The Increased Expression of Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 2 (RGS2) Inhibits Insulin-Induced Akt Phosphorylation and Is Associated with Uncontrolled Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
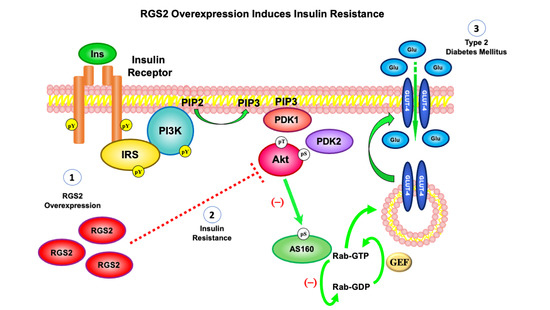
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PA Increased RGS2 Expression in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial-CS (HUVEC-CS) Cells
2.2. The Overexpression of RGS2 Inhibited Insulin-Induced Akt Phosphorylation
2.3. Platelets from T2DM Patients Displayed Increased RGS2 Protein Expression
2.4. Principal Component Analysis Displayed a Positive Correlation between the RGS2 Protein Expression Level and the Percentage of Glycated Hemoglobin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.3. Study Population
4.3.1. Ethical Statement
4.3.2. Subjects
4.3.3. Measurement of Serum Parameters
4.4. Preparation of Human Plasma and Platelets Purification
4.5. Immunoblot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Multidimensional Correlation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olivares-Reyes, J.A.; Arellano-Plancarte, A.; Castillo-Hernandez, J.R. Angiotensin II and the development of insulin resistance: Implications for diabetes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: Integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Rodelo, C.; Roura-Guiberna, A.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance: An update. Gac. Med. Mex. 2017, 153, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, C.M.; Belsham, D.D. Palmitate attenuates insulin signaling and induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in hypothalamic neurons: Rescue of resistance and apoptosis through adenosine 5′ monophosphate-activated protein kinase activation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Jimenez, J.G.; Chavez-Reyes, J.; Romero-Garcia, T.; Zarain-Herzberg, A.; Valdes-Flores, J.; Galindo-Rosales, J.M.; Rueda, A.; Guerrero-Hernandez, A.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. Palmitic acid but not palmitoleic acid induces insulin resistance in a human endothelial cell line by decreasing SERCA pump expression. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, M.; Willard, F.S.; Kimple, A.J.; Turnbull, A.P.; Ball, L.J.; Schoch, G.A.; Gileadi, C.; Fedorov, O.Y.; Dowler, E.F.; Higman, V.A.; et al. Structural diversity in the RGS domain and its interaction with heterotrimeric G protein alpha-subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6457–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heximer, S.P.; Watson, N.; Linder, M.E.; Blumer, K.J.; Hepler, J.R. RGS2/G0S8 is a selective inhibitor of Gqα function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14389–14393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klepac, K.; Yang, J.; Hildebrand, S.; Pfeifer, A. RGS2: A multifunctional signaling hub that balances brown adipose tissue function and differentiation. Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcnabb, H.J.; Zhang, Q.; Sjögren, B. Emerging roles for regulator of G protein signaling 2 in (patho)physiology. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 98, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-S.; Kim, J.I.; Noh, M.; Rhee, M.H.; Park, K.M. Regulator of G protein signaling 2 (RGS2) deficiency accelerates the progression of kidney fibrosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Kim, D.S.; Wu, H.; Sjögren, B.; Gao, W.; Luttrell, L.; Wang, H. Regulator of G protein signaling 2 is a key regulator of pancreatic β-cell mass and function. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, M.-X.; Roy, A.A.; Zhao, Q.; Kirshenbaum, L.A.; Karmazyn, M.; Chidiac, P. RGS2 is upregulated by and attenuates the hypertrophic effect of α1-adrenergic activation in cultured ventricular myocytes. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, C.; Zhao, P.; Zou, M.X.; Summers, K.; Guglielmo, C.G.; Chidiac, P. Resistance to age-related, normal body weight gain in RGS2 deficient mice. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-C.; Zhang, X.-Y. Role of regulator of G protein signaling in desensitization of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide receptor. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4470–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, M.; Ceolotto, G.; Dorigatti, F.; Mos, L.; Santonastaso, M.; Bratti, P.; Papparella, I.; Semplicini, A.; Palatini, P. RGS2 C1114G polymorphism and body weight gain in hypertensive patients. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2008, 57, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freson, K.; Stolarz, K.; Aerts, R.; Brand, E.; Brand-Herrmann, S.M.; Kawecka-Jaszcz, K.; Kuznetsova, T.; Tikhonoff, V.; Thijs, L.; Vermylen, J.; et al. -391 C to G substitution in the regulator of G-protein signalling-2 promoter increases susceptibility to the metabolic syndrome in white European men: Consistency between molecular and epidemiological studies. J. Hypertens. 