Numerical Simulation of Large Wave Heights from Super Typhoon Nepartak (2016) in the Eastern Waters of Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
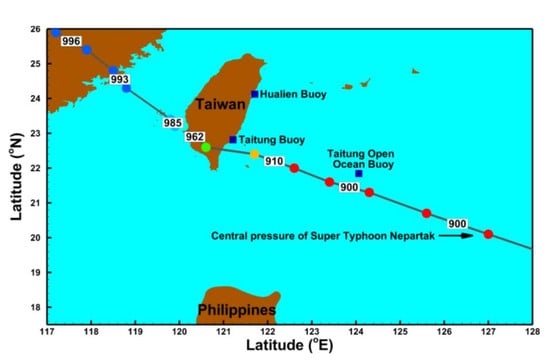
2.1. Super Typhoon Nepartak (2016)
2.2. Wave Buoy
2.3. Description and Configuration of the Wave-Circulation Model
2.4. Tidal and Atmospheric Forcing
2.4.1. Tidal Forcing
2.4.2. CFSV2 Wind Field
2.4.3. ERA5 Reanalysis Wind Field
2.4.4. Parametric Typhoon Wind Field
2.4.5. Hybrid Typhoon Wind Field
2.5. Model Performance Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Effects of the Spatial Resolutions of Wind Fields on Storm Wave Simulation
3.2. Effects of the Temporal Resolutions of Wind Fields on Storm Wave Simulation
3.3. Effects of Hybrid Wind Fields on Storm Wave Simulation Through Different Superposed Techniques
4. Discussion
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, Z.; Liang, B.; Li, H.; Wu, G.; Wu, Z. Blended wind fields for wave modeling of tropical cyclones in the South China Sea and East China Sea. Appl. Ocean Res. 2018, 71, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.-J.; Chang, C.-H.; Chen, W.-B.; Lin, L.-Y. Identifying the Optimal Offshore Areas for Wave Energy Converter Deployments in Taiwanese Waters Based on 12-Year Model Hindcasts. Energies 2018, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-H.; Shih, H.-J.; Chen, W.-B.; Su, W.-R.; Lin, L.-Y.; Yu, Y.-C.; Jang, J.-H. Hazard Assessment of Typhoon-Driven Storm Waves in the Nearshore Waters of Taiwan. Water 2018, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-B.; Chen, H.; Hsiao, S.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Lin, L.-Y. Wind forcing effect on hindcasting of typhoon-driven extreme waves. Ocean Eng. 2019, 188, 106260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, P.N.L.; Srinivas, K.S.; Rao Rama Pattabhi, E.; Bhaskaran, P.K.; Shenoi, S.S.C.; Padmanabham, J. Improved cyclone wind fields over the Bay of Bengal and their application in storm surge and wave computations. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 95, 102048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Xu, S. Super typhoon activity over the western North Pacific and its relationship with ENSO. J. Ocean Univ. China 2010, 9, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaguru, K.; Foltz, G.R.; Leung, L.R.; Emanuel, K.A. Global warming-induced upper-ocean freshening and the intensification of super typhoons. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akpınar, A.; Bingölbali, B.; van Vledder, G.P. Wind and wave characteristics in the Black Sea based on the SWAN wave model forced with the CFSR winds. Ocean Eng. 2016, 126, 276–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Manuel, L.; Curcic, M.; Chen, S.S.; Phillips, C.; Veers, P. On the Use of Coupled Wind, Wave, and Current Fields in the Simulation of Loads on Bottom Supported Offshore Wind Turbines during Hurricanes; Technical Report NREL/TP-5000-65283; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Pan, S.; Pan, Y.; Fang, J.; Sowa, D.M.A. Estimation of mean and extreme waves in the East China Seas. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 56, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, A.F.; Montoya, R.D.; Ortiz, J.C.; Peláez, D. Construction of synthetic ocean wave series along the Colombian Caribbean Coast: A wave climate analysis. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 56, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimolade, A.P.; Haver, S.; Gudmestad, O.T. Estimation of extreme significant wave heights and the associated uncertainties: A case study using NORA10 hindcast data for the Barents Sea. Mar. Struct. 2016, 49, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraleedharan, G.; Lucas, C.; Soares, C.G. Regression quantile models for estimating trends in extreme significant wave heights. Ocean Eng. 2016, 118, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.Y.A.; Terry, J.P.T.; Ziegler, A.D.; Switzer, A.D.; Lee, Y.; Etienne, S. Understanding the history of extreme wave events in the Tuamotu Archipelago of French Polynesia from large carbonate boulders on Makemo Atoll, with implications for future threats in the central South Pacific. Mar. Geol. 2016, 380, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.-C.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.-B.; Chang, C.-H.; Lin, L.-Y. Quantifying the contribution of nonlinear interactions to storm tide simulations during a super typhoon event. Ocean Eng. 2019, 194, 106661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Ye, F.; Stanev, E.V.; Grashorn, S. Seamless cross-scale modelling with SCHISM. Ocean Model. 2016, 102, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Baptista, A.M. SELFE: A semi-implicit Eulerian-Lagrangian finite-element model for cross-scale ocean circulation. Ocean Model. 