Riboswitches as Drug Targets for Antibiotics
Abstract
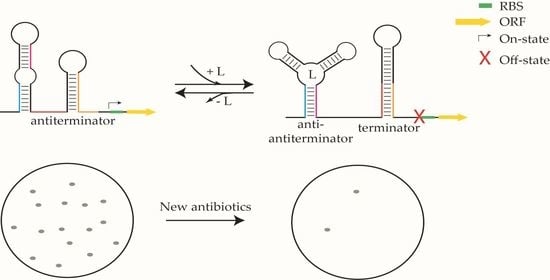
:1. Introduction
2. TPP Riboswitch Ligands
3. FMN Riboswitch Ligands
4. glmS Riboswitch Ligands
5. Guanine Riboswitch Ligands
6. General Considerations for Riboswitch Drug Discovery
6.1. High-Throughput Screening (HTS)
6.2. Fragment-Based Screening
6.3. Structure-Based Virtual Screening
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neil, J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations; Review on Antimicrobial Resistance: London, UK, 2014; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Global Multifaceted Phenomenon. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Młynarczyk-Bonikowska, B.; Majewska, A.; Malejczyk, M.; Młynarczyk, G.; Majewski, S. Multiresistant Neisseria Gonor-Rhoeae: A New Threat in Second Decade of the XXI Century. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 209, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, G.; Dowson, C.G.; Overington, J. Meeting the Discovery Challenge of Drug-Resistant Infections: Progress and Focusing Resources. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monserrat-Martinez, A.; Gambin, Y.; Sierecki, E. Thinking Outside the Bug: Molecular Targets and Strategies to Overcome Antibiotic Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, E.D.; Wright, G.D. Antibacterial Drug Discovery in the Resistance Era. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 529, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lünse, C.E.; Schüller, A.; Mayer, G. The Promise of Riboswitches as Potential Antibacterial Drug Targets. Int. J. Med Microbiol. 2014, 304, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deigan, K.E.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Riboswitches: Discovery of Drugs That Target Bacterial Gene-Regulatory RNAs. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blouin, S.; Mulhbacher, J.; Penedo, J.C.; Lafontaine, D.A. Riboswitches: Ancient and Promising Genetic Regulators. Chem. Biochem. 2009, 10, 400–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, N.J.; Kulshina, N.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Riboswitch Function: Flipping the Switch or Tuning the Dimmer? RNA Biol. 2010, 7, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breaker, R.R. Riboswitches and the RNA World. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 4, a003566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blount, K.F.; Breaker, R.R. Riboswitches as Antibacterial Drug Targets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastet, L.; Turcotte, P.; Wade, J.T.; Lafontaine, D.A. Maestro of Regulation: Riboswitches Orchestrate Gene Expression at the Levels of Translation, Transcription and mRNA Decay. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bédard, A.-S.V.; Hien, E.D.; Lafontaine, D.A. Riboswitch Regulation Mechanisms: RNA, Metabolites and Regulatory Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2020, 1863, 194501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCown, P.J.; Corbino, K.A.; Stav, S.; Sherlock, M.E.; Breaker, R.R. Riboswitch Diversity and Distribution. RNA 2017, 23, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.; Kaloudas, D.; Penchovsky, R. Riboswitch Distribution, Structure, and Function in Bacteria. Gene 2019, 708, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, M.T.; Moulin, M.; Webb, M.E.; Smith, A.G. Thiamine Biosynthesis in Algae Is Regulated by Riboswitches. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20770–20775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donovan, P.D.; Holland, L.M.; Lombardi, L.; Coughlan, A.Y.; Higgins, D.G.; Wolfe, K.H.; Butler, G. TPP Ri-Boswitch-Dependent Regulation of an Ancient Thiamin Transporter in Candida. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, M.; Petrova, S.A.; Gelfand, M.S. Comparative Genomic Analysis of Fungal TPP-Riboswitches. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2018, 114, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, M.T.; Wachter, A.; Sudarsan, N.; Breaker, R.R. Control of Alternative RNA Splicing and Gene Expression by Eu-Karyotic Riboswitches. Nature 2007, 447, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocobza, S.; Adato, A.; Mandel, T.; Shapira, M.; Nudler, E.; Aharoni, A. Riboswitch-Dependent Gene Regulation and Its Evolution in the Plant Kingdom. Genes. Dev. 2007, 21, 2874–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subki, A.; Ho, C.L.; Ismail, N.F.N.; Abidin, A.A.Z.; Yusof, Z.N.B. Identification and Characterisation of Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP) Riboswitch in Elaeis Guineensis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalvari, I.