Study of the Metabolic Profiles of “Indazole-3-Carboxamide” and “Isatin Acyl Hydrazone” (OXIZID) Synthetic Cannabinoids in a Human Liver Microsome Model Using UHPLC-QE Orbitrap MS
Abstract
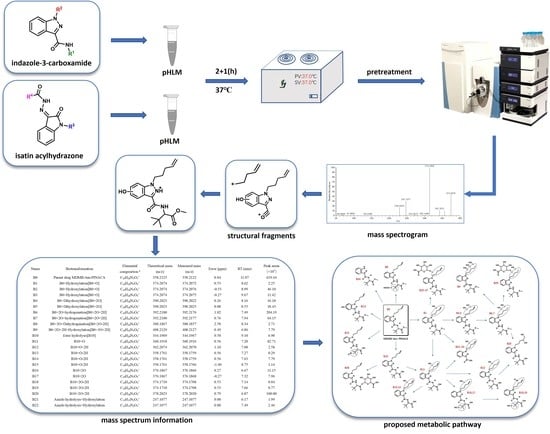
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Incubation in pHLMs
2.3. LC-MS Analysis
3. Results
3.1. “Indazole-3-Carboxamide” Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists (SCRAs)
3.1.1. Parent Compounds
3.1.2. Phase I and II Metabolites
Hydroxylation
Dihydrodiol Formation
Hydrolysis
Dehydrogenation and Oxidate-to-Ketone and Carboxylate Conversions
N-Dealkylation
Glucuronidation
3.2. “Isatin Acyl Hydrazone” SCRAs
3.2.1. Parent Compounds
3.2.2. Phase I and II Metabolites
Hydroxylation
Dehydrogenation and Oxidate-to-Ketone and Carboxylate Conversions
Defluorination
Dihydrodiol Formation
Amido Hydrolysis
N-Dealkylation
Glucuronidation
3.3. Suggested Biomarkers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Drug Report 2022: Booklet 4: Drug Market Trends of Cocaine, Amphetamine-Type Stimulants and New Psychoactive Substances. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/res/wdr2022/MS/WDR22_Booklet_4.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Sparkes, E.; Cairns, E.A.; Kevin, R.C.; Lai, F.; Grafinger, K.E.; Chen, S.; Deventer, M.H.; Ellison, R.; Boyd, R.; Martin, L.J.; et al. Structure–activity relationships of valine, tert-leucine, and phenylalanine amino acid-derived synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists related to ADB-BUTINACA, APP-BUTINACA, and ADB-P7AICA. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, A.J.; Cano, C.; Thomas, S.H.L.; Hill, S.L. Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists: Classification and Nomenclature. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, R.M.; Keating, J.J. Adding More “Spice” to the Pot: A Review of the Chemistry and Pharmacology of Newly Emerging Heterocyclic Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manini, A.F.; Krotulski, A.J.; Schimmel, J.; Allen, L.; Hurd, Y.L.; Richardson, L.D.; Vidal, K.; Logan, B.K. Respiratory Failure in Confirmed Synthetic Cannabinoid Overdose. Clin. Toxicol. 2022, 60, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labay, L.M.; Caruso, J.L.; Gilson, T.P.; Phipps, R.J.; Knight, L.D.; Lemos, N.P.; McIntyre, I.M.; Stoppacher, R.; Tormos, L.M.; Wiens, A.L.; et al. Synthetic Cannabinoid Drug Use as a Cause or Contributory Cause of Death. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 260, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourouni, I.; Mourad, B.; Khouli, H.; Shapiro, J.M.; Mathew, J.P. Critical Illness Secondary to Synthetic Cannabinoid Ingestion. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e208516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Hua, Z.D.; Jia, W.; Li, T. Identification of AD-18, 5F-MDA-19, and Pentyl MDA-19 in Seized Materials after the Class-Wide Ban of Synthetic Cannabinoids in China. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deventer, M.H.; Uytfanghe, K.V.; Vinckier, I.M.J.; Reniero, F.; Guillou, C.; Stove, C.P. Cannabinoid Receptor Activation Potential of the Next Generation, Generic Ban Evading OXIZID Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shen, M.; Shen, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Deng, H.; Xiang, P.; Shi, Y. Application of a UPLC-MS/MS method for quantitative analysis of 29 synthetic cannabinoids and their metabolites, such as ADB-BUTINACA and MDMB-4en-PINACA in human hair in real cases. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 331, 111139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Huestis, M.A. New Synthetic Cannabinoids Metabolism and Strategies to Best Identify Optimal Marker Metabolites. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, F.; Jechle, H.; Wilde, M.; Angerer, V.; Huppertz, L.M.; Longworth, M.; Kassiou, M.; Jung, M.; Auwärter, V. Structure-Metabolism Relationships of Valine and Tert-Leucine-Derived Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists: A Systematic Comparison of the in Vitro Phase I Metabolism Using Pooled Human Liver Microsomes and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Forensic Toxicol. 