar, S.G. Real-Time Variable Rate Spraying in Orchards and Vineyards: A Review. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 2018, 99, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.; Liu, J.; Faheem, M.; Noor, R.N.; Shaikh, S.A.; Solangi, K.A.; Raza, S.M. Different sensor based intelligent spraying systems in Agriculture. Sens. Actuators 2020, 316, 112265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xue, X.; Salcedo, R.; Zhang, Z.; Gil, E.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Shen, J.; He, Q.; Dou, Q.; et al. Key Technologies for an Orchard Variable-Rate Sprayer: Current Status and Future Prospects. Agronomy 2022, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.S.; Zahid, A.; He, L.; Martin, P. Opportunities and Possibilities of Developing an Advanced Precision Spraying System for Tree Fruits. Sensors 2021, 21, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhai, C. Research progress on variable-rate spraying technology orchards. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2020, 36, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabula, J.V.; Sharda, A.; Flippo, D.; Ciampiti, I.; Kang, Q. Boom pressure and droplet size uniformity of a pulse width modulation (PWM) spray technology. In Proceedings of the 2020 ASABE Annual International Virtual Meeting, Paper Number 2001041, ASABE Annual Meeting, Omaha, NB, USA, 12–15 July 2020; Volume 2001041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butts, T.R.; Butts, L.E.; Luck, J.D.; Fritz, B.K.; Hoffmann, W.C.; Kruger, G.R. Droplet size and nozzle tip pressure from a pulse-width modulation sprayer. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 178, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabula, J.; Sharda, A.; Kang, Q.; Flippo, D. Nozzle flow rate, pressure drop, and response time of pulse width modulation (PWM) nozzle control systems. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 1519–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, R.; Zhu, H.; Jeon, H.; Wei, Z.; Ozkan, E.; Gil, E. Characterization of volumetric droplet size distributions from PWM-controlled hollow-cone nozzles designed for variable-rate air-assisted sprayers. In Proceedings of the 2021 ASABE Annual International Virtual Meeting, Paper Number 2100038, ASABE Annual Meeting, Virtual, 12–18 July 2021; Volume 2100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, R.; Zhu, H.; Jeon, H.; Ozkan, E.; Wei, Z.; Gil, E.; Campos, J.; Román, C. Droplet Size Distributions from Hollow-Cone Nozzles Coupled with PWM Valves. J. ASABE 2022, 65, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortí, E.; Cuenca, A.; Pérez, M.; Torregrosa, A.; Ortiz, C.; Rovira-Más, F. Preliminary Evaluation of a Blast Sprayer Controlled by Pulse-Width-Modulated Nozzles. Sensors 2022, 22, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.; Zhu, H.; Jeon, H.; Ozkan, E.; Salcedo, R. Evaluation of PWM solenoid valves to manipulate hollow cone nozzles operated at high pressures and frequencies. In Proceedings of the 2022 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Houston, TX, USA, 17–20 July 2022; p. 2200396. [Google Scholar]
- Salcedo, R.; Zhu, H.; Jeon, H.; Ozkan, E.; Wei, Z.; Gil, E. Characterisation of activation pressure, flowrate and spray angle for hollow-cone nozzles controlled by pulse width modulation. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 218, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Ratio | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between groups | 0.388384 | 9 | 0.043153 | 411.15 | 10 |
| Intra groups | 0.001155 | 11 | 0.000011 | ||
| Total | 0.389531 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saiz-Rubio, V.; Ortiz, C.; Torregrosa, A.; Ortí, E.; Pérez, M.; Cuenca, A.; Rovira-Más, F. Modelling Vineyard Spraying by Precisely Assessing the Duty Cycles of a Blast Sprayer Controlled by Pulse-Width-Modulated Nozzles. Agriculture 2023, 13, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020499
Saiz-Rubio V, Ortiz C, Torregrosa A, Ortí E, Pérez M, Cuenca A, Rovira-Más F. Modelling Vineyard Spraying by Precisely Assessing the Duty Cycles of a Blast Sprayer Controlled by Pulse-Width-Modulated Nozzles. Agriculture. 2023; 13(2):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020499
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaiz-Rubio, Verónica, Coral Ortiz, Antonio Torregrosa, Enrique Ortí, Montano Pérez, Andrés Cuenca, and Francisco Rovira-Más. 2023. "Modelling Vineyard Spraying by Precisely Assessing the Duty Cycles of a Blast Sprayer Controlled by Pulse-Width-Modulated Nozzles" Agriculture 13, no. 2: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020499
APA StyleSaiz-Rubio, V., Ortiz, C., Torregrosa, A., Ortí, E., Pérez, M., Cuenca, A., & Rovira-Más, F. (2023). Modelling Vineyard Spraying by Precisely Assessing the Duty Cycles of a Blast Sprayer Controlled by Pulse-Width-Modulated Nozzles. Agriculture, 13(2), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13020499