Long-Term Tetrabromobisphenol A Exposure Induces Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Metabolic Disorders via the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Signaling Pathway in the Regenerated Gut of Apostichopus japonicus
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Statement of Ethics
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. TBBPA Exposure Experiment
2.4. Enzymatic Activity Analysis
2.5. Genomic DNA Preparation and Sequencing of 16S rRNA Gene
2.6. Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota Diversity
2.7. RNA Preparation, Library Formulation, and DGE Sequencing
2.8. GO and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analyses
2.9. RNA Preparation and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT‒PCR)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
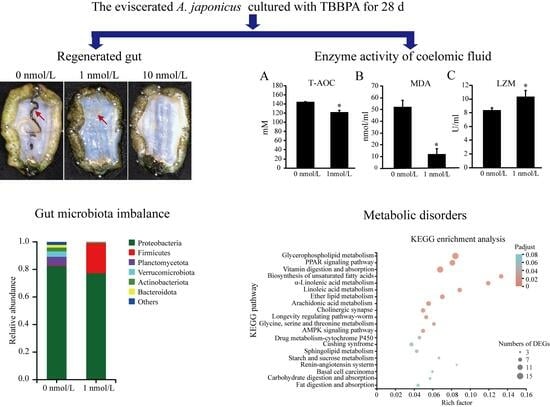
3.1. Analysis of Survival Rate and Regenerated Intestine Morphology
3.2. Enzymatic Activities in Antioxidant and Immune Systems in Regenerated Intestine
3.3. Microbial Diversity Decreased in the Regenerated Intestines of A. japonicus
3.4. The Gene Expression Related to Metabolism Decreased in the Regenerated Intestine of A. japonicus
3.5. PPAR Signaling Pathway Genes Play Vital Roles in the Regenerated Intestine of A. japonicus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, H.; Yin, N.; Faiola, F. Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA): A controversial environmental pollutant. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 54–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, D.Y.; Kacew, S.; Dekant, W. Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA): Possible modes of action of toxicity and carcinogenicity in rodents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Abdallah, M.A.; Geens, T.; Harrad, S.; Law, R.J. Analytical and environmental aspects of the flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol-A and its derivatives. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, P.; Eljarrat, E.; Barcelo, D. Simultaneous determination of hexabromocyclododecane, tetrabromobisphenol A, and related compounds in sewage sludge and sediment samples from Ebro River basin (Spain). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 2817–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.G.; Zeng, H. HBCD and TBBPA in particulate phase of indoor air in Shenzhen, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458–460, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Y.; Zhao, H.Q.; Liu, C.P.; Sun, C.X. Characteristics, sources, and transport of tetrabromobisphenol A and bisphenol A in soils from a typical e-waste recycling area in South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 5818–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, G.A.; Sanders, J.M.; Sadik, A.M.; Birnbaum, L.S. TITLE Disposition and kinetics of Tetrabromobisphenol A in female Wistar Han rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Li, J.; Xiao, Z.; Shi, Z. Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane isomers in breast milk from the general population in Beijing, China: Contamination levels, temporal trends, nursing infant’s daily intake, and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ji, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Y.; Shi, L. TBBPA induces developmental toxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in embryos and zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieminska, E.; Lenart, J.; Diamandakis, D.; Lazarewicz, J.W. The Role of Ca2+ Imbalance in the Induction of Acute Oxidative Stress and Cytotoxicity in Cultured Rat Cerebellar Granule Cells Challenged with Tetrabromobisphenol A. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steves, A.N.; Bradner, J.M.; Fowler, K.L.; Clarkson-Townsend, D.; Gill, B.J.; Turry, A.C.; Caudle, W.M.; Miller, G.W.; Chan, A.W.S.; Easley, C.A., IV. Ubiquitous Flame-Retardant Toxicants Impair Spermatogenesis in a Human Stem Cell Model. iScience 2018, 3, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Zhao, G.; Yang, L.; Zhou, B. Tetrabromobisphenol A caused neurodevelopmental toxicity via disrupting thyroid hormones in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, A.; Lange, A.; Hutchinson, T.H.; Miyagawa, S.; Iguchi, T.; Kudoh, T.; Tyler, C.R. Molecular mechanisms and tissue targets of brominated flame retardants, BDE-47 and TBBPA, in embryo-larval life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 209, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; An, J.; Shang, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Regulation of TBBPA-induced oxidative stress on mitochondrial apoptosis in L02 cells through the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.H.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J. High dose tetrabromobisphenol A impairs hippocampal neurogenesis and memory retention. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saegusa, Y.; Fujimoto, H.; Woo, G.H.; Ohishi, T.; Wang, L.; Mitsumori, K.; Nishikawa, A.; Shibutani, M. Transient aberration of neuronal development in the hippocampal dentate gyrus after developmental exposure to brominated flame retardants in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Saigusa, D.; Tetsu, N.; Yamakuni, T.; Tomioka, Y.; Hishinuma, T. Neurobehavioral effects of tetrabromobisphenol A, a brominated flame retardant, in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 189, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienthal, H.; Verwer, C.M.; van der Ven, L.T.; Piersma, A.H.; Vos, J.G. Exposure to tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) in Wistar rats: Neurobehavioral effects in offspring from a one-generation reproduction study. Toxicology 2008, 246, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riu, A.; McCollum, C.W.; Pinto, C.L.; Grimaldi, M.; Hillenweck, A.; Perdu, E.; Zalko, D.; Bernard, L.; Laudet, V.; Balaguer, P.; et al. Halogenated bisphenol-A analogs act as obesogens in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 139, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, C.; Li, F.; Zhan, J.; Sun, T.; Tang, J.; Wu, H. Tetrabromobisphenol A induced reproductive endocrine-disrupting effects in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Pan, L.; Xiu, M.; Liu, D. Dietary accumulation of tetrabromobisphenol A and its effects on the scallop Chlamys farreri. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C 2015, 167, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Pan, L.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T.; Jin, Q. Deep sequencing of the scallop Chlamys farreri transcriptome response to tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) stress. Mar. Genom. 2015, 19, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Miao, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Pan, L. Inhibition of growth in juvenile manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum: Potential adverse outcome pathway of TBBPA. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Ley, R. Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Ursell, L.K.; Parfrey, L.W.; Knight, R. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: An integrative view. Cell 2012, 148, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adamovsky, O.; Buerger, A.N.; Wormington, A.M.; Ector, N.; Griffitt, R.J.; Bisesi, J.H., Jr.; Martyniuk, C.J. The gut microbiome and aquatic toxicology: An emerging concept for environmental health. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2758–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, M.V.; Dutta, M.; Suvorov, A.; Shi, X.; Gu, H.; Mani, S.; Cui, J.Y. Early Life Exposure to Environmental Contaminants (BDE-47, TBBPA, and BPS) Produced Persistent Alterations in Fecal Microbiome in Adult Male Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 179, 14–30. [Google Scholar]
- Manickam, R.; Duszka, K.; Wahli, W. PPARs and Microbiota in Skeletal Muscle Health and Wasting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8056. [Google Scholar]
- Jayachandran, M.; Christudas, S.; Zheng, X.; Xu, B. Dietary fiber konjac glucomannan exerts an antidiabetic effect via inhibiting lipid absorption and regulation of PPAR-gamma and gut microbiome. Food Chem. 2022, 403, 134336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, H.; Han, Y.; Xiang, M.; Chen, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, Z. Tetrabromobisphenol A: Disposition, kinetics and toxicity in animals and humans. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Byndloss, M.X.; Olsan, E.E.; Rivera-Chávez, F.; Tiffany, C.R.; Cevallos, S.A.; Lokken, K.L.; Torres, T.P.; Byndloss, A.J.; Faber, F.; Gao, Y.; et al. Microbiota-activated PPAR-gamma signaling inhibits dysbiotic Enterobacteriaceae expansion. Science 2017, 357, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.W.; Mercier, A.; Conand, C.; Hamel, J.F.; Toral-Granda, M.V.; Lovatelli, A.; Uthicke, S. Sea cucumber fisheries: Global analysis of stocks, management measures and drivers of overfishing. Fish Fish. 2013, 14, 34–59. [Google Scholar]
- José, M.-N.; José, P.-H.; Siday, M.-M.; Enrique, N.-F.; Sergi, D. Sea Cucumber as Bioindicator of Trace Metal Pollution in Coastal Sediments. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, P.-L.; Laura, M.-P.; Felix, H.; Alberto, Z.-G. Common sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) and sea cucumber of the genus Holothuria as bioindicators of pollution in the study of chemical contaminants in aquatic media. A revision. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106185. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Arraras, J.E.; Greenberg, M.J. Visceral regeneration in holothurians. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 55, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Wang, J.; Cui, W.; Zhu, L. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of TBBPA in seawater and zooplankton in northern sea areas, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4759–4769. [Google Scholar]
- Hyman, H. Echinodermata. In The Invertebrates; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA; Toronto, ON, Canada; London, UK, 1955; p. 763. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Arraras, J.E.; Estrada-Rodgers, L.; Santiago, R.; Torres, I.I.; Diaz-Miranda, L.; Torres-Avillan, I. Cellular mechanisms of intestine regeneration in the sea cucumber, Holothuria glaberrima Selenka (Holothuroidea:Echinodermata). J. Exp. Zool. 1998, 281, 288–304. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, S.A.; Torres-Gutierrez, V.; Rodriguez-Flores, E.J.; Toledo-Roman, E.J.; Rodriguez, N.; Diaz-Diaz, L.M.; Vázquez-Figueroa, L.D.; Cuesta, J.M.; Grillo-Alvarado, V.; Amador, A.; et al. Insights into intestinal regeneration signaling mechanisms. Dev. Biol. 2020, 458, 12–31. [Google Scholar]
