In Vitro High Throughput Screening, What Next? Lessons from the Screening for Aurora Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
3. Results and Discussion
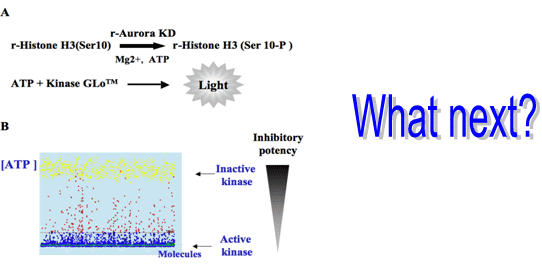
3.1. Elaboration of a Test Suitable for HTS
3.2. In Vitro Aurora Kinase Assay

3.3. HTS Results
3.4. Selection of the Active Molecules
3.5. Characterization of the Hits
3.5.1. Results with Flavone Molecules
3.5.2. Results with the Benzo[e]pyridoindole Family

| Kinases | Accession Number | Remaining Activity (in %) |
|---|---|---|
| GCK ”Germinal central kinase” | BC047865 | 32 ± 1 |
| TrkA “Tropomyosin Related kinase A” | NM_001007792.1 | 36 ± 2 |
| NUAK1–ARK5 “SnF1-like Kinase” | NM_014840 | 53 ± 2 |
| PHK “Phosphorylase b kinase” | X80590 | 53 ± 7 |
| Tak1 “Transforming growth factor beta activated kinase” | NM_003188 | 55 ± 3 |
| Aurora kinase-B | NM_004217 | 86 ± 2 |
| Aurora kinase-A | BC027464 | 96 ± 4 |
3.6. General Discussion

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vader, G.; Lens, S.M. The aurora kinase family in cell division and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1786, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Carmena, M.; Ruchaud, S.; Earnshaw, W.C. Making the Auroras glow: Regulation of Aurora A and B kinase function by interacting proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardon, T.; Peset, I.; Petrova, B.; Vernos, I. Dissecting the role of Aurora A during spindle assembly. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2567–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannak, E.; Kirkham, M.; Hyman, A.A.; Oegema, K. Aurora-A kinase is required for centrosome maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, A.; Coppinger, J.A.; Jang, C.Y.; Yates, J.R.; Fang, G. Bora and the kinase Aurora A cooperatively activate the kinase Plk1 and control mitotic entry. Science 2008, 320, 1655–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lens, S.M.; Medema, R.H. The survivin/Aurora B complex: Its role in coordinating tension and attachment. Cell Cycle 2003, 2, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurin, A.T.; van der Waal, M.S.; Medema, R.H.; Lens, S.M.; Kops, G.J. Aurora B potentiates Mps1 activation to ensure rapid checkpoint establishment at the onset of mitosis. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.; Norden, C.; Durrer, K.; Rauter, H.; Uhlmann, F.; Barral, Y. A mechanism for chromosome segregation sensing by the NoCut checkpoint. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Zhou, H.; White, R.A. A putative serine/threonine kinase encoding gene BTAK on chromosome 20q13 is amplified and overexpressed in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 1997, 14, 2195–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Garuti, L.; Roberti, M.; Bottegoni, G. Small molecule aurora kinases inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 1949–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdler, F.; Gascoigne, K.E.; Eyers, P.A.; Hartmuth, S.; Crafter, C.; Foote, K.M.; Keen, N.J.; Taylor, S.S. Validating Aurora B as an anti-cancer drug target. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3664–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.R.; Patrick, D.R.; Dar, M.M.; Huang, P.S. Targeted anti-mitotic therapies: Can we improve on tubulin agents? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncini, C.; Carpinelli, P.; Gianellini, L.; Fancelli, D.; Vianello, P.; Rusconi, L.; Storici, P.; Zugnoni, P.; Pesenti, E.; Croci, V. PHA-680632, a novel Aurora kinase inhibitor with potent antitumoral activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4080–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.M.-N.; Favier, B.; Valette, A.; Barette, C.; Nguyen, C.H.; Lafanechère, L.; Grierson, D.S.; Dimitrov, S.; Molla, A. Benzo[e]pyridoindoles, novel inhibitors of the Aurora kinases. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacour-Larose, M.; Molla, A.; Skoufias, D.A.; Margolis, R.L.; Dimitrov, S. Distinct dynamics of Aurora B and Survivin during mitosis. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacour-Larose, M.; Thi, M.N.; Dimitrov, S.; Molla, A. Role of survivin phosphorylation by aurora B in mitosis. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1878–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garuti, L.; Roberti, M.; Bottegoni, G. Non-ATP competitive protein kinase inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2804–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The French Patrimonial Library. Available online: http://chimiotheque-nationale.enscm.fr/?lang=en/ (accessed on 2 January 2007).
- Rees, D.C.; Howard, J.B. Structural bioenergetics and energy transduction mechanisms. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 293, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudé, C.; Nguyen, C.H.; Kukreti, S.; Janin, Y.; Sun, J.-S.; Bisagni, E.; Garestier, T.; Hélène, C. Rational design of a triple helix-specific intercalating ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3591–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.T.; Vu, H.L.; Naud-Martin, D.; Bombled, M.; Nguyen, C.H.; Molla, A. Hydrosoluble benzo[e]pyridoindolones as potent inhibitors of aurora kinases. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.T.; Vu, H.L.; Nguyen, C.H.; Molla, A. Basal aurora kinase B activity is sufficient for histone H3 phosphorylation in prophase. Biol. Open 2013, 2, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ulbrich, J.; Müller, J.; Wüstefeld, T.; Aeberhard, L.; Kress, T.R.; Muthalagu, N.; Rycak, L.; Rudalska, R.; Moll, R.; et al. Deregulated MYC expression induces dependence upon AMPK-related kinase 5. Nature 2012, 483, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sweeney, M.F.; Yu, M.; Burger, A.; Greninger, P.; Benes, C.; Haber, D.A.; Settleman, J. TAK1 inhibition promotes apoptosis in KRAS-dependent colon cancers. Cell 2012, 148, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, S.; Quevedo, C.; Menéndez, S.; Paramonov, I.; Stouten, P.F.; Janssen, R.A.; Rueb, S.; He, S.; Snaar-Jagalska, B.E.; Laricchia-Robbio, L.; et al. Identification of phosphorylase kinase as a novel therapeutic target through high-throughput screening for anti-angiogenesis compounds in zebrafish. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4333–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoang, T.-M.-N.; Vu, H.-L.; Le, L.-T.-T.; Nguyen, C.-H.; Molla, A. In Vitro High Throughput Screening, What Next? Lessons from the Screening for Aurora Kinase Inhibitors. Biology 2014, 3, 167-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology3010167
Hoang T-M-N, Vu H-L, Le L-T-T, Nguyen C-H, Molla A. In Vitro High Throughput Screening, What Next? Lessons from the Screening for Aurora Kinase Inhibitors. Biology. 2014; 3(1):167-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology3010167
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoang, Thi-My-Nhung, Hong-Lien Vu, Ly-Thuy-Tram Le, Chi-Hung Nguyen, and Annie Molla. 2014. "In Vitro High Throughput Screening, What Next? Lessons from the Screening for Aurora Kinase Inhibitors" Biology 3, no. 1: 167-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology3010167
APA StyleHoang, T. -M. -N., Vu, H. -L., Le, L. -T. -T., Nguyen, C. -H., & Molla, A. (2014). In Vitro High Throughput Screening, What Next? Lessons from the Screening for Aurora Kinase Inhibitors. Biology, 3(1), 167-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology3010167