Study on the Chloride Threshold and Risk Assessment of Rebar Corrosion in Simulated Concrete Pore Solutions under Applied Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Electrodes and Solutions
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. Corrosion Morphology Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Establishment of the Relationship between Applied Potential and Chloride Concentration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of the Sample
3.2. Effect of pH on the Passivation Behavior of Reinforcing Steel
3.3. Effect of the Chloride Threshold on the Passivation Behavior of Reinforcing Steel under Certain pH Circumstance
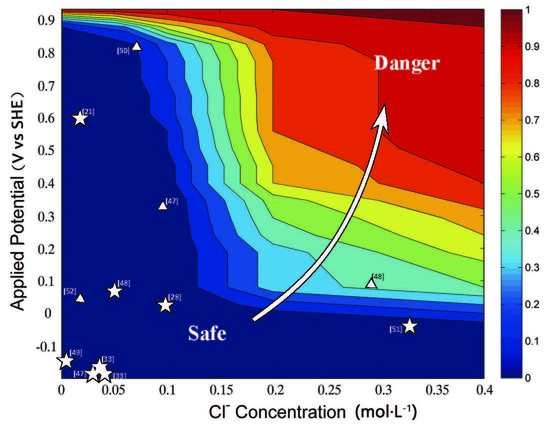
3.4. Probability Estimation of the Chloride Threshold on the Pitting Corrosion of Reinforcing Steel with Different Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pradhan, B.; Bhattacharjee, B. Rebar corrosion in chloride environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almusallam, A.A. Effect of degree of corrosion on the properties of reinforcing steel bars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2001, 15, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.G.; Yunovich, M.; Dunmire, D. Cost of corrosion and corrosion maintenance strategies. Corros. Rev. 2007, 25, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A. Chloride attack of reinforced concrete: An overview. Mater. Struct. 1995, 28, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Haleem, S.M.; Abd El Wanees, S.; Abd El Aal, E.E.; Diab, A. Environmental factors affecting the corrosion behavior of reinforcing steel II. Role of some anions in the initiation and inhibition of pitting corrosion of steel in Ca(OH)2 solutions. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemor, M.F.; Simões, A.M.P.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Chloride-induced corrosion on reinforcing steel: From the fundamentals to the monitoring techniques. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raupach, M.; SchießI, P. Macrocell sensor systems for monitoring of the corrosion risk of the reinforcement in concrete structures. NDT & E Int. 2001, 34, 435–442. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, C.; Yang, Z.M.; Wamg, H.M. Comprehensive properties of 400 mpa grade corrosion-resistant rebar. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2012, 19, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Angst, U.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, C.K.; Vennesland, Ø. Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete—A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 1122–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S. Reinforcement corrosion in concrete structures, its monitoring and service life prediction––A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; d’Andrea, R.; Rebolledo, N. Chloride ion penetration in concrete: The reaction factor in the electrical resistivity model. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 47, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Keddam, M.; Nóvoa, X.R.; Pérez, M.C.; Rangel, C.M.; Takenouti, H. Electrochemical behaviour of steel rebars in concrete: Influence of environmental factors and cement chemistry. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 46, 3905–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckie, H.P.; Uhlig, H.H. Environmental factors affecting the critical potential for pitting in 18–8 stainless steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1966, 113, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouli, B.; Simescu, F.; Debicki, G.; Idrissi, H. Detection and identification of concrete cracking during corrosion of reinforced concrete by acoustic emission coupled to the electrochemical techniques. NDT & E Int. 2005, 38, 682–689. [Google Scholar]
- Gouda, V.K. Corrosion and corrosion inhibition of reinforcing steel: I. immersed in alkaline solutions. Br. Corros. J. 1970, 5, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, A.; Hendrickson, C. Steel versus steel-reinforced concrete bridges: Environmental assessment. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 1998, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glass, G.K.; Buenfeld, N.R. The presentation of the chloride threshold level for corrosion of steel in concrete. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, K.Y.; Song, H.-W. Chloride threshold level for corrosion of steel in concrete. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 4113–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.H.; Jang, S.Y.; Shin, Y.S. Experimental investigation of the threshold chloride concentration for corrosion initiation in reinforced concrete structures. Mag. Concr. Res. 2003, 55, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, M.; Mahallati, E. A study on chloride-induced depassivation of mild steel in simulated concrete pore solution. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Morris, W.; Alvarez, M.G.; Duffó, G.S. Corrosion of reinforcing steel in simulated concrete pore solutions. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 2681–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, A.; Blanco, G.; Velasco, F. Corrosion behaviour of low-nickel austenitic stainless steels reinforcements: A comparative study in simulated pore solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1922–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, P.; Page, C.L.; Vassie, P.R.W. Investigations of reinforcement corrosion. 2. Electrochemical monitoring of steel in chloride-contaminated concrete. Mater. Struct. 1991, 24, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheeduzzafar; Ehtesham Hussain, S.; Al-Saadoun, S.S. Effect of cement composition on chloride binding and corrosion of reinforcing steel in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1991, 21, 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, D.; Alonso, C.; Andrade, C.; Castellote, M. Potentiostatic determination of chloride threshold values for rebar depassivation. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.; Rønnquist, A.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, C.K.; Vennesland, Ø. Probabilistic considerations on the effect of specimen size on the critical chloride content in reinforced concrete. Corrosion Science 2011, 53, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursaee, A.; Hansson, C. Reinforcing steel passivation in mortar and pore solution. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chiang, K.-T.K.; Yang, L. Threshold chloride level and characteristics of reinforcement corrosion initiation in simulated concrete pore solutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamuti, M.M.; Nouri, H.; Jamali, S. Effects of earthing systems on stray current for corrosion and safety behaviour in practical metro systems. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2011, 1, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Meng, G.; Shao, Y.; Wang, F. Effect of pitting nucleation on critical pitting temperature of 316L stainless steel by nitric acid passivation. Corros. Sci. 2015, 91, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 8407:2009. Corrosion of Metals and Alloys. Removal of Corrosion Products from Corrosion Test Specimens; Switzerland, Geneva: ISO, 2009; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, G.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F. Effect of Cl− on the properties of the passive films formed on 316L stainless steel in acidic solution. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, L.; Xu, J.; Xiong, C.; Song, Z. Influence of carbonation on chloride-induced reinforcement corrosion in simulated concrete pore solutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 56, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zi, G.; Lee, W.; Kim, S.; Kong, J. Probabilistic analysis of reinforcement corrosion due to the combined action of carbonation and chloride ingress in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllauer, W.; Beddoe, R.E.; Heinz, D. Effect of carbonation, chloride and external sulphates on the leaching behaviour of major and trace elements from concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Ghahari, S.A.; Esmaeili, M. Effect of combined carbonation and chloride ion ingress by an accelerated test method on microscopic and mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 58, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions; National Association of Corrosion Engineers: Houston, TX, USA, 1974; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini, L.; Carsana, M.; Pedeferri, P. Corrosion behaviour of steel in concrete in the presence of stray current. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Takeyama, T. Stochastic theory of pitting corrosion. Corrosion 1977, 33, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Asl, S.; Mao, F.; Lu, P.; Kursten, B.; Macdonald, D.D. Exploration of the effect of chloride ion concentration and temperature on pitting corrosion of carbon steel in saturated Ca(OH)2 solution. Corros. Sci. 2015, 98, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Macdonald, D.D. Theoretical and experimental studies of the pitting of type 316L stainless steel in borate buffer solution containing nitrate ion. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, G.; Stretton, P.; Beynon, J.G. Initiation and Growth of Pits on High-Purity Iron and its Alloys with Chromium and Copper in Neutral Chloride Solutions. Br. Corros. J. 1972, 7, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surbrook, T.C.; Reese, N.D.; Kehrle, A.M. Stray Voltage: Sources and Solutions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1986, 2, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona Calero, J.; Climent Llorca, M.A.; Garcés Terradillos, P. Influence of different ways of chloride contamination on the efficiency of cathodic protection applied on structural reinforced concrete elements. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 793, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagüés, A.A.; Powers, R.G. Sprayed-zinc sacrificial anodes for reinforced concrete in marine service. Corrosion 1996, 52, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US-ASTM. Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.T.; Wijesinghe, S.L.; Blackwood, D.J. The inhibitive effect of bicarbonate and carbonate ions on carbon steel in simulated concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2014, 88, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, P.; Isgor, O.B.; McRae, G.A.; Gu, G.P. Electrochemical investigation of chloride-induced depassivation of black steel rebar under simulated service conditions. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Haleem, S.M.; Abd El Wanees, S.; Bahgat, A. Environmental factors affecting the corrosion behaviour of reinforcing steel. V. Role of chloride and sulphate ions in the corrosion of reinforcing steel in saturated Ca(OH)2 solutions. Corros. Sci. 2013, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.M.; Miao, Y.F.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, G.D.; Wang, C.L. Corrosion behavior of steel in simulated concrete pore solutions treated with calcium silicate hydrates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Jin, Z.; Liu, H. Corrosion behavior of Cr modified HRB400 steel rebar in simulated concrete pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Haleem, S.M.; Abd El Wanees, S.; Bahgat, A. Environmental factors affecting the corrosion behaviour of reinforcing steel. VI. Benzotriazole and its derivatives as corrosion inhibitors of steel. Corros. Sci. 2014, 87, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, H.; Meng, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, F. Study on the Chloride Threshold and Risk Assessment of Rebar Corrosion in Simulated Concrete Pore Solutions under Applied Potential. Coatings 2020, 10, 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050505
An H, Meng G, Wang Y, Wang J, Liu B, Wang F. Study on the Chloride Threshold and Risk Assessment of Rebar Corrosion in Simulated Concrete Pore Solutions under Applied Potential. Coatings. 2020; 10(5):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050505
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Hongze, Guozhe Meng, Yanqiu Wang, Junyi Wang, Bin Liu, and Fuhui Wang. 2020. "Study on the Chloride Threshold and Risk Assessment of Rebar Corrosion in Simulated Concrete Pore Solutions under Applied Potential" Coatings 10, no. 5: 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050505
APA StyleAn, H., Meng, G., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Liu, B., & Wang, F. (2020). Study on the Chloride Threshold and Risk Assessment of Rebar Corrosion in Simulated Concrete Pore Solutions under Applied Potential. Coatings, 10(5), 505. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10050505