2019, 37, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, M.; Brents, L.K.; Franks, L.N.; Moran, J.H.; Prather, P.L. Human metabolites of synthetic cannabinoids JWH-018 and JWH-073 bind with high affinity and act as potent agonists at cannabinoid type-2 receptors. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 269, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamage, T.F.; Farquhar, C.E.; McKinnie, R.J.; Kevin, R.C.; McGregor, I.S.; Trudell, M.L.; Wiley, J.L.; Thomas, B.F. Synthetic Cannabinoid Hydroxypentyl Metabolites Retain Efficacy at Human Cannabinoid Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 368, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, S.; Fantegrossi, W.E. Pharmacological and Toxicological Effects of Synthetic Cannabinoids and Their Metabolites. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 32, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florian, F.; Angerer, V.; Moosmann, B.; Auwärter, V. Phase I metabolism of the highly potent synthetic cannabinoid MDMB-CHMICA and detection in human urine samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogler, L.; Wilde, M.; Huppertz, L.M.; Weinfurtner, G.; Franz, F.; Auwärter, V. Phase I metabolism of the recently emerged synthetic cannabinoid CUMYL-PEGACLONE and detection in human urine samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogler, L.; Franz, F.; Wilde, M.; Huppertz, L.M.; Halter, S.; Angerer, V.; Moosmann, B.; Auwärter, V. Phase I metabolism of the carbazole-derived synthetic cannabinoids EG-018, EG-2201, and MDMB-CHMCZCA and detection in human urine samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsen, A.B.; Mardal, M.; Linnet, K. In Vitro Metabolism and Hepatic Intrinsic Clearance of the Synthetic Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist JWH-122 and Its Four ω-Halogenated Analogues. AAPS J. 2019, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, C.H.; Wang, Z.; Goh, E.M.L.; Tan, Y.L.; Fong, C.Y.; Moy, H.Y.; Chan, E.C.Y. Urinary Metabolite Biomarkers for the Detection of Synthetic Cannabinoid ADB-BUTINACA Abuse. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 1534–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, P.; Pechnikov, A.; Nikolaev, I.; Dowling, G.; Kolosova, M.; Grigoryev, A. Detection of ADB-BUTINACA Metabolites in Human Urine, Blood, Kidney and Liver. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2021, 46, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronstrand, R.; Norman, C.; Vikingsson, S.; Biemans, A.; Crespo, B.V.; Edwards, D.; Fletcher, D.; Gilbert, N.; Persson, M.; Reid, R.; et al. The metabolism of the synthetic cannabinoids ADB-BUTINACA and ADB-4en-PINACA and their detection in forensic toxicology casework and infused papers seized in prisons. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 634–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Vikingsson, S.; Åstrand, A.; Gréen, H.; Kronstrand, R. Biotransformation of the New Synthetic Cannabinoid with an Alkene, MDMB-4en-PINACA, by Human Hepatocytes, Human Liver Microsomes, and Human Urine and Blood. AAPS J. 2019, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Qin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xin, G.; Shi, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J. Metabolic profiles and screening tactics for MDMB-4en-PINACA in human urine and serum samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 220, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Z.H.; Wang, Z.; Fong, C.Y.; Goh, E.M.L.; Moy, H.Y.; Chan, E.C.Y. Identification of Optimal Urinary Biomarkers of Synthetic Cannabinoids BZO-HEXOXIZID, BZO-POXIZID, 5F-BZO-POXIZID, and BZO-CHMOXIZID for Illicit Abuse Monitoring. Clin. Chem. 2022, 68, 1436–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, L.H.J.; Maurer, H.H.; Meyer, M.R. Metabolic fate of the new synthetic cannabinoid 7’N-5F-ADB in rat, human, and pooled human S9 studied by means of hyphenated high-resolution mass spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, Y.E.; Yeter, O. In Vitro Phase I Metabolism of the Recently Emerged Synthetic MDMB-4en-PINACA and its Detection in Human Urine Samples. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guengerich, F.P. Common and uncommon cytochrome P450 reactions related to metabolism and chemical toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 611–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P. Mechanisms of Cytochrome P450-Catalyzed Oxidations. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 10964–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staeheli, S.N.; Poetzsch, M.; Veloso, V.P.; Bovens, M.; Bissig, C.; Steuer, A.E.; Kraemer, T. In vitro metabolism of the synthetic cannabinoids CUMYL-PINACA, 5F-CUMYL-PINACA, CUMYL-4CN-BINACA, 5F-CUMYL-P7AICA and CUMYL-4CN-B7AICA. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.L.; Goncalves, J.L.; Aguiar, J.; Teixeira, H.M.; Camara, J.S. The Synthetic Cannabinoids Phenomenon: From Structure to Toxicological Properties. A Review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zong, X.; Liu, J.; Ke, X.; Huang, Z.; Xu, Y. Development of a Fragmentation Pattern of Synthetic Cannabinoids Based on Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry in Positive Ion Mode to Screen Synthetic Cannabinoids in Illicit Products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safont, D.F.; Mardal, M.; Noble, C.; Cannaert, A.; Stove, C.P.; Sancho, J.V.; Linnet, K.; Hernández, F.; Ibáñez, M. Comprehensive investigation on synthetic cannabinoids: Metabolic behavior and potency testing, using 5F-APP-PICA and AMB-FUBINACA as model compounds. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfarth, A.; Castaneto, M.S.; Zhu, M.; Pang, S.; Scheidweiler, K.B.; Kronstrand, R.; Huestis, M.A. Pentylindole/Pentylindazole Synthetic Cannabinoids and Their 5-Fluoro Analogs Produce Different Primary Metabolites: Metabolite Profiling for AB-PINACA and 5F-AB-PINACA. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambaro, V.; Arnoldi, S.; Bellucci, S.; Casagni, E.; Acqua, L.D.; Fumagalli, L.; Pallavicini, M.; Roda, G.; Rusconi, C.; Valoti, E. Characterization of in vitro metabolites of JWH-018, JWH-073 and their 4-methyl derivatives, markers of the abuse of these synthetic cannabinoids. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 957, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogler, L.; Franz, F.; Rentsch, D.; Angerer, V.; Weinfurtner, G.; Longworth, M.; Banister, S.D.; Kassiou, M.; Moosmann, B.; Auwärter, V. Detection of the recently emerged synthetic cannabinoid 5F–MDMB-PICA in ‘legal high’ products and human urine samples. Drug Test. Anal. 2018, 10, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apirakkan, O.; Gavrilovic, I.; Cowan, D.A.; Abbate, V. In Vitro Phase I Metabolic Profiling of the Synthetic Cannabinoids AM-694, 5F-NNEI, FUB-APINACA, MFUBINAC, and AMB-FUBINACA. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakata, K.; Nozawa, H.; Yamagishi, I.; Hasegawa, K.; Saitoh, T.; Yoshino, A.; Suzuki, M.; Kitamoto, T.; Suzuki, O.; Watanabe, K. Sensitive quantification of 5F-NNEI and characterization of its several metabolites in authentic urine and/or serum specimens obtained from three individuals by LC–QTRAP-MS/MS and high-resolution LC–Orbitrap-MS/MS. Forensic Toxicol. 2018, 36, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Carlier, J.; Zhu, M.; Huestis, M.A. Human Hepatocyte Metabolism of Novel Synthetic Cannabinoids MN-18 and Its 5-Fluoro Analog 5F-MN-18. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuldermans, W.; Van, P.A.; Hendrickx, J.; Lauwers, W.; Swysen, E.; Bockx, M.; Woestenborghs, R.; Heykants, J. Excretion and biotransformation of cisapride in dogs and humans after oral administration. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1988, 16, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koerts, J.; Soffers, A.E.; Vervoort, J.; Jager, D.A.; Rietjens, I.M. Occurrence of the NIH shift upon the cytochrome P450-catalyzed in vivo and in vitro aromatic ring hydroxylation of fluorobenzenes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1998, 11, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montellano, P.R.O.D.; Nelson, S.D. Rearrangement reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450s. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 507, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Wu, X.; Dahlen, J.; Konradsson, P.; Vikingsson, S.; Kronstrand, R.; Gréen, H. Metabolism of MMB022 and identification of dihydrodiol formation in vitro using synthesized standards. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obach, R.S. Cytochrome P450-catalyzed metabolism of ezlopitant alkene (CJ-12,458), a pharmacologically active metabolite of ezlopitant: Enzyme kinetics and mechanism of an alkene hydration reaction. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Costa, K.S.; Black, S.R.; Thomas, B.F.; Burgess, J.P.; Mathews, J.M. Metabolism and disposition of α-methylstyrene in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montellano, P.R.O.D.; Mico, B.A.; Yost, G.S. Suicidal inactivation of cytochrome P-450. Formation of a heme-substrate covalent adduct. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1978, 83, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montellano, P.R.O.D.; Yost, G.S.; Mico, B.A.; Dinizo, S.E.; Correia, M.A.; Kumbara, H. Destruction of cytochrome P-450 by 2-isopropyl-4-pentenamide and methyl 2-isopropyl-4-pentenoate: Mass spectrometric characterization of prosthetic heme adducts and nonparticipation of epoxide metabolites. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1979, 197, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montellano, P.R.O.D.; Kunze, K.L.; Mico, B.A. Destruction of cytochrome P-450 by olefins: N-alkylation of prosthetic heme. Mol. Pharmacol. 1980, 18, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.W.; Britt, S.G.; Pohl, L.R. Carbon tetrachloride and 2-isopropyl-4-pentenamide-induced inactivation of cytochrome P-450 leads to heme-derived protein adducts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1986, 244, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, P.; Grigoryev, A.; Krupina, N. Detection of metabolites of two synthetic cannabimimetics, MDMB-FUBINACA and ADB-FUBINACA, in authentic human urine specimens by accurate mass LC–MS: A comparison of intersecting metabolic patterns. Forensic Toxicol. 2017, 35, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Keefer, C.; Scott, D.O.; Strelevitz, T.J.; Chang, G.; Bi, Y.A.; Lai, Y.; Duckworth, J.; Fenner, K.; Troutman, M.D.; et al. Mechanistic insights from comparing intrinsic clearance values between human liver microsomes and hepatocytes to guide drug design. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 57, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksits, M.; Sulyok, M.; Schuhmacher, R.; Szekeres, T.; Jäger, W. In-vitro sulfation of piceatannol by human liver cytosol and recombinant sulfotransferases. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thum, T.; Erpenbeck, V.J.; Moeller, J.; Hohlfeld, J.M.; Krug, N.; Borlak, J. Expression of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in different lung compartments of smokers and nonsmokers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.; Shin, I.; Yang, W.; Chang, H.; Yoo, H.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, E. Determination of major metabolites of MAM-2201 and JWH-122 in in vitro and in vivo studies to distinguish their intake. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 244, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janis, G.C. Analysis of Synthetic Cannabinoid Metabolites by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1872, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, J.; Wen, D.; Zhao, J.; Xiang, P.; Shi, Y.; Ma, C. Study of the Metabolic Profiles of “Indazole-3-Carboxamide” and “Isatin Acyl Hydrazone” (OXIZID) Synthetic Cannabinoids in a Human Liver Microsome Model Using UHPLC-QE Orbitrap MS. Metabolites 2023, 13, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040576
Xiang J, Wen D, Zhao J, Xiang P, Shi Y, Ma C. Study of the Metabolic Profiles of “Indazole-3-Carboxamide” and “Isatin Acyl Hydrazone” (OXIZID) Synthetic Cannabinoids in a Human Liver Microsome Model Using UHPLC-QE Orbitrap MS. Metabolites. 2023; 13(4):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040576
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Jiahong, Di Wen, Junbo Zhao, Ping Xiang, Yan Shi, and Chunling Ma. 2023. "Study of the Metabolic Profiles of “Indazole-3-Carboxamide” and “Isatin Acyl Hydrazone” (OXIZID) Synthetic Cannabinoids in a Human Liver Microsome Model Using UHPLC-QE Orbitrap MS" Metabolites 13, no. 4: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040576
APA StyleXiang, J., Wen, D., Zhao, J., Xiang, P., Shi, Y., & Ma, C. (2023). Study of the Metabolic Profiles of “Indazole-3-Carboxamide” and “Isatin Acyl Hydrazone” (OXIZID) Synthetic Cannabinoids in a Human Liver Microsome Model Using UHPLC-QE Orbitrap MS. Metabolites, 13(4), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13040576