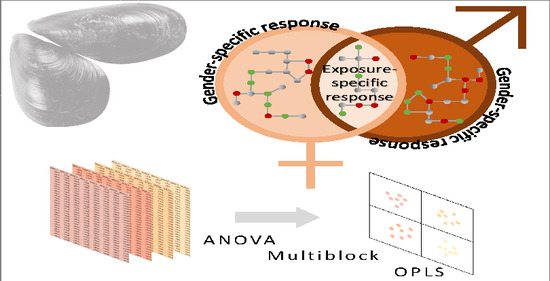
Multifactorial Analysis of Environmental Metabolomic Data in Ecotoxicology: Wild Marine Mussel Exposed to WWTP Effluent as a Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. General Overview of the Dataset
2.2. Contribution of Experimental Factors to the Total Variability
2.3. Impact of Exposure
2.4. Impact of the Interaction Exposure × Gender
2.5. Perspective of Environmental Metabolomics in Ecotoxicology Based on Multifactorial Experiments
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. WWTP Effluent Extract Preparation
3.3. Animals and Experimental Design
3.4. Tissue Sample Preparation
3.5. Metabolic Fingerprint LC-HRMS Analysis
3.6. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3.6.1. Data Processing
3.6.2. Analysis of Variance Multiblock Orthogonal Partial Least Squares (AMOPLS)
3.6.3. Multivariate Metabolite Selection and Univariate Statistical Evaluation
3.7. Metabolite Annotation and Identification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fent, K.; Weston, A.; Caminada, D. Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76, 122–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; Meyer, M.T.; Thurman, M.E.; Zaugg, S.D.; Barber, L.B.; Buxton, H.T. Pharmaceuticals, Hormones, and Other Organic Wastewater Contaminants in U.S. Streams, 1999−2000: A National Reconnaissance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loos, R.; Carvalho, R.; António, D.C.; Comero, S.; Locoro, G.; Tavazzi, S.; Paracchini, B.; Ghiani, M.; Lettieri, T.; Blaha, L.; et al. EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpin-Pont, L.; Bueno, M.J.M.; Gomez, E.; Fenet, H. Occurrence of PPCPs in the marine environment: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4978–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodder, N.G.; Maruya, K.A.; Lee Ferguson, P.; Grace, R.; Klosterhaus, S.; La Guardia, M.J.; Lauenstein, G.G.; Ramirez, J. Occurrence of contaminants of emerging concern in mussels (Mytilus spp.) along the California coast and the influence of land use, storm water discharge, and treated wastewater effluent. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzelani, M.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environments: Evidence of emerged threat and future challenges for marine organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot Groz, M.; Martinez Bueno, M.J.; Rosain, D.; Fenet, H.; Casellas, C.; Pereira, C.; Maria, V.; Bebianno, M.J.; Gomez, E. Detection of emerging contaminants (UV filters, UV stabilizers and musks) in marine mussels from Portuguese coast by QuEChERS extraction and GC-MS/MS. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Avila, J.; Tauler, R.; Lacorte, S. Organic micropollutants in coastal waters from NW Mediterranean Sea: Sources distribution and potential risk. Environ. Int. 2012, 46, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankadurai, B.P.; Nagato, E.G.; Simpson, M.J. Environmental metabolomics: an emerging approach to study organism responses to environmental stressors. Environ. Rev. 2013, 21, 180–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Viant, M.R.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Metabolomics: methodologies and applications in the environmental sciences. J. Pestic. Sci. 2006, 31, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.G. Environmental Metabolomics: A SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats). J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courant, F.; Antignac, J.-P.; Dervilly-Pinel, G.; Le Bizec, B. Basics of mass spectrometry based metabolomics. Proteomics 2014, 14, 2369–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.M. Establishing Causality between Environmental Stressors and Effects on Aquatic Ecosystems. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2003, 9, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J. A framework and methods for incorporating gender-related issues in wildlife risk assessment: gender-related differences in metal levels and other contaminants as a case study. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Feswick, A.; Simmons, D.; Martyniuk, C.J. Environmental toxicology and omics: A question of sex. J. Proteomics 2018, 172, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClellan-Green, P.; Romano, J.; Oberdörster, E. Does gender really matter in contaminant exposure? A case study using invertebrate models. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Vervoort, J.; Maslowska-Górnicz, A.; Van den Brink, N.; Beekmann, K. Use of proteomics to detect sex-related differences in effects of toxicants: implications for using proteomics in toxicology. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2018, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, C.; Wu, H.; Wei, L.; Zhao, J.; Yu, J. Proteomic and metabolomic analysis reveal gender-specific responses of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis to 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 47). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–141, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Jia, X.; Cai, W. Gender-specific metabolic responses in gonad of mussel Perna viridis to triazophos. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Z.; Wu, H. An integrated proteomic and metabolomic study on the gender-specific responses of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis to tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA). Chemosphere 2016, 144, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Wei, L.; Zhao, J.; Wu, H. Metabolomic analysis revealed that female mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis was sensitive to bisphenol A exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, J.A.; Cope, W.G.; Barnhart, M.C.; Bringolf, R.B. Metabolomic, behavioral, and reproductive effects of the aromatase inhibitor fadrozole hydrochloride on the unionid mussel Lampsilis fasciola. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 206, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Y. Gender-specific metabolic responses in hepatopancreas of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis challenged by Vibrio harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 40, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Alfaro, A.C.; Merien, F.; Young, T.; Grandiosa, R. Metabolic and immunological responses of male and female new Zealand GreenshellTM mussels (Perna canaliculus) infected with Vibrio sp. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 157, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.B.D.; Benskin, J.P.; Cosgrove, J.R.; Duncker, B.P.; Ekman, D.R.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Sherry, J.P. Omics for aquatic ecotoxicology: Control of extraneous variability to enhance the analysis of environmental effects. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boccard, J.; Rudaz, S. Harnessing the complexity of metabolomic data with chemometrics. J. Chemom. 2014, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccard, J.; Rudaz, S. Exploring Omics data from designed experiments using analysis of variance multiblock Orthogonal Partial Least Squares. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 920, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, T.; Bonnefille, B.; Gomez, E.; Boccard, J.; Castro, N.A.; Fenet, H.; Courant, F. Metabolomics approach reveals disruption of metabolic pathways in the marine bivalve Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to a WWTP effluent extract. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, P.; Micalizzi, G.; Oteri, M.; Rigano, F.; Sciarrone, D.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Comprehensive lipid profiling in the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) using hyphenated and multidimensional chromatography techniques coupled to mass spectrometry detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3297–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, L.; Losito, I.; Cianci, C.; Cataldi, T.R.I.; Palmisano, F. Structural characterization and profiling of lyso-phospholipids in fresh and in thermally stressed mussels by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography—electrospray ionization—Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudicella, V.A.; Whitfield, P.D.; Carboni, S.; Doherty, M.K.; Hughes, A.D. Application of lipidomics in bivalve aquaculture, a review. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokina, N.N.; Ruokolainen, T.R.; Bakhmet, I.N.; Nemova, N.N. Role of lipids in adaptation of mussels Mytilus edulis L. of the White Sea to rapid changes in temperature. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 457, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makide, K.; Kitamura, H.; Sato, Y.; Okutani, M.; Aoki, J. Emerging lysophospholipid mediators, lysophosphatidylserine, lysophosphatidylthreonine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine and lysophosphatidylglycerol. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2009, 89, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergent, O.; Morel, I.; Cillard, J. Involvement of metal ions in lipid peroxidation: biological implications. Met. Ions Biol. Syst. 1999, 36, 251–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albergamo, A.; Rigano, F.; Purcaro, G.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S.; Mondello, L. Free fatty acid profiling of marine sentinels by nanoLC-EI-MS for the assessment of environmental pollution effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappello, T.; Fernandes, D.; Maisano, M.; Casano, A.; Bonastre, M.; Bebianno, M.J.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S.; Porte, C. Sex steroids and metabolic responses in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to drospirenone. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokina, N.N.; Ruokolainen, T.R.; Nemova, N.N.; Bakhmet, I.N. Changes of Blue Mussels Mytilus edulis L. Lipid Composition Under Cadmium and Copper Toxic Effect. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 154, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peteiro, L.G.; Labarta, U.; Fernández-Reiriz, M.J. Variability in biochemical components of the mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) cultured after Prestige oil spill. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 145, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signa, G.; Di Leonardo, R.; Vaccaro, A.; Tramati, C.D.; Mazzola, A.; Vizzini, S. Lipid and fatty acid biomarkers as proxies for environmental contamination in caged mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.-H.; Chan, M.-L.; Marathe, G.K.; Parveen, F.; Chen, C.-H.; Ke, L.-Y. An Updated Review of Lysophosphatidylcholine Metabolism in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balsinde, J.; Winstead, M.V.; Dennis, E.A. Phospholipase A2 regulation of arachidonic acid mobilization. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deridovich, I.I.; Reunova, O.V. Prostaglandins: Reproduction control in bivalve molluscs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1993, 104, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pita, I.; Sánchez-Lazo, C.; Ruíz-Jarabo, I.; Herrera, M.; Mancera, J.M. Biochemical composition, lipid classes, fatty acids and sexual hormones in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis from cultivated populations in south Spain. Aquaculture 2012, 358–359, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Portuguez, R.; Sutphin, G.L. Kynurenine pathway, NAD+ synthesis, and mitochondrial function: Targeting tryptophan metabolism to promote longevity and healthspan. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 132, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ruiz, V.; Pezzatti, J.; Roux, A.; Stoppini, L.; Boccard, J.; Rudaz, S. Unravelling the effects of multiple experimental factors in metabolomics, analysis of human neural cells with hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography hyphenated to high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1527, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonnefille, B.; Gomez, E.; Alali, M.; Rosain, D.; Fenet, H.; Courant, F. Metabolomics assessment of the effects of diclofenac exposure on Mytilus galloprovincialis: Potential effects on osmoregulation and reproduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, M.C.; Maclean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, C.; Tautenhahn, R.; Böttcher, C.; Larson, T.R.; Neumann, S. CAMERA: An Integrated Strategy for Compound Spectra Extraction and Annotation of Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Data Sets. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling of animal and human tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccard, J.; Tonoli, D.; Strajhar, P.; Jeanneret, F.; Odermatt, A.; Rudaz, S. Removal of batch effects using stratified subsampling of metabolomic data for in vitro endocrine disruptors screening. Talanta 2019, 195, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Factor | RSS | p-Value | Block Contributions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tp1 | tp2 | tp3 | to | |||
| Gender | 3.6% | >0.05 | 3.6% | 7.3% | 84.1% | 25.5% |
| Exposure | 7.5% | <0.01 | 89.2% | 6.1% | 4.9% | 23.2% |
| Gender × Exposure | 3.9% | <0.05 | 3.5% | 78.7% | 5.4% | 25.1% |
| Residuals | 85.0% | N/A | 3.7% | 6.9% | 5.5% | 26.2% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumas, T.; Boccard, J.; Gomez, E.; Fenet, H.; Courant, F. Multifactorial Analysis of Environmental Metabolomic Data in Ecotoxicology: Wild Marine Mussel Exposed to WWTP Effluent as a Case Study. Metabolites 2020, 10, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070269
Dumas T, Boccard J, Gomez E, Fenet H, Courant F. Multifactorial Analysis of Environmental Metabolomic Data in Ecotoxicology: Wild Marine Mussel Exposed to WWTP Effluent as a Case Study. Metabolites. 2020; 10(7):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070269
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumas, Thibaut, Julien Boccard, Elena Gomez, Hélène Fenet, and Frédérique Courant. 2020. "Multifactorial Analysis of Environmental Metabolomic Data in Ecotoxicology: Wild Marine Mussel Exposed to WWTP Effluent as a Case Study" Metabolites 10, no. 7: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070269
APA StyleDumas, T., Boccard, J., Gomez, E., Fenet, H., & Courant, F. (2020). Multifactorial Analysis of Environmental Metabolomic Data in Ecotoxicology: Wild Marine Mussel Exposed to WWTP Effluent as a Case Study. Metabolites, 10(7), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070269