Plasticized Starch/Agar Composite Films: Processing, Morphology, Structure, Mechanical Properties and Surface Hydrophilicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pasting Properties
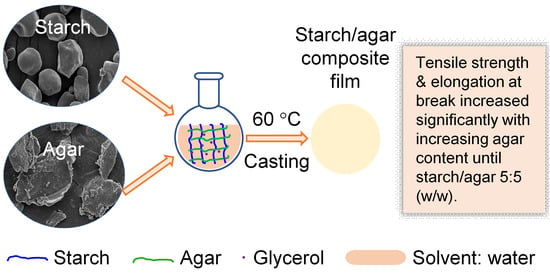
2.3. Preparation of Starch/Agar Composite Films
2.4. Characterization of Starch/Agar Composite Films
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4.3. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
2.4.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.5. Mechanical Properties
2.4.6. Surface Hydrophobicity and Wettability
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rapid Visco Analysis of Starch/Agar Pastes
3.2. Morphology of Starch/Agar Films
3.3. Crystalline Structure of Starch/Agar Films
3.4. Nanoscale Structure of Starch in Starch/Agar Films
3.5. Molecular Interactions of Starch/Agar Films
| Bands (cm−1) | Assignment | References |
|---|---|---|
| Starch and agar | – | – |
| 2850 | Methoxy groups (R–O–CH3) | [22,40] |
| 3700–3100 | O–H stretching | [1,2,6,10,11,12,22,24,38,40,44] |
| 2900 | C–H stretching (CH2 or CH3) | [1,6,10,11,12,22,24,38,40] |
| 1450–1400 | O–H bending | [10,11,12] |
| Starch | – | – |
| 1640 | Tightly bound water in starch | [1,10,38] |
| 1164–928 | C–O stretching | [1,10,38] |
| 1089–1020 | C–O stretching of anhydro-glucose ring | [1,10,11,12,38] |
| 770–1120 | C–O–C stretching of glucose units | [6] |
| Agar | – | – |
| 1644 | Conjugated peptide bond formed by amine group (–NH) and acetone group (–CO) | [1,10,24,40,44,45,52] |
| 1075, 1039, 930 | C–O stretching of 3,6-anhydro-galactose | [1,10,24,40,41,45] |
| 886 | C–H of β-galactose residues | [1,40,44,52] |
| 1371 | Ester sulfate group | [1,24,40,44,45] |
3.6. Mechanical Properties of Starch/Agar Films
3.7. Surface Hydrophobicity of Starch/Agar Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Geng, F.; Chang, P.R.; Yu, J.; Ma, X. Effect of agar on the microstructure and performance of potato starch film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongphan, P.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Characterization of starch, agar and maltodextrin blends for controlled dissolution of edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Xie, F.; Yu, L.; Liu, H.; Meng, L.; Khalid, S.; Chen, L. Preparation and characterization of starch-based composite films reinfoced by polysaccharide-based crystals. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 133, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiak, E.; Lenart, A.; Debeaufort, F. How glycerol and water contents affect the structural and functional properties of starch-based edible films. Polymers 2018, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, F.; Pollet, E.; Halley, P.J.; Avérous, L. Starch-based nano-biocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1590–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kochkina, N.E.; Butikova, O.A. Effect of fibrous TiO2 filler on the structural, mechanical, barrier and optical characteristics of biodegradable maize starch/PVA composite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, E.; Bella, É.; Csiszár, E.; Móczó, J. Improving physical properties and retrogradation of thermoplastic starch by incorporating agar. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan The, D.; Debeaufort, F.; Voilley, A.; Luu, D. Biopolymer interactions affect the functional properties of edible films based on agar, cassava starch and arabinoxylan blends. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.D.; Debeaufort, F.; Luu, D.; Voilley, A. Functional properties of edible agar-based and starch-based films for food quality preservation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaidin, R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Jawaid, M.; Ishak, M.R.; Sahari, J. Characteristics of thermoplastic sugar palm starch/agar blend: Thermal, tensile, and physical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumaidin, R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Jawaid, M.; Ishak, M.R.; Sahari, J. Thermal, mechanical, and physical properties of seaweed/sugar palm fibre reinforced thermoplastic sugar palm starch/agar hybrid composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumaidin, R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Jawaid, M.; Ishak, M.R.; Sahari, J. Effect of seaweed on mechanical, thermal, and biodegradation properties of thermoplastic sugar palm starch/agar composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagar, M.; Sharanagat, V.S.; Kumar, Y.; Singh, L. Development and characterization of elephant foot yam starch-hydrocolloids based edible packaging film: Physical, optical, thermal and barrier properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, S.; Bertoft, E. The molecular structures of starch components and their contribution to the architecture of starch granules: A comprehensive review. Starch Stärke 2010, 62, 389–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Xie, F.; Chen, L. Supramolecular structure of A- and B-type granules of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abral, H.; Basri, A.; Muhammad, F.; Fernando, Y.; Hafizulhaq, F.; Mahardika, M.; Sugiarti, E.