A Dynamic Emotional Propagation Model over Time for Competitive Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Objectives and Contributions
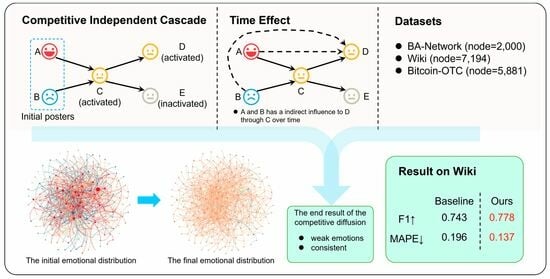
- To study how to build an appropriate emotional propagation rule in a competitive environment with the ability to capture the influence of opinion leaders.
- To study how individuals’ emotions evolve over time.
- Instead of the predetermined partial time snippet, the proposed method models a continuous emotional propagation process over a complete event with a time-decay effect.
- We propose a novel dynamic emotional propagation model based on an independent cascade to describe the competitive environment.
- Experimental results prove that our proposed model outperforms baseline methods in emotional propagation research. It reveals that emotions in social networks are assimilated by opinion leaders, eventually become weak, and tend to be consistent.
2. Related Work
2.1. Information Diffusion
2.2. Emotional Propagation
3. Method
3.1. Problem Formalization
3.2. Reinforced Poisson Process
3.3. Model Description
| Algorithm 1 Algorithmic description of DepIC |
Input: N: The number of users. E: The matrix storing the social relationship of users. T: The number of evolutionary steps. : A set storing the initial opinion leaders. O: The N-dimensional vector storing the emotional values of users. Output:Y: The matrix storing the emotions of users at each time step.
|
- Lines 3–5 update the emotional values of all users according to the emotional cascade path at each time step.
- Lines 6–10 walk through all the activated users from previous time steps and calculate the propagation probability to judge whether their inactive neighbors should activate or not.
- Lines 11–15 will happen if an activation action occurs. The user v who is activated successfully by u would update his/her emotional value, build up the link in the emotional cascade path, and become the active user in the next time step.
- Lines 19–21 transform the emotional value into specific emotions in each time step.
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metric
4.3. Baselines
4.4. Experimental Settings
4.5. Simulation Experiment
4.6. Experimental Results
4.7. Case Study
5. Theoretical and Practical Implications
5.1. Theoretical Implication
5.2. Practical Implication
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dezecache, G.; Jacob, P.; Grèzes, J. Emotional contagion: Its scope and limits. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2015, 19, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, E.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Rapson, R.L. Emotional contagion. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 1993, 2, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, S.; Kempe, D.; Salek, M. Competitive Influence Maximization in Social Networks. In Proceedings of the Internet and Network Economics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4858, pp. 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Neumann, S. A Viral Marketing-Based Model For Opinion Dynamics in Online Social Networks. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, WWW ’22. Association for Computing Machinery, Virtual, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Xiong, F.; Pan, S.; Wang, L.; Xiong, X. Hierarchical attention neural network for information cascade prediction. Inf. Sci. 2023, 622, 1109–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Danny Du, B.; Wang, S.; Li, D. Position-Enhanced and Time-Aware Graph Convolutional Network for Sequential Recommendations. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2023, 41, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Chen, D.B.; Zhou, T. The small world yields the most effective information spreading. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 123005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovetter, M. Threshold models of collective behavior. Am. J. Sociol. 1978, 83, 1420–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, J.; Libai, B.; Muller, E. Talk of the network: A complex systems look at the underlying process of word-of-mouth. Mark. Lett. 2001, 12, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wang, D.; Song, C.; Barabási, A. Modeling and Predicting Popularity Dynamics via Reinforced Poisson Processes. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Québec City, QC, Canada, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 291–297. Available online: http://www.aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI14/paper/view/8370 (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Nickel, M.; Le, M. Modeling Sparse Information Diffusion at Scale via Lazy Multivariate Hawkes Processes. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021 WWW ’21. Association for Computing Machinery, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 19–23 April 2021; pp. 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhan, M.; Kou, G.; Ding, Z.; Liang, H. A survey on the fusion process in opinion dynamics. Inf. Fusion 2018, 43, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, P.; Sudbury, A. A model for spatial conflict. Biometrika 1973, 60, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galam, S.; Gefen, Y.; Shapir, Y. Sociophysics: A new approach of sociological collective behaviour. I. mean-behaviour description of a strike. J. Math. Sociol. 1982, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sznajd-Weron, K.; Sznajd, J. Opinion evolution in closed community. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2000, 11, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lin, Z.; Jin, Y.; Cheng, S.; Yang, T. ESIS: Emotion-based spreader-ignorant-stifler model for information diffusion. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 81, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deffuant, G.; Neau, D.; Amblard, F.; Weisbuch, G. Mixing beliefs among interacting agents. Adv. Complex Syst. 2000, 3, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegselmann, R.; Krause, U. Opinion dynamics and bounded confidence: Models, analysis and simulation. J. Artifical Soc. Soc. Simul. 2002, 5. Available online: http://jasss.soc.surrey.ac.uk/5/3/2.html (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Moreno, Y.; Nekovee, M.; Vespignani, A. Efficiency and reliability of epidemic data dissemination in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 055101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S. Efficient influence maximization in social networks. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’09, Paris, France, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Li, Y.; Qiao, S.; Han, N.; Wu, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, B. An emotional contagion model for heterogeneous social media with multiple behaviors. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 490, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Huberman, B.A. Novelty and collective attention. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17599–17601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, C.; Wang, T.; Wen, S.; Chen, C.; Xiang, Y. Capturing Dynamics of Information Diffusion in SNS: A Survey of Methodology and Techniques. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 22:1–22:51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y. An information diffusion model based on retweeting mechanism for online social media. Phys. Lett. A 2012, 376, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guan, Z.H.