Exploring Metabolic Signature of Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Metabolic Profiles Separation between Groups Using Multivariate Data Analysis
2.2. Metabolites Identification and Quantification
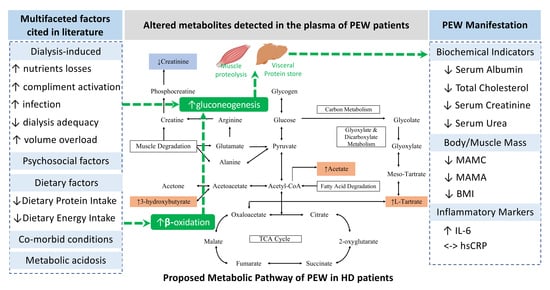
2.3. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
2.4. Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subject Selection and Grouping
4.2. Plasma Samples Collection and Biochemical Analysis
4.3. Sample Preparation for Metabolite Profiling
4.4. 1H-NMR Analysis
4.5. Multivariate Data Analysis
4.6. Metabolites Identification, Quantification and Pathway Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrero, J.J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Cuppari, L.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kaysen, G.; Mitch, W.E.; Price, S.R.; Wanner, C.; Wang, A.Y.M.; et al. Etiology of the Protein-Energy Wasting Syndrome in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Statement From the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM). J. Ren. Nutr. 2013, 23, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obi, Y.; Qader, H.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Latest Consensus and Update on Protein Energy-Wasting in Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 18, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Iguacel, C.; González-Parra, E.; Barril-Cuadrado, G.; Sánchez, R.; Egido, J.; Ortiz-Arduán, A.; Carrero, J.J. Defining protein-energy wasting syndrome in chronic kidney disease: Prevalence and clinical implications. Nefrologia 2014, 34, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.A.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Elder, S.J.; Ginsberg, N.; Goodkin, D.A.; Pifer, T.; Lameire, N.; Marshall, M.R.; Asano, Y.; Akizawa, T. Independent and joint associations of nutritional status indicators with mortality risk among chronic hemodialysis patients in the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). J. Ren. Nutr. 2010, 20, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, R. Daily protein intake and survival in patients on peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3715–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chmielewski, M.; Carrero, J.J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Axelsson, J.; Heimbürger, O.; Berglund, L.; Barany, P.; Rutkowski, B.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Temporal discrepancies in the association between the apoB/apoA-I ratio and mortality in incident dialysis patients. J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouque, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.; Cano, N.; Chauveau, P.; Cuppari, L.; Franch, H.; Guarnieri, G.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kaysen, G.; et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein–energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frisancho, A.R. New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 2540–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imboden, M.T.; Swartz, A.M.; Finch, H.W.; Harber, M.P.; Kaminsky, L.A. Reference standards for lean mass measures using GE dual energy x-ray absorptiometry in Caucasian adults. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, B.B.; Bross, R.; Morrison, G.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.D. Self-Reported Interview-Assisted Diet Records Underreport Energy Intake in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2015, 25, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaz, I.M.F.; Freitas, A.T.V.d.S.; Peixoto, M.d.R.G.; Ferraz, S.F.; Campos, M.I.V.A.M. Is energy intake underreported in hemodialysis patients? Braz. J. Nephrol. 2015, 37, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Koh, E.S.; Shin, S.J.; Park, C.W. Malnutrition in patients with chronic kidney disease. Open J. Intern. Med. 2012, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bharadwaj, S.; Ginoya, S.; Tandon, P.; Gohel, T.D.; Guirguis, J.; Vallabh, H.; Jevenn, A.; Hanouneh, I. Malnutrition: Laboratory markers vs nutritional assessment. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 4, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Barany, P.; Chung, S.H.; Lindholm, B.; Heimbürger, O. A comparative analysis of nutritional parameters as predictors of outcome in male and female ESRD patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struijk, D.G.; Krediet, R.T.; Koomen, G.C.; Boeschoten, E.W.; Arisz, L. The effect of serum albumin at the start of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis treatment on patient survival. Perit. Dial. Int. 1994, 14, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama-Axelsson, T.; Heimbürger, O.; Stenvinkel, P.; Bárány, P.; Lindholm, B.; Qureshi, A.R. Serum albumin as predictor of nutritional status in patients with ESRD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Qian, Q. Protein Nutrition and Malnutrition in CKD and ESRD. Nutrients 2017, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajis, N.; Maulidiani, M.; Abas, F.; Ismail, I.S. Metabolomics Approach in Pharmacognosy. Pharmacognosy 2017, 597–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanczyk-Wochniak, E.; Luedemann, A.; Kopka, J.; Selbig, J.; Roessner-Tunali, U.; Willmitzer, L.; Fernie, A.R. Parallel analysis of transcript and metabolic profiles: A new approach in systems biology. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horgan, R.P.; Kenny, L.C. Omic technologies: Proteomics and metabolomics. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 13, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, A.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, H.; Gong, L.; Chen, E.; Cui, N.; Ji, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, H. Metabolomics Research Reveals the Mechanism of Action of Astragalus Polysaccharide in Rats with Digestive System Disorders. Molecules 2018, 23, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shommu, N.S.; Jenne, C.N.; Blackwood, J.; Joffe, A.R.; Martin, D.A.; Thompson, G.C.; Vogel, H.J. Metabolomic and inflammatory mediator based biomarker profiling as a potential novel method to aid pediatric appendicitis identification. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheelock, Å.M.; Wheelock, C.E. Trials and tribulations of ’omics data analysis: Assessing quality of SIMCA-based multivariate models using examples from pulmonary medicine. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, L.; Johansson, E.; Kettaneh-Wold, N.; Trygg, J.; Wikstrom, C.; Wold, S. Multi- and Megavariate Data Analysis. Part I Basic Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; MKS Umetrics AB: Umea, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, L.; Trygg, J.; Wold, S. CV-ANOVA for significance testing of PLS and OPLS® models. J. Chemom. 2008, 22, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Mehrotra, R.; Rhee, C.M.; Molnar, M.Z.; Lukowsky, L.R.; Patel, S.S.; Nissenson, A.R.; Kopple, J.D.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Serum creatinine level, a surrogate of muscle mass, predicts mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Streja, E.; Molnar, M.Z.; Lukowsky, L.R.; Krishnan, M.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Greenland, S. Mortality prediction by surrogates of body composition: An examination of the obesity paradox in hemodialysis patients using composite ranking score analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 175, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, C.-T.; Yabes, J.; Pike, F.; Weiner, D.E.; Beddhu, S.; Burrowes, J.D.; Rocco, M.V.; Unruh, M.L. Changes in Anthropometry and Mortality in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients in the HEMO Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hoedt, C.H.; Bots, M.L.; Grooteman, M.P.C.; van der Weerd, N.C.; Penne, E.L.; Mazairac, A.H.A.; Levesque, R.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Nubé, M.J.; ter Wee, P.M.; et al. Clinical predictors of decline in nutritional parameters over time in ESRD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.M.; Jeon, J.Y.; Lee, B.J.; Lee, H.; Choi, H.K. Application of metabolomics to quality control of natural product derived medicines. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cañadas-Garre, M.; Anderson, K.; McGoldrick, J.; Maxwell, A.P.; McKnight, A.J. Proteomic and metabolomic approaches in the search for biomarkers in chronic kidney disease. J. Proteomics 2019, 193, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, L.; Chen, J.; Yin, P.; Lu, X.; Xu, G. Serum metabonomics study of chronic renal failure by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with Q-TOF mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, P.W. Metabolic changes in malnutrition. Eye 2005, 19, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, P.S. Adaptation to low energy intakes: The responses and limits to low intakes in infants, children and adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, s14–s33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roshanravan, B.; Zelnick, L.R.; Djucovic, D.; Gu, H.; Alvarez, J.A.; Ziegler, T.R.; Gamboa, J.L.; Utzschneider, K.; Kestenbaum, B.; Himmelfarb, J.; et al. Chronic kidney disease attenuates the plasma metabolome response to insulin. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e122219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagavan, N.V. Medical Biochemistry, 4th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 485–519. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L. (Eds.) Food intake and starvation induce metabolic changes. In Biochemistry; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, R.; Greenhaff, P.; Curtis, S.; Perry, A.; Cowley, A.J. The effect of dietary creatine supplementation on skeletal muscle metabolism in congestive heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 1998, 19, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaysen, G.A. Diabetes, a cause of progressive sarcopenia in dialysis patients? Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2396–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Axelsson, J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Divino-Filho, J.C.; Bárány, P.; Heimbürger, O.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Are insulin-like growth factor and its binding proteins 1 and 3 clinically useful as markers of malnutrition, sarcopenia and inflammation in end-stage renal disease? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, A. Biochemistry of Hypoglycin and Toxic Hypoglycemic Syndrome. In Food Safety and Quality Systems in Developing Countries; Gordon, A., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, P.F.; Dice, J.F. Proteolytic and lipolytic responses to starvation. Nutrition 2006, 22, 830–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanikarla-Marie, P.; Jain, S.K. Hyperketonemia and ketosis increase the risk of complications in type 1 diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhyu, H.-S.; Cho, S.-Y.; Roh, H.-T. The effects of ketogenic diet on oxidative stress and antioxidative capacity markers of Taekwondo athletes. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2014, 10, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, S.; Jarrett, I.; Filsell, O.; Ballard, F. Production and utilization of acetate in mammals. Biochem. J. 1974, 142, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, E.J. On the nature of malonate-insensitive oxidation of pyruvate and glutamate by heart sarcosomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1968, 162, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Korff, R.W. Substrate Transformations dependent on Respiratory States of Mitochondria: Changes in Metabolic Control Sites of Rabbit Heart Mitochondria. Nature 1967, 214, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, D.J.; Tubbs, P.K. Carnitine and derivatives in rat tissues. Biochem. J. 1967, 105, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snoswell, A.M.; Koundakjian, P.P. Relationships between carnitine and coenzyme A esters in tissues of normal and alloxan-diabetic sheep. Biochem. J. 1972, 127, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jarrett, I.G.; Filsell, O.H.; Ballard, F.J. Metabolic and endocrine interrelationships in normal and diabetic sheep. Horm. Metab. Res. 1974, (Suppl. 4), 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Fituri, N.; Allawi, N.; Bentley, M.; Costello, J. The effect of a high intake of tartaric acid on urinary and plasma oxalate. In Urolithiasis and Related Clinical Research; Schwille, P.O., Smith, L.H., Robertson, W.G., Vahlensieck, W., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 379–382. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, M.H.M. Acidulants for Foods and Beverages; Food Trade Press: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Butch, C.; Cope, E.D.; Pollet, P.; Gelbaum, L.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Liotta, C.L. Production of tartrates by cyanide-mediated dimerization of glyoxylate: A potential abiotic pathway to the citric acid cycle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13440–13445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertow, G.M.; Johansen, K.L.; Lew, N.; Lazarus, J.M.; Lowrie, E.G. Vintage, nutritional status, and survival in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beckonert, O.P.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Bundy, J.G.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geamanu, A.; Gupta, S.V.; Bauerfeld, C.; Samavati, L. Metabolomics connects aberrant bioenergetic, transmethylation, and gut microbiota in sarcoidosis. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregory, J.F.; Park, Y.; Lamers, Y.; Bandyopadhyay, N.; Chi, Y.Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; da Silva, V.; Hove, N.; Ranka, S.; et al. Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Extended Metabolic Consequences of Marginal Vitamin B-6 Deficiency in Healthy Human Subjects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maulidiani; Abas, F.; Khatib, A.; Perumal, V.; Suppaiah, V.; Ismail, A.; Hamid, M.; Shaari, K.; Lajis, N.H. Metabolic alteration in obese diabetes rats upon treatment with Centella asiatica extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 180, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Shi, Q.; Feng, F. Metabolomics approach to identify therapeutically potential biomarkers of the Zhi-Zi-Da-Huang decoction effect on the hepatoprotective mechanism. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 84048–84055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Tian, N.; Yang, M.; Kong, L. 1H NMR-based metabolomics approach to evaluate the effect of Xue-Fu-Zhu-Yu decoction on hyperlipidemia rats induced by high-fat diet. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 78, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altermann, E.; Klaenhammer, T.R. PathwayVoyager: Pathway mapping using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Characteristics | PEW Subjects (n = 53) | NPEW Subjects (n = 53) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Age (years) | 55 ± 14 | 56 ± 14 | ns |
| Gender (males, %) | 29 (54.7) | 29 (54.7) | ns |
| Ethnicity | ns | ||
| Malay (n, %) | 8 (15.1) | 11 (20.8) | |
| Chinese (n, %) | 36 (67.9) | 32 (60.4) | |
| Indian (n, %) | 9 (17) | 10 (18.9) | |
| Clinical and Biochemistry | |||
| Dialysis vintage (months) | 89.96 ± 85.52 | 58.74 ± 56.30 | 0.041 |
| Kt/V | 1.28 ± 0.97 | 1.17 ± 0.69 | ns |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 712 ± 160 | 891 ± 214 | <0.001 |
| Serum urea (mmol/L) | 18.88 ± 4.43 | 20.88 ± 5.14 | 0.036 |
| Insulin (mU/L) | 6.75 ± 5.29 | 13.83 ± 5.85 | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.84 ± 1.80 | 4.23 ± 2.82 | <0.001 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 3.71 ± 3.28 | 5.73 ± 5.87 | ns |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 7.15 ± 5.66 | 4.27 ± 3.58 | 0.006 |
| Parameters | Cutoff for PEW Criterion | PEW Subjects (n = 53) | NPEW Subjects (n = 53) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochemical | ||||
| Serum albumin (g/L) | <3.8 g/dl | 36.45 ± 4.85 | 39.77 ± 3.62 | <0.001 |
| TC (mmol/L) | <2.59 mmol/L | 4.21 ± 1.16 | 4.07 ± 0.93 | ns |
| Body Mass | ||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | <23 kg/m2 | 20.34 ± 2.68 | 26.76 ± 3.74 | <0.001 |
| Muscle Mass | ||||
| MAMC (cm) | Decreased mid-arm muscle circumference area (reduction >10% in relation to 50th percentile of reference population) | 20.31 ± 2.63 | 24.63 ± 2.68 | <0.001 |
| MAMA (cm2) | Muscle mass loss >5% over 3 months or >10% over 6 months | 24.95 ± 7.68 | 40.48 ± 10.75 | <0.001 |
| Dietary Intake | ||||
| DEI (kcal/kg IBW/day) | <0.80 g/kg/day for at least 2 months | 22.63 ± 4.49 | 24.67 ± 7.55 | 0.040 |
| DPI (g/kg IBW/day) | <25 kcal/kg/day for at least 2 months | 0.90 ± 0.29 | 0.94 ± 0.37 | ns |
| Metabolites | PEW | NPEW | Differences | p-Value | Adjusted pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Hydroxybutyrate | 0.051 ± 0.008 | 0.024 ± 0.002 | 0.027 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| Acetate | 0.188 ± 0.006 | 0.172 ± 0.005 | 0.017 | 0.027 | 0.039 |
| Arabinose | 0.228 ± 0.020 | 0.222 ± 0.034 | 0.006 | 0.029 | ns |
| Maltose | 0.174 ± 0.014 | 0.157 ± 0.022 | 0.0164 | 0.021 | ns |
| Ribose | 0.523 ± 0.035 | 0.459 ± 0.038 | 0.0645 | 0.041 | ns |
| Sucrose | 0.144 ± 0.117 | 0.111 ± 0.010 | 0.0333 | 0.008 | ns |
| Tartrate | 0.202 ± 0.027 | 0.182 ± 0.032 | 0.0202 | 0.018 | ns |
| Creatinine | 0.270 ± 0.008 | 0.331 ± 0.010 | −0.0609 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pauzi, F.A.; Sahathevan, S.; Khor, B.-H.; Narayanan, S.S.; Zakaria, N.F.; Abas, F.; Karupaiah, T.; Daud, Z.A.M. Exploring Metabolic Signature of Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients. Metabolites 2020, 10, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070291
Pauzi FA, Sahathevan S, Khor B-H, Narayanan SS, Zakaria NF, Abas F, Karupaiah T, Daud ZAM. Exploring Metabolic Signature of Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients. Metabolites. 2020; 10(7):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070291
Chicago/Turabian StylePauzi, Fatin Athirah, Sharmela Sahathevan, Ban-Hock Khor, Sreelakshmi Sankara Narayanan, Nor Fadhlina Zakaria, Faridah Abas, Tilakavati Karupaiah, and Zulfitri Azuan Mat Daud. 2020. "Exploring Metabolic Signature of Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients" Metabolites 10, no. 7: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070291
APA StylePauzi, F. A., Sahathevan, S., Khor, B.-H., Narayanan, S. S., Zakaria, N. F., Abas, F., Karupaiah, T., & Daud, Z. A. M. (2020). Exploring Metabolic Signature of Protein Energy Wasting in Hemodialysis Patients. Metabolites, 10(7), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070291