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Argasinska, J.; Quinones-Olvera, N.; Finn, R.D.; Bateman, A.; Petrov, I.A. Non-Coding RNA Analysis Using the Rfam Database. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2018, 62, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, M.; Boese, B.; Barrick, E.J.; Winkler, W.C.; Breaker, R.R. Riboswitches Control Fundamental Biochemical Pathways in Bacillus subtilis and Other Bacteria. Cell 2003, 113, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thore, S.; Leibundgut, M.; Ban, N. Structure of the Eukaryotic Thiamine Pyrophosphate Riboswitch with Its Regulatory Ligand. Science 2006, 312, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Winkler, W.C.; Nakamura, S.; Scott, V.; Breaker, R.R. Molecular-Recognition Characteristics of SAM-Binding RI-Boswitches. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.; Breaker, R.R. The Structural and Functional Diversity of Metabolite-Binding Riboswitches. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serganov, A. Determination of Riboswitch Structures: Light at the End of the Tunnel? RNA Biol. 2010, 7, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garst, A.D.; Edwards, A.L.; Batey, R.T. Riboswitches: Structures and Mechanisms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 3, a003533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serganov, A.; Nudler, E. A Decade of Riboswitches. Cell 2013, 152, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warner, K.D.; Homan, P.; Weeks, K.M.; Smith, A.G.; Abell, C.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Validating Fragment-Based Drug Discovery for Biological RNAs: Lead Fragments Bind and Remodel the TPP Riboswitch Specifically. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rekand, I.H.; Brenk, R. Ligand Design for Riboswitches, an Emerging Target Class for Novel Antibiotics. Futur. Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 1649–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicens, Q.; Mondragón, E.; Reyes, F.E.; Coish, P.; Aristoff, P.; Berman, J.; Kaur, H.; Kells, K.W.; Wickens, P.; Wilson, J.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationship of Flavin Analogs That Target the FMN Riboswitch. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 2908–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serganov, A.; Huang, L.; Patel, D.J. Structural Insights into Amino Acid Binding and Gene Control by a Lysine Riboswitch. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 455, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matyjasik, M.M.; Hall, S.D.; Batey, R.T. High Affinity Binding of N2-Modified Guanine Derivatives Significantly Disrupts the Ligand Binding Pocket of the Guanine Riboswitch. Molecules 2020, 25, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.D.; Reyes, F.E.; Edwards, A.L.; Batey, R.T. Adaptive Ligand Binding by the Purine Riboswitch in the Recognition of Guanine and Adenine Analogs. Structure 2009, 17, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serganov, A.; Polonskaia, A.; Phan, A.T.; Breaker, R.R.; Patel, D.J. Structural Basis for Gene Regulation by a Thiamine Py-Rophosphate-Sensing Riboswitch. Nature 2006, 441, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serganov, A.; Huang, L.; Patel, D.J. Coenzyme Recognition and Gene Regulation by a Flavin Mononucleotide Riboswitch. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 458, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weickhmann, A.K.; Keller, H.; Wurm, J.P.; Strebitzer, E.; Juen, M.A.; Kremser, J.; Weinberg, Z.; Kreutz, C.; Duchardt-Ferner, E.; Wöhnert, J. The structure of the SAM/SAH-binding riboswitch. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2654–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trausch, J.J.; Xu, Z.; Edwards, A.L.; Reyes, F.E.; Ross, P.E.; Knight, R.; Batey, R.T. Structural Basis for Diversity in the SAM Clan of Riboswitches. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6624–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melander, R.J.; Zurawski, D.V.; Melander, C. Narrow-Spectrum Antibacterial Agents. Med. Chem. Comm. 2018, 9, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, K.D.; Hajdin, C.E.; Weeks, K.M. Principles for Targeting RNA with Drug-Like Small Molecules. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, W.M.; Calabrese, D.R.; Schneekloth, J.S. Evidence for Ligandable Sites in Structured RNA throughout the Protein Data Bank. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekand, I.H.; Brenk, R. DrugPred_RNA-Structure-Based Druggability Predictions for RNA Binding Sites. ChemRxiv 2020. Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsan, N.; Cohen-Chalamish, S.; Nakamura, S.; Emilsson, G.M.; Breaker, R.R. Thiamine Pyrophosphate Riboswitches Are Targets for the Antimicrobial Compound Pyrithiamine. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, J.; Shen, H.; Tu, Y.; Yu, A.; Li, C. The Riboswitch Regulates a Thiamine Pyrophosphate ABC Transporter of the Oral Spirochete Treponema denticola. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3912–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brody, T. Vitamins. In Nutritional Biochemistry; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 1999; pp. 491–692. ISBN 978-0-12-134836-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bocobza, S.E.; Aharoni, A. Small Molecules That Interact with RNA: Riboswitch-Based Gene Control and Its Involvement in Metabolic Regulation in Plants and Algae. Plant J. 2014, 79, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlova, N.; Penchovsky, R. Genome-Wide Bioinformatics Analysis of FMN, SAM-I, glmS, TPP, Lysine, Purine, Cobalamin, and SAH Riboswitches for their Applications as Allosteric Antibacterial Drug Targets in Human Pathogenic Bacteria. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, D.W.; White, A.G.C. Selective Reversible Inhibition of Microbial Growth with Pyrithiamine. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 78, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tracy, A.H.; Elderfield, R.C. Studies in the Pyridine Series. II. Synthesis of 2-Methyl-3-(β-Hydroxyethyl)Pyridine and of the Pyridine Analog of Thiamine (Vitamin B1). J. Org. Chem. 1941, 6, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cressina, E.; Dixon, N.; Erixon, K.; Agyei-Owusu, K.; Micklefield, J.; Smith, A.G.; Abell, C.; Wainman, Y.A. Probing Riboswitch–Ligand Interactions Using Thiamine Pyrophosphate Analoguesa. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lünse, C.C.E.; Scott, F.J.; Suckling, C.J.; Mayer, G. Novel TPP- Riboswitch Activators Bypass Metabolic Enzyme Dependency. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thore, S.; Frick, C.; Ban, N. Structural Basis of Thiamine Pyrophosphate Analogues Binding to the Eukaryotic Riboswitch. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8116–8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cressina, E.; Chen, L.; Abell, C.; Leeper, F.J.; Smith, A.G. Fragment Screening against the Thiamine Pyrophosphate RI-Boswitch ThiM. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, M.S.; Mironov, A.A.; Jomantas, J.; Kozlov, Y.I.; Perumov, D.A. A Conserved RNA Structure Element Involved in the Regulation of Bacterial Riboflavin Synthesis Genes. Trends Genet. 1999, 15, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, W.C.; Cohen-Chalamish, S.; Breaker, R.R. An mRNA Structure That Controls Gene Expression by Binding FMN. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15908–15913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. The Thioredoxin Antioxidant System. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 66, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.M.; Greening, C.; Hards, K.; Berney, M. Energetics of Pathogenic Bacteria and Opportunities for Drug Development. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2014, 65, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Karunaratne, K.; Kohen, A. Flavin-Dependent Thymidylate Synthase as a New Antibiotic Target. Molecules 2016, 21, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howe, J.A.; Wang, H.; Fischmann, T.O.; Balibar, C.J.; Xiao, L.; Galgoci, A.M.; Malinverni, J.C.; Mayhood, T.W.; Villafania, A.; Nahvi, A.; et al. Selective Small-Molecule Inhibition of an RNA Structural Element. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 526, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.R.; Blount, K.F.; Breaker, R.R. Roseoflavin Is a Natural Antibacterial Compound That Binds to FMN Riboswitches and Regulates Gene Expression. