d-Amino Acids and Classical Neurotransmitters in Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes-Affected Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans
Abstract
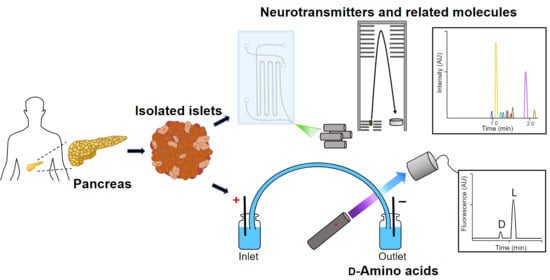
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Collection of Human Pancreatic Islets
2.3. Human Pancreatic Islet Processing
2.4. Amino Acid Extraction
2.5. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis (CZE)-LIF for Chiral Separation
2.5.1. Amino Acid Derivatization
2.5.2. Enzyme Treatment for Confirmation of d-AA Identification
2.5.3. CZE-LIF
2.6. ZipChip-CZE-ESI-MS for Neurotransmitters
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Determination of d-AAs in Islets of Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes-Diagnosed Individuals
3.2. Determination of Neurotransmitters in Islets of Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes-Diagnosed Individuals
3.3. Assessing the Correlation between Analyte Levels or Ratios and Donor Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otter, S.; Lammert, E. Exciting Times for Pancreatic Islets: Glutamate Signaling in Endocrine Cells. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 27, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.E.; Newgard, C.B. Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, B.B. Glucagon and regulation of glucose metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E671–E678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, F.C.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; van Apeldoorn, A.; LaPointe, V.L.S. The functional importance of the cellular and extracellular composition of the islets of Langerhans. J. Immunol. Regen. Med. 2021, 13, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudish, L.I.; Reusch, J.E.B.; Sussel, L. β Cell dysfunction during progression of metabolic syndrome to type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, H.; Kudoh, K. Diversity of pathophysiology in type 2 diabetes shown by islet pathology. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilimnik, G.; Zhao, B.; Jo, J.; Periwal, V.; Witkowski, P.; Misawa, R.; Hara, M. Altered Islet Composition and Disproportionate Loss of Large Islets in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaça, J.; Molina, J.; Menegaz, D.; Pronin, A.N.; Tamayo, A.; Slepak, V.; Berggren, P.-O.; Caicedo, A. Human Beta Cells Produce and Release Serotonin to Inhibit Glucagon Secretion from Alpha Cells. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 3281–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegaz, D.; Hagan, D.W.; Almaça, J.; Cianciaruso, C.; Rodriguez-Diaz, R.; Molina, J.; Dolan, R.M.; Becker, M.W.; Schwalie, P.C.; Nano, R.; et al. Mechanism and effects of pulsatile GABA secretion from cytosolic pools in the human beta cell. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 1110–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, R.; Menegaz, D.; Caicedo, A. Neurotransmitters act as paracrine signals to regulate insulin secretion from the human pancreatic islet. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 3413–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, R.; Dando, R.; Jacques-Silva, M.C.; Fachado, A.; Molina, J.; Abdulreda, M.H.; Ricordi, C.; Roper, S.D.; Berggren, P.-O.; Caicedo, A. Alpha cells secrete acetylcholine as a non-neuronal paracrine signal priming beta cell function in humans. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henquin, J.-C. Paracrine and autocrine control of insulin secretion in human islets: Evidence and pending questions. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E78–E86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gylfe, E.; Tengholm, A. Neurotransmitter control of islet hormone pulsatility. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chieffi Baccari, G.; Falvo, S.; Santillo, A.; Di Giacomo Russo, F.; Di Fiore, M.M. d-Amino acids in mammalian endocrine tissues. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockridge, A.D.; Baumann, D.C.; Akhaphong, B.; Abrenica, A.; Miller, R.F.; Alejandro, E.U. Serine racemase is expressed in islets and contributes to the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Islets 2016, 8, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiasa, M.; Moriyama, Y. Immunohistochemical Localization of D-Aspartate in Islets of Langerhans. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1251–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, A.; Hamase, K.; Ohgusu, T.; Etoh, S.; Tanaka, H.; Koshiishi, I.; Shoyama, Y.; Zaitsu, K. Immunohistochemical localization of d-alanine to β-cells in rat pancreas. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 355, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G. An overview on d-amino acids. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolosker, H. NMDA Receptor Regulation by D-serine: New Findings and Perspectives. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 36, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, N.; Shi, T.; Sweedler, J.V. D-aspartate acts as a signaling molecule in nervous and neuroendocrine systems. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1873–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molnár, E.; Váradi, A.; McIlhinney, R.A.; Ashcroft, S.J. Identification of functional ionotropic glutamate receptor proteins in pancreatic beta-cells and in islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett. 1995, 371, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, N.; Kuromi, H.; Gonoi, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ishida, H.; Seino, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Iwanaga, T.; Seino, S. Expression and role of ionotropic glutamate receptors in pancreatic islet cells. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, O.; Welters, A.; Lammert, E. Role of NMDA Receptors in Pancreatic Islets. In The NMDA Receptors; Hashimoto, K., Ed.; The Receptors; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 30, pp. 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Marquard, J.; Stirban, A.; Schliess, F.; Sievers, F.; Welters, A.; Otter, S.; Fischer, A.; Wnendt, S.; Meissner, T.; Heise, T.; et al. Effects of dextromethorphan as add-on to sitagliptin on blood glucose and serum insulin concentrations in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, multiple crossover, single-dose clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welters, A.; Klüppel, C.; Mrugala, J.; Wörmeyer, L.; Meissner, T.; Mayatepek, E.; Heiss, C.; Eberhard, D.; Lammert, E. NMDAR antagonists for the treatment of diabetes mellitus—Current status and future directions. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricordi, C.; Goldstein, J.S.; Balamurugan, A.N.; Szot, G.L.; Kin, T.; Liu, C.; Czarniecki, C.W.; Barbaro, B.; Bridges, N.D.; Cano, J.; et al. National Institutes of Health–Sponsored Clinical Islet Transplantation Consortium Phase 3 Trial: Manufacture of a Complex Cellular Product at Eight Processing Facilities. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3418–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, J.; Manning Fox, J.E.; Spigelman, A.F.; Kim, R.; Smith, N.; O’Gorman, D.; Kin, T.; Shapiro, A.M.J.; Rajotte, R.V.; MacDonald, P.E. Research-Focused Isolation of Human Islets From Donors With and Without Diabetes at the Alberta Diabetes Institute IsletCore. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.V.; Kawai, T.; Wang, L.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Sweedler, J.V. Chiral Measurement of Aspartate and Glutamate in Single Neurons by Large-Volume Sample Stacking Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12375–12382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothet, J.-P.; Billard, J.-M.; Pollegioni, L.; Coyle, J.T.; Sweedler, J.V. Investigating brain d-serine: Advocacy for good practices. Acta Physiol. 2019, 226, e13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szökő, É.; Vincze, I.; Tábi, T. Chiral separations for d-amino acid analysis in biological samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S. d-Aspartate oxidase: Distribution, functions, properties, and biotechnological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2883–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, K.M.V.; Boyle, J.P.; Thompson, T.J.; Gregg, E.W.; Williamson, D.F. Effect of BMI on Lifetime Risk for Diabetes in the U.S. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwani, S.I.; Khan, H.A.; Ekhzaimy, A.; Masood, A.; Sakharkar, M.K. Significance of HbA1c Test in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Diabetic Patients. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boye, K.S.; Lage, M.J.; Shinde, S.; Thieu, V.; Bae, J.P. Trends in HbA1c and Body Mass Index Among Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: Evidence from a US Database 2012–2019. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iharada, M.; Hiasa, M.; Kobara, A.; Moriyama, Y. Exocytosis of D-Aspartate from INS-1E Clonal β Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1329–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, N.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Sweedler, J.V. d-Alanine in the islets of Langerhans of rat pancreas. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 447, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, F.K.; Ortalli, A.; Canouil, M.; Huyvaert, M.; Salazar-Cardozo, C.; Lecoeur, C.; Verbanck, M.; Pawlowski, V.; Boutry, R.; Durand, E.; et al. Expression and functional assessment of candidate type 2 diabetes susceptibility genes identify four new genes contributing to human insulin secretion. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockridge, A.; Gustafson, E.; Wong, A.; Miller, R.F.; Alejandro, E.U. Acute D-Serine Co-Agonism of β-Cell NMDA Receptors Potentiates Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion and Excitatory β-Cell Membrane Activity. Cells 2021, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwandhi, L.; Hausmann, S.; Braun, A.; Gruber, T.; Heinzmann, S.S.; Gálvez, E.J.C.; Buck, A.; Legutko, B.; Israel, A.; Feuchtinger, A.; et al. Chronic d-serine supplementation impairs insulin secretion. Mol. Metab. 