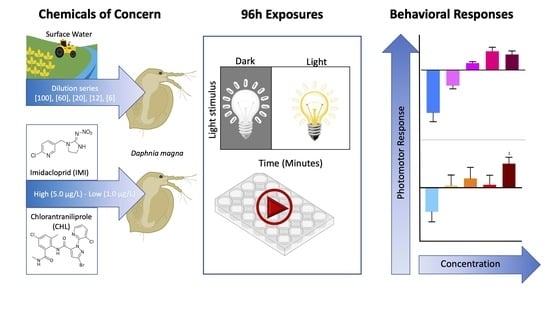
Swimming Behavior of Daphnia magna Is Altered by Pesticides of Concern, as Components of Agricultural Surface Water and in Acute Exposures
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Toxicity Testing
2.1.1. Test Organisms
2.1.2. Acute Exposure Conditions
2.2. Surface Water Sample Collection
Surface Water Exposures Dilution Series
2.3. Imidacloprid and Chlorantraniliprole
2.4. Chemical Analyses
2.5. Behavioral Assays and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Analyses
3.1.1. Surface Water Analytical Chemistry—Before First Flush (September 2019)
3.1.2. Surface Water Analytical Chemistry—After First Flush (November 2019)
3.1.3. Relative Change of Target Chemicals before and after First Flush
3.1.4. Chlorantraniliprole and Imidacloprid
3.2. Mortality and Behavioral Assays
3.2.1. Surface Water Exposures September 2019 (before First Flush Event)
3.2.2. Surface Water Exposures November 2019 (after First Flush)
3.2.3. Chlorantraniliprole and Imidacloprid Exposures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colón-Cruz, L.; Kristofco, L.; Crooke-Rosado, J.; Acevedo, A.; Torrado, A.; Brooks, B.W.; Sosa, M.A.; Behra, M. Alterations of larval photo-dependent swimming responses (PDR): New endpoints for rapid and diagnostic screening of aquatic contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Jones, O.; Dorne, J.-L.C.; Svendsen, C.; Swain, S.C.; Stürzenbaum, S.R. Systems toxicology approaches for understanding the joint effects of environmental chemical mixtures. Sci. Total. Environ. 2010, 408, 3725–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfram, J.; Stehle, S.; Bub, S.; Petschick, L.L.; Schulz, R. Meta-Analysis of Insecticides in United States Surface Waters: Status and Future Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14452–14460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, P. Status and outlook for acaricide and insecticide discovery. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-M.; Chai, W.-G.; Wu, Y.-L. Residues of chlorantraniliprole in rice field ecosystem. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsala, R.Z.; Capri, E.; Russo, E.; Bisagni, M.; Colla, R.; Lucini, L.; Gallo, A.; Suciu, N.A. First evaluation of pesticides occurrence in groundwater of Tidone Valley, an area with intensive viticulture. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 736, 139730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsuah, J.F.; Messer, T.L.; Snow, D.D.; Comfort, S.D.; Mittelstet, A.R. Literature Review: Global Neonicotinoid Insecticide Occurrence in Aquatic Environments. Water 2020, 12, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, T.P.; Lahm, G.P.; Stevenson, T.M. A retrospective look at anthranilic diamide insecticides: Discovery and lead optimization to chlorantraniliprole and cyantraniliprole: A Retrospective Look at Anthranilic Diamide Insecticides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pes, M.P.; Melo, A.A.; Stacke, R.S.; Zanella, R.; Perini, C.R.; Silva, F.M.A.; Guedes, J.V.C. Translocation of chlorantraniliprole and cyantraniliprole applied to corn as seed treatment and foliar spraying to control Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, E.A.D.; Mulhauser, B.; Mulot, M.; Mutabazi, A.; Glauser, G.; Aebi, A. A worldwide survey of neonicotinoids in honey. Science 2017, 358, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon-Delso, N.; Amaralrogers, V.; Belzunces, L.P.; Bonmatin, J.M.; Chagnon, M.; Downs, C.; Furlan, L.; Gibbons, D.W.; Giorio, C.; Girolami, V.; et al. Systemic insecticides (neonicotinoids and fipronil): Trends, uses, mode of action and metabolites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Chai, T.; Qian, L.; Wang, C. Effects of three diamides (chlorantraniliprole, cyantraniliprole and flubendiamide) on life history, embryonic development and oxidative stress biomarkers of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SURF. California Department of Pesticide Regulation Surface Water Database; SURF: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Su, H.; You, J.; Wang, W.-X. High Tolerance and Delayed Responses of Daphnia magna to Neonicotinoid Insecticide Imidacloprid: Toxicokinetic and Toxicodynamic Modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanguenat, A. The story of a new insecticidal chemistry class: The diamides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, E.B.; Pessah, I.N. Structure–activity relationship of non-coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls toward skeletal muscle ryanodine receptors in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–141, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troczka, B.J.; Williamson, M.S.; Field, L.M.; Davies, T. Rapid selection for resistance to diamide insecticides in Plutella xylostella via specific amino acid polymorphisms in the ryanodine receptor. Neurotoxicology 2017, 60, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tišler, T.; Jemec, A.; Mozetič, B.; Trebše, P. Hazard identification of imidacloprid to aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, Z.C.; Anastasio, C.