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motika, S.E.; Ulrich, R.J.; Geddes, E.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Lau, G.W.; Hergenrother, P.J. Gram-Negative Antibiotic Active Through Inhibition of an Essential Riboswitch. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 10856–10862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, M.; Grill, S. Riboflavin Analogs and Inhibitors of Riboflavin Biosynthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, S.; Takatsu, M.; Nakano, M.; Kasai, S.; Miura, R. Letter: Roseoflavin, a New Antimicrobial Pigment from Strepto-Myces. J. Antibiot. 1974, 27, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, E.; Stolz, J.; Mack, M. RNA Biology the RFN Riboswitch of Bacillus Subtilis Is a Target for the Antibiotic Roseoflavin Produced by Streptomyces Davawensis. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansjö, M.; Johansson, J. The Riboflavin Analog Roseoflavin Targets an FMN- Riboswitch and Blocks Listeria Monocytogenes Growth, but Also Stimulates Virulence Gene-Expression and Infection. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedrolli, D.B.; Jankowitsch, F.; Schwarz, J.; Langer, S.; Nakanishi, S.; Mack, M. Natural Riboflavin Analogs. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1146, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matern, A.; Pedrolli, D.; Großhennig, S.; Johansson, J.; Mack, M. Uptake and Metabolism of Antibiotics Roseoflavin and 8-Demethyl-8-Aminoriboflavin in Riboflavin-Auxotrophic Listeria Monocytogenes. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vicens, Q.; Mondragón, E.; Batey, R.T. Molecular Sensing by the Aptamer Domain of the FMN Riboswitch: A General Model for Ligand Binding by Conformational Selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8586–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baird, N.J.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Idiosyncratically Tuned Switching Behavior of Riboswitch Aptamer Domains Revealed by Comparative Small-Angle X-Ray Scat-Tering Analysis. RNA 2010, 16, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blount, K.F.; Megyola, C.; Plummer, M.; Osterman, D.; O’Connell, T.; Aristoff, P.; Quinn, C.; Chrusciel, R.A.; Poel, T.J.; Schostarez, H.J.; et al. Novel Riboswitch-Binding Flavin Analog that Protects Mice against Clostridium Difficile Infection without Inhibiting Cecal Flora. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 5736–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howe, J.A.; Xiao, L.; Fischmann, T.O.; Wang, H.; Tang, H.; Villafania, A.; Zhang, R.; Barbieri, C.M.; Roemer, T. Atomic Resolution Mechanistic Studies of Ribocil: A Highly Selective Unnatural Ligand Mimic of the E. Coli FMN Riboswitch. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Mann, P.A.; Xiao, L.; Gill, C.; Galgoci, A.M.; Howe, J.A.; Villafania, A.; Barbieri, C.M.; Malinverni, J.C.; Sher, X.; et al. Dual-Targeting Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Staphylococcus Aureus FMN Riboswitch Disrupt Riboflavin Homeostasis in an Infectious Setting. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 576–588.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizvi, N.F.; Howe, J.A.; Nahvi, A.; Klein, D.J.; Fischmann, T.O.; Kim, H.-Y.; McCoy, M.A.; Walker, S.S.; Hruza, A.; Richards, M.P.; et al. Discovery of Selective RNA-Binding Small Molecules by Affinity-Selection Mass Spectrometry. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milewski, S. Glucosamine-6-Phosphate Synthase—The Multi-Facets Enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 2002, 1597, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCown, P.J.; Roth, A.; Breaker, R.R. An Expanded Collection and Refined Consensus Model of GlmS Ribozymes. RNA 2011, 17, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkler, W.C.; Nahvi, A.; Roth, A.; Collins, J.A.; Breaker, R.R. Control of Gene Expression by a Natural Metabo-Lite-Responsive Ribozyme. Nature 2004, 428, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Hamelberg, D. Deciphering the role of glucosamine-6-phosphate in the riboswitch action of glmS ribozyme. RNA 2010, 16, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, J.A.; Irnov, I.; Baker, S.; Winkler, W.C. Mechanism of mRNA Destabilization by the GlmS Ribozyme. Genes. Dev. 2007, 21, 3356–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.A.; Göpel, Y.; Milewski, S.; Görke, B. Two small RNAs conserved in enterobacteriaceae provide intrinsic resistance to antibiotics targeting the cell wall biosynthesis enzyme glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, M.; Milewski, S.; Mazerski, J.; Borowski, E. Glucosamine-6-Phosphate Synthase, A Novel Target for Anti-fungal Agents. Molecular Modelling Studies in Drug Design. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2005, 52, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsuzawa, H.; Fujiwara, T.; Nishi, H.; Yamada, S.; Ohara, M.; McCallum, N.; Berger-Bächi, B.; Sugai, M. The Gate Controlling Cell Wall Synthesis in Staphylococcus Aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, T.J.; Plog, M.A.; Floy, S.A.; Jansen, J.A.; Soukup, J.K.; Soukup, G.A. Ligand Requirements for glmS Ribozyme Self-Cleavage. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, J.C.; Lipchock, S.V.; Smith, K.D.; Strobel, S.A. Structural and Chemical Basis for Glucosamine 6-Phosphate Binding and Activation of the GlmS Ribozyme. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 3239–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klein, D.J.; Wilkinson, S.R.; Been, M.D.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Requirement of Helix P2.2 and Nucleotide G1 for Positioning the Cleavage Site and Cofactor of the glmS Ribozyme. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, J.C.; Lipchock, S.V.; Strobel, S.A. Structural Investigation of the GlmS Ribozyme Bound to Its Catalytic Cofactor. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klein, D.J.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Structural Basis of GlmS Ribozyme Activation by Glucosamine-6-Phosphate. Science 2006, 313, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, K.; Puskarz, I.; Penchovsky, R.; Breaker, R. Development and Application of a High-Throughput Assay for glmS Ri-boswitch Activators. RNA Biol. 2006, 3, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.; Grove, B.C.; Roth, A.; Breaker, R.R. Characteristics of Ligand Recognition by a GlmS Self-Cleaving Ribozyme. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 6689–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, G.; Famulok, M. High-Throughput-Compatible Assay for glmS Riboswitch Metabolite Dependence. Chem. Biochem. 2006, 7, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lünse, C.E.; Schmidt, M.S.; Wittmann, V.; Mayer, G. Carba-Sugars Activate the GlmS-Riboswitch of Staphylococcus Aureus. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzner, D.; Schüller, A.; Seitz, T.; Wittmann, V.; Mayer, G. Fluoro-Carba-Sugars are Glycomimetic Activators of the GlmS Ribozyme. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 12604–12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Holmes, T.; Diddle, J.; Hintz, L.; Delaney, D.; Stock, A.; Renner, D.; McDevitt, M.; Berkowitz, D.B.; Soukup, J.K. Phosphatase-Inert Glucosamine 6-Phosphate Mimics Serve as Actuators of the Glms Riboswitch. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 2875–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.N.; Blount, K.F.; Puskarz, I.; Lim, J.; Link, K.H.; Breaker, R.R. Design and Antimicrobial Action of Purine Analogues That Bind Guanine Riboswitches. ACS Chem. Biol. 2009, 4, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serganov, A.; Yuan, Y.-R.; Pikovskaya, O.; Polonskaia, A.; Malinina, L.; Phan, A.T.; Hobartner, C.; Micura, R.; Breaker, R.R.; Patel, D.J. Structural Basis for Discriminative Regulation of Gene Expression by Adenine- and Guanine-Sensing mRNAs. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 1729–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batey, R.T.; Gilbert, S.D.; Montange, R.K. Structure of a Natural Guanine-Responsive Riboswitch Complexed with the Me-Tabolite Hypoxanthine. Nature 2004, 432, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, M.; Nakayasu, M.; Aonuma, S.; Wakabayashi, K.; Hirose, M.; Sugimura, T. Mutagenic Properties of 2-Amino-N6-Hydroxyadenine in Salmonella and in Chinese Hamster Lung Cells in Culture. Mutat. Res. Mutagen. Relat. Subj. 1991, 253, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiyama, H.; Atsumi, G.