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, D.X. A stochastic SIR epidemic on scale-free network with community structure. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2013, 392, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Rizoiu, M.A.; Xie, L. Modeling Information Cascades with Self-Exciting Processes via Generalized Epidemic Models. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, WSDM ’20, Houston, TX, USA, 3–7 February 2020; pp. 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Ratkiewicz, J.; Perra, N.; Gonçalves, B.; Castillo, C.; Bonchi, F.; Schifanella, R.; Menczer, F.; Flammini, A. The Role of Information Diffusion in the Evolution of Social Networks. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’13, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013; pp. 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsaka, N.; Sonobe, T.; Fujita, S.; Kawarabayashi, K.i. Coarsening Massive Influence Networks for Scalable Diffusion Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Conference on Management of Data, SIGMOD ’17, Singapore, 6–10 November 2017; pp. 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Ohara, K.; Yamagishi, Y.; Kimura, M.; Motoda, H. Learning Diffusion Probability Based on Node Attributes in Social Networks. In Proceedings of the Foundations of Intelligent Systems, ISMIS 2011, Warsaw, Poland, 28–30 June 2011; Volume 6804, pp. 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shen, H.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, X.; Liao, X. CT LIS: Learning Influences and Susceptibilities through Temporal Behaviors. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2019, 13, 57:1–57:21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y. Opinion-aware information diffusion model based on multivariate marked Hawkes process. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 279, 110883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierri, F.; Piccardi, C.; Ceri, S. Topology comparison of Twitter diffusion networks effectively reveals misleading information. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, A.K. Temporal Pattern of Retweet(s) Help to Maximize Information Diffusion in Twitter. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, WSDM ’20, Houston, TX, USA, 3–7 February 2020; pp. 913–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourigault, S.; Lamprier, S.; Gallinari, P. Representation Learning for Information Diffusion through Social Networks: An Embedded Cascade Model. In Proceedings of the Ninth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–25 February 2016; pp. 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, J.; Guo, X.; Mei, Q. DeepCas: An End-to-End Predictor of Information Cascades. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web, WWW ’17, Perth, Australia, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Shen, H.; Cen, K.; Ouyang, W.; Cheng, X. DeepHawkes: Bridging the Gap between Prediction and Understanding of Information Cascades. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, CIKM ’17, Singapore, 6–10 November 2017; pp. 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, W. Hierarchical Diffusion Attention Network. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI 2019, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; pp. 3828–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S. DyHGCN: A Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Convolutional Network to Learn Users’ Dynamic Preferences for Information Diffusion Prediction. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases—European Conference, ECML PKDD 2020, Ghent, Belgium, 14–18 September 2020; Volume 12459, pp. 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liao, D.; Huang, W.; Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Shen, M. Fully Exploiting Cascade Graphs for Real-time Forwarding Prediction. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtually, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, L.; Katarya, R.; Sachdeva, S. Opinion Leaders for Information Diffusion Using Graph Neural Network in Online Social Networks. ACM Trans. Web 2023, 17, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lu, W.; Zhang, N. Time-Critical Influence Maximization in Social Networks with Time-Delayed Diffusion Process. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–26 July 2012; pp. 592–598. Available online: http://www.aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI12/paper/view/5024 (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, J.; Paris, C.; Nepal, S. Learning Influence Probabilities and Modelling Influence Diffusion in Twitter. In Proceedings of the Companion of the 2019 World Wide Web Conference, WWW 2019, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Q.; Du, R. Identifying underlying influential factors in information diffusion process on social media platform: A hybrid approach of data mining and time series regression. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Yue, Z. Understanding information diffusion with psychological field dynamic. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, B.; Molaei, S.; Pan, S.; Rahimi, S.A. GCNFusion: An efficient graph convolutional network based model for information diffusion. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Chang, C.; Liu, Y. Consensus and Polarization of Binary Opinions in Structurally Balanced Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2016, 3, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.; Sly, A. Evolving voter model on dense random graphs. Ann. Appl. Probab. 2017, 27, 1235–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Xia, X.; Pan, Y.; She, Y.; Feng, X.; Wu, J. Sentiment mutation and negative emotion contagion dynamics in social media: A case study on the Chinese Sina Microblog. Inf. Sci. 2022, 594, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ding, Z.; Martínez-López, L.; Herrera, F. Managing consensus based on leadership in opinion dynamics. Inf. Sci. 2017, 397, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gao, J. The Co-Evolution Model for Social Network Evolving and Opinion Migration. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Association for Computing Machinery, Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 August 2017; pp. 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, X. An emotion role mining approach based on multiview ensemble learning in social networks. Inf. Fusion 2022, 88, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Duan, W. Large-scale three-way group consensus decision considering individual competition behavior in social networks. Inf. Sci. 2023, 641, 119077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, D.; Musial, K.; Dang, J. Topic Enhanced Sentiment Spreading Model in Social Networks Considering User Interest. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 989–996. Available online: https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/5447 (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Gomez-Rodriguez, M.; Balduzzi, D.; Schölkopf, B. Uncovering the Temporal Dynamics of Diffusion Networks. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2011, Bellevue, WA, USA, 28 June–2 July 2011; pp. 561–568. Available online: https://icml.cc/2011/papers/354_icmlpaper.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2023).
