Metagenomic, Metabolomic, and Functional Evaluation of Kimchi Broth Treated with Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Abstract
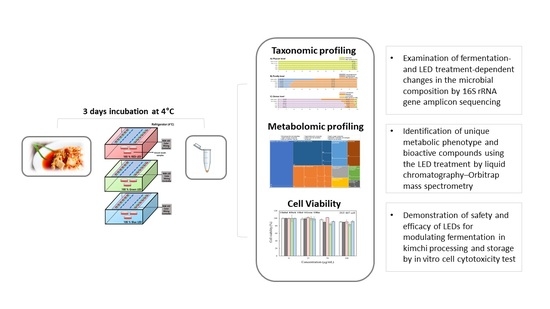
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Compositional Characteristics of Kimchi Microbiota Treated Using Different Colors of LED Treatment
2.2. Metabolomic Modulation Triggered by Different Colors of LED Treatment
2.3. Cellular Toxicity of Kimchi Broth Extracts Treated with LEDs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Light Emitting Diode (LED) Light Chamber Setup
3.3. LED Treatment
3.4. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification, Quantification, and Metagenome Sequencing of 16S Ribosomal RNA
3.5. Metagenomics Sequence Analysis
3.6. Metabolomic Analysis of Kimchi Extracts
3.7. Statistical Analysis
3.8. Cell Viability Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jeon, C.O. Kimchi microflora: History, current status, and perspectives for industrial kimchi production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.A.; Pichiah, P.B.T.; Yu, J.J.; Oh, S.-H.; Daily, J.W.; Cha, Y.S. Anti-obesity effect of kimchi fermented with Weissella koreensis OK1-6 as starter in high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.Y.; Jeong, J.K.; Lee, Y.E.; Daily, J.W. Health benefits of kimchi (korean fermented vegetables) as a probiotic food. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Choi, Y.; Yoon, Y. Lactic acid bacteria in kimchi might be a cause for carcinogen production in intestine. Food Control 2021, 126, 108045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Paramithiotis, S.; Shin, H.S. Kimchi and other widely consumed traditional fermented foods of Korea: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.-K.; Cho, E.J.; Park, K.Y. Anti-aging activity of kimchi during fermentation period against oxidative stress-induced premature senescence in cellular model. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 340.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.H.; Park, H.D. Isolation and Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Producing Antimutagenic Substance from Korean Kimchi. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 1999, 27, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Mun, E.G.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Park, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Cha, Y.S. A survey of research papers on the health benefits of kimchi and kimchi lactic acid bacteria. J. Nutr. Health 2018, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.M.; Park, M.S.; Bae, J.W.; Hahn, Y.; Madsen, E.L.; Jeon, C.O. Metagenomic analysis of kimchi, a Traditional Korean fermented food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, C.J.; Kunz, B. Identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from kimchi and studies on their suitability for application as starter culture in the production of fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Whon, T.W.; Roh, S.W.; Jeon, C.O. Unraveling microbial fermentation features in kimchi: From classical to meta-omics approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7731–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nam, Y.; Chang, H.W.; Kim, K.H.; Roh, S.W.; Bae, J.W. Metatranscriptome analysis of lactic acid bacteria during kimchi fermentation with genome-probing microarrays. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 130, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, L.B.; Martins, T.J.; da Silva, R.S.; Hamblin, M.R. Photobiomodulation combined with photodynamic therapy using ruthenium phthalocyanine complexes in A375 melanoma cells: Effects of nitric oxide generation and ATP production. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 198, 111564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, A.P.; Demidova, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: Part one—photosensitizers, photochemistry and cellular localization. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2004, 1, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwiatkowski, S.; Knap, B.; Przystupski, D.; Saczko, J.; Kędzierska, E.; Knap-Czop, K.; Kotlińska, J.; Michel, O.; Kotowski, K.; Kulbacka, J. Photodynamic therapy—Mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharkwal, G.B.; Sharma, S.K.; Huang, Y.Y.; Dai, T.; Hamblin, M.R. Photodynamic therapy for infections: Clinical applications. Lasers Surg. Med. 2011, 43, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polat, E.; Kang, K. Natural Photosensitizers in Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogonowska, P.; Woźniak, A.; Pierański, M.; Wasylew, T.; Kwiek, P.; Brasel, M.; Grinholc, M.; Nakonieczna, J. Application and characterization of light-emitting diodes for photodynamic inactivation of bacteria. Light. Res. Technol. 2019, 51, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, C.P.; Wainwright, M.; dos Anjos, C.; Sellera, F.P.; Baptista, M.S.; Lincopan, N.; Ribeiro, M.S. Inactivation kinetics and lethal dose analysis of antimicrobial blue light and photodynamic therapy. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 28, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplik, F.; Deng, D.; Crielaard, W.; Buchalla, W.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Maisch, T. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy—What we know and what we don’t. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Freitas, L.F.; Hamblin, M.R. Proposed Mechanisms of Photobiomodulation or Low-Level Light Therapy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2016, 22, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, F.; Magni, G.; Tatini, F.; Banchelli, M.; Cherchi, F.; Rossi, M.; Coppi, E.; Pugliese, A.M.; degl’Innocenti, D.R.; Alfieri, D.; et al. Photobiomodulation of Human Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes with Blue Light: Implications in Wound Healing. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamalis, A.; Siegel, D.; Jagdeo, J. Visible Red Light Emitting Diode Photobiomodulation for Skin Fibrosis: Key Molecular Pathways. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eells, J.T.; Henry, M.M.; Summerfelt, P.; Wong-Riley, M.T.T.; Buchmann, E.V.; Kane, M.; Whelan, N.T.; Whelan, H.T. Therapeutic photobiomodulation for methanol-induced retinal toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3439–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pigatto, G.R.; Silva, C.S.; Parizotto, N.A. Photobiomodulation therapy reduces acute pain and inflammation in mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 196, 111513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, M.M.; Garcez, A.S.; Sperandio, M. High energy density LED-based photobiomodulation inhibits squamous cell carcinoma progression in co-cultures in vitro. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 199, 111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailioaie, L.M.; Litscher, G. Probiotics, Photobiomodulation, and Disease Management: Controversies and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Dong, X.; Yin, H.; Shi, X.; Su, S.; Che, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Gut flora-targeted photobiomodulation therapy improves senile dementia in an Aß-induced Alzheimer’s disease animal model. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2021, 216, 112152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.H.; Huang, M.Y.; Huang, W.D.; Hsu, M.H.; Yang, Z.W.; Yang, C.M. The effects of red, blue, and white light-emitting diodes on the growth, development, and edible quality of hydroponically grown lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. capitata). Sci. Hortic. 2013, 150, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, G.D.; Kim, H.H.; Wheeler, R.M.; Mitchell, C.A. Plant productivity in response to LED lighting. In Proceedings of the HortScience; American Society for Horticultural Science: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2008; Volume 43, pp. 1951–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Penha, C.B.; Bonin, E.; da Silva, A.F.; Hioka, N.; Zanqueta, É.B.; Nakamura, T.U.; de Abreu Filho, B.A.; Campanerut-Sá, P.A.Z.; Mikcha, J.M.G. Photodynamic inactivation of foodborne and food spoilage bacteria by curcumin. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srimagal, A.; Ramesh, T.; Sahu, J.K. Effect of light emitting diode treatment on inactivation of Escherichia coli in milk. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Shi, L.; Chen, W.; Cao, S.; Su, X.; Yang, Z. Effect of blue light treatment on fruit quality, antioxidant enzymes and radical-scavenging activity in strawberry fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 175, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.Y.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Song, H.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Ahn, S.W.; Kim, J.S.; Roh, S.W.; Lee, S.H. Role of jeotgal, a Korean traditional fermented fish sauce, in microbial dynamics and metabolite profiles during kimchi fermentation. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Seo, S.H.; Park, S.E.; Lim, Y.W.; Roh, S.W.; Son, H.S. Initial storage of kimchi at room temperature alters its microbial and metabolite profiles. LWT 2020, 134, 110160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, D.; Bai, E. Decreasing soil microbial diversity is associated with decreasing microbial biomass under nitrogen addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenes, K.; Bauer, R.; Meurle, T.; Spellerberg, B.; Hessling, M. Inactivation Effect of Violet and Blue Light on ESKAPE Pathogens and Closely Related Non-pathogenic Bacterial Species—A Promising Tool Against Antibiotic-Sensitive and Antibiotic-Resistant Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hu, L.; Jiang, D.; Xi, W. Effect of Post-Harvest LED and UV Light Irradiation on the Accumulation of Flavonoids and Limonoids in the Segments of Newhall Navel Oranges (Citrus sinensis Osbeck). Molecules 2019, 24, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loi, M.; Villani, A.; Paciolla, F.; Mulè, G.; Paciolla, C. Challenges and Opportunities of Light-Emitting Diode (LED) as Key to Modulate Antioxidant Compounds in Plants. A Review. Antioxidants 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Gu, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; Ye, N. Exploration of the Effects of Different Blue LED Light Intensities on Flavonoid and Lipid Metabolism in Tea Plants via Transcriptomics and Metabolomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhong, Q.S.; Zhan, S.; Liu, H.; Cai, C. Serum polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites as useful tool for screening potential biomarker of colorectal cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2017, 120, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, L.; Tontonoz, P.; Alvarez, J.G.A.; Chen, H.; Evans, R.M. Oxidized LDL regulates macrophage gene expression through ligand activation of PPARγ. Cell 1998, 93, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, T.; Fairall, L.; Amin, K.; Inaba, Y.; Szanto, A.; Balint, B.L.; Nagy, L.; Yamamoto, K.; Schwabe, J.W.R. Structural basis for the activation of PPARg by oxidized fatty acids. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, G.T.; Nie, D. PPAR gamma, bioactive lipids, and cancer progression. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 1816–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawayama, H.; Ishimoto, T.; Watanabe, M.; Yoshida, N.; Sugihara, H.; Kurashige, J.; Hirashima, K.; Iwatsuki, M.; Baba, Y.; Oki, E.; et al. Small molecule agonists of PPAR-γ exert therapeutic effects in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, A.; Lee, S.M. Estimating the number of classes via sample coverage. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1992, 87, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scan. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zahl, S. Jackknifing An Index of Diversity. Ecology 1977, 58, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Lee, D.Y. Metabolomic Investigation on Fermentation Products of Achyranthes japonica Nakai by Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.-J.; Park, Y.-R.; Hong, J.; Lee, D.-Y. Metagenomic, Metabolomic, and Functional Evaluation of Kimchi Broth Treated with Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Metabolites 2021, 11, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080472
Oh Y-J, Park Y-R, Hong J, Lee D-Y. Metagenomic, Metabolomic, and Functional Evaluation of Kimchi Broth Treated with Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Metabolites. 2021; 11(8):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080472
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Yeong-Ji, Ye-Rin Park, Jungil Hong, and Do-Yup Lee. 2021. "Metagenomic, Metabolomic, and Functional Evaluation of Kimchi Broth Treated with Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs)" Metabolites 11, no. 8: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080472
APA StyleOh, Y. -J., Park, Y. -R., Hong, J., & Lee, D. -Y. (2021). Metagenomic, Metabolomic, and Functional Evaluation of Kimchi Broth Treated with Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Metabolites, 11(8), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11080472