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Quantum Yield for the Aqueous Photochemical Degradation of Chlorantraniliprole and Simulation of Its Environmental Fate in a Model California Rice Field. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, T.C.; Van Staalduinen, M.A.; Van der Sluijs, J.P. Macro-Invertebrate Decline in Surface Water Polluted with Imidacloprid. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, A.; Audira, G.; Malhotra, N.; Uapipatanakul, B.; Chen, J.-R.; Lai, Y.-H.; Huang, J.-C.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Lai, H.-T.; Hsiao, C.-D. Multiple Screening of Pesticides Toxicity in Zebrafish and Daphnia Based on Locomotor Activity Alterations. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, K.T.; Hou, F.; Tian, Z.; Wu, C.; Goehring, M.; Liu, F.; Kolodziej, E.P. More Than a First Flush: Urban Creek Storm Hydrographs Demonstrate Broad Contaminant Pollutographs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6152–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, O.; Khodorkovsky, M.; Gassmann, M.; Friedler, E.; Schneider, M.; Dubowski, Y. Fate of Pesticides and Their Transformation Products: First Flush Effects in a Semi-Arid Catchment. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lau, S.-L.; Kayhanian, M.; Stenstrom, M.K. Seasonal first flush phenomenon of urban stormwater discharges. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4153–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayhoe, K.; Cayan, D.; Field, C.B.; Frumhoff, P.C.; Maurer, E.P.; Miller, N.L.; Moser, S.C.; Schneider, S.H.; Cahill, K.N.; Cleland, E.E.; et al. Emissions pathways, climate change, and impacts on California. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12422–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levy, K.; Woster, A.P.; Goldstein, R.S.; Carlton, E.J. Untangling the Impacts of Climate Change on Waterborne Diseases: A Systematic Review of Relationships between Diarrheal Diseases and Temperature, Rainfall, Flooding, and Drought. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4905–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerny, M.; Bytel, J. Density and size distribution of Daphnia populations at different fish predation levels. Hydrobiologia 1991, 225, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodré, E.D.O.; Bozelli, R.L. How planktonic microcrustaceans respond to environment and affect ecosystem: A functional trait perspective. Int. Aquat. Res. 2019, 11, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanazato, T. Pesticide effects on freshwater zooplankton: An ecological perspective. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagi, T. Bioconcentration, Bioaccumulation, and Metabolism of Pesticides in Aquatic Organisms. In Review of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.B.; Abrantes, N.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Duarte, A.; Freitas, A.; Gomes, A.; Carvalho, A.; Marques, J.; Gonçalves, F.; Pereira, R. Effects of dietary exposure to herbicide and of the nutritive quality of contaminated food on the reproductive output of Daphnia magna. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 179, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; EPA-821-R-02-012. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Liang, C.; Li, W.; Letcher, R.J.; Liu, C. A comprehensive system for detection of behavioral change of D. magna exposed to various chemicals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, G.; Ford, A.T. Behaviour revised: Contaminant effects on aquatic animal behaviour. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 182, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beggel, S.; Werner, I.; Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.P. Sublethal toxicity of commercial insecticide formulations and their active ingredients to larval fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Sci. Total. Environ. 2010, 408, 3169–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolter, C.; Arlinghaus, R. Navigation impacts on freshwater fish assemblages: The ecological relevance of swimming performance. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2003, 13, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristofco, L.A.; Cruz, L.C.; Haddad, S.P.; Behra, M.L.; Chambliss, C.K.; Brooks, B.W. Age matters: Developmental stage of Danio rerio larvae influences photomotor response thresholds to diazinion or diphenhydramine. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steele, W.B.; Kristofco, L.A.; Corrales, J.; Saari, G.N.; Haddad, S.P.; Gallagher, E.P.; Kavanagh, T.J.; Kostal, J.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Voutchkova-Kostal, A.; et al. Comparative behavioral toxicology with two common larval fish models: Exploring relationships among modes of action and locomotor responses. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1587–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, Z. Differences in the behavior characteristics between Daphnia magna and Japanese madaka in an on-line biomonitoring system. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenbein, S.; Lawler, S.P.; Geist, J.; Connon, R.E. The use of growth and behavioral endpoints to assess the effects of pesticide mixtures upon aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Dodson, S.; Hanazato, T. Commentary on effects of anthropogenic and natural organic chemicals on development, swimming behavior, and reproduction of Daphnia, a key member of aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wagner, S.; Wang, D.; Luo, Y.; Goh, K.S. Pesticide Detections, Benchmark Exceedances, and Temporal Trends in Surface Water of California’s Imperial, Salinas, and Santa Maria Valleys; ACS Symposium Series; Goh, K.S., Gan, J., Young, D.F., Luo, Y., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Volume 1308, pp. 119–142. ISBN 978-0-8412-3410-9. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Aquatic Life Benchmarks and Ecological Risk Assessments for Registered Pesticides; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances Pesticide Fact Sheet: Chlorantraniliprole; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention Preliminary Aquatic Risk Assessment to Support the Registration Review of Imidacloprid; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Gajbhiye, V.T.; Available, N.A.N.; Agnihotri, N.P. Leaching Behavior of Imidacloprid Formulations in Soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 68, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Ensminger, M.; Budd, R. Methodology for Prioritizing Pesticides for Surface Water Monitoring in Agricultural and Urban Areas of California; ACS Symposium Series; Zhang, M., Jackson, S., Robertson, M.A., Zeiss, M.R., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Volume 1283, pp. 307–322. ISBN 978-0-8412-3290-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Department of Pesticide Regulation Analytical Methods. Environmental Monitoring Analytical Methods 2022. Available online: https://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/emon/pubs/em_methd_main.htm (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- USEPA. Short-Term Methods for Estimating the Chronic Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Organisms; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Teerlink, J.; DaSilva, A. Standard Operating Procedure QAQC012.00—Guide for Analytical Method Development for Surface Water and Sediment Samples, 2017. Available online: https://www.cdpr.ca.gov/docs/emon/pubs/sops/qaqc01200.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Stinson, S.A.; Hasenbein, S.; Connon, R.E.; Deng, X.; Alejo, J.S.; Lawler, S.P.; Holland, E.B. Agricultural surface water, imidacloprid, and chlorantraniliprole result in altered gene expression and receptor activation in Pimephales promelas. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 806, 150920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.; Oliveri, A.; Zhang, C.; Frazier, J.; Mackinnon, S.; Cole, G.; Levin, E. Long-term behavioral impairment following acute embryonic ethanol exposure in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bownik, A. Daphnia swimming behaviour as a biomarker in toxicity assessment: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 601–602, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Zhao, R.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Ren, Z.; Yang, M.; Pan, H.; Xu, S.; Zhu, J.; et al. The Role of AChE in Swimming Behavior of Daphnia magna: Correlation Analysis of Both Parameters Affected by Deltamethrin and Methomyl Exposure. J. Toxicol. 