2018, 16, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, L.J.; Buschard, K. L-serine: A neglected amino acid with a potential therapeutic role in diabetes. APMIS 2019, 127, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuellig, R.A.; Hornemann, T.; Othman, A.; Hehl, A.B.; Bode, H.; Güntert, T.; Ogunshola, O.O.; Saponara, E.; Grabliauskaite, K.; Jang, J.-H.; et al. Deoxysphingolipids, Novel Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes, Are Cytotoxic for Insulin-Producing Cells. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1326–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drábková, P.; Šanderová, J.; Kovařík, J.; Kanďár, R. An Assay of Selected Serum Amino Acids in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganz, M.L.; Wintfeld, N.; Li, Q.; Alas, V.; Langer, J.; Hammer, M. The association of body mass index with the risk of type 2 diabetes: A case–control study nested in an electronic health records system in the United States. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Matos, A.F. The role of glucagon on type 2 diabetes at a glance. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, R.H.; Cherrington, A.D. Glucagonocentric restructuring of diabetes: A pathophysiologic and therapeutic makeover. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangipurapu, J.; Stancáková, A.; Smith, U.; Kuusisto, J.; Laakso, M. Nine Amino Acids Are Associated With Decreased Insulin Secretion and Elevated Glucose Levels in a 7.4-Year Follow-up Study of 5,181 Finnish Men. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo Bascuñan, L.R.; Lyons, C.; Bennet, H.; Artner, I.; Fex, M. Serotonergic regulation of insulin secretion. Acta Physiol. 2019, 225, e13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, H.; Balhuizen, A.; Medina, A.; Dekker Nitert, M.; Ottosson Laakso, E.; Essén, S.; Spégel, P.; Storm, P.; Krus, U.; Wierup, N.; et al. Altered serotonin (5-HT) 1D and 2A receptor expression may contribute to defective insulin and glucagon secretion in human type 2 diabetes. Peptides 2015, 71, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennet, H.; Mollet, I.G.; Balhuizen, A.; Medina, A.; Nagorny, C.; Bagge, A.; Fadista, J.; Ottosson-Laakso, E.; Vikman, P.; Dekker-Nitert, M.; et al. Serotonin (5-HT) receptor 2b activation augments glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in human and mouse islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, S.; Bunting, B.P.; Carr, E.; Strain, J.J.; Stewart-Knox, B.J. Obesity, Whole Blood Serotonin and Sex Differences in Healthy Volunteers. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erritzoe, D.; Frokjaer, V.G.; Haahr, M.T.; Kalbitzer, J.; Svarer, C.; Holst, K.K.; Hansen, D.L.; Jernigan, T.L.; Lehel, S.; Knudsen, G.M. Cerebral serotonin transporter binding is inversely related to body mass index. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, M.; Ramracheya, R.; Bengtsson, M.; Clark, A.; Walker, J.N.; Johnson, P.R.; Rorsman, P. γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Is an Autocrine Excitatory Transmitter in Human Pancreatic β-Cells. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Yokoi, N.; Seino, S. Glutamate as intracellular and extracellular signals in pancreatic islet functions. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2019, 95, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.J.; Schnieders, J.H.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Patel, A.V.; Liu, C.; Naji, A.; Sweedler, J.V. d-Amino Acids and Classical Neurotransmitters in Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes-Affected Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans. Metabolites 2022, 12, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090799
Lee CJ, Schnieders JH, Rubakhin SS, Patel AV, Liu C, Naji A, Sweedler JV. d-Amino Acids and Classical Neurotransmitters in Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes-Affected Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans. Metabolites. 2022; 12(9):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090799
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Cindy J., Jack H. Schnieders, Stanislav S. Rubakhin, Amit V. Patel, Chengyang Liu, Ali Naji, and Jonathan V. Sweedler. 2022. "d-Amino Acids and Classical Neurotransmitters in Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes-Affected Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans" Metabolites 12, no. 9: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090799
APA StyleLee, C. J., Schnieders, J. H., Rubakhin, S. S., Patel, A. V., Liu, C., Naji, A., & Sweedler, J. V. (2022). d-Amino Acids and Classical Neurotransmitters in Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes-Affected Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans. Metabolites, 12(9), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090799