Effect of Heating Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of Cr–Mo Duplex-Alloyed Coating Prepared by Double Glow Plasma Surface Alloying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Composition of the Coating
3.2. Effect of Annealing on Coating Microstructure
3.3. Effect of Q&T on the Coating Microstructure
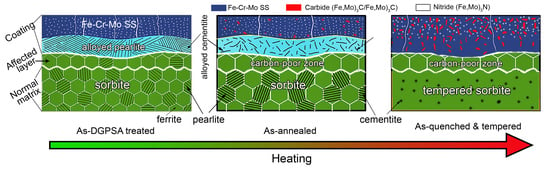
3.4. Microstructure Evolution during Heating
3.5. Hardness
3.6. Polarization Test
4. Conclusions
- A structured gradient coating (about 180 μm) composed of an Fe–Cr–Mo SS layer and an alloyed pearlite layer is obtained on the steel surface after DGPSA treatment. As carbon atoms diffuse to form alloy cementite in the coating, the carbon content in the subsurface is significantly reduced, forming an affected layer (about 52 μm).
- After annealing or Q&T, more carbides precipitate in both the Fe–Cr–Mo SS layer and the alloyed pearlite layer. All the C atoms in the subsurface are dragged into the coating to form the carbides in the Fe–Cr–Mo SS and the alloyed pearlite layers of the coating, resulting in the conversion of the affected layer into a carbon-poor zone.
- Annealing and Q&T hardly change the thickness of the coating but the hardness of both the coating and steel substrate varies greatly by tailoring the microstructure. Annealing results in grain and second phase coarsening, while Q&T refines the second phase size, resulting in annealing softening and Q&T hardening. Both the coatings and substrate of the Q&T treated samples have higher hardness than that of the as-DGPSA treated and annealed samples.
- After annealing or Q&T, the corrosion potential does not vary dramatically, but the corrosion current decreases. Compared with the as-DGPSA treated state, the corrosion rates of the as-annealed state and the Q&T treated state are reduced by 22 times and 43 times, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behrens, B.-A.; Chugreev, A.; Matthias, T.; Poll, G.; Pape, F.; Coors, T.; Hassel, T.; Maier, H.J.; Mildebrath, M. Manufacturing and evaluation of multi-material axial-bearing washers by tailored forming. Metals 2019, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Guo, N.; Li, R.; Yu, H. Effect of B content on microstructure and wear resistance of Fe-3Ti-4C hardfacing alloys produced by plasma-transferred arc welding. Coatings 2019, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yao, Q. Fabrication of microalloy nitrided layer on low carbon steel by nitriding combined with surface nano-alloying pretreatment. Coatings 2016, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Jian, W.; Fu, L.; Zheng, C.; Shen, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhi, S. Ultrahigh hardness of carbon steel surface realized by novel solid carburizing with rapid diffusion of carbon nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertek, A.; Kulka, M. Two-step treatment carburizing followed by boriding on medium-carbon steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 173, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.C.; Mohanty, B.C.; Nayak, B.B. Arc plasma nitriding of low carbon steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2001, 145, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Majumdar, J.D.; Alphonsa, J.; Mukherjee, S.; Manna, I. Corrosion resistance improvement of high carbon low alloy steel by plasma nitriding. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3117–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, K.; Fan, L.; Dong, L.; Deng, J.; Li, D.; Xue, W. Investigation of anodic plasma electrolytic carbonitriding on medium carbon steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 313, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulka, M.; Pertek, A. Characterization of complex (B + C) diffusion layers formed on chromium and nickel-based low-carbon steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 218, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zhang, P.; Wei, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Isothermal oxidation behavior of Zr-Y coating on γ-TiAl by Double glow plasma surface metal alloying Technique. Coatings 2018, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; He, Z. Double glow plasma surface alloying and plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 4822–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Lin, N.; Zou, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L.; Qin, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Tang, B.; et al. Effect of laser surface texturing (LST) on tribological behavior of double glow plasma surface zirconizing coating on Ti6Al4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 368, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.; Yao, Z.; Zhu, X. Sliding wear of low carbon steel modified by double-glow plasma surface alloying with nickel and chromium at various temperatures. Wear 2010, 268, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.Y.; Lin, H.L.; Zhang, B.; Lv, J.W.; Jing, Q.; Liu, R.P. Hydrogen-free nitriding of ZrTiAlV by double glow plasma discharge improving the wear resistance. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ma, C.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Guo, N.; Yu, H. Microstructure Evolution During Continuous Cooling in AISI 5140 Steel Processed by Induction Heating Chromizing. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 5530–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, C.; Dong, Q.; Guo, N.; Yao, Z. Effect of pack-chromizing temperature on microstructure and performance of AISI 5140 steel with Cr-coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 344, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ma, C.; Xu, H.; Guo, N.; Hou, T. Development of a composite technique for preconditioning of 41Cr4 Steel Used as gear material: examination of its microstructural characteristics and properties. Sci. Technol. Nucl. Ins. 2016, 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Jiang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Jin, Y.; Ma, C.; Dong, Q.; Guo, N. Effect of annealing treatment on microstructure and properties of cr-coatings deposited on aisi 5140 steel by brush-plating. Coatings 2018, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cheng, J.; Liang, X. Effects of Cr and Mo additions on formation and mechanical properties of Arc-sprayed FeBSiNb-based glassy coatings. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 499, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Miao, Q.; Liang, W.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, P. Characteristics of Mo–Cr duplex-alloyed layer on Ti 6 Al 4 V by double glow plasma surface metallurgy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 228, S206–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, C.; Yulin, Z.; Weiguang, L.; Wenran, F.; Yingge, Y. Corrosion behavior of W-Mo Co-penetrated layer produced by glow discharge plasma technique in acid solution. Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 2018, 47, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, C.M.; Dalbauer, V.; Kirnbauer, A.; Löffler, S.; Kolozsvári, S.; Ramm, J.; Mayrhofer, P.H. Selective phase formation in substoichiometric Al-Cr-based oxides. Scripta Mater. 2017, 139, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbauer, V.; Kolozsvári, S.; Ramm, J.; Koller, C.M.; Mayrhofer, P.H. In-situ XRD studies of arc evaporated Al-Cr-O coatings during oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczerzak, K.; Bala, P.; Stepien, M.; Cios, G.; Koziel, T. Formation of eutectic carbides in Fe–Cr–Mo–C alloy during non-equilibrium crystallization. Mater. Des. 2016, 94, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shi, Y.N.; Sauvage, X.; Sha, G.; Lu, K. Grain boundary stability governs hardening and softening in extremely fine nanograined metals. Science 2017, 355, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liang, A.; Zhang, J. Tribological and electrochemical behavior of thick Cr–C alloy coatings electrodeposited in trivalent chromium bath as an alternative to conventional Cr coatings. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinschitz, K.J.; Daniel, R.; Mitterer, C.; Keckes, J. Stress evolution in CrN/Cr coating systems during thermal straining. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 1972–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.-L.; Luo, C.-b.; You, F.-y. Crack restraining methods and their effects on the microstructures and properties of laser cladded WC/Fe coatings. Materials 2018, 11, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtansky, D.V.G. Phase Transformation in Fe-Mo-C and Fe-W-C Steels—II. Eutectoid Reaction of M23C6 Carbide Decomposition during Austenitization. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 2879–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Liu, Q.; Xin, Y.; Luan, B.; Zhou, Z. The application of back-scattered electron imaging for characterization of pearlitic steels. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Lun, Q.Y.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Song, L.G. Corrosion mitigation behavior of an alternately wetted steel electrode in oil/water media. Corros. Sci. 2019, 152, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, S.; Iwamae, S.; Akebono, H.; Komotori, J.; Misaka, Y. Improvement of the electrochemical characteristics of medium carbon steel using atmospheric-controlled induction-heating fine particle peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 354, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, M.; Oliveira, R.M.; Rossi, J.O.; Mello, C.B.; Rangel, R.C.C.; Vieira, M.S. Improvements of plasma immersion ion implantation (PIII) and deposition (PIII&D) processing for materials surface modification. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 229, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mello, C.B.; Ueda, M.; Oliveira, R.M.; Garcia, J.A. Corrosion effects of plasma immersion ion implantation-enhanced Cr deposition on SAE 1070 carbon steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, S151–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khara, S.; Choudhary, S.; Sangal, S.; Mondal, K. Corrosion resistant Cr-coating on mild steel by powder roll bonding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 296, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Processing Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Spacing between source electrode and cathode (mm) | 10 |
| Voltage of the source electrode (V) | 900 |
| Voltage of the cathode (V) | 800 |
| Working pressure (nitrogen/Pa) | 204 |
| Duty ratio of the source electrode | 73.9 |
| Duty ratio of the cathode | 78.3 |
| Samples | Corrosion Potential Eccor (v) | Corrosion Current Iccor (A) | Corrosion Rate (mm/y) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 5140 | −0.7 | 2.29 × 10−6 | 0.026 |
| AISI 304 | −0.65 | 2.25 × 10−6 | 0.025 |
| CrMo-6 | −0.37 | 2.28 × 10−6 | 0.026 |
| CrMo-6-A | −0.38 | 1.00 × 10−7 | 0.0012 |
| CrMo-6-QT | −0.33 | 4.79 × 10−8 | 0.0006 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Guo, N. Effect of Heating Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of Cr–Mo Duplex-Alloyed Coating Prepared by Double Glow Plasma Surface Alloying. Coatings 2019, 9, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050336
Hu J, Wang J, Jiang J, Yang X, Xu H, Li H, Guo N. Effect of Heating Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of Cr–Mo Duplex-Alloyed Coating Prepared by Double Glow Plasma Surface Alloying. Coatings. 2019; 9(5):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050336
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jianjun, Jing Wang, Jie Jiang, Xian Yang, Hongbin Xu, Hui Li, and Ning Guo. 2019. "Effect of Heating Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of Cr–Mo Duplex-Alloyed Coating Prepared by Double Glow Plasma Surface Alloying" Coatings 9, no. 5: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050336
APA StyleHu, J., Wang, J., Jiang, J., Yang, X., Xu, H., Li, H., & Guo, N. (2019). Effect of Heating Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of Cr–Mo Duplex-Alloyed Coating Prepared by Double Glow Plasma Surface Alloying. Coatings, 9(5), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9050336