An Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties of Stabilized Oil-In-Water Emulsions Using Different Cationic Surfactant Blends for Potential Use in the Cosmetic Industry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Surface Tension and Contact Angle Measurements
2.3. Determination of the Required HLB for the Oil Phase
2.4. Preparation of Emulsions
2.5. Accelerated Stability Tests
2.6. Zeta Potential, pH, and Conductivity Measurements
2.7. Particle Size Analysis
2.8. Rheological Profile and Viscosity
2.9. Creaming Index (CI)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Tension and Contact Angle Measurements
3.2. Determining the Required HLB for the Oil Phase
3.3. Emulsion Preparation
3.4. Accelerated Stability Tests
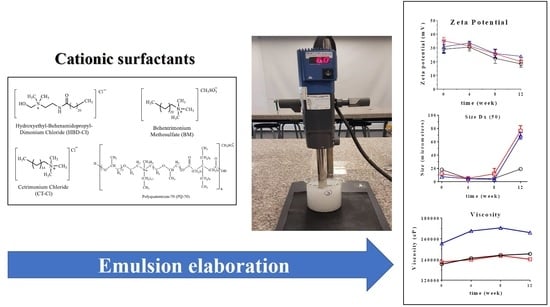
3.5. pH, Electrical Conductivity, Zeta Potential, and Droplet Size
3.6. Rheological Profile and Viscosity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Im, S.H.; Jeong, Y.H.; Ryoo, J.J. Simultaneous analysis of anionic, amphoteric, nonionic and cationic surfactant mixtures in shampoo and hair conditioner by RP-HPLC/ELSD and LC/MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 619, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Perchyonok, V.T. Stability of high internal phase emulsions with sole cationic surfactant and its tailoring morphology of porous polymers based on the emulsions. Polymer 2008, 50, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askvik, K.M.; Gundersen, S.A.; Sjöblom, J.; Merta, J.; Stenius, P. Complexation between lignosulfonates and cationic surfactants and its influence on emulsion and foam stability. Colloids Surf. 1999, 159, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; Gillies, G.; Gore, J.; Saunders, B.R. Flocculation and Coalescence of Oil-in-Water Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 227, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataller, H.; Lamaallam, S.; Lachaise, J.; Graciaa, A.; Dicharry, C. Cutting fluid emulsions produced by dilution of a cutting fluid concentrate containing a cationic/nonionic surfactant mixture. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 152, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, D.; Trevisan, A.; Lapasin, R.; Partal, P.; Gallegos, C. Rheological characterization of polysaccharide–surfactant matrices for cosmetic O/W emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 290, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, K.; Cui, Z.; Binks, B.P. Switchable pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a conventional cationic surfactant. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BinKs, B.P.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Frith, W.J. Synergistic interaction in emulsions stabilized bya mixture of silica nono particles and cationic surfactant. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3626–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.V.; Robbins, C.R.; Barnhurst, J.D. Sorption of Ouaternary Ammonium Surfactants by Human Hair. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1969, 20, 135–152. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidts, T.; Schlupp, P.; Gross, A.; Dobler, D.; Runkel, F. Required HLB Determination of Some Pharmaceutical Oils in Submicron Emulsions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2012, 33, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, R.C.; Taurozzi, M.P.; Bregni, C. Some considerations about the hydrophilic–lipophilic balance system. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 356, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.; Pasquali, R.C.; Bregni, C.; Taurozzi, M.P.; Pasquali, R.C.; Bregni, C.; Taurozzi, M.P. New Values of the Required Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance for Oil in Water Emulsions of Solid Fatty Acids and Alcohols Obtained from Solubility Parameter and Dielectric Constant Values New Values of the Required Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance for Oil in W. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2009, 30, 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Rong, Z.; Ying, X. Calculation of hydrophile–lipophile balance for polyethoxylated surfactants by group contribution method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barel, A.; Paye, M.; Maibach, H. Cosmetic Science and Technology, 3rd ed.; Informa Healtcare: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781420069631. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Tao, D. An experimental study of stability of oil–water emulsion. Fuel Process. Technol. 2005, 86, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztukowski, D.M.; Yarranton, H.W. Oilfield solids and water-in-oil emulsion stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 285, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wydila, J.E.; Mark, D.I.; Brandt, L.M.; Neill, P.H. Leave-On or Rinse-Out Hair Care Conditioner Compositions Containing Silicone Quaternary Compounds and Thickeners. U.S. Patent No. 6,696,053, 24 February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, P.-C.; Ding, W.-H. Determination of alkyltrimethylammonium surfactants in hair conditioners and fabric softeners by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry with electron-impact and chemical ionization. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1027, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.D.; Neeson, M.J.; Dagastine, R.R.; Chan, D.Y.C.; Tabor, R.F. Measurement of surface and interfacial tension using pendant drop tensiometry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 454, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, H.; Wadewitz, T.; Winkelmann, J. Surface Tension of Pure Liquids and Binary Liquid Mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2003, 48, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, M. Work of Adhesion of a Sessile Drop to a Clean Surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 213, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, M.E. Young- Dupre Revisited. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3585–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacy, R. Contact Angle Measurement Technique for Rough Surfaces. Master’s, Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Klinkesorn, U.; Sophanodora, P.; Chinachoti, P.; McClements, D.J. Stability and rheology of corn oil-in-water emulsions containing maltodextrin. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, A.R.; Fustier, P.; Ramaswamy, H.S. Effect of added oil and modified starch on rheological properties, droplet size distribution, opacity and stability of beverage cloud emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posocco, P.; Perazzo, A.; Preziosi, V.; Laurini, E.; Pricl, S.; Guido, S. Interfacial tension of oil/water emulsions with mixed non-ionic surfactants: Comparison between experiments and molecular simulations. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 4723–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azum, N.; Rub, M.A.; Asiri, A.M.; Bawazeer, W.A. Micellar and interfacial properties of amphiphilic drug–non-ionic surfactants mixed systems: Surface tension, fluorescence and UV–vis studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 522, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mandal, A. Studies on interfacial behavior and wettability change phenomena by ionic and nonionic surfactants in presence of alkalis and salt for enhanced oil recovery. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 372, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B. Évaluation of Physico-Chemical Properties of Biorefinery-Derived Amphiphilic Molecules and Their Effects on Multi-Scale Biological Models; Université de Technologie de Compiègne: Compiègne, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gavazzoni Dias, M.F.R. Hair cosmetics: An overview. Int. J. Trichol. 2015, 7, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Puerto, M.; Bao, X.; Zhang, W.; Jin, J.; Su, Z.; Shen, S.; Hirasaki, G.; Miller, C. Synergism and Performance for Systems Containing Binary Mixtures of Anionic/Cationic Surfactants for Enhanced Oil Recovery. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2017, 20, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F. Experimental investigation of coal dust wetting ability of anionic surfactants with different structures. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 121, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.N.; Ambrusi, R.E.; Miraglia, D.B.; Schulz, E.P.; García, S.G.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Schulz, P.C. Evaluation of oil-in-water emulsions with cationic–anionic surfactants mixtures for potential use in the oil industry. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 490, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koiteh, Z. Conditioning Cleansing Cream. U.S. Patent No. 8,449,895, 28 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mirhosseini, H.; Tan, C.P.; Hamid, N.S.A.; Yusof, S. Effect of Arabic gum, xanthan gum and orange oil contents on ζ-potential, conductivity, stability, size index and pH of orange beverage emulsion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 315, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryżak, M.; Bieganowski, A. Methodological aspects of determining soil particle-size distribution using the laser diffraction method. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2011, 174, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Nanoscale characterization of human hair and hair conditioners. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 585–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krongsin, J.; Nuisin, R.; Noppakundilograt, S.; Kiatkamjornwong, S. Preparation and Assessment of Chitosan Encapsulated Menthol Microcapsules for Leave-on Conditioners. J. R. Inst. Thail. 2012, 37, 94–107. [Google Scholar]
- Verica, J.; Sovilj, L.B.P. Influence of hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose–sodium dodecylsulfate interaction on the solution conductivity and viscosity and emulsion stability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 41–49. [Google Scholar]






| Individual Component | Ingredients | % (w/w) |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Phase | Cetearyl-alcohol | 4.8 |
| Coco-caprylate | ||
| Shea butter | ||
| Viscosity agent | Hydroxy-ethyl-cellulose | 0.5 |
| Wetting agent | Glycerin | 0.2 |
| Preservative | Methyl-isothiazolinone | 0.2 |
| Phenethyl-alcohol | ||
| Propylene-Glycol-2-methyl ether | ||
| pH modifier | Citric acid | 0.05 |
| Emulsifier system | Lauryl-glucoside (neutral) | 0.2 |
| Cationic Surfactant 1 | 1 | |
| Cationic Surfactant 2 | ||
| Dispersing phase | Water | q.s. |
| Emulsified System Prototype | Cationic Surfactant Mixture | Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HBD-Cl and BT-MS | 1:3 |
| 2 | HBD-Cl and BT-MS | 1:1 |
| 3 | HBD-Cl and BT-MS | 3:1 |
| 4 | HBD-Cl and CT-Cl | 1:3 |
| 5 | HBD-Cl and CT-Cl | 1:1 |
| 6 | HBD-Cl and CT-Cl | 3:1 |
| 7 | HBD-Cl and PQ-70 | 1:3 |
| 8 | HBD-Cl and PQ-70 | 1:1 |
| 9 | HBD-Cl and PQ-70 | 3:1 |
| 10 | BT-MS and CT-Cl | 1:3 |
| 11 | BT-MS and CT-Cl | 1:1 |
| 12 | BT-MS and CT-Cl | 3:1 |
| 13 | BT-MS and PQ-70 | 1:3 |
| 14 | BT-MS and PQ-70 | 1:1 |
| 15 | BT-MS and PQ-70 | 3:1 |
| 16 | CT-Cl and PQ-70 | 1:3 |
| 17 | CT-Cl and PQ70 | 1:1 |
| 18 | CT-Cl and PQ-70 | 3:1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agredo, P.; Rave, M.C.; Echeverri, J.D.; Romero, D.; Salamanca, C.H. An Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties of Stabilized Oil-In-Water Emulsions Using Different Cationic Surfactant Blends for Potential Use in the Cosmetic Industry. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6010012
Agredo P, Rave MC, Echeverri JD, Romero D, Salamanca CH. An Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties of Stabilized Oil-In-Water Emulsions Using Different Cationic Surfactant Blends for Potential Use in the Cosmetic Industry. Cosmetics. 2019; 6(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgredo, Pamela, Maria C. Rave, Juan D. Echeverri, Daniela Romero, and Constain H. Salamanca. 2019. "An Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties of Stabilized Oil-In-Water Emulsions Using Different Cationic Surfactant Blends for Potential Use in the Cosmetic Industry" Cosmetics 6, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6010012
APA StyleAgredo, P., Rave, M. C., Echeverri, J. D., Romero, D., & Salamanca, C. H. (2019). An Evaluation of the Physicochemical Properties of Stabilized Oil-In-Water Emulsions Using Different Cationic Surfactant Blends for Potential Use in the Cosmetic Industry. Cosmetics, 6(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics6010012