Low-Cost Electrodeposition of Size-Tunable Single-Crystal ZnO Nanorods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Cleaning Procedure
2.2. Preparation of ZnO Seed Layers
2.2.1. EBPVD
2.2.2. ZnO Nanoparticles (NPs)
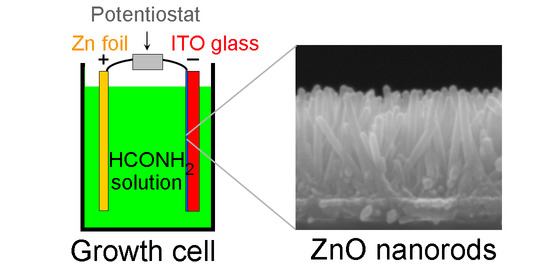
2.3. Electrochemical Growth of ZnO Nanorods (NRs)
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doğan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willander, M.; Nur, O.; Zhao, Q.X.; Yang, L.L.; Lorenz, M.; Cao, B.Q.; Pérez, J.Z.; Czekalla, C.; Zimmermann, G.; Grundmann, M.; et al. Zinc oxide nanorod based photonic devices: Recent progress in growth, light emitting diodes and lasers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 332001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhati, V.S.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Kumar, M. Enhanced sensing performance of ZnO nanostructures-based gas sensors: A review. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerthagiri, J.; Salla, S.; Senthil, R.; Nithyadharseni, P.; Madankumar, A.; Arunachalam, P.; Maiyalagan, T.; Kim, H.-S. A review on ZnO nanostructured materials: Energy, environmental and biological applications. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 392001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrà, A.; Gómez, E.; Philippe, L. Bioinspired ZnO-Based Solar Photocatalysts for the Effcient Decontamination of Persistent Organic Pollutants and Hexavalent Chromium in Wastewater. Catalysts 2019, 9, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qadir, A.M.; Erdoğan, I.Y. Structural properties and enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of ZnO films decorated with Cu2O nanocubes. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 18694–18702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borysiewicz, M.A. ZnO as a Functional Material: A Review. Crystals 2019, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, G.; Al-Dossary, O.; Umar, A. ZnO nanostructured thin films: Depositions, properties and applications—A review. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sasikumar, C. Electrodeposition of Nanostructured ZnO Thin Film: A Review. Am. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc Oxide—From Synthesis to Application: A Review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, G.; Singh, P.S. Synthesis of zinc oxide by sol-gel method and to study its structural properties. AIP 2020, 2220, 020184. [Google Scholar]
- Aldalbahi, A.; Alterary, S.; Almoghim, R.A.A.; Awad, M.A.; Aldosari, N.S.; Alghannam, S.F.; Alabdan, A.N.; Alharbi, S.; Alateeq, B.A.M.; Mohsen, A.; et al. Greener Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Characterization and Multifaceted Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skompska, M.; Zarebska, K. Electrodeposition of ZnO Nanorod Arrays on Transparent Conducting Substrates—A Review. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 127, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, Y.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D. Morphological Control of ZnO Nanostructures by Electrodeposition. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13519–13522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alev, O.; Sarıca, N.; Ozdemir, O.; Arslan, L.Ç.; Büyükkose, S.; Oztürk, Z.Z. Cu-doped ZnO nanorods based QCM sensor for hazardous gases. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, O.; Pauporte, T.; Chow, L.; Viana, B.; Pelle, F.; Ono, L.K.; Cuenya, B.R.; Heinrich, H. Effects of annealing on properties of ZnO thin films prepared by electrochemical deposition in chloride medium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1895–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukos, N.; Chandrinou, C.; Giannakopoulos, K.; Pistolis, G.; Travlos, A. Growth of ZnO nanorods by a simple chemical method. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 88, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, M.; Weller, H.; Henglein, A. Photochemistry and radiation chemistry of colloidal semiconductors. 