2008, 21, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchepetkin, A.F.; McWilliams, J.C. The regional oceanic modeling system (ROMS): A split-explicit, free-surface, topography-following-coordinate, oceanic model. Ocean Model. 2005, 9, 347–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.V.; Loftis, J.D.; Liu, Z.; Forrest, D.; Zhang, J. The storm surge and sub-grid inundation modeling in New York City during hurricane Sandy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-B.; Liu, W.-C. Modeling flood inundation Induced by river flow and storm surges over a river basin. Water 2014, 6, 3182–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-B.; Liu, W.-C. Assessment of storm surge inundation and potential hazard maps for the southern coast of Taiwan. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 591–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-B.; Chen, H.; Lin, L.-Y.; Yu, Y.-C. Tidal Current Power Resource and Influence of Sea-Level Rise in the Coastal Waters of Kinmen Island, Taiwan. Energies 2017, 10, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Liu, C.-H.; Shih, H.-J.; Chang, C.-H.; Chen, W.-B.; Yu, Y.-C.; Su, W.-R.; Lin, L.-Y. An Operational Forecasting System for Flash Floods in Mountainous Areas in Taiwan. Water 2019, 11, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komen, G.J.; Cavaleri, L.; Donelan, M.; Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, S.; Janssen, P.A.E. Dynamics and Modelling of Ocean Waves; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; p. 532. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, A. Development of WWM II: Spectral Wave Modeling on Unstructured Meshes. Ph.D. Thesis, Technology University Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yanenko, N.N. The Method of Fractional Steps; Springer: Berlin/Hamburg, Germany, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselmann, K.; Barnett, T.P.; Bouws, E.; Carlson, H.; Cartwright, D.E.; Enke, K.; Ewing, J.A.; Gienapp, H.; Hasselmann, D.E.; Kruseman, P.; et al. Measurements of Wind-Wave Growth and Swell Decay during the Joint North Sea Wave Project (JONSWAP); Deutsches Hydrographisches Institut: Berlin/Hamburg, Germany, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, A.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, H.V.; Meng, Y.; Teng, Y.-C.; Maderich, V.; Brovchenko, I.; Dutour-Sikiric, M.; Zanke, U. A fully coupled 3D wave-current interaction model on unstructured grids. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C00J33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sheng, J. Estimation of extreme sea levels over the eastern continental shelf of North America. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6253–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muis, S.; Verlaan, M.; Winsemius, H.C.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; Ward, P.J. A global reanalysis of storm surges and extreme sea levels. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marsooli, R.; Lin, N. Numerical Modeling of Historical Storm Tides and Waves and Their Interactions Along the U.S. East and Gulf Coasts. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 3844–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zu, T.; Gana, J.; Erofeevac, S.Y. Numerical study of the tide and tidal dynamics in the South China Sea. Deep Sea Res. 2008, 55, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Pan, H.-L.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.-T.; Chuang, H.-Y.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Version 2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T. Pressure distribution within typhoon. Geophys. Mag. 1952, 23, 437–451. [Google Scholar]
- Jelesnianski, C.P. A numerical computation of storm tides induced by a tropical storm impinging on a continental shelf. Mon. Weather Rev. 1965, 93, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holland, G.J. An analytical model of the wind and pressure profiles in hurricanes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1980, 108, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A.C.; Martino, C.D.; Cheung, K.F.; Houston, S.H. Modeling of tropical cyclone winds and waves for emergency management. Ocean Eng. 2003, 30, 553–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, W.; Yan, T. An elliptical wind field model of typhoons. J. Ocean Univ. China 2004, 3, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAfee, A.W.; Pearson, G.W. Development and testing of tropical Cyclone parametric wind models tailored for midlatitude application-preliminary results. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2006, 45, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, V.T.; White, L.W.; Willoughby, H.E.; Jorgensen, D.P. A new parametric tropical cyclone tangential wind profile model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 1884–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.F.; Tang, L.; Donnelly, J.P.; Scileppi, E.M.; Liu, K.B.; Mao, K.B.; Houston, S.H.; Murnane, R.J. Numerical modeling and field evidence of coastal overwash in southern New England from Hurricane Bob and implications for paleotempestology. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F03024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastidas, L.A.; Knighton, J.; Kline, S.W. Parameter sensitivity and uncertainty analysis for a storm surge and wave model. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 2195–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolman, H.L.; Alves, J.H.G.M. Numerical modeling of waves generated by tropical cyclones using moving grids. Ocean Model. 2005, 9, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-C.; Chen, H.; Shih, H.-J.; Chang, C.-H.; Hsiao, S.-C.; Chen, W.-B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Su, W.-R.; Lin, L.-Y. Assessing the Potential Highest Storm Tide Hazard in Taiwan Based on 40-year Historical Typhoon Surge Hindcasting. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atkinson, G.D.; Holliday, C.R. Tropical cyclone minimum sea level pressure/maximum sustained wind relationship for the western North Pacific. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1977, 105, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Li, J.X.; Ding, X.L. Improvement of wind field hindcasts for tropical cyclones. Water Sci. Eng. 2016, 9, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Pan, S.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Y.M.; Pan, Y. Numerical estimation of extreme waves and surges over the northwest Pacific Ocean. Ocean Eng. 2018, 153, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Song, J.; He, H.; Li, F. Application of different wind filed models and wave boundary layer model to typhoon waves numerical simulation in WAVEWATCH III model. Tellus A 2019, 7, 1657552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanna, S.; Heinold, D. Development and Application of a Simple Method for Evaluating Air Quality; API Pub.: Washington, DC, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Mentaschi, L.; Besio, G.; Cassola, F.; Mazzino, A. Problems in RMSE-based wave model validations. Ocean Model. 2013, 72, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, L.; Bernardino, M.; Guedes Soares, C. Influence of Wind Resolution on Prediction of Waves Generated in an Estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 56, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vledder, G.P.; Akpınar, A. Wave model predictions in the Black Sea: Sensitivity to wind fields. Appl. Ocean Res. 2015, 53, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















| Buoy Name | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Water Depth (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taitung Ocean | 124.0742 | 21.7664 | 5610 |
| Taitung | 121.1450 | 22.7240 | 30 |
| Hualien | 121.6314 | 24.0319 | 21 |
| Buoy Name | SI | CC | HH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taitung Ocean | 0.47 | 0.97 | 0.32 |
| Taitung | 0.50 | 0.94 | 0.33 |
| Hualien | 0.61 | 0.92 | 0.45 |
| Buoy Name | SI | CC | HH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taitung Ocean | 0.39 | 0.96 | 0.28 |
| Taitung | 0.39 | 0.92 | 0.35 |
| Hualien | 0.36 | 0.95 | 0.31 |
| Buoy Name | [−2,0) | [0,2) | [2,4) | [4,6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taitung Ocean | 67.48 | 26.29 | 4.34 | 1.90 |
| Taitung | 64.02 | 32.95 | 2.27 | 0.76 |
| Hualien | 85.12 | 13.77 | 1.10 | 0.00 |
| Buoy Name | [−2,0) | [0,2) | [2,4) | [4,6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taitung Ocean | 77.51 | 19.75 | 1.08 | 1.63 |
| Taitung | 76.89 | 20.08 | 2.27 | 0.76 |
| Hualien | 88.71 | 11.29 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsiao, S.-C.; Chen, H.; Wu, H.-L.; Chen, W.-B.; Chang, C.-H.; Guo, W.-D.; Chen, Y.-M.; Lin, L.-Y. Numerical Simulation of Large Wave Heights from Super Typhoon Nepartak (2016) in the Eastern Waters of Taiwan. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8030217
Hsiao S-C, Chen H, Wu H-L, Chen W-B, Chang C-H, Guo W-D, Chen Y-M, Lin L-Y. Numerical Simulation of Large Wave Heights from Super Typhoon Nepartak (2016) in the Eastern Waters of Taiwan. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(3):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8030217
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsiao, Shih-Chun, Hongey Chen, Han-Lun Wu, Wei-Bo Chen, Chih-Hsin Chang, Wen-Dar Guo, Yung-Ming Chen, and Lee-Yaw Lin. 2020. "Numerical Simulation of Large Wave Heights from Super Typhoon Nepartak (2016) in the Eastern Waters of Taiwan" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 3: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8030217
APA StyleHsiao, S. -C., Chen, H., Wu, H. -L., Chen, W. -B., Chang, C. -H., Guo, W. -D., Chen, Y. -M., & Lin, L. -Y. (2020). Numerical Simulation of Large Wave Heights from Super Typhoon Nepartak (2016) in the Eastern Waters of Taiwan. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(3), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8030217