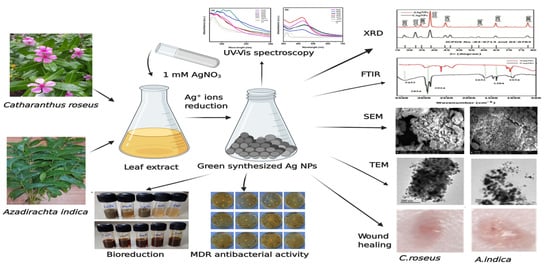
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Wound Healing Efficacy Using a Murine Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Biosynthesized Ag NPs release free silver ions that traverse into cells, causing further breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation and promotingthe replication of DNA.
- Ag NPs, along with Ag+ ions, enhance the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in an antioxidant mechanism.
- Ag NPs cause cell membrane damage directly.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bioreduction and Synthesis of Ag NPs
2.2. UV–Vis Spectra Analysis of Ag NPs
2.3. X-ray Diffraction Studies
2.4. FTIR Analysis
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.8. Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles
2.8.1. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
2.8.2. Bacterial Reduction Assay
2.9. Wound-Healing Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles In Vivo
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Leaf Extracts Preparation from C. roseus and A. indica
3.2. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticlesfrom Leaf Extract
3.3. Microbial Strains
3.4. Silver Nanoparticles Characterization
3.5. Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles
3.6. Wound Healing Activity of Silver Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Latha, T.S.; Lomada, D.; Dharani, P.K.; Muthukonda, S.V.; Reddy, M.C. Ti–O based nanomaterials ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and collagen-induced arthritis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 8870–8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, J. Synthetic micro/nanomotors in drug delivery. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10486–10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latha, T.S.; Reddy, M.C.; Muthukonda, S.V.; Srikanth, V.V.; Lomada, D. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of anti-cancer activity: Shape-dependent properties of TiO2 nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaniselvam, T.; Valappil, M.O.; Illathvalappil, R.; Kurungot, S. Nanoporous graphene by quantum dots removal from graphene and its conversion to a potential oxygen reduction electrocatalyst via nitrogen doping. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröfel, A.; Kratošová, G.; Šafařík, I.; Šafaříková, M.; Raška, I.; Shor, L.M. Applications of biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles—A review. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4023–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Singh, S.; Prasad, S.; Gambhir, I. Nanotechnology in medicine and antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2008, 3, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Sakthivel, N. Green synthesis of biogenic metal nanoparticles by terrestrial and aquatic phototrophic and heterotrophic eukaryotes and biocompatible agents. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanpuria, P.; Rana, N.; Yadav, S. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles: Technological concepts and future applications. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Yusoff, M.M.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N. Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications—An updated report. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukunthan, K.; Elumalai, E.; Patel, T.N.; Murty, V.R. Catharanthusroseus: A natural source for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jha, A.K.; Prasad, K.; Kumar, V.; Prasad, K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Eclipta leaf. Biotechnol. Prog. 2009, 25, 1476–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallavali, R.R.; Avula, S.; Degati, V.L.; Penubala, M.; Damu, A.; Durbaka, V.R.P. Data of antibacterial activity of plant leaves crude extract on bacterial isolates of wound infections. Data Brief 2019, 24, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, C.-Y. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffi, M.; Hussain, F.; Bhatti, T.; Akhter, J.; Hameed, A.; Hasan, M. Antibacterial characterization of silver nanoparticles against E. coli ATCC-15224. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carisse, O.; Van Der Heyden, H. Relationship of airborne Botrytis cinerea conidium concentration to tomato flower and stem infections: A threshold for de-leafing operations. Plant. Dis. 2015, 99, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Yu, X.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum L. extract. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanghi, R.; Verma, P. Biomimetic synthesis and characterisation of protein capped silver nanoparticles. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.N.; Vats, P.; Suri, S.; Shyam, R.; Kumria, M.; Ranganathan, S.; Sridharan, K. Effect of an antidiabetic extract of Catharanthusroseus on enzymic activities in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 76, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.; Verpoorte, R. Methyljasmonate accelerates catabolism of monoterpenoid indole alkaloids in Catharanthusroseus during leaf processing. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, O.P.; Kumar, V.; Behl, H.M. Variability in triterpenoids (nimbin and salanin) composition of neem among different provenances of India. Ind. Crops Prod. 2004, 19, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaiye, A.; Youngs, W.J. Silver and its application as an antimicrobial agent. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2005, 15, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Staphylococcus aureus Infections: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ansari, S.; Jha, R.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Tiwari, B.R.; Asaad, A.M. Recent advances in Staphylococcus aureus infection: Focus on vaccine development. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ki, V.; Rotstein, C. Bacterial Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in Adults: A Review of Their Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Site of Care. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 19, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic Basis of Antimicrobial Actions of Silver Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaikh, R.; Zainuddin Syed, I.; Bhende, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using root extracts of Cassia toral L. and its antimicrobial activities. Asian J. Green Chem. 2019, 3, 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick, S.; Koul, V. Assessment of PVA/silver nanocomposite hydrogel patch as antimicrobial dressing scaffold: Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Díaz, M.; Alvarado-Gomez, E.; Magaña-Aquino, M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Velasquillo, C.; Gonzalez, C.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F. Anti-biofilm activity of chitosan gels formulated with silver nanoparticles and their cytotoxic effect on human fibroblasts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 60, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, E.T.; Lee, J.H.; Chae, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, B.C.; Sang, B.I.; Gu, M.B. Analysis of the toxic mode of action of silver nanoparticles using stress-specific bioluminescent bacteria. Small 2008, 4, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedki, M.; Mohamed, M.B.; Fawzy, M.; Abdelrehim, D.A.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M. Phytosynthesis of silver–reduced graphene oxide (Ag–RGO) nanocomposite with an enhanced antibacterial effect using Potamogetonpectinatus extract. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 17358–17365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femi-Adepoju, A.G.; Dada, A.O.; Otun, K.O.; Adepoju, A.O.; Fatoba, O.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using terrestrial fern (Gleichenia Pectinata (Willd.) C. Presl.): Characterization and antimicrobial studies. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srour, J.; Berg, E.; Mahltig, B.; Smolik, T.; Wollenberg, A. Evaluation of antimicrobial textiles for atopic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchi, S.; Inamuddin; Khan, A. Biogenic synthesis of selenium nanoparticles with edible mushroom extract: Evaluation of cytotoxicity on prostate cancer cell lines and their antioxidant, and antibacterial activity. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 10, 6629–6639. [Google Scholar]
- Mulvaney, P. Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir 1996, 12, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarrajan, M.; Jeelani, A.; Santhanam, V.; Durgadevi, S.; Abirami, S. Effect of Concentration, pH and Time on the Morphology of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Green Method using Phyllanthus niruri and Solanum nigrum Leaf Extracts. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shmgani, H.S.A.; Mohammed, W.H.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Saadoon, A.H. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Catharanthus roseus leaf extract and assessing their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and wound-healing activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udayasoorian, C.; Kumar, R.; Jayabalakrishnan, M. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Cassia auriculata. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2011, 6, 279–283. [Google Scholar]
- Wiley, B.J.; Im, S.H.; Li, Z.-Y.; McLellan, J.; Siekkinen, A.; Xia, Y. Maneuvering the surface plasmon resonance of silver nanostructures through shape-controlled synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 15666–15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakya, S.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Sukumaran, M.; Muthukumar, M. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 5, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthukrishnan, S.; Bhakya, S.; Kumar, T.S.; Rao, M. Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial effect of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using Ceropegia thwaitesii—An endemic species. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 63, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaja, M.; Annadurai, G. Coleus aromaticus leaf extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its bactericidal activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2013, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shankar, S.S.; Ahmad, A.; Pasricha, R.; Sastry, M. Bioreduction of chloroaurate ions by geranium leaves and its endophytic fungus yields gold nanoparticles of different shapes. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameli, K.; Ahmad, M.B.; Zargar, M.; Yunus, W.M.Z.W.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Shabanzadeh, P.; Moghaddam, M.G. Synthesis and characterization of silver/montmorillonite/chitosan bionanocomposites by chemical reduction method and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, A.; Kumari, M.; Pandey, S.; Chaudhry, V.; Gupta, K.; Nautiyal, C. Biocatalytic and antimicrobial activities of gold nanoparticles synthesized by Trichoderma sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 166, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Satapathy, M.; Mukhopahayay, A.; Das, P. Leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from widely available Indian plants: Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial property and toxicity analysis. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2014, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prathna, T.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Studies on aggregation behaviour of silver nanoparticles in aqueous matrices: Effect of surface functionalization and matrix composition. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 390, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Taghdiri, M.; Makari, V.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Procedure optimization for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by aqueous extract of Eucalyptus oleosa. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzadeh, E.; Esmaeili, A.; Abadi, R.E.N.; Kazemipour, N.; Pahlevanneshan, Z.; Beheshti, S. Quercetin conjugated with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles improves learning and memory better than free quercetin via interacting with proteins involved in LTP. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.; Gowri, S.; Arumugam, A. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Pterocarpus santalinus leaf extract and their antibacterial properties. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2013, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yliniemi, K.; Vahvaselka, M. Antimicrobial activity of colloidal silver nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel method. Chem 2008, 18, 199. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosoky, N.S.; Setzer, W.N. Chemical composition and biological activities of essential oils of Curcuma species. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akarchariya, N.; Sirilun, S.; Julsrigival, J.; Chansakaowa, S. Chemical profiling and antimicrobial activity of essential oil from Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb., Curcuma glans K. Larsen & J. Mood and Curcuma cf. xanthorrhizaRoxb. collected in Thailand. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 881–885. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.; Bulut, O.; Some, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Yilmaz, M.D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2673–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Kwon, D.-N.; Kim, J.-H. Enhanced antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of silver nanoparticles against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahayaraj, K.; Rajesh, S. Bionanoparticles: Synthesis and antimicrobial applications. Sci. Microb. Pathog. Commun. Curr. Res. Technol. Adv. 2011, 23, 228–244. [Google Scholar]
- Beddy, D.; Watson, R.; Fitzpatrick, J.; O’connell, P. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor production in fibroblasts isolated from strictures in patients with Crohn’s disease. Br. J. Surg. 2004, 91, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, N.K.; Chowdhury, A.; Dey, U.; Mukhopadhya, P.; Chatterjee, S.; Das, K.; Datta, J.K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its application for mosquito control. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, S204–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wong, K.K.; Ho, C.M.; Lok, C.N.; Yu, W.Y.; Che, C.M.; Tam, P.K. Topical delivery of silver nanoparticles promotes wound healing. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, P.Y.; Ho, C.M.; Lui, V.C.; Chen, Y.; Che, C.M.; Wong, K.K. Silver nanoparticles mediate differential responses in keratinocytes and fibroblasts during skin wound healing. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vivek, R.; Thangam, R.; Muthuchelian, K.; Gunasekaran, P.; Kaveri, K.; Kannan, S. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Annona squamosa leaf extract and its in vitro cytotoxic effect on MCF-7 cells. Process.Biochem. 2012, 47, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Pollini, M. Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing Application: Progress and Future Trends. Materials 2019, 12, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keat, C.L.; Aziz, A.; Eid, A.M.; Elmarzugi, N.A. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles and silver nanoparticles. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2015, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Mohammed, W.H.; Marzoog, T.R.; Al-Amiery, A.A.A.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B. Green synthesis, antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles using Eucalyptus chapmaniana leaves extract. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, B.; Dash, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Ghosh, T.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Tripathy, S.; Roy, S. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles destroy multidrug-resistant bacteria via reactive oxygen species mediated membrane damage. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Laha, D.; Baral, R.; Pramanik, P.; Roy, S. Surface-modified cobalt oxide nanoparticles: New opportunities for anti-cancer drug development. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, S.; Somasagara, R.R.; Hegde, M.; Nishana, M.; Tadi, S.K.; Srivastava, M.; Raghavan, S.C. Quercetin, a Natural Flavonoid Interacts with DNA, Arrests Cell Cycle and Causes Tumor Regression by Activating Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]













| Ag NPs Conc. | C. roseus Silver Nanoparticles (Mean Zone of Inhibition in mm) | A. indica Silver Nanoparticles (Mean Zone of Inhibition in mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | KP | SA | PA | EC | KP | SA | PA | |
| 10 μg/μL | 7 | 11 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| 30 μg/μL | 11 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 60 μg/μL | 12 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 9 | 11 | 9 | 8 |
| 90 μg/μL | 15 | 17 | 15 | 16 | 10 | 15 | 12 | 10 |
| 120 μg/μL | 17 | 19 | 19 | 17 | 12 | 16 | 14 | 12 |
| Group | Treatment Groups | % of Wound Contraction in Days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | ||
| Group-I | Control | 4 ± 1 | 24 ± 4 | 40 ± 5 | 48 ± 3 | 65 ± 3 | 74 ± 1 |
| Group-II | Betadine (Povidone–Iodine) | 5 ± 1 | 23 ± 3 | 32 ± 5 | 53 ± 4 | 69 ± 1 | 79 ± 1 |
| Group-III | Vaseline | 4 ± 1 | 24 ± 3 | 36 ± 3 | 55 ± 2 | 68 ± 1 | 76 ± 1 |
| Group-IV | 1% C. roseus Ag NPs | 5 ± 1 | 29 ± 3 | 45 ± 3 | 60 ± 2 | 83 ± 1 | 94 ± 1 |
| Group-V | 1% A. indica Ag NPs | 5 ± 1 | 23 ± 2 | 46 ± 2 | 59 ± 4 | 78 ± 2 | 87 ± 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lakkim, V.; Reddy, M.C.; Pallavali, R.R.; Reddy, K.R.; Reddy, C.V.; Inamuddin; Bilgrami, A.L.; Lomada, D. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Wound Healing Efficacy Using a Murine Model. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120902
Lakkim V, Reddy MC, Pallavali RR, Reddy KR, Reddy CV, Inamuddin, Bilgrami AL, Lomada D. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Wound Healing Efficacy Using a Murine Model. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(12):902. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120902
Chicago/Turabian StyleLakkim, Vajravathi, Madhava C. Reddy, Roja Rani Pallavali, Kakarla Raghava Reddy, Ch Venkata Reddy, Inamuddin, Anwar L. Bilgrami, and Dakshayani Lomada. 2020. "Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Wound Healing Efficacy Using a Murine Model" Antibiotics 9, no. 12: 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120902
APA StyleLakkim, V., Reddy, M. C., Pallavali, R. R., Reddy, K. R., Reddy, C. V., Inamuddin, Bilgrami, A. L., & Lomada, D. (2020). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Wound Healing Efficacy Using a Murine Model. Antibiotics, 9(12), 902. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120902