23. Electron storage on zinc oxide particles and size quantization. J. Phys. Chem. 1988, 92, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, Z.L.S.; Wong, A.S.W.; Thavasi, V.; Jose, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Ho, G.W. Controlled synthesis and application of ZnO nanoparticles, nanorods and nanospheres in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology 2008, 20, 045604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Shao, X.; Han, M. Near-Room-Temperature Production of Diameter-Tunable ZnO Nanorod Arrays through Natural Oxidation of Zinc Metal. Chem. A Eur. J. 2005, 11, 3149–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakellis, I.; Giamini, S.; Moschos, I.; Chandrinou, C.; Travlos, A.; Kim, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-G.; Boukos, N. A novel method for the growth of Cu2O/ZnO heterojunctions. Energy Proc. 2014, 60, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupan, O.; Guérina, V.M.; Tiginyanub, I.M.; Ursakib, V.V.; Chowc, L.; Heinrichc, H.; Pauporté, T. Well-aligned arrays of vertically oriented ZnO nanowires electrodeposited on ITO-coated glass and their integration in dye sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2010, 211, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauporte, T.; Bataille, G.; Joulaud, L.; Vermersch, F.J. Well-aligned ZnO nanowire arrays prepared by seed-layer-free electrodeposition and their Cassie–Wenzel transition after hydrophobization. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, M.-Y. Aggregation-driven growth of well-oriented ZnO nanorod arrays. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2994–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Shi, E.W.; Zhong, W.Z.; Yin, Z.W. Growth mechanism and growth habit of oxide crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 1999, 203, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsanulhaq, Q.; Umar, A.; Hahn, Y.B. Growth of aligned ZnO nanorods and nanopencils on ZnO/Si in aqueous solution: Growth mechanism and structural and optical properties. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbam, S.O.; Nwonu, S.E.; Orelaja, O.A.; Nwigwe, U.S.; Gou, X.-F. Thin-film coating; historical evolution, conventional deposition technologies, stress-state micro/nano-level measurement/models and prospects projection: A critical review. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Srivastava, A.K. Band gap narrowing in zinc oxide-based semiconductor thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 134904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.K.; Alves, H.; Hofmann, D.M.; Kriegseis, W.; Forster, D.; Bertram, F.; Christen, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Straßburg, M.; Dworzak, M.; et al. Bound exciton and donor–acceptor pair recombinations in ZnO. Phys. Status Solidi 2004, 241, 231–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodnyi, P.A.; Khodyuk, I.V. Optical and luminescence properties of zinc oxide (Review). Opt. Spectrosc. 2011, 111, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chris, A.J.; Van De Walle, G. Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 72, 126501. [Google Scholar]
- Sakellis, I. Determining the activation volumes in ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 13504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, A.F.; Ceder, G.; Morgan, D.; Van De Walle, C.G. First-principles study of native point defects in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 61, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, B.; Qiu, Z.R.; Wong, K.S. Intensity dependence and transient dynamics of donor–acceptor pair recombination in ZnO thin films grown on (001) silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gua, S.L.; Ye, J.D.; Zhu, S.M.; Liu, S.M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, R.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, Y.D. Blue-yellow ZnO homostructural light-emitting diode realized by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition technique. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 092101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, F.H.; Alves, H.R.; Hofstaetter, A.; Hofmann, D.M.; Meyer, B.K. The Oxygen Vacancy as the Origin of a Green Emission in Undoped ZnO. Phys. Status Solidi 2001, 226, R4–R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, F.H.; Alves, H.; Pfisterer, D.; Romanov, N.G.; Hofmann, D.M.; Meyer, B.K. Identification of oxygen and zinc vacancy optical signals in ZnO. Physica B 2003, 201, 340. