Pitfalls Associated with Discriminating Mixed-Species Biofilms by Flow Cytometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Planktonic versus Biofilm Cells
2.2. Effect of Hyphae and Biofilm Matrix on Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.3. Influence of Sonication on Biofilm Cell Viability
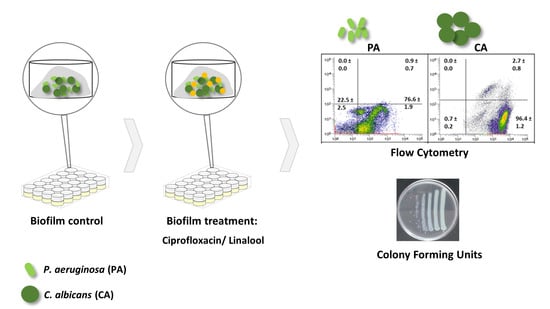
2.4. Analysis of Mixed-Species Biofilms
2.5. Antimicrobial Effect on Mixed-Species Biofilms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microorganisms and Culture Conditions
4.2. Biofilm Formation
4.3. Hyphal Induction
4.4. Biofilm Quantification
4.4.1. Determination of Culturable Cells
4.4.2. Extraction of Biofilm Matrix
4.4.3. Flow Cytometry Assay
4.5. Influence of Sonication on Biofilm Cell Viability
4.6. Antimicrobial Effect on Mixed-Species Biofilms
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nickzad, A.; Déziel, E. The involvement of rhamnolipids in microbial cell adhesion and biofilm development—An approach for control? Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 58, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Branda, S.S.; Vik, Å.; Friedman, L.; Kolter, R. Biofilms: The matrix revisited. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingender, J.; Neu, T.R.; Flemming, H.-C. What are Bacterial Extracellular Polymeric Substances? Microb. Extracell. Polym. Subst. 1999, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decho, A.W.; Visscher, P.T.; Reid, R.P. Production and cycling of natural microbial exopolymers (EPS) within a marine stromatolite. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2005, 219, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.M.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A.; O’May, G.A.; Costerton, J.W.; Shirtliff, M.E. Polymicrobial interactions: Impact on pathogenesis and human disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fourie, R.; Ells, R.; Swart, C.W.; Sebolai, O.M.; Albertyn, J.; Pohl, C.H. Candida albicans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Interaction, with Focus on the Role of Eicosanoids. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Hogan, D.A.; Mylonakis, E. Medically important bacterial-fungal interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, E.M.; Bennett, R.J. Sensing of the microbial neighborhood by Candida albicans. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirota, K.; Yumoto, H.; Sapaar, B.; Matsuo, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Miyake, Y. Pathogenic factors in Candida biofilm-related infectious diseases. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.J.; Johnson, A.D. Candida albicans Biofilms and Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, S.M.; Prince, L.R.; McPhillips, K.; Allen, L.; Marriott, H.M.; Taylor, G.W.; Hellewell, P.G.; Sabroe, I.; Dockrell, D.H.; Henson, P.W.; et al. Impairment of apoptotic cell engulfment by pyocyanin, a toxic metabolite of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlester, G.; O’Gara, F.; Morrissey, J.P. Signal-mediated interactions between Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Percival, S.L.; Suleman, L.; Vuotto, C.; Donelli, G. Healthcare-Associated infections, medical devices and biofilms: Risk, tolerance and control. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fux, C.A.; Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Stoodley, P. Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalhais, V.; Pérez-Cabezas, B.; Oliveira, C.; Vitorino, R.; Vilanova, M.; Cerca, N. Tetracycline and rifampicin induced a viable but nonculturable state in Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, J.; Collard, J.-M.; Whaley, M.J.; Bassira, I.; Seidou, I.; Diarra, S.; Ouédraogo, R.T.; Kambiré, D.; Taylor, T.H.; Sacchi, C.; et al. Development of Real-Time PCR Methods for the Detection of Bacterial Meningitis Pathogens without DNA Extraction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zemanick, E.T.; Wagner, B.D.; Sagel, S.D.; Stevens, M.J.; Accurso, F.J.; Harris, J.K. Reliability of quantitative real-time PCR for bacterial detection in cystic fibrosis airway specimens. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, M.E.; Lopes, S.P.; Pereira, C.R.; Azevedo, N.F.; Lourenço, A.; Henriques, M.; Pereira, M.O. Polymicrobial Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Fighting In Vitro Candida albicans-Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms with Antifungal-Antibacterial Combination Therapy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, A.; Almeida, C.; Salgueiro, D.; Henriques, A.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Vieira, M.J.; Rodrigues, L.; Azevedo, N.F.; Cerca, N. Fluorescence in situ Hybridization method using Peptide Nucleic Acid probes for rapid detection of Lactobacillus and Gardnerella spp. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almeida, C.; Azevedo, N.F.; Bento, J.C.; Cerca, N.; Ramos, H.; Vieira, M.J.; Keevil, C.W. Rapid detection of urinary tract infections caused by Proteus spp. using PNA-FISH. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, S.; Nebe-von-Caron, G. Functional single-cell analyses: Flow cytometry and cell sorting of microbial populations and communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 554–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davey, H.M.; Kell, D.B. Flow cytometry and cell sorting of heterogeneous microbial populations: The importance of single-cell analyses. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 60, 641–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharíková, S.; lè ne Tournu, H.; Lagrou, K.; Van Dijck, P.; Bujdá ková, H. Detailed comparison of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata biofilms under different conditions and their susceptibility to caspofungin and anidulafungin. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Cook, A.E.; Fukushima, T.; Bond, P.L. Evidence of compositional differences between the extracellular and intracellular DNA of a granular sludge biofilm. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Costa-Oliveira, S.; Melo, L.D.R.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Azeredo, J.; Henriques, M.; Silva, S. Susceptibility testing of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata to Glycyrrhiza glabra L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerca, F.; Trigo, G.; Correia, A.; Cerca, N.; Azeredo, J.; Vilanova, M. SYBR green as a fluorescent probe to evaluate the biofilm physiological state of Staphylococcus epidermidis, using flow cytometry. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerstens, M.; Boulet, G.; Van Kerckhoven, M.; Clais, S.; Lanckacker, E.; Delputte, P.; Maes, L.; Cos, P. A flow cytometric approach to quantify biofilms. Folia Microbiol. 2015, 60, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.; Lima, C.A.; Brás, S.; França, Â.; Cerca, N. Evidence for inter- and intraspecies biofilm formation variability among a small group of coagulase-negative staphylococci. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, G.-X.; Katagori, N.; Chen, H. A comparison of conventional methods for the quantification of bacterial cells after exposure to metal oxide nanoparticles. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rüger, M.; Bensch, G.; Tüngler, R.; Reichl, U. A flow cytometric method for viability assessment of Staphylococcus aureus and Burkholderia cepacia in mixed culture. Cytom. Part A 2012, 81A, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cos, P.; Toté, K.; Horemans, T.; Maes, L. Biofilms: An extra hurdle for effective antimicrobial therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 2279–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, G.; Saville, S.P.; Thomas, D.P.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. Candida Biofilms: An Update. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilain, S.; Pretorius, J.M.; Theron, J.; Brözel, V.S. DNA as an adhesin: Bacillus cereus requires extracellular DNA to form biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuneda, S.; Aikawa, H.; Hayashi, H.; Yuasa, A.; Hirata, A. Extracellular polymeric substances responsible for bacterial adhesion onto solid surface. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 223, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hancock, R.E.W. A brief on bacterial biofilms. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.H.; Jahn, A. Extraction of EPS. In Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 49–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dosler, S.; Karaaslan, E. Inhibition and destruction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms by antibiotics and antimicrobial peptides. Peptides 2014, 62, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, E.; Hidalgo-Bastida, L.A.; Verran, J.; Williams, D.; Malic, S. Antifungal activity of commercial essential oils and biocides against Candida albicans. Pathogens 2018, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, J.L. Effect of antibiotics on bacterial populations: A multi-hierachical selection process. F1000Research 2017, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Bambeke, F.; Michot, J.-M.; Van Eldere, J.; Tulkens, P.M. Quinolones in 2005: An update. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, F.; Lourenço, O.; Queiroz, J.A.; Domingues, F.C. Bacteriostatic versus bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin in Escherichia coli assessed by flow cytometry using a novel far-red dye. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O.; Johansen, H.K.; Song, Z.J.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Bjarnsholt, T. The Clinical Impact of Bacterial Biofilms. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 3, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, A.; Ribeiro, H.G.; Silva, A.C.; Silva, M.D.; Sousa, J.C.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Melo, L.D.R.; Henriques, A.F.; Sillankorva, S. Synergistic antimicrobial interaction between honey and phage against Escherichia coli biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fostel, J.M.; Montgomery, D.A.; Shen, L.L. Characterization of DNA topoisomerase I from Candida albicans as a target for drug discovery. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.L.; Baranowski, J.; Fostel, J.; Montgomery, D.A.; Lartey, P.A. DNA topoisomerases from pathogenic fungi: Targets for the discovery of antifungal drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 2778–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.L.; Fostel, J.M. DNA Topoisomerase Inhibitors as Antifungal Agents. In Advances in Pharmacology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; Volume 29, pp. 