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ilyas, R.A.; Stephane, I. A simple method for improving the properties of the sago starch films prepared by using ultrasonication treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardana, A.A.; Widyaningsih, T.D. Development of edible films from tapioca starch and agar, enriched with red cabbage (Brassica oleracea) as a sausage deterioration bio-indicator. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 109, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Song, X.; Li, Y. Antimicrobial, physical and mechanical properties of kudzu starch–chitosan composite films as a function of acid solvent types. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Maran, J.; Sivakumar, V.; Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Kandasamy, S. Modeling and analysis of film composition on mechanical properties of maize starch based edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, C.S.; Ferreira, M.S.; Magalhães, M.T.; Santos, W.J.; Oliveira, J.C.; Silva, J.B.A.; José, N.M. Mechanical, thermal and barrier properties of starch-based films plasticized with glycerol and lignin and reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, F.S.; Zaeim, D. Agar-based edible films for food packaging applications—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campa-Siqueiros, P.I.; Vargas-Arispuro, I.; Quintana-Owen, P.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Azamar-Barrios, J.A.; Madera-Santana, T.J. Physicochemical and transport properties of biodegradable agar films impregnated with natural semiochemical based-on hydroalcoholic garlic extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahaye, M.; Rochas, C. Chemical structure and physico-chemical properties of agar. Hydrobiologia 1991, 221, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.-W.; Jaiswal, L. Bioactive agar-based functional composite film incorporated with copper sulfide nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Qiao, D.; Jia, C.; Niu, M.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, B. An insight into starch slowly digestible features enhanced by microwave treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, F.; Wang, D.K.; Zhao, S.; Niu, M.; Qiao, D.; Xiong, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.; Yu, L. An improved approach for evaluating the semicrystalline lamellae of starch granules by synchrotron SAXS. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 158, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratne, A.; Ranaweera, S.; Corke, H. Thermal, pasting, and gelling properties of wheat and potato starches in the presence of sucrose, glucose, glycerol, and hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, F.; Shamshina, J.L.; Rogers, R.D.; McNally, T.; Halley, P.J.; Truss, R.W.; Chen, L.; Zhao, S. Dissolution of starch with aqueous ionic liquid under ambient conditions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3737–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagar, M.; Sharanagat, V.S.; Kumar, Y.; Singh, L.; Mani, S. Influence of xanthan and agar-agar on thermo-functional, morphological, pasting and rheological properties of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius) starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Calderón, P.; MacNaughtan, B.; Hill, S.; Foster, T.; Enrione, J.; Mitchell, J. Changes in gelatinisation and pasting properties of various starches (wheat, maize and waxy maize) by the addition of bacterial cellulose fibrils. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Dhital, S.; Hasjim, J. Effects of grain milling on starch structures and flour/starch properties. Starch Stärke 2014, 66, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beta, T.; Obilana, A.B.; Corke, H. Genetic diversity in properties of starch from Zimbabwean sorghum landraces. Cereal Chem. 2001, 78, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiao, A.; Jin, Z. Effect of frying on the pasting and rheological properties of normal maize starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, W.; Sun, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wei, X.; Luan, G.; Hu, Y.; Tatsumi, E. Grinding of maize: The effects of fine grinding on compositional, functional and physicochemical properties of maize flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 68, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yu, L.; Chen, L.; Li, X. Morphology and microstructure of maize starches with different amylose/amylopectin content. Starch Stärke 2006, 58, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Xie, F.; Zhang, B.; Zou, W.; Zhao, S.; Niu, M.; Lv, R.; Cheng, Q.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J. A further understanding of the multi-scale supramolecular structure and digestion rate of waxy starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, G.; Dai, L.; Ji, N.; Xiong, L. Green preparation and characterisation of waxy maize starch nanoparticles through enzymolysis and recrystallisation. Food Chem. 2014, 162, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Feng, L.; Shi, M.; Cui, C.; Liu, Y. Effect of plasma-activated water on the structure and in vitro digestibility of waxy and normal maize starches during heat-moisture treatment. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Xu, G.; Yang, B.; Guo, G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of soy protein/agar blend films: Effect of composition and processing methods. J. Food Eng. 2011, 107, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Y.; Dong, H.; Hou, H. Effects of hydrophobic agents on the physicochemical properties of edible agar/maltodextrin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Soest, J.J.G.; Vliegenthart, J.F.G. Crystallinity in starch plastics: Consequences for material properties. Trends Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagnelli, D.; Hebelstrup, K.H.; Leroy, E.; Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Guilois, S.; Kirkensgaard, J.J.K.; Mortensen, K.; Lourdin, D.; Blennow, A. Plant-crafted starches for bioplastics production. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madera-Santana, T.J.; Freile-Pelegrín, Y.; Azamar-Barrios, J.A. Physicochemical and morphological properties of plasticized poly(vinyl alcohol)–agar biodegradable films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Tu, W.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, F. Microstructure and mechanical/hydrophilic features of agar-based films incorporated with konjac glucomannan. Polymers 2019, 11, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, W.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, L.; Xie, F. Changes in nanoscale chain assembly in sweet potato starch lamellae by downregulation of biosynthesis enzymes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6302–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blazek, J.; Gilbert, E.P. Application of small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering techniques to the characterisation of starch structure: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Zhang, B.; Huang, J.; Xie, F.; Wang, D.K.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, J. Hydration-induced crystalline transformation of starch polymer under ambient conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. Structure and enzymatic resistivity of debranched high temperature–pressure treated high-amylose corn starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Cai, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xu, T.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Huang, Q.; Niu, M.; Jia, C.; et al. Hierarchical structure and slowly digestible features of rice starch following microwave cooking with storage. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindman, B.; Medronho, B.; Alves, L.; Norgren, M.; Nordenskiöld, L. Hydrophobic interactions control the self-assembly of DNA and cellulose. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2021, 54, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Agar-based antioxidant composite films incorporated with melanin nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan The, D.; Debeaufort, F.; Voilley, A.; Luu, D. Influence of hydrocolloid nature on the structure and functional properties of emulsified edible films. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żołek-Tryznowska, Z.; Holica, J. Starch films as an environmentally friendly packaging material: Printing performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, F.; Tang, F.; McNally, T. Influence of plasticiser type and nanoclay on the properties of chitosan-based materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 144, 110225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Starch (g) | Agar (g) | Glycerol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S10A0 | 10 | 0 | 15 |
| S8A2 | 8 | 2 | 15 |
| S6A4 | 6 | 5 | 15 |
| S5A5 | 5 | 5 | 15 |
| S4A6 | 4 | 6 | 15 |
| S2A8 | 2 | 8 | 15 |
| S0A10 | 0 | 10 | 15 |
| Sample | Pasting Temperature (°C) | Peak Viscosity (cP) | Final Viscosity (cP) | Breakdown (cP) | Setback (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S10A0 | 89.33 ± 0.90 a | 21.50 ± 1.73 g | 23.75 ± 2.06 g | 1.50 ± 1.29 de | 3.75 ± 1.71 g |
| S8A2 | 88.25 ± 2.28 a | 32.50 ± 1.29 f | 46.25 ± 1.89 f | 1.00 ± 0.82 e | 14.75 ± 1.71 f |
| S6A4 | 84.59 ± 2.42 b | 51.00 ± 0.82 e | 76.75 ± 1.26 e | 2.25 ± 0.50 cde | 28.00 ± 1.63 e |
| S5A5 | 84.33 ± 2.90 b | 63.00 ± 0.82 d | 103.00 ± 0.82 d | 2.75 ± 0.50 cd | 42.75 ± 0.96 d |
| S4A6 | 83.74 ± 2.75 b | 76.25 ± 0.96 c | 138.25 ± 1.26 c | 3.75 ± 0.50 c | 65.75 ± 0.96 c |
| S2A8 | 81.93 ± 1.23 bc | 110.75 ± 1.89 b | 231.75 ± 2.75 b | 9.25 ± 0.96 b | 130.25 ± 0.96 b |
| S0A10 | 78.54 ± 2.94 c | 169.25 ± 2.63 a | 366.75 ± 4.50 a | 21.25 ± 1.71 a | 218.75 ± 3.10 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Qiao, D.; Xie, F. Plasticized Starch/Agar Composite Films: Processing, Morphology, Structure, Mechanical Properties and Surface Hydrophilicity. Coatings 2021, 11, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030311
Guo Y, Zhang B, Zhao S, Qiao D, Xie F. Plasticized Starch/Agar Composite Films: Processing, Morphology, Structure, Mechanical Properties and Surface Hydrophilicity. Coatings. 2021; 11(3):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030311
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yabin, Binjia Zhang, Siming Zhao, Dongling Qiao, and Fengwei Xie. 2021. "Plasticized Starch/Agar Composite Films: Processing, Morphology, Structure, Mechanical Properties and Surface Hydrophilicity" Coatings 11, no. 3: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030311
APA StyleGuo, Y., Zhang, B., Zhao, S., Qiao, D., & Xie, F. (2021). Plasticized Starch/Agar Composite Films: Processing, Morphology, Structure, Mechanical Properties and Surface Hydrophilicity. Coatings, 11(3), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11030311