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Kitai, A.; Mascher, P. Point defects and luminescence centres in zinc oxide and zinc oxide doped with manganese. J. Lumin. 1992, 54, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.C.; Look, D.C.; Jogai, B.; Hoelscher, J.E.; Sherriff, R.E.; Harris, M.T.; Callahan, M.J. Time-resolved photoluminescence lifetime measurements of the Γ5 and Γ6 free excitons in ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingle, R. Luminescent Transitions Associated With Divalent Copper Impurities and the Green Emission from Semiconducting Zinc Oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1969, 23, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studenikin, S.A.; Golego, N.; Cocivera, M. Fabrication of green and orange photoluminescent, undoped ZnO films using spray pyrolysis. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivov, Y.I.; Chukichev, M.V.; Nikitenko, V.A. Green luminescence band of zinc oxide films copper-doped by thermal diffusion. Semiconductors 2004, 38, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrinou, C.; Boukos, N.; Stogios, C.; Travlos, A. PL study of oxygen defect formation in ZnO nanorods. Microelectron. J. 2009, 40, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlos, A.; Boukos, N.; Chandrinou, C.; Kwack, H.-S.; Dang, L.S. Zinc and oxygen vacancies in ZnO nanorods. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 104307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Procedure A Growth Method: Electrodeposition Seeding Layer: ZnO Film (EBPVD) O2 Supply: No | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formamide C (% vol) | Lrod (nm) | Drod (nm) | Lrod/Drod | Charge (C) | Density ρ (rods/μm2) | (eV) | PL Peak (nm) |
| 0.05% | 480 | 70 | 6.9 | 1.206 | 31 | 3.31 | 396 |
| 0.1% | 640 | 75 | 8.5 | 1.378 | 38 | 3.34 | 380 |
| 0.5% | 750 | 85 | 8.8 | 2.374 | 23 | 3.31 | 376 |
| 1% | 900 | 95 | 9.5 | 5.452 | 21 | 3.33 | 381 |
| Procedure B Growth Method: Electrodeposition Seeding Layer: Chem. Synthesized ZnO NPs (Spin Coating) O2 Supply: No | |||||||
| Formamide C (% vol) | Lrod (nm) | Drod (nm) | Lrod/Drod | Charge (C) | Density ρ (rods/μm2) | (eV) | PL Peak (nm) |
| 0.05% | 300 | 40 | 7.5 | 1.246 | 60 | 3.31 | 380 |
| 0.1% | 490 | 50 | 9.8 | 1.527 | 64 | 3.31 | 380 |
| 0.5% | 690 | 65 | 10.6 | 3.226 | 45 | 3.33 | 380 |
| 1% | 810 | 75 | 10.8 | 4.099 | 43 | 3.35 | 376 |
| Procedure C Growth Method: Electrodeposition Seeding Layer: Chem. Synthesized ZnO NPs (Spin Coating) O2 Supply: Yes | |||||||
| Formamide C (% vol) | Lrod (nm) | Drod (nm) | Lrod/Dred | Charge (C) | Density ρ (rods/μm2) | (eV) | PL Peak (nm) |
| 0.05% | 590 | 80 | 7.4 | 2.217 | 30 | 3.27 | 381 |
| 0.1% | 630 | 75 | 8.4 | 2.883 | 32 | 3.26 | 380 |
| 0.5% | 1040 | 100 | 10.4 | 6.223 | 30 | 3.30 | 381 |
| 1% | 1500 | 125 | 12.0 | 9.787 | 25 | 3.31 | 380 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakellis, E.; Markopoulos, A.; Tzouvelekis, C.; Chatzigeorgiou, M.; Travlos, A.; Boukos, N. Low-Cost Electrodeposition of Size-Tunable Single-Crystal ZnO Nanorods. Fibers 2021, 9, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9060038
Sakellis E, Markopoulos A, Tzouvelekis C, Chatzigeorgiou M, Travlos A, Boukos N. Low-Cost Electrodeposition of Size-Tunable Single-Crystal ZnO Nanorods. Fibers. 2021; 9(6):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9060038
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakellis, Elias, Antonis Markopoulos, Christos Tzouvelekis, Manolis Chatzigeorgiou, Anastasios Travlos, and Nikos Boukos. 2021. "Low-Cost Electrodeposition of Size-Tunable Single-Crystal ZnO Nanorods" Fibers 9, no. 6: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9060038
APA StyleSakellis, E., Markopoulos, A., Tzouvelekis, C., Chatzigeorgiou, M., Travlos, A., & Boukos, N. (2021). Low-Cost Electrodeposition of Size-Tunable Single-Crystal ZnO Nanorods. Fibers, 9(6), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9060038