Apoptotic Bodies: Particular Extracellular Vesicles Involved in Intercellular Communication
Abstract
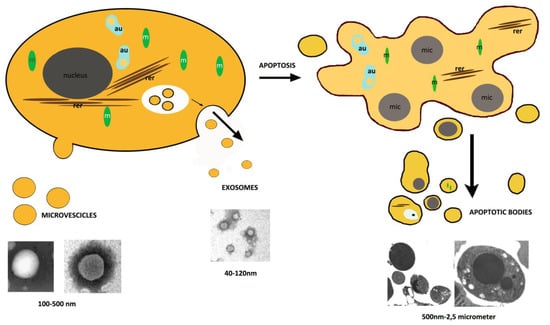
:1. Introduction
1.1. Extracellular Vesicles
1.2. Brief Presentation of the Aim of the Review
2. Apoptosis
3. Extracellular Vesicles, Other than Apoptotic Bodies
3.1. Exosomes
3.2. Microvesicles
4. Apoptotic Bodies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gangoda, L.; Boukouris, S.; Liem, M.; Kalra, H.; Mathivanan, S. Extracellular vesicles including exosomes are mediators of signal transduction: Are they protective or pathogenic? Proteomics 2015, 15, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maas, S.L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Weaver, A.M. Extracellular vesicles: Unique intercellular delivery vehicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauser, P.; Wang, S.; Didenko, V.V. Apoptotic Bodies: Selective Detection in Extracellular Vesicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1554, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Filková, M.; Jüngel, A.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: Potential role in diagnosis and therapy. BioDrugs 2012, 26, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headland, S.E.; Jones, H.R.; Norling, L.V.; Kim, A.; Souza, P.R.; Corsiero, E.; Gil, C.D.; Nerviani, A.; Dell’Accio, F.; Pitzalis, C.; et al. Neutrophil-derived microvesicles enter cartilage and protect the joint in inflammatory arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 315ra190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, M.; Fonseka, P.; Chitti, S.V.; Kang, T.; Sanwlani, R.; Van Deun, J.; Hendrix, A.; Mathivanan, S. Vesiclepedia 2019: A compendium of RNA, proteins, lipids and metabolites in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D516–D519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gézsi, A.; Kovács, Á.; Visnovitz, T.; Buzás, E.I. Systems biology approaches to investigating the roles of extracellular vesicles in human diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwland, R.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Soekmadji, C.; Boilard, E.; Carter, D.; Buzas, E.I. Essentials of extracellular vesicles: Posters on basic and clinical aspects of extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1548234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.B. Extracellular vesicles: How they interact with endothelium, potentially contributing to metastatic cancer cell implants. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL Andaloussi, S.; Mäger, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J. Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. Discovery of Double-Stranded Genomic DNA in Circulating Exosomes. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2016, 81, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Citterio, B.; Albertini, M.C.; Ghibelli, L.; Falcieri, E.; Battistelli, M.; Canonico, B.; Rocchi, M.B.; Teodori, L.; Ciani, M.; Piatti, E. Multiparameter analysis of apoptosis in puromycin-treated Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcioni, T.; Papa, S.; Campana, R.; Manti, A.; Battistelli, M.; Baffone, W. State transitions of Vibrio parahaemolyticus VBNC cells evaluated by flow cytometry. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2008, 74, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin-Smith, G.K.; Poon, I.K.H. Disassembly of the Dying: Mechanisms and Functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.L.; Cidlowski, J.A. Cell cycle regulation and apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbury, C.J.; Hickson, I.D. Cellular responses to DNA damage. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 367–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povea-Cabello, S.; Oropesa-Ávila, M.; de la Cruz-Ojeda, P.; Villanueva-Paz, M.; de la Mata, M.; Suárez-Rivero, J.; Álvarez-Córdoba, M.; Villalón-García, I.; Cotán, D.; Ybot-González, P.; et al. Dynamic Reorganization of the Cytoskeleton during Apoptosis: The Two Coffins Hypothesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akers, J.C.; Gonda, D.; Kim, R.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Biogenesis of extracellular vesicles (EV): Exosomes, microvesicles, retrovirus-like vesicles, and apoptotic bodies. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burattini, S.; Ferri, P.; Battistelli, M.; D’Emilio, A.; Biagiotti, L.; Sestili, P.; Rocchi, M.B.; Falcieri, E. Apoptotic DNA fragmentation can be revealed in situ: An ultrastructural approach. Microsc. Res. Technol. 2009, 72, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.B.; Lai, Y.Y.; Zi, C.-H. Apoptosis and apoptotic body: Disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falcieri, E.; Gobbi, P.; Zamai, L.; Vitale, M. Ultrastructural features of apoptosis. Scanning Microsc. 1994, 8, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falcieri, E.; Gobbi, P.; Cataldi, A.; Zamai, L.; Faenza, I.; Vitale, M. Nuclear pores in the apoptotic cell. Histochem. J. 1994, 26, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuppia, L.; Gobbi, P.; Zamai, L.; Palka, G.; Vitale, M.; Falcieri, E. Morphometric and functional study of apoptotic cell chromatin. Cell Death Differ. 1996, 3, 397–405. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, L.F.; Kanaseki, T.; Sabirov, R.; Morishima, S.; Castro, J.; Bittner, C.X.; Maeno, E.; Ando-Akatsuka, Y.; Okada, Y. Apoptotic and necrotic blebs in epithelial cells display similar neck diameters but different kinase dependency. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charras, G.T.; Yarrow, J.C.; Horton, M.A.; Mahadevan, L.; Mitchison, T.J. Non-equilibration of hydrostatic pressure in blebbing cells. Nature 2005, 435, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, D.R.; Coleman, M.L.; Li, S.; Robertson, D.; Sullivan, T.; Stewart, C.L.; Olson, M.F. Actin-myosin-based contraction is responsible for apoptotic nuclear disintegration. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 168, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beaudouin, J.; Gerlich, D.; Daigle, N.; Eils, R.; Ellenberg, J. Nuclear envelope breakdown proceeds by microtubule-induced tearing of the lamina. Cell 2002, 108, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broers, J.L.; Ramaekers, F.C. Dynamics of nuclear lamina assembly and disassembly. In The Nuclear Envelope; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; Volume 56, pp. 177–192. [Google Scholar]
- Oropesa-Ávila, M.; Fernández-Vega, A.; de la Mata, M.; Maraver, J.G.; Cordero, M.D.; Cotán, D.; de Miguel, M.; Calero, C.P.; Paz, M.V.; Pavón, A.D.; et al. Apoptotic microtubules delimit an active caspase free area in the cellular cortex during the execution phase of apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ndozangue-Touriguine, O.; Hamelin, J.; Breard, J. Cytoskeleton and apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, S.M.; Strickland, D.; Ireland, C.M. Polymerization of tubulin in apoptotic cells is not cell cycle dependent. Exp. Cell Res. 1994, 215, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engeland, M.; Kuijpers, H.J.; Ramaekers, F.C.; Reutelingsperger, C.P.; Schutte, B. Plasma membrane alterations and cytoskeletal changes in apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 235, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moss, D.K.; Betin, V.M.; Malesinski, S.D.; Lane, J.D. A novel role for microtubules in apoptotic chromatin dynamics and cellular fragmentation. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2362–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desouza, M.; Gunning, P.W.; Stehn, J.R. The actin cytoskeleton as a sensor and mediator of apoptosis. Bioarchitecture 2012, 2, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiraly, G.; Simonyi, A.S.; Turani, M.; Juhasz, I.; Nagy, G.; Banfalvi, G. Micronucleus formation during chromatin condensation and under apoptotic conditions. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenquer, M.; Amorim, M.J. Exosome Biogenesis, Regulation, and Function in Viral Infection. Viruses 2015, 7, 5066–5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: Shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, M.; Raposo, G. Exosomes-vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guescini, M.; Guidolin, D.; Vallorani, L.; Casadei, L.; Gioacchini, A.M.; Tibollo, P.; Battistelli, M.; Falcieri, E.; Battistin, L.; Agnati, L.F.; et al. C2C12 myoblasts release micro-vesicles containing mtDNA and proteins involved in signal transduction. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1977–198418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.K.; Giebel, B. Exosomes: Small vesicles participating in intercellular communication. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricarico, C.; Clancy, J.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Biology and biogenesis of shed microvesicles. Small GTPases 2017, 8, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borràs, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience 2015, 65, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ihara, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Sugamata, M.; Okumura, H.; Ueno, Y. The process of ultrastructural changes from nuclei to apoptotic body. Virchows Arch. 1998, 433, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, R.; Van Roosbroeck, K.; Calin, G.A. Cell-to-cell communication: microRNAs as hormones. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crescitelli, R.; Lässer, C.; Szabó, T.G.; Kittel, A.; Eldh, M.; Dianzani, I.; Buzás, E.I.; Lötvall, J. Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savill, J.; Fadok, V. Corpse clearance defines the meaning of cell death. Nature. 2000, 407, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blander, J.M. The many ways tissue phagocytes respond to dying cells. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Poon, I.K.H. Methods for monitoring the progression of cell death, cell disassembly and cell clearance. Apoptosis 2019, 24, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renò, F.; Burattini, S.; Rossi, S.; Luchetti, F.; Columbaro, M.; Santi, S.; Papa, S.; Falcieri, E. Phospholipid rearrangement of apoptotic membrane does not depend on nuclear activity. Histochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 110, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, I.K.H.; Lucas, C.D.; Rossi, A.G.; Ravichandran, K.S. Apoptotic cell clearance: Basic biology and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagata, S.; Suzuki, J.; Segawa, K.; Fujii, T. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the cell surface. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birge, R.B.; Boeltz, S.; Kumar, S.; Carlson, J.; Wanderley, J.; Calianese, D.; Barcinski, M.; Brekken, R.A.; Huang, X.; Hutchins, J.T.; et al. Phosphatidylserine is a global immunosuppressive signal in efferocytosis, infectious disease, and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 962–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rysavy, N.M.; Shimoda, L.M.; Dixon, A.M.; Speck, M.; Stokes, A.J.; Turner, H.; Umemoto, E.Y. Beyond apoptosis: The mechanism and function of phosphatidylserine asymmetry in the membrane of activating mast cells. Bioarchitecture 2014, 4, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Depraetere, V. “Eat me” signals of apoptotic bodies. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, E104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsugi, T.; Schroit, A.J.; Connor, J.; Bucana, C.D.; Fidler, I.J. Elevated expression of phosphatidylserine in the outer membrane leaflet of human tumor cells and recognition by activated human blood monocytes. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 3062–3066. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woehlecke, H.; Antje, P.O.; Alder-Baerens, N.; Hermann, L.A.; Herrmann, A. Enhanced exposure of phosphatidylserine in human gastric carcinoma cells overexpressing the half-size ABC transporter BCRP (ABCG2). Biochem. J. 2003, 376, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamai, L.; Burattini, S.; Luchetti, F.; Canonico, B.; Ferri, P.; Melloni, E.; Gonelli, A.; Guidotti, L.; Papa, S.; Falcieri, E. In vitro apoptotic cell death during erythroid differentiation. Apoptosis 2004, 9, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea, J.; Sharma, R.; Yang, F.; Zhu, H.; Ward, E.S.; Schroit, A.J. Detection of phosphatidylserine-positive exosomes as a diagnostic marker for ovarian malignancies: A proof of concept study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 14395–14407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zernecke, A.; Bidzhekov, K.; Noels, H.; Shagdarsuren, E.; Gan, L.; Denecke, B.; Hristov, M.; Köppel, T.; Jahantigh, M.N.; Lutgens, E.; et al. Delivery of microRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci. Signal 2009, 2, ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.Y.; Chen, C.J. Toward characterizing extracellular vesicles at a single-particle level. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, M.; Parcina, M.; Heyder, P.; Foermer, S.; Ostrop, J.; Leo, A.; Heeg, K.; Herrmann, M.; Lorenz, H.M.; Bekeredjian-Ding, I. Induction of type I IFN is a physiological immune reaction to apoptotic cell-derived membrane microparticles. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berda-Haddad, Y.; Robert, S.; Salers, P.; Zekraoui, L.; Farnarier, C.; Dinarello, C.A.; Dignat-George, F.; Kaplanski, G. Sterile inflammation of endothelial cell-derived apoptotic bodies is mediated by interleukin-1alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20684–20689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiller, M.; Bekeredjian-Ding, I.; Heyder, P.; Blank, N.; Ho, A.D.; Lorenz, H.M. Autoantigens are translocated into small apoptotic bodies during early stages of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhsin-Sharafaldine, M.R.; Kennedy, B.R.; Saunderson, S.C.; Buchanan, C.R.; Dunn, A.C.; Faed, J.M.; McLellan, A.D. Mechanistic insight into the procoagulant activity of tumor-derived apoptotic vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhsin-Sharafaldine, M.R.; Saunderson, S.C.; Dunn, A.C.; Faed, J.M.; Kleffmann, T.; McLellan, A.D. Procoagulant and immunogenic properties of melanoma exosomes, microvesicles and apoptotic vesicles. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56279–56294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, J.H.; Huber, L.C.; Hueber, A.J.; Reich, C.F.; Gay, S.; Distler, O.; Pisetsky, D.S. The release of microparticles by apoptotic cells and their effects on macrophages. Apoptosis 2005, 10, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Flores, L.; Gutiérrez, R.; Alvarez-Argüelles, H.; Díaz-Flores, L., Jr.; González, R.; Martín-Vasallo, P.; Carrasco, J.L. Extracellular multivesicular bodies in tissues affected by inflammation/repair and tumors. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2018, 42, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, L.; Szeles, A.; Rajnavölgyi, E.; Folkman, J.; Klein, G.; Ernberg, I.; Falk, K.I. Horizontal transfer of DNA by the uptake of apoptotic bodies. Blood 1999, 93, 3956–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Battistelli, M.; Falcieri, E. Apoptotic Bodies: Particular Extracellular Vesicles Involved in Intercellular Communication. Biology 2020, 9, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9010021
Battistelli M, Falcieri E. Apoptotic Bodies: Particular Extracellular Vesicles Involved in Intercellular Communication. Biology. 2020; 9(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleBattistelli, Michela, and Elisabetta Falcieri. 2020. "Apoptotic Bodies: Particular Extracellular Vesicles Involved in Intercellular Communication" Biology 9, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9010021
APA StyleBattistelli, M., & Falcieri, E. (2020). Apoptotic Bodies: Particular Extracellular Vesicles Involved in Intercellular Communication. Biology, 9(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9010021