- Pittinger, C.A.; Pecquet, A.M. Review of historical aquatic toxicity and bioconcentration data for the brominated flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA): Effects to fish, invertebrates, algae, and microbial communities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 14361–14372. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Qin, Z. Tetrabromobisphenol A: A neurotoxicant or not? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 54466–54476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dilip, K.C.; Sumner, R.; Lippmann, S. Gut microbiota and health. Postgrad. Med. 2020, 132, 274. [Google Scholar]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: Mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mueller, K.; Ash, C.; Pennisi, E.; Smith, O. The gut microbiota. Introduction. Science 2012, 336, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, B.L. Sea Cucumber Intestinal Regeneration Reveals Deterministic Assembly of the Gut Microbiome. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00489-20. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Xue, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, A.; Fu, Q.; Yang, K.; Zhang, F.; Ran, L. Distinct microbiota assembly mechanisms revealed in different reconstruction stages during gut regeneration in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Microbiologyopen 2021, 10, e1250. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yang, R.; Yin, N.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Faiola, F. Developmental toxicity assessments for TBBPA and its commonly used analogs with a human embryonic stem cell liver differentiation model. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136924. [Google Scholar]
- Mashanov, V.S.; Garcia-Arraras, J.E. Gut regeneration in holothurians: A snapshot of recent developments. Biol. Bull. 2011, 221, 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Pineda, P.A.; Ramírez-Gómez, F.; Pérez-Ortiz, J.; González-Díaz, S.; Jesús, S.D.; Hernández-Pasos, J.; Valle-Avila, D.; Rojas-Cartagena, C.; Suárez-Castillo, E.C.; Tossas, K.; et al. Gene expression profiling of intestinal regeneration in the sea cucumber. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.N.; Yang, H.S.; Chen, M.Y.; Xu, D.X. Cloning and expression analysis of Wnt6 and Hox6 during intestinal regeneration in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 5321–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Gao, Y.; Sun, L.; Jin, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Wnt Signaling Pathway Linked to Intestinal Regeneration via Evolutionary Patterns and Gene Expression in the Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girich, A.S.; Isaeva, M.P.; Dolmatov, I.Y. Wnt and frizzled expression during regeneration of internal organs in the holothurian Eupentacta fraudatrix. Wound Repair Regen. 2017, 25, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, R.E.; Trexler, A.W.; Knudsen, G.A.; Evans, R.A.; Birnbaum, L.S. Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) Alters ABC Transport at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 169, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtowicz, A.K.; Szychowski, K.A.; Kajta, M. PPAR-γ agonist GW1929 but not antagonist GW9662 reduces TBBPA-induced neurotoxicity in primary neocortical cells. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 25, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.-T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.-J.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.F. Upregulation of the PPAR signaling pathway and accumulation of lipids are related to the morphological and structural transformation of the dragon-eye goldfish eye. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 1031–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatol, P.; Saraf, S.; Jain, A. Peroxisome Proliferated Activated Receptors (PPARs): Opportunities and Challenges for Ocular Therapy. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2018, 35, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratman, D.; Mylka, V.; Bougarne, N.; Pawlak, M.; Caron, S.; Hennuyer, N.; Paumelle, R.; De Cauwer, L.; Thommis, J.; Rider, M.H.; et al. Chromatin recruitment of activated AMPK drives fasting response genes co-controlled by GR and PPARα. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 10539–10553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougarne, N.; Weyers, B.; Desmet, S.J.; Deckers, J.; Ray, D.W.; Staels, B.; De Bosscher, K. Molecular Actions of PPARα in Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 39, 760–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Rong, J.; et al. Long-Term Tetrabromobisphenol A Exposure Induces Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Metabolic Disorders via the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Signaling Pathway in the Regenerated Gut of Apostichopus japonicus. Biology 2023, 12, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111365
Song X, Lin Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Li X, Liu J, Jiang W, Chen J, Wu L, Rong J, et al. Long-Term Tetrabromobisphenol A Exposure Induces Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Metabolic Disorders via the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Signaling Pathway in the Regenerated Gut of Apostichopus japonicus. Biology. 2023; 12(11):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111365
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xiaojun, Ying Lin, Yinfeng Zhang, Zi Wang, Xiaohan Li, Jixiang Liu, Wenwen Jiang, Jianing Chen, Linxuan Wu, Junjie Rong, and et al. 2023. "Long-Term Tetrabromobisphenol A Exposure Induces Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Metabolic Disorders via the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Signaling Pathway in the Regenerated Gut of Apostichopus japonicus" Biology 12, no. 11: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111365
APA StyleSong, X., Lin, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Li, X., Liu, J., Jiang, W., Chen, J., Wu, L., Rong, J., Xu, K., & Wang, G. (2023). Long-Term Tetrabromobisphenol A Exposure Induces Gut Microbiota Imbalance and Metabolic Disorders via the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Signaling Pathway in the Regenerated Gut of Apostichopus japonicus. Biology, 12(11), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111365