2007, 25, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizuka, M.; Honda, K.; Tsuchiya, T.; Nishihara, T.; Imagawa, M. RGS2 promotes adipocyte differentiation in the presence of ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29625–29627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imagawa, M.; Tsuchiya, T.; Nishihara, T. Identification of inducible genes at the early stage of adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 254, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zheng, H.; Wei, N.; Nathan, D.M. Estimating HbA1c from timed self-monitored blood glucose values. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 141, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pérez, F.J. Glycated hemoglobin, fasting, two-hour post-challenge and postprandial glycemia in the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus: Are we giving them the right interpretation and use? Rev. Investig. Clin. 2015, 67, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- UKPDS-Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UKPDS-Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998, 352, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubig, R.R.; Siderovski, D.P. Regulators of G-Protein signalling as new central nervous system drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.B.; Wilkinson, J.C.; Roman, D.L. Regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS) proteins as drug targets: Progress and future potentials. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 18571–18585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iankova, I.; Chavey, C.; Clapé, C.; Colomer, C.; Guérineau, N.C.; Grillet, N.; Brunet, J.-F.o.; Annicotte, J.-S.b.; Fajas, L. Regulator of g protein signaling-4 controls fatty acid and glucose homeostasis. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 5706–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivot, K.; Moullé, V.S.; Zarrouki, B.; Tremblay, C.; Mancini, A.D.; Maachi, H.; Ghislain, J.; Poitout, V. The regulator of G-protein signaling RGS16 promotes insulin secretion and β-cell proliferation in rodent and human islets. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Wang, X.; Xiao, J.; Chen, K.; Zhou, H.; Shen, D.; Li, H.; Tang, Q. Loss of regulator of G protein signaling 5 exacerbates obesity, hepatic steatosis, inflammation and insulin resistance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.N.; Lu, X.; Nguyen, C.; Feng, Q.; Chidiac, P. Cardiomyocyte specific overexpression of a 37 amino acid domain of regulator of G protein signalling 2 inhibits cardiac hypertrophy and improves function in response to pressure overload in mice. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2017, 108, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nunn, C.; Zou, M.X.; Sobiesiak, A.J.; Roy, A.A.; Kirshenbaum, L.A.; Chidiac, P. RGS2 inhibits beta-adrenergic receptor-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briscoe, C.P.; Tadayyon, M.; Andrews, J.L.; Benson, W.G.; Chambers, J.K.; Eilert, M.M.; Ellis, C.; Elshourbagy, N.A.; Goetz, A.S.; Minnick, D.T.; et al. The orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR40 is activated by medium and long chain fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11303–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Cáceres, M.P.; Toledo-Valenzuela, L.; Díaz-Castro, F.; Ávalos, Y.; Burgos, P.; Narro, C.; Peña-Oyarzun, D.; Espinoza-Caicedo, J.; Cifuentes-Araneda, F.; Navarro-Aguad, F.; et al. Palmitic acid reduces the autophagic flux and insulin sensitivity through the activation of the free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFAR1) in the hypothalamic neuronal cell line N43/5. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, H.; Shachar, S.; Sekler, I.; Hershfinkel, M.; Walker, M.D. Role of GPR40 in fatty acid action on the beta cell line INS-1E. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Hui, L.; Zheng, K.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Lv, W. Silencing of RGS2 enhances hippocampal neuron regeneration and rescues depression-like behavioral impairments through activation of cAMP pathway. Brain Res. 2020, 1746, 147018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.L.; Lassègue, B.; Griendling, K.K.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Lyons, P.R.; Alexander, R.W. Specific regulation of RGS2 messenger RNA by angiotensin II in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raveh, A.; Schultz, P.J.; Aschermann, L.; Carpenter, C.; Tamayo-Castillo, G.; Cao, S.; Clardy, J.; Neubig, R.R.; Sherman, D.H.; Sjögren, B. Identification of protein kinase C activation as a novel mechanism for RGS2 protein upregulation through phenotypic screening of natural product extracts. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 86, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Jimenez, J.G.; Roura-Guiberna, A.; Jimenez-Mena, L.R.