-I.; Matsuda, A.; Negishi, K.; Hayatsu, H. Analysis of 2-Amino-N6-Hydroxyadenine-Induced Mutagenesis in Phage M13mp2. Mutat. Res. Mutagen. Relat. Subj. 1991, 253, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulhbacher, J.; Brouillette, E.; Allard, M.; Fortier, L.-C.; Malouin, F.; Lafontaine, D.A. Novel Riboswitch Ligand Analogs as Selective Inhibitors of Guanine-Related Metabolic Pathways. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, L.-H.; Le Roux, A.; Boyapelly, K.; Lamontagne, A.-M.; Archambault, M.-A.; Picard-Jean, F.; Lalonde-Seguin, D.; St-Pierre, E.; Najmanovich, R.J.; Fortier, L.-C.; et al. Purine Analogs Targeting the Guanine Riboswitch as Potential Antibiotics against Clostridioides Difficile. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ster, C.; Allard, M.; Boulanger, S.; Boulet, M.L.; Mulhbacher, J.; Lafontaine, D.; Marsault, E.; Lacasse, P.; Malouin, F. Experimental Treatment of Staphylococcus Aureus Bovine Intramammary Infection Using a Guanine Riboswitch Ligand Analog. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kofoed, E.M.; Yan, D.; Katakam, A.K.; Reichelt, M.; Lin, B.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Date, S.V.; Monk, I.R.; Xu, M.; et al. De Novo Guanine Biosynthesis but Not the Riboswitch-Regulated Purine Salvage Pathway Is Required for Staphylococcus Aureus in-Fection in Vivo. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 2001–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blount, K.F.; Wang, J.X.; Lim, J.; Sudarsan, N.; Breaker, R.R. Antibacterial Lysine Analogs That Target Lysine Riboswitches. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 3, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Hu, F.M.; Chen, N.Y.; Paulus, H. Comparison of the Three Aspartokinase Isozymes in Bacillus Subtilis Marburg and 168. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bassalo, M.C.; Garst, A.D.; Choudhury, A.; Grau, W.C.; Oh, E.J.; Spindler, E.; Lipscomb, T.; Gill, R.T. Deep Scanning Lysine Metabolism in Escherichia Coli. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2018, 14, e8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alreshidi, M.M.; Dunstan, R.H.; Macdonald, M.M.; Gottfries, J.; Roberts, T.K. The Uptake and Release of Amino Acids by Staphylococcus Aureus at Mid-exponential and Stationary Phases and Their Corre-Sponding Responses to Changes in Tem-Perature, pH and Osmolality. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickiser, J.K. Kinetics of Riboswitch Regulation Studied By In Vitro Transcription. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2009, 540, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-C.; Yoon, J.; Hyeon, C.; Thirumalai, D. Using Simulations and Kinetic Network Models to Reveal the Dynamics and Functions of Riboswitches. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier BV: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 553, pp. 235–258. [Google Scholar]
- Guedich, S.; Puffer-Enders, B.; Baltzinger, M.; Hoffmann, G.; Da Veiga, C.; Jossinet, F.; Thore, S.; Bec, G.; Ennifar, E.; Burnouf, D.Y.; et al. Quantitative and Predictive Model of Kinetic Regulation byE. coliTPP Riboswitches. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, B.; Jones, C.P.; Mitra, J.; Murray, P.J.; Rosenthal, R.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R.; Ha, T. Real-Time Monitoring of Single ZTP Riboswitches Reveals a Complex and Kinetically Controlled Decision Landscape. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J.V. Molecular Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrick, J.E.; Breaker, R.R. The Distributions, Mechanisms, and Structures of Metabolite-Binding Riboswitches. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R239–R319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matzner, D.; Mayer, G. (Dis)similar Analogues of Riboswitch Metabolites as Antibacterial Lead Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3275–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lünse, C.E.; Mayer, G. Reporter Gene-Based Screening for TPP Riboswitch Activators. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1520, pp. 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner, M.; Schorpp, K.; Hadian, K.; Schneider, S. an in Vivo High-Throughput Screening for Riboswitch Ligands Using a Reverse Reporter Gene System. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chinnappan, R.; Dubé, A.; Lemay, J.-F.; Lafontaine, D.A. Fluorescence Monitoring of Riboswitch Transcription Regulation Using a Dual Molecular Beacon Assay. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connelly, C.M.; Numata, T.; Boer, R.E.; Moon, M.; Sinniah, R.S.; Barchi, J.J.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R.; Schneekloth, J.S., Jr. Synthetic Ligands for PreQ1 Riboswitches Provide Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Targeting RNA Tertiary Structure. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehler, T.; Brenk, R. Structure-Based Discovery of Small Molecules Binding to RNA. In RNA Therapeutics. Topics in Medicinal Chemistry; Garner, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 27, pp. 47–78. [Google Scholar]
