PI3K as Mediator of Apoptosis and Contractile Dysfunction in TGFβ1-Stimulated Cardiomyocytes
Abstract
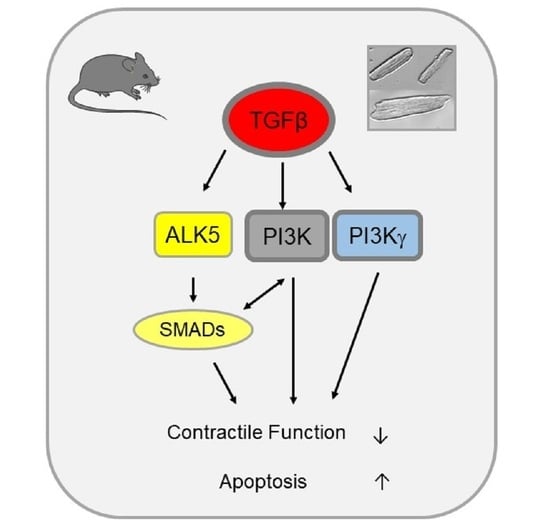
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Materials
2.3. Isolation of Murine Cardiomyocytes
2.4. Isolation of Rat Cardiomyocytes
2.5. Determination of Cell Function
2.6. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Real-Time RT-PCR
2.9. Caspase 3/7 Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TGFβ1–Induced Apoptosis Depends on PI3K
3.2. Involvement of PI3K in TGFβ1-Dependent SMAD Binding Activity and TGFβ Target Genes
3.3. PI3K Affected TGFβ1-Dependent Depression of Contractile Function
3.4. PI3Kγ Is Involved in TGFβ1-Dependent Depression of Contractile Function and in TGFβ-Dependent Apoptosis Induction
3.5. PI3Kγ Action Is Independent of SMAD Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenkranz, S. TGF—Beta1 and angiotensin networking in cardiac remodeling. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobaczewski, M.; Chen, W.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac remodeling. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heger, J.; Warga, B.; Meyering, B.; Abdallah, Y.; Schluter, K.D.; Piper, H.M.; Euler, G. TGFbeta Receptor Activation Enhances Cardiac Apoptosis Via SMAD Activation and Concomitant NO Release. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeland, U.; Schäffer, A.; Selejan, S.; Hohl, M.; Reil, J.C.; Müller, P.; Rosenkranz, S.; Böhm, M. Effects of AT1- and beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists on TGF-beta1-induced fibrosis in transgenic mice. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 39, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Zheng, H.; Xie, B.; Bidasee, K.R.; Rozanski, G.J. Pro-Oxidant Effect of Transforming Growth Factor—Beta1 Mediates Contractile Dysfunction in Rat Ventricular Myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 77, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mufti, S.; Wenzel, S.; Euler, G.; Piper, H.M.; Schluter, K.D. Angiotensin II-Dependent Loss of Cardiac Function: Mechanisms and Pharmacological Targets Attenuating This Effect. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 217, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntgeburth, M.; Tiemann, K.; Shahverdyan, R.; Schluter, K.D.; Schreckenberg, R.; Gross, M.L.; Modersheim, S.; Caglayan, E.; Muller-Ehmsen, J.; Ghanem, A.; et al. Transforming Growth Factor Beta(1) Oppositely Regulates the Hypertrophic and Contractile Response to Beta-Adrenergic Stimulation in the Heart. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Dijke, P.; Franzén, P.; Yamashita, H.; Ichijo, H.; Heldin, C.H.; Miyazono, K. Serine/threonine kinase receptors. Prog. Growth Factor Res. 1994, 5, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.J.; Burgess, A.W. Regulation of transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. Res. Commun. 2001, 4, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Massagué, J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 2003, 13, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamato, D.; Burch, M.L.; Piva, T.J.; Rezaei, H.B.; Rostam, M.A.; Xu, S.; Zheng, W.; Little, P.J.; Osman, N. Transforming growth factor-β signalling: Role and consequences of Smad linker region phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hébert, M.C.; Zhang, Y.E. TGF-beta receptor-activated p38 MAP kinase mediates Smad-independent TGF—Beta responses. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3749–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulder, K.M. Role of Ras and Mapks in TGFbeta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000, 11, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaba, M.; Zimmerman, C.M.; Mathews, L.S. Modulation of Smad2-mediated signaling by extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41361–41368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griswold-Prenner, I.; Kamibayashi, C.; Maruoka, E.M.; Mumby, M.C.; Derynck, R. Physical and functional interactions between type I transforming growth factor b receptors and Ba, a WD-40 repeat subunit of phosphatase 2A. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6595–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engel, M.E.; McDonnell, M.A.; Law, B.K.; Moses, H.L. Interdependent SMAD and JNK signaling in transforming growth factor-beta-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37413–37420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-Dependent and Smad-Independent Pathways in TGF-Beta Family Signalling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad Pathways in TGF-Beta Signaling. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, J.Y.; Shin, I.; Arteaga, C.L. Type I Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor Binds to and Activates Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10870–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhalla, N.S.; Müller, A.L. Protein Kinases as Drug Development Targets for Heart Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2111–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jean, S.; Kiger, A.A. Classes of phosphoinositide 3-kinases at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Vogt, P.K.; Rommel, C. PI3K: From the bench to the clinic and back. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 347, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krygowska, A.A.; Castellano, E. PI3K: A Crucial Piece in the RAS Signaling Puzzle. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a031450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghigo, A.; Morello, F.; Perino, A.; Damilano, F.; Hirsch, E. Specific PI3K Isoform Modulation in Heart Failure: Lessons from Transgenic Mice. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2011, 8, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcucci, S.; Ramos-Delgado, F.; Cayron, C.; Therville, N.; Gratacap, M.P.; Basset, C.; Thibault, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J. Organismal roles for the PI3Kα and β isoforms: Their specificity, redundancy or cooperation is context-dependent. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 1199–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siragusa, M.; Katare, R.; Meloni, M.; Damilano, F.; Hirsch, E.; Emanueli, C.; Madeddu, P. Involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma in angiogenesis and healing of experimental myocardial infarction in mice. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crackower, M.A.; Oudit, G.Y.; Kozieradzki, I.; Sarao, R.; Sun, H.; Sasaki, T.; Hirsch, E.; Suzuki, A.; Shioi, T.; Irie-Sasaki, J.; et al. Regulation of Myocardial Contractility and Cell Size by Distinct PI3K-PTEN Signaling Pathways. Cell 2002, 110, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shioi, T.; Kang, P.M.; Douglas, P.S.; Hampe, J.; Yballe, C.M.; Lawitts, J.; Cantley, L.C.; Izumo, S. The Conserved Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Pathway Determines Heart Size in Mice. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMullen, J.R.; Shioi, T.; Zhang, L.; Tarnavski, O.; Sherwood, M.C.; Kang, P.M.; Izumo, S. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase(P110alpha) Plays a Critical Role for the Induction of Physiological, but Not Pathological, Cardiac Hypertrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12355–12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, R.C.; Weeks, K.L.; Gao, X.M.; Williams, R.B.; Bernardo, B.C.; Kiriazis, H.; Matthews, V.B.; Woodcock, E.A.; Bouwman, R.D.; Mollica, J.P.; et al. PI3K(P110 Alpha) Protects Against Myocardial Infarction-Induced Heart Failure: Identification of PI3K-Regulated MiRNA and MRN. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McMullen, J.R.; Amirahmadi, F.; Woodcock, E.A.; Schinke-Braun, M.; Bouwman, R.D.; Hewitt, K.A.; Mollica, J.P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shioi, T.; et al. Protective Effects of Exercise and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase(P110alpha) Signaling in Dilated and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, D.; Thiyam, G.; Bodiga, S.; Kassiri, Z.; Oudit, G.Y. Uncoupling between enhanced excitation-contraction coupling and the response to heart disease: Lessons from the PI3Kγ knockout murine model. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2011, 50, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghigo, A.; Perino, A.; Mehel, H.; Zahradnikova, A., Jr.; Morello, F.; Leroy, J.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Damilano, F.; Cimino, J.; De Luca, E.; et al. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Gamma Protects Against Catecholamine-Induced Ventricular Arrhythmia Through Protein Kinase A-Mediated Regulation of Distinct Phosphodiesterases. Circulation 2012, 126, 2073–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patrucco, E.; Notte, A.; Barberis, L.; Selvetella, G.; Maffei, A.; Brancaccio, M.; Marengo, S.; Russo, G.; Azzolino, O.; Rybalkin, S.D.; et al. PI3Kgamma modulates the cardiac response to chronic pressure overload by distinct kinase-dependent and -independent effects. Cell 2004, 118, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerfant, B.G.; Rose, R.A.; Sun, H.; Backx, P.H. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma regulates cardiac contractility by locally controlling cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 16, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper--Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, S.J.; Borthwick, G.M.; Oakenfull, R.; Robson, A.; Arthur, H.M. Angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in vitro is TAK1-dependent and Smad2/3-independent. Hypertens Res. 2012, 35, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, I.; Carrion, K.; Serrano, R.; Dyo, J.; Sasik, R.; Lund, S.; Willems, E.; Aceves, S.; Meili, R.; Mercola, M.; et al. Cyclic Stretch of Embryonic Cardiomyocytes Increases Proliferation, Growth, and Expression While Repressing Tgf-Beta Signaling. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 79, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oudit, G.Y.; Kassiri, Z. Role of PI3 Kinase Gamma in Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Heart Disease. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2007, 7, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, N.; Tseng, A.; Zhao, T.C.; Robbins, J.; Padbury, J.F.; Tseng, Y.T. Temporally Controlled Overexpression of Cardiac-Specific PI3Kalpha Induces Enhanced Myocardial Contractility--A New Transgenic Model. Am. J. Physiol Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 295, H1690–H1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Jiang, Y.P.