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. Role of free fatty acids on insulin resistance. Gac. Med. Mex. 2018, 2018, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, Y.; Hongwei, W.; Ueno, H.; Mizuta, M.; Nakazato, M. Telmisartan attenuates fatty-acid-induced oxidative stress and NAD(P)H oxidase activity in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, T.; Vollenweider, P.; Egawa, K.; Clodi, M.; Ishibashi, K.; Nakashima, N.; Ugi, S.; Adams, J.W.; Brown, J.H.; Olefsky, J.M. G alpha-q/11 protein plays a key role in insulin-induced glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 6765–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sears, D.D.; Hsiao, A.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Chapman, J.; He, W.; Olefsky, J.M. Selective modulation of promoter recruitment and transcriptional activity of PPARgamma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Zhao, P.; Sobiesiak, A.J.; Chidiac, P. RGS2 is a component of the cellular stress response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.J.; Chidiac, P. RGS2 promotes the translation of stress-associated proteins ATF4 and CHOP via its eIF2B-inhibitory domain. Cell. Signal. 2019, 59, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, S13–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pienimaeki-Roemer, A.; Kuhlmann, K.; Bottcher, A.; Konovalova, T.; Black, A.; Orso, E.; Liebisch, G.; Ahrens, M.; Eisenacher, M.; Meyer, H.E.; et al. Lipidomic and proteomic characterization of platelet extracellular vesicle subfractions from senescent platelets. Transfusion 2015, 55, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okutucu, B.; Dincer, A.; Habib, O.; Zihnioglu, F. Comparison of five methods for determination of total plasma protein concentration. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Healthy | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Gender | Age | HbA1c | RGS2 Densitometry | BMI (Kg/m2) | TC (mg/dL) | TGC (mg/dL) | HDL (mg/dL) | LDL (mg/dL) | ID | Gender | Age | HbA1c | RGS2 Densitometry | BMI (Kg/m2) |
| P3 | Female | 60 | 5.6% | 138.4991 | 31.63 | 193 | 202 | 47 | 105.6 | 1 | Male | 25 | 5.0 | 100 | 20.4 |
| P6 | Male | 59 | 5.7% | 237.5115 | 21.73 | 161 | 127 | 52 | 83.6 | 2 | Male | 27 | 4.8 | 103.2773 | 19.9 |
| P9 | Female | 58 | 6.1% | 270.1421 | 20.31 | 260 | 205 | 73 | 70 | 3 | Female | 23 | 4.8 | 100 | 21.5 |
| P14 | Female | 58 | 6.2% | 356.1189 | 37.28 | 199 | 565 | 36 | 50 | 4 | Male | 23 | 5.4 | 116.2006 | 20.2 |
| P13 | Male | 67 | 7.3% | 312.7119 | 30.82 | 172 | 108 | 55 | 95.4 | 5 | Female | 24 | 5.0 | 100 | 21.2 |
| P4 | Female | 29 | 7.4% | 568.4774 | 26.17 | 163 | 74 | 54 | 94.2 | 6 | Female | 24 | 4.4 | 93.20259 | 17.3 |
| P8 | Female | 52 | 7.5% | 465.9215 | 35.086 | 148 | 120 | 56 | 68 | ||||||
| P10 | Male | 50 | 7.6% | 440.2003 | 30.47 | 147 | 90 | 42 | 87 | ||||||
| P11 | Male | 48 | 7.9% | 681.8213 | 32.62 | 151 | 210 | 28.9 | 80.1 | ||||||
| P17 | Female | 35 | 9.5% | 856.7031 | 29.31 | 173 | 232 | 25 | 101.6 | ||||||
| P2 | Male | 57 | 10% | 330.433 | 30.035 | 247 | 355 | 43 | 133 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vazquez-Jimenez, J.G.; Corpus-Navarro, M.S.; Rodriguez-Chavez, J.M.; Jaramillo-Ramirez, H.J.; Hernandez-Aranda, J.; Galindo-Hernandez, O.; Machado-Contreras, J.R.; Trejo-Trejo, M.; Guerrero-Hernandez, A.; Olivares-Reyes, J.A. The Increased Expression of Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 2 (RGS2) Inhibits Insulin-Induced Akt Phosphorylation and Is Associated with Uncontrolled Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites 2021, 11, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020091
Vazquez-Jimenez JG, Corpus-Navarro MS, Rodriguez-Chavez JM, Jaramillo-Ramirez HJ, Hernandez-Aranda J, Galindo-Hernandez O, Machado-Contreras JR, Trejo-Trejo M, Guerrero-Hernandez A, Olivares-Reyes JA. The Increased Expression of Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 2 (RGS2) Inhibits Insulin-Induced Akt Phosphorylation and Is Associated with Uncontrolled Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites. 2021; 11(2):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020091
Chicago/Turabian StyleVazquez-Jimenez, J. Gustavo, M. Stephanie Corpus-Navarro, J. Miguel Rodriguez-Chavez, Hiram J. Jaramillo-Ramirez, Judith Hernandez-Aranda, Octavio Galindo-Hernandez, J. Rene Machado-Contreras, Marina Trejo-Trejo, Agustin Guerrero-Hernandez, and J. Alberto Olivares-Reyes. 2021. "The Increased Expression of Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 2 (RGS2) Inhibits Insulin-Induced Akt Phosphorylation and Is Associated with Uncontrolled Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes" Metabolites 11, no. 2: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020091
APA StyleVazquez-Jimenez, J. G., Corpus-Navarro, M. S., Rodriguez-Chavez, J. M., Jaramillo-Ramirez, H. J., Hernandez-Aranda, J., Galindo-Hernandez, O., Machado-Contreras, J. R., Trejo-Trejo, M., Guerrero-Hernandez, A., & Olivares-Reyes, J. A. (2021). The Increased Expression of Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 2 (RGS2) Inhibits Insulin-Induced Akt Phosphorylation and Is Associated with Uncontrolled Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Metabolites, 11(2), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020091