The Application of ResNet-34 Model Integrating Transfer Learning in the Recognition and Classification of Overseas Chinese Frescoes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Cultural and Historical Background of Overseas Chinese
1.2. Fresco Culture
1.3. Fresco Recognition and Classification Methods
1.4. Heritage Conservation and Cultural Significance
2. Related Theories
2.1. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
2.2. Convolution Layer
2.3. ResNet-34 Network
2.4. Image Feature Extraction
2.5. Transfer Learning
3. Materials and Methods
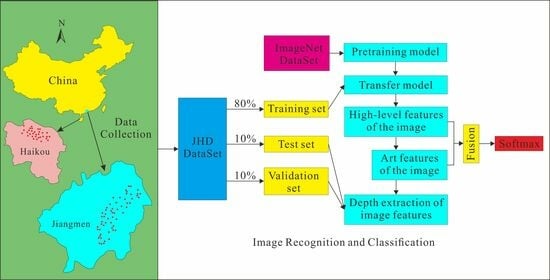
3.1. Study Area and Datasets
3.2. Data Preprocessing
3.3. Classification Model of Expatriate Frescoes Integrating Transfer Learning
3.4. Improved Classification Model for Overseas Chinese Frescoes
3.4.1. Integrating Transfer Learning to Enhance the Stability of the Model
3.4.2. Introducing Cross Entropy Function to Stabilize Model Gradient
3.4.3. Increasing the Number of Fully Connected Layers to Enhance Image Feature Expression
3.5. Classification Process of Overseas Chinese Architectural Frescoes
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Environment
4.2. Evaluation Index
4.3. Results and Analysis
4.3.1. Model Training and Validation
4.3.2. Comparison of Different Fresco Features
4.3.3. Comparison of Performance between Different Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Chan, C.K.D.; Chen, W. Research on Image Classification and Retrieval Using Deep Learning with Attention Mechanism on Diaspora Chinese Architectural Heritage in Jiangmen, China. Buildings 2023, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, F.; Vagnini, M.; Vivani, R.; Malagodi, M.; Fiocco, G. Non-invasive identification of red and yellow oxide and sulfide pigments in wall-paintings with portable ER-FTIR spectroscopy. J. Cult. Herit. 2023, 63, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Hernandez, R.; Antela, K.U.; Gallello, G.; Cervera, M.; Mauri-Aucejo, A.R. A smartphone-based innovative approach to discriminate red pigments in roman frescoes mock-ups. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 58, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego, E.; Herraez, J.; Denia, J.L.; Navarro, P. Technical study for restoration of mural paintings through the transfer of a photographic image to the vault of a church. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 58, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, R.; Wang, W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, M. Multi-analytical approach to the mural painting from an ancient tomb of Ming Dynasty in Jiyuan, China: Characterization of materials and techniques. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 279, 121419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerme, N.; Hegarat-Mascle, S.L.; Zhang, B.; Aldea, E. Fast and efficient reconstruction of digitized frescoes. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, D. Computer-Aided Virtual Restoration of Frescoes Based on Intelligent Generation of Line Drawings. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 1, 9092765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondi, P.; Lombardi, L.; Setti, A. DAFNE: A dataset of fresco fragments for digital anastlylosis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 138, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yan, M.; Jia, Y.; Tian, X. Application of inception-v3 model integrated with transfer learning in dynasty identification of ancient murals. J. Comput. Appl. 2021, 11, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Lu, D.; Yang, B.; Xu, D. Similarity metrics between mural images with constraints of the overall structure of contours. J. Image Graph. 2013, 8, 968–975. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, T.S.; Andrade, M.L.S.C.; Luz, M.R. Reconstruction of frescoes by sequential layers of feature extraction. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 147, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Gao, L.; Lu, Y.; Jing, H.; Hong, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, Z. Attention-guided cascaded network with pixel-importance-balance loss for retinal vessel segmentation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1196191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Intelligent identification and prediction mineral resources deposit based on deep learning. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najeeb, R.M.; Syed, A.R.A.; Usman, U.S.; Asma, C.; Nirvana, P. Cascading pose features with CNN-LSTM for multiview human action recognition. Signals 2023, 4, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedric, A.; Lionel, H.; Chiara, P.; Ondrej, M.; Olivier, C.; William, P.; Francesca, A.; Kiran, P.; Sophie, M. CNN-Based cell analysis: From image to quantitative representation. Front. Phys. 2022, 9, 776805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.; Giles, C.L.; Tsoi, A.C.; Back, A.D. Face recognition: A convolutional neural-network approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1997, 1, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.B.; Ma, F.; Zhou, J.M.; Du, C.W. Applying convolutional neural networks (CNN) for end-to-end soil analysis based on laser- induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) with less spectral preprocessing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, G.; Moyal, V.; Nandankar, P.; Pandithurai, O.; Pimo, E.S. A novel CNN method for the accurate spatial data recovery from digital images. Mater. Proc. 2021, 80, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrage-Alava, J.; Alcivar-Cevallos, R.; Riascos, J.A.; Becerra, M.A. Aphids detection on lemons leaf image using convolutional neural networks. Systems and Information Sciences. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020, 1273, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raki, H.; Gonzalez-Vergara, J.; Aalaila, Y.; Elhamdi, M.; Bamansour, S.; Guachi-Guachi, L.; Peluffo-Ordonez, D.H. Crop classification using deep learning: A quick comparative study of modern approaches. Applied Informatics. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 1643, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 11, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, K.; Ilya, S.; Geoffrey, E.H. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Y.; Zajicek, G.; Werman, M.; Pizov, G.; Sherman, Y. Similarity measurement method for the classification of architecturally differentiated images. Comput. Biomed. Res. Int. J. 1999, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarimajd, A.; Hoertel, N.; Hussain, M.A.; Neshat, A.A.; Marhamati, M.; Bakhtoor, M.; Momeny, M. Learning-to-augment incorporated noise-robust deep CNN for detection of COVID-19 in noisy X-ray images. J. Comput. Sci. 2022, 63, 101763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.J.; Xu, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, K.; Li, H.X.; Ma, L.F.; Li, J. Mask R-CNN based automated identification and extraction of oil well sites. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Park, K.R. MTS-CNN: Multi-task semantic segmentation-convolutional neural network for detecting crops and weeds. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 199, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsinelli, M.; Cinque, L.; Placidig, G. A light CNN for detecting COVID-19 from CT scans of the chest. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 140, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, S.; Patidar, S.; Xia, X.; Liang, Q.H.; Neal, J.; Pender, G. A deep convolutional neural network model for rapid prediction of fluvial flood inundation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks. Comput. Vis. ECCV 2016, 9908, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.Z.; Xue, J.N.; Duan, F.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.H. An exploratory study of transfer learning frameworks in the context of few available shots of neurophysiological signals. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 101, 108091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael, L.J.; Jose, M.M.; Casilari, E. Analytical and empirical evaluation of the impact of Gaussian noise on the modulations employed by Bluetooth Enhanced Data Rates. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2012, 2012, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, Z.; Ren, W. Linear contrast enhancement network for low-illumination image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D. Kriging-weighted laplacian kernels for grayscale image sharpening. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 57094–57106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tian, Y.Z. Research and analysis of deep learning image enhancement algorithm based on fractional differential. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 131, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Goyal, G.; Chandel, A. AlexNet architecture based convolutional neural network for toxic comments classification. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 7547–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, A.; Topuz, V.; Midi, I. Motor imagery EEG signal classification using image processing technique over GoogLeNet deep learning algorithm for controlling the robot manipulator. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 72, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Zhao, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, M.; Shen, S.; Wang, W. One-dimensional VGGNet for high-dimensional data. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 135, 110035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Layer Name | Output Size | 34-Layer |
|---|---|---|
| conv1 | 112 × 112 | 7 × 7, 64, stride 2 |
| Max pooling | 3 × 3 | stride 2 |
| conv2_x | 56 × 56 | |
| conv3_x | 28 × 28 | 4 |
| conv4_x | 14 × 14 | |
| conv5_x | 7 × 7 | |
| Global Average Pooling | ||
| Fully Connected Layer | ||
| Softmax | ||
| Number | LR | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.01 | 89.80% |
| 2 | 0.001 | 94.37% |
| 3 | 0.0001 | 98.41% |
| Color Feature | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Original Image | 98.41% |
| Increase Grayscale Value | 36.88% |
| Saturation Add | 96.65% |
| Inverse Transformation | 71.26% |
| Resolution Ratio | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 224 × 224 | 98.41% |
| 448 × 448 | 91.58% |
| 896 × 896 | 89.79% |
| Model | Accuracy | Recall Rate |
|---|---|---|
| AlexNet-10 | 85.41% | 83.79% |
| AlexNet-S6 | 86.68% | 84.55% |
| GoogLeNet | 90.29% | 89.61% |
| VGGNet-16 | 89.26% | 88.15% |
| Ours | 98.41% | 98.53% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Wang, B.; Li, J. The Application of ResNet-34 Model Integrating Transfer Learning in the Recognition and Classification of Overseas Chinese Frescoes. Electronics 2023, 12, 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173677
Gao L, Zhang X, Yang T, Wang B, Li J. The Application of ResNet-34 Model Integrating Transfer Learning in the Recognition and Classification of Overseas Chinese Frescoes. Electronics. 2023; 12(17):3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173677
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Le, Xin Zhang, Tian Yang, Baocang Wang, and Juntao Li. 2023. "The Application of ResNet-34 Model Integrating Transfer Learning in the Recognition and Classification of Overseas Chinese Frescoes" Electronics 12, no. 17: 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173677
APA StyleGao, L., Zhang, X., Yang, T., Wang, B., & Li, J. (2023). The Application of ResNet-34 Model Integrating Transfer Learning in the Recognition and Classification of Overseas Chinese Frescoes. Electronics, 12(17), 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173677