Effect of Electrode Coating with Graphene Suspension on Power Generation of Microbial Fuel Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MFC System and Preparation of Electrodes
2.2. Microorganisms and Anode Solution
2.3. Measurements and Analyses
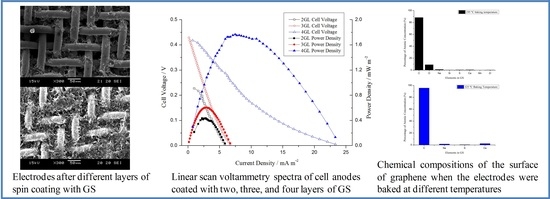
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. GS Coated Electrodes
3.2. Effect of Electrode Baking Temperature on MFC Performance
3.3. Biofilm Morphology
3.4. Effect of the Number of GS Coated Layers on MFC Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lovley, D.R. Bug juice: Harvesting electricity with microorganisms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.C. Electrical effects accompanying the decomposition of organic compounds. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1911, 84, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Wu, C.H.; Huang, W.T.; Tsai, S.L. Evaluation of different cell-immobilization strategies for simultaneous distillery wastewater treatment and electricity generation in microbial fuel cells. Fuel 2015, 144, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, U.; Jin, W.; Pervez, A.; Bhatti, Z.A.; Tariq, M.; Shaheen, S.; Iqbal, A.; Mahmood, Q. Anaerobic microbial fuel cell treating combined industrial wastewater: Correlation of electricity generation with pollutants. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. Nutrient and organics removal from swine slurry with simultaneous electricity generation in an alum sludge-based constructed wetland incorporating microbial fuel cell technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Logan, B.E. Continuous electricity generation from domestic wastewater and organic substrates in a flat plate microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5809–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ramnarayanan, R.; Logan, B.E. Production of electricity during wastewater treatment using a single chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2281–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Mo, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ye, J.; Huang, X.; Yu, C. A graphene modified anode to improve the performance of microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 5402–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.H.; Tsai, H.Y.; Huang, Y.C. Characteristics of carbon nanotubes/graphene coatings on stainless steel meshes used as electrodes for air-cathode microbial fuel cells. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 9875301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.Y.; Hsu, W.H.; Huang, Y.C. Characteristics of carbon nanotube/graphene on carbon cloth as electrode for air-cathode microbial fuel cell. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 686891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Yang, Q.; Lee, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, N. The use of double-sided cloth without diffusion layers as air-cathode in microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 8409–8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, Md.T.; Mukherjee, C.K.; Ghangrekar, M.M. Enhancing performance of microbial fuel cell by using graphene supported V2O5-nanorod catalytic cathode. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 228, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, Md.T.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Mukherjee, C.K. V2O5 microflower decorated cathode for enhancing power generation in air-cathode microbial fuel cell treating fish market wastewater. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 3638–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Logan, B.E. Electricity generation using an air-cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell in the presence and absence of a proton exchange membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4040–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Jia, B.; Liu, H. Effects of the Pt loading side and cathode-biofilm on the performance of a membrane-less and single-chamber microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cercado-Quezada, B.; Delia, M.L.; Bergel, A. Treatment of dairy wastes with a microbial anode formed from garden compost. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menicucci, J.; Beyenal, H.; Marsili, E.; Veluchamy, R.A.; Demir, G.; Lewandowski, Z. Procedure for determining maximum sustainable power generated by microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E.; Murano, C.; Scott, K.; Gray, N.D.; Head, I.M. Electricity generation from cysteine in a microbial fuel cell. Water Res. 2005, 39, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Logan, B.E. Increased power generation in a continuous flow MFC with advective flow through the porous anode and reduced electrode spacing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Liang, P.; Huang, X. Recent progress in electrodes for microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9335–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, W.; Ge, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, H. Methods for understanding microbial community structures and functions in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvankar, N.S.; Lovley, D.R. Microbial nanowires: A new paradigm for biological electron transfer and bioelectronics. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, U. Anodic electron transfer mechanisms in microbial fuel cells and their energy efficiency. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 2619–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Logan, B.E. Ammonia treatment of carbon cloth anodes to enhance power generation of microbial fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Y. A comparative study of graphene-coated stainless steel fiber felt and carbon cloth as anodes in MFCs. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, S.; Harding, G.L.; Payling, R. Auger lineshape analysis of carbon bonding in sputtered metal-carbon thin films. Surf. Sci. 1983, 124, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.J.; Wang, X.; Yao, H.M.; Gorb, S.; Arzt, E. Mechanics of hierarchical adhesion structures of geckos. Mech. Mater. 2005, 37, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, H.-Y.; Hsu, W.-H.; Liao, Y.-J. Effect of Electrode Coating with Graphene Suspension on Power Generation of Microbial Fuel Cells. Coatings 2018, 8, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8070243
Tsai H-Y, Hsu W-H, Liao Y-J. Effect of Electrode Coating with Graphene Suspension on Power Generation of Microbial Fuel Cells. Coatings. 2018; 8(7):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8070243
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Hung-Yin, Wei-Hsuan Hsu, and Yi-Jhu Liao. 2018. "Effect of Electrode Coating with Graphene Suspension on Power Generation of Microbial Fuel Cells" Coatings 8, no. 7: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8070243
APA StyleTsai, H. -Y., Hsu, W. -H., & Liao, Y. -J. (2018). Effect of Electrode Coating with Graphene Suspension on Power Generation of Microbial Fuel Cells. Coatings, 8(7), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8070243