2017, 2017, 3265727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebrun, J.D.; De Jesus, K.; Rouillac, L.; Ravelli, M.; Guenne, A.; Tournebize, J. Single and combined effects of insecticides on multi-level biomarkers in the non-target amphipod Gammarus fossarum exposed to environmentally realistic levels. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 218, 105357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivetti, C.; Campos, B.; Barata, C. Low environmental levels of neuro-active pharmaceuticals alter phototactic behaviour and reproduction in Daphnia magna. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Kowalczyk, M.; Bańczerowski, J. Lambda-cyhalothrin affects swimming activity and physiological responses of Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S. The ecological role of chemical stimuli for the zooplankton: Predator-avoidance behavior in Daphnia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 33, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, T.; Piovano, S.; Fick, J.; Klaminder, J.; Heynen, M.; Jonsson, M. Ecological effects of pharmaceuticals in aquatic systems—Impacts through behavioural alterations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loraine, G.A.; Pettigrove, M.E. Seasonal Variations in Concentrations of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Drinking Water and Reclaimed Wastewater in Southern California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk, A.; Bownik, A.; Dudka, J.; Kowal, K.; Ślaska, B. Daphnia magna model in the toxicity assessment of pharmaceuticals: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 763, 143038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A.; Szabelak, A. Short-term effects of pesticide fipronil on behavioral and physiological endpoints of Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 33254–33264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brausch, K.A.; Anderson, T.A.; Smith, P.N.; Maul, J.D. Effects of functionalized fullerenes on bifenthrin and tribufos toxicity to Daphnia magna: Survival, reproduction, and growth rate. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 2600–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.B.M.; Candolin, U. Behavioral responses to changing environments. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 26, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerhardt, A. Aquatic Behavioral Ecotoxicology—Prospects and Limitations. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assessment: Int. J. 2007, 13, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, S.D.; Wilson, S.P. The utility of behavioral studies for aquatic toxicology testing: A meta-analysis. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Percentage of Ambient Water | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (100) | (60) | (35) | (20) | (12) | Control | ||
| Site ID | Percentage of D. magna Mortality | Toxicity | |||||
| Quail Creek | 100 **** | 100 **** | 100 **** | 100 **** | 87.5 **** | 0 | TOXIC |
| Alisal Creek | 100 **** | 100 **** | 62.5 **** | 27.5 **** | 15 **** | 0 | TOXIC |
| Salinas River | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 | NON-OXIC |
| Percentage of Ambient Water | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (100) | (20) | (12) | (6) | Control | ||
| Site ID | Percentage of D. magna Mortality | Toxicity | ||||
| Quail Creek | 100 **** | 22.5 | 12.5 | 2.5 | 0 | TOXIC |
| Alisal Creek | 100 **** | 50 *** | 25 | 7.5 | 0 | TOXIC |
| Salinas River | 15 | 15 | 15 | 5 | 5 | NON-TOXIC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egan, N.; Stinson, S.A.; Deng, X.; Lawler, S.P.; Connon, R.E. Swimming Behavior of Daphnia magna Is Altered by Pesticides of Concern, as Components of Agricultural Surface Water and in Acute Exposures. Biology 2023, 12, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030425
Egan N, Stinson SA, Deng X, Lawler SP, Connon RE. Swimming Behavior of Daphnia magna Is Altered by Pesticides of Concern, as Components of Agricultural Surface Water and in Acute Exposures. Biology. 2023; 12(3):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030425
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgan, Nicole, Sarah A. Stinson, Xin Deng, Sharon P. Lawler, and Richard E. Connon. 2023. "Swimming Behavior of Daphnia magna Is Altered by Pesticides of Concern, as Components of Agricultural Surface Water and in Acute Exposures" Biology 12, no. 3: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030425
APA StyleEgan, N., Stinson, S. A., Deng, X., Lawler, S. P., & Connon, R. E. (2023). Swimming Behavior of Daphnia magna Is Altered by Pesticides of Concern, as Components of Agricultural Surface Water and in Acute Exposures. Biology, 12(3), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030425