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.H.; Mathias, R.T.; Entcheva, E.; Ballou, L.M.; Cohen, I.S.; Lin, R.Z. Loss of Cardiac Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase P110 Alpha Results in Contractile Dysfunction. Circulation 2009, 120, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerfant, B.G.; Gidrewicz, D.; Sun, H.; Oudit, G.Y.; Penninger, J.M.; Backx, P.H. Cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release and load are enhanced by subcellular cAMP elevations in PI3Kgamma-deficient mice. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damilano, F.; Franco, I.; Perrino, C.; Schaefer, K.; Azzolino, O.; Carnevale, D.; Cifelli, G.; Carullo, P.; Ragona, R.; Ghigo, A.; et al. Distinct Effects of Leukocyte and Cardiac Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Gamma Activity in Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Failure. Circulation 2011, 123, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandel, E.; Hay, N. The regulation and activities of the multifunctional serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 253, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Cornelius, S.C.; Reiss, M.; Danielpour, D. Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits transcriptional responses of transforming growth factor-β by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent suppression of the activation of Smad3 but not Smad2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38342–38351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conery, A.R.; Cao, Y.; Thompson, E.A.; Townsend, C.M., Jr.; Ko, T.C.; Luo, K. Akt interacts directly with Smad3 to regulate the sensitivity to TGF-beta induced apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; ten Dijke, P. Signaling interplay between transforming growth factor-β receptor and PI3K/AKT pathways in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakin, A.V.; Tomlinson, A.K.; Bhowmick, N.A.; Moses, H.L.; Arteaga, C.L. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 03–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suwanabol, P.A.; Seedial, S.M.; Zhang, F.; Shi, X.; Si, Y.; Liu, B.; Kent, K.C. TGF-β and Smad3 modulate PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H2211–H2219, Erratum in: Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 2014, 306, H1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voloshenyuk, T.G.; Landesman, E.S.; Khoutorova, E.; Hart, A.D.; Gardner, J.D. Induction of cardiac fibroblast lysyl oxidase by TGF-β1 requires PI3K/Akt, Smad3, and MAPK signaling. Cytokine 2011, 55, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aki, S.; Yoshioka, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Takuwa, N.; Takuwa, Y. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Class II Alpha-Isoform PI3K-C2alpha Is Required for Transforming Growth Factor Beta-Induced Smad Signaling in Endothelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6086–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edlund, S.; Landström, M.; Heldin, C.H.; Aspenström, P. Smad7 is required for TGF-beta-induced activation of the small GTPase Cdc42. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Runyan, C.E.; Schnaper, H.W.; Poncelet, A.C. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway enhances Smad3-stimulated mesangial cell collagen I expression in response to transforming growth factor-beta1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2632–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Gene | Accession Numbers | Forward Primer 5′→3′ | Reverse Primer 5′→3′ |
|---|---|---|---|
| B2M | NM_012512 | GCCGTCGTGCTTGCCATTC | CTG AGG TGG GTG GAA CTG AGA C |
| 18sRNA | Qiagen QT00199374 | ||
| HPRT | NM_012583 | CCA GCG TCG TGA TTA GTG AT | CAA GTC TTT CAG TCC TGT CC |
| GAPDH | NM_017008 | TCCATGCCATCACTGCCACTC | TGACCTTGCCCACAGCCTTG |
| SMAD7 | AF042499 | AGAGGCTGTGTTGCTGTG | CATCGGGTATCTGGAGTAAGG |
| Collagen1 | NM_053304 | GCG AAC AAG GTG ACA GAG | CCA GGA GAA CCA GCA GAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brosinsky, P.; Bornbaum, J.; Warga, B.; Schulz, L.; Schlüter, K.-D.; Ghigo, A.; Hirsch, E.; Schulz, R.; Euler, G.; Heger, J. PI3K as Mediator of Apoptosis and Contractile Dysfunction in TGFβ1-Stimulated Cardiomyocytes. Biology 2021, 10, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070670
Brosinsky P, Bornbaum J, Warga B, Schulz L, Schlüter K-D, Ghigo A, Hirsch E, Schulz R, Euler G, Heger J. PI3K as Mediator of Apoptosis and Contractile Dysfunction in TGFβ1-Stimulated Cardiomyocytes. Biology. 2021; 10(7):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070670
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrosinsky, Paulin, Julia Bornbaum, Björn Warga, Lisa Schulz, Klaus-Dieter Schlüter, Alessandra Ghigo, Emilio Hirsch, Rainer Schulz, Gerhild Euler, and Jacqueline Heger. 2021. "PI3K as Mediator of Apoptosis and Contractile Dysfunction in TGFβ1-Stimulated Cardiomyocytes" Biology 10, no. 7: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070670
APA StyleBrosinsky, P., Bornbaum, J., Warga, B., Schulz, L., Schlüter, K. -D., Ghigo, A., Hirsch, E., Schulz, R., Euler, G., & Heger, J. (2021). PI3K as Mediator of Apoptosis and Contractile Dysfunction in TGFβ1-Stimulated Cardiomyocytes. Biology, 10(7), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10070670