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- Stergiopoulou, T.; Meletiadis, J.; Sein, T.; Papaioannidou, P.; Tsiouris, I.; Roilides, E.; Walsh, T.J. Isobolographic analysis of pharmacodynamic interactions between antifungal agents and ciprofloxacin against Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brilhante, R.S.N.; Caetano, E.P.; Sidrim, J.J.C.; Cordeiro, R.A.; Camargo, Z.P.; Fechine, M.A.B.; Lima, R.A.C.; Castelo Branco, D.S.C.M.; Marques, F.J.F.; Mesquita, J.R.L.; et al. Ciprofloxacin shows synergism with classical antifungals against Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum and Coccidioides posadasii. Mycoses 2013, 56, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stergiopoulou, T.; Meletiadis, J.; Sein, T.; Papaioannidou, P.; Tsiouris, I.; Roilides, E.; Walsh, T.J. Comparative pharmacodynamic interaction analysis between ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin and levofloxacin and antifungal agents against Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zore, G.B.; Thakre, A.D.; Jadhav, S.; Karuppayil, S.M. Terpenoids inhibit Candida albicans growth by affecting membrane integrity and arrest of cell cycle. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alviano, W.S.; Mendonca-Filho, R.R.; Alviano, D.S.; Bizzo, H.R.; Souto-Padron, T.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Bolognese, A.M.; Alviano, C.S.; Souza, M.M.G.; Mendonça-Filho, R.R.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of Croton cajucara Benth linalool-rich essential oil on artificial biofilms and planktonic microorganisms. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 20, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Lai, W.-L.; Chuang, K.-C.; Lee, M.-H.; Tsai, Y.-C. The inhibitory activity of linalool against the filamentous growth and biofilm formation in Candida albicans. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Léonard, L.; Chibane, L.B.; Bouhedda, B.O.; Degraeve, P.; Oulahal, N. Recent advances on multi-parameter flow cytometry to characterize antimicrobial treatments. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasquaroli, S.; Zandri, G.; Vignaroli, C.; Vuotto, C.; Donelli, G.; Biavasco, F. Antibiotic pressure can induce the viable but non-culturable state in Staphylococcus aureus growing in biofilms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Mendis, N.; Trigui, H.; Oliver, J.D.; Faucher, S.P. The importance of the viable but non-culturable state in human bacterial pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Ahmad, A.; Akhtar, F.; Yousuf, S.; Xess, I.; Khan, L.A.; Manzoor, N. Ocimum sanctum essential oil and its active principles exert their antifungal activity by disrupting ergosterol biosynthesis and membrane integrity. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soković, M.; Glamočlija, J.; Marin, P.D.; Brkić, D.; Griensven, L.J.L.D. van Antibacterial Effects of the Essential Oils of Commonly Consumed Medicinal Herbs Using an In Vitro Model. Molecules 2010, 15, 7532–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, S.P.; Dias, N.M.; Melo, L.D.R.; Azeredo, J.; Santos, S.B.; Carvalho, C.M. A novel flow cytometry assay based on bacteriophage-derived proteins for Staphylococcus detection in blood. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Dakić, I.; Savić, B.; Švabić-Vlahović, M. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 2000, 40, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Henriques, M.; Martins, A.; Oliveira, R.; Williams, D.; Azeredo, J. Biofilms of non-Candida albicans Candida species: Quantification, structure and matrix composition. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Condition | P. aeruginosa | C. albicans | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCM Counts/mL | CFU/mL | FCM Counts/mL | CFU/mL | |
| 24 h-old biofilm | 5.69 ± 0.03 | 6.99 ± 0.45 | 6.11 ± 0,17 | 6.51 ± 0.55 |
| 48 h-old biofilm | 7.37 ± 0.02 | 8.53 ± 0.48 | 6.87 ± 0.10 | 7.46 ± 0.69 |
| Ciprofloxacin (0.25 mg/L) | 5.36 ± 0.24# | 6.08 ± 0.94 # | 6.44 ± 0.23 | 6.64 ± 0.82 |
| Ciprofloxacin (8 mg/L) | 4.85 ± 0.62# | 4.99 ± 1.31 *,# | 6.43 ± 0.23 | 6.82 ± 0.44 |
| Linalool (0.3% v/v) | 6.26 ± 0.21 | 7.62 ± 0.70 | 6.07 ± 0.19 | 2.02 ± 1.91 *,# |
| Linalool (1.2% v/v) | 6.27 ± 0.07 | 7.38 ± 0.41 | 6.28 ± 0.03 | 0.00 *,# |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grainha, T.; Magalhães, A.P.; Melo, L.D.R.; Pereira, M.O. Pitfalls Associated with Discriminating Mixed-Species Biofilms by Flow Cytometry. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9110741
Grainha T, Magalhães AP, Melo LDR, Pereira MO. Pitfalls Associated with Discriminating Mixed-Species Biofilms by Flow Cytometry. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(11):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9110741
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrainha, Tânia, Andreia P. Magalhães, Luís D. R. Melo, and Maria O. Pereira. 2020. "Pitfalls Associated with Discriminating Mixed-Species Biofilms by Flow Cytometry" Antibiotics 9, no. 11: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9110741
APA StyleGrainha, T., Magalhães, A. P., Melo, L. D. R., & Pereira, M. O. (2020). Pitfalls Associated with Discriminating Mixed-Species Biofilms by Flow Cytometry. Antibiotics, 9(11), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9110741