- Barabási, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovec, J.; Huttenlocher, D.P.; Kleinberg, J.M. Signed networks in social media. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–15 April 2010; pp. 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovec, J.; Huttenlocher, D.P.; Kleinberg, J.M. Predicting positive and negative links in online social networks. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web, WWW 2010, Raleigh, NC, USA, 26–30 April 2010; pp. 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Spezzano, F.; Subrahmanian, V.S.; Faloutsos, C. Edge Weight Prediction in Weighted Signed Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining, ICDM 2016, Barcelona, Spain, 12–15 December 2016; pp. 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Hooi, B.; Makhija, D.; Kumar, M.; Faloutsos, C.; Subrahmanian, V.S. REV2: Fraudulent User Prediction in Rating Platforms. In Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, WSDM 2018, Marina Del Rey, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2018; pp. 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Prakash, B.A.; Li, L.; Faloutsos, C. Rise and fall patterns of information diffusion: Model and implications. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’12, Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2012; pp. 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Time-Series/Data-Driven | Method | Contributions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time-series | SIR-based | Distinguished the different states of individuals during information diffusion on a macroscopic scale | [25,26,27] |
| Graph models | Observed how individuals affect each other on a microscopic scale | [28,29,30] | |
| Stochastic processes | Modeled the time effect and exciting mechanism | [11,12,31,32] | |
| Data-driven | Feature learning | Captured the representative features to reveal important factors influencing information diffusion | [33,34,35] |
| Deep learning | Improved prediction accuracy with neural networks | [36,37,38,39,40,41] |
| Discrete/Continuous Models | Method | Contributions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discrete | Binary classification | Established fundamental emotional propagation rules between individuals | [14,15,16,47,48] |
| Multi-classification | Expanded more categories to describe fine-grained emotions | [17,49] | |
| Continuous | Neighbor-based | Improved the case for either positive or negative in the discrete approach | [18,19] |
| Network-based | Expanded the scale of emotional propagation abilities to portray complex social phenomena. | [22,50,51,52,53] |
| Datasets | Nodes | Edges | Avg_Degree | Positive | Emotions Neutral | Negative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA Network | 2000 | 5991 | 5.991 | - | - | - |
| WIKI | 7194 | 110,087 | 30.605 | 4926 | 1332 | 936 |
| Bitcoin-OTC | 5881 | 35,592 | 12.104 | 5159 | 169 | 553 |
| Parameters | Wiki | Bitcoin-OTC |
|---|---|---|
| Activation Intensity | 0.15 | 0.3 |
| Positive Emotion Intensity | 0.2 | 0.35 |
| Negative Emotion Intensity | 0.1 | 0.25 |
| Time Decay factor | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| Maximum Propagation Step T | 80 | 80 |
| Datasets | WIKI | Bitcoin-OTC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | Precision | Recall | F1-score | MAPE↓ | Precision | Recall | F1-score | MAPE↓ |
| ESIS | 0.815 | 0.576 | 0.675 | 0.360 | 0.963 | 0.747 | 0.841 | 0.792 |
| eIC | 0.741 | 0.336 | 0.462 | 0.675 | 0.957 | 0.272 | 0.424 | 2.537 |
| TSSM | 0.813 | 0.684 | 0.743 | 0.196 | 0.874 | 0.964 | 0.917 | 0.367 |
| DepIC | 0.739 | 0.821 | 0.778 | 0.137 | 0.879 | 0.966 | 0.921 | 0.354 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Xu, B.; Cai, T.; Yang, Z.; Liao, X. A Dynamic Emotional Propagation Model over Time for Competitive Environments. Electronics 2023, 12, 4937. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12244937
Chen Z, Xu B, Cai T, Yang Z, Liao X. A Dynamic Emotional Propagation Model over Time for Competitive Environments. Electronics. 2023; 12(24):4937. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12244937
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhihao, Bingbing Xu, Tiecheng Cai, Zhou Yang, and Xiangwen Liao. 2023. "A Dynamic Emotional Propagation Model over Time for Competitive Environments" Electronics 12, no. 24: 4937. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12244937
APA StyleChen, Z., Xu, B., Cai, T., Yang, Z., & Liao, X. (2023). A Dynamic Emotional Propagation Model over Time for Competitive Environments. Electronics, 12(24), 4937. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12244937