- Binas, O.; De Jesus, V.; Landgraf, T.; Völklein, A.E.; Martins, J.; Hymon, D.; Berg, H.; Bains, J.K.; Biedenbänder, T.; Fürtig, B.; et al. 19F-NMR-Based Fragment Screening for 14 Different Biologically Active RNAs and 10 DNA and Protein Counter-Screens. Chem. Biochem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daldrop, P.; Reyes, F.E.; Robinson, D.A.; Hammond, C.M.; Lilley, D.M.; Batey, R.T.; Brenk, R. Novel Ligands for a Purine Riboswitch Discovered by RNA-Ligand Docking. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colizzi, F.; Lamontagne, A.-M.; Lafontaine, D.A.; Bussi, G. Probing Riboswitch Binding Sites with Molecular Docking, Focused Libraries, and In-line Probing Assays. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2013, 1103, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhathoki, P.; Bernal-Perez, L.F.; Annunziata, O.; Ryu, Y. Rationally-Designed Fluorescent Lysine Riboswitch Probes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, S.F.; Hammond, M.C. Structure-Guided Design of Fluorescent S-Adenosylmethionine Analogs for a High-Throughput Screen to Target SAM-I Riboswitch RNAs. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Wei, W.; Waldispühl, J.; Moitessier, N. Challenges and Current Status of Computational Methods for Docking Small Molecules to Nucleic Acids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 168, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Riboswitch | Type | Cognate Ligand | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| FMN | Off |  flavin mononucleotide (FMN) | Acinetobacter baumannii (1), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1), Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus faecium (1–2), Staphylococcus aureus (2), Streptococcus pneumoniae (1–2), Haemophilus influenzae (1), Shigella spp. (1) |
| c-di-AMP | Off |  cyclic diadenine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) | Mycobacterium tuberculosis (1) |
| Fluoride | On | F- | A. baumannii (2), P. aeruginosa (2), E. faecium (1–3), |
| glmS | Off |  glucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcN6P) | S. aureus (1), E. faecium (1) |
| Glycine | On |  glycine | H. influenzae (1), S. pneumoniae (1), Neisseria gonorrhoeae (1), S. aureus (1), A. baumannii (1), M. tuberculosis (2) |
| Lysine | Off |  lysine | E. faecium (1), S. aureus (2), H. influenzae (1), Shigella spp. (1) |
| Moco | Off |  molybdenum cofactor (Moco) | Enterobacteriaceae, H. influenzae (2), Shigella spp. (2) |
| PreQ1 | Off |  7-aminomethyl-7-deazaguanine (preQ1) | E. faecium (1–2), N. gonorrhoeae (1), S. pneumoniae (1), H. influenzae (1) |
| Purine | Off |  guanine | E. faecium (1), S. aureus (1) |
| On |  adenine | ||
| SAM | Off |  S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) | S. aureus (1–4), N. gonorrhoeae (1), M. tuberculosis (1) |
| TPP | Off |  thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) | A. baumannii (1), P. aeruginosa (1), Enterobacteriaceae, E. faecium (2), S. aureus (1–2), H. pylori (1), Campylobacter spp. (1–2), Salmonellae (1–3), N. gonorrhoeae (2), S. pneumoniae (1–5), H. influenzae (3), M. tuberculosis (2) and Shigella (3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panchal, V.; Brenk, R. Riboswitches as Drug Targets for Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010045
Panchal V, Brenk R. Riboswitches as Drug Targets for Antibiotics. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010045
Chicago/Turabian StylePanchal, Vipul, and Ruth Brenk. 2021. "Riboswitches as Drug Targets for Antibiotics" Antibiotics 10, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010045
APA StylePanchal, V., & Brenk, R. (2021). Riboswitches as Drug Targets for Antibiotics. Antibiotics, 10(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010045