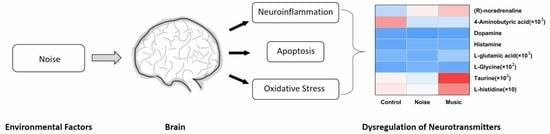
Effect of Noise and Music on Neurotransmitters in the Amygdala: The Role Auditory Stimuli Play in Emotion Regulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Management
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Serum Sampling and Measurement of Oxidative Stress
2.5. Tissue Sampling and Measurement of Cytokines and Oxidative Stress
2.6. Histopathological Studies
2.7. Electron Microscopy
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Neurotransmitter Detection
2.11. Behavioral Observation
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Responses of Piglets to Noise and Music Exposure
3.2. Changes in the Levels of Neurotransmitters in the Amygdala
3.3. Noise Exposure Activated the Apoptosis Pathway in the Amygdala
3.4. Noise-Related Stress Causes Neuroinflammation
3.5. Prolonged Noise Exposure Decreases the Activity of CAT and SOD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarosińska, D.; Héroux, M.-È.; Wilkhu, P.; Creswick, J.; Verbeek, J.; Wothge, J.; Paunović, E. Development of the WHO Environmental Noise Guidelines for the European Region: An Introduction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Münzel, T.; Schmidt, F.P.; Steven, S.; Herzog, J.; Daiber, A.; Sørensen, M. Environmental Noise and the Cardiovascular System. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, C.; Kwan, M.-P.; Kou, L.; Chai, Y. Assessing Personal Noise Exposure and Its Relationship with Mental Health in Beijing Based on Individuals’ Space-Time Behavior. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.H.; Henderson, D.; Nicotera, T.M. Extremely Rapid Induction of Outer Hair Cell Apoptosis in the Chinchilla Cochlea Following Exposure to Impulse Noise. Hear. Res. 2006, 211, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.H.; Cai, Q.; Manohar, S.; Jiang, H.; Ding, D.; Coling, D.E.; Zheng, G.; Salvi, R. Differential Expression of Apoptosis-Related Genes in the Cochlea of Noise-Exposed Rats. Neuroscience 2009, 161, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoshsirat, S.; Abbaszadeh, H.-A.; Peyvandi, A.A.; Heidari, F.; Peyvandi, M.; Simani, L.; Niknazar, S. Apelin-13 Prevents Apoptosis in the Cochlear Tissue of Noise-Exposed Rat via Sirt-1 Regulation. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 114, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.-Q.; Zheng, H.-W.; Hill, K.; Sha, S.-H. Traumatic Noise Activates Rho-Family GTPases through Transient Cellular Energy Depletion. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12421–12430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kragel, P.A.; Čeko, M.; Theriault, J.; Chen, D.; Satpute, A.B.; Wald, L.W.; Lindquist, M.A.; Feldman Barrett, L.; Wager, T.D. A Human Colliculus-Pulvinar-Amygdala Pathway Encodes Negative Emotion. Neuron 2021, 109, 2404–2412.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamietto, M.; de Gelder, B. Neural Bases of the Non-Conscious Perception of Emotional Signals. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gelder, B.; van Honk, J.; Tamietto, M. Emotion in the Brain: Of Low Roads, High Roads and Roads Less Travelled. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corder, G.; Ahanonu, B.; Grewe, B.F.; Wang, D.; Schnitzer, M.J.; Scherrer, G. An Amygdalar Neural Ensemble That Encodes the Unpleasantness of Pain. Science 2019, 363, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tye, K.M.; Prakash, R.; Kim, S.-Y.; Fenno, L.E.; Grosenick, L.; Zarabi, H.; Thompson, K.R.; Gradinaru, V.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Deisseroth, K. Amygdala Circuitry Mediating Reversible and Bidirectional Control of Anxiety. Nature 2011, 471, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, P.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; He, X.; Wu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Processing of Visually Evoked Innate Fear by a Non-Canonical Thalamic Pathway. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quirk, G.J.; Armony, J.L.; LeDoux, J.E. Fear Conditioning Enhances Different Temporal Components of Tone-Evoked Spike Trains in Auditory Cortex and Lateral Amygdala. Neuron 1997, 19, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sander, K.; Scheich, H. Auditory Perception of Laughing and Crying Activates Human Amygdala Regardless of Attentional State. Cogn. Brain Res. 2001, 12, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, A.; Oommen, A. Chronic Noise Stress-Induced Alterations of Glutamate and Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Their Metabolism in the Rat Brain. Noise Health 2014, 16, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Wu, M.; She, X. Effects of Chronic Noise Exposure on Spatial Learning and Memory of Rats in Relation to Neurotransmitters and NMDAR2B Alteration in the Hippocampus. J. Occup. Health 2009, 51, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindran, R.; Devi, R.S.; Samson, J.; Senthilvelan, M. Noise-Stress-Induced Brain Neurotransmitter Changes and the Effect of Ocimum Sanctum (Linn) Treatment in Albino Rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 98, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di, G.; Xu, Y. Influences of Combined Traffic Noise on Anxiety in Mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilloteau, P.; Zabielski, R.; Hammon, H.M.; Metges, C.C. Nutritional Programming of Gastrointestinal Tract Development. Is the Pig a Good Model for Man? Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radlowski, E.C.; Conrad, M.S.; Lezmi, S.; Dilger, R.N.; Sutton, B.; Larsen, R.; Johnson, R.W. A Neonatal Piglet Model for Investigating Brain and Cognitive Development in Small for Gestational Age Human Infants. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Qian, Q.H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Bao, J. Effects of Music Stimulus on Behavior Response, Cortisol Level and Immunity Horizontal of Growing Pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 224–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissy, A.; Manteuffel, G.; Jensen, M.B.; Moe, R.O.; Spruijt, B.; Keeling, L.J.; Winckler, C.; Forkman, B.; Dimitrov, I.; Langbein, J.; et al. Assessment of Positive Emotions in Animals to Improve Their Welfare. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 92, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, I.C.; Ekkel, E.D.; van de Burgwal, J.A.; Lambooij, E.; Korte, S.M.; Ruis, M.A.W.; Koolhaas, J.M.; Blokhuis, H.J. Effects of Strawbedding on Physiological Responses to Stressors and Behavior in Growing Pigs. Physiol. Behav. 1998, 64, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, J.A. Core Affect and the Psychological Construction of Emotion. Psychol. Rev. 2003, 110, 145–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solvi, C.; Baciadonna, L.; Chittka, L. Unexpected Rewards Induce Dopamine-Dependent Positive Emotion–like State Changes in Bumblebees. Science 2016, 353, 1529–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahi, A.; Dreyer, J.-L. Dopamine Transporter (DAT) Knockdown in the Nucleus Accumbens Improves Anxiety- and Depression-Related Behaviors in Adult Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devidze, N.; Lee, A.W.; Zhou, J.; Pfaff, D.W. CNS Arousal Mechanisms Bearing on Sex and Other Biologically Regulated Behaviors. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 88, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, M.; Mochizuki, H.; Iwabuchi, K.; Sakurada, Y.; Itoh, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yanai, K. Roles of Histamine in Regulation of Arousal and Cognition: Functional Neuroimaging of Histamine H1 Receptors in Human Brain. Life Sci. 2002, 72, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämmerer, D.; Hopkins, A.; Betts, M.J.; Maaß, A.; Dolan, R.J.; Düzel, E. Emotional Arousal and Recognition Memory Are Differentially Reflected in Pupil Diameter Responses during Emotional Memory for Negative Events in Younger and Older Adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 58, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Kaneko, K.; Kato, H.; Fujii, S.; Jing, Y.; Xu, A.; Sakurai, E.; Kato, M.; Okamura, N.; Kuramasu, A.; et al. Selective Cognitive Dysfunction in Mice Lacking Histamine H1 and H2 Receptors. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 57, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, N.; Liu, K.; Arai, T. Prevention of Brain Infarction by Postischemic Administration of Histidine in Rats. Brain Res. 2005, 1039, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prell, G.D.; Hough, L.B.; Khandelwal, J.; Green, J.P. Lack of a Precursor-Product Relationship Between Histamine and Its Metabolites in Brain After Histidine Loading. J. Neurochem. 2002, 67, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, O.-N.; Majid, A. Role of Histidine/Histamine in Carnosine-Induced Neuroprotection during Ischemic Brain Damage. Brain Res. 2013, 1527, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Xia, S.; He, J.; Lu, G.; Xie, Z.; Han, H. Roles of Taurine in Cognitive Function of Physiology, Pathologies and Toxication. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.C.; Davis, J.M.; Himwich, W.A. Developmental changes in mouse brain: Weight, water content and free amino acids. J. Neurochem. 1968, 15, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasantes-Morales, H.; Hernández-Benítez, R. Taurine and Brain Development: Trophic or Cytoprotective Actions? Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldar, E.; Cohen, J.D.; Niv, Y. The Effects of Neural Gain on Attention and Learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win-Shwe, T.-T.; Mitsushima, D.; Nakajima, D.; Ahmed, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Tsukahara, S.; Kakeyama, M.; Goto, S.; Fujimaki, H. Toluene Induces Rapid and Reversible Rise of Hippocampal Glutamate and Taurine Neurotransmitter Levels in Mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.W.; Rothman, S.M. The Role of Glutamate Neurotoxicity in Hypoxic-Ischemic Neuronal Death. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1990, 13, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknazar, S.; Abbaszadeh, H.-A.; Peyvandi, H.; Rezaei, O.; Forooghirad, H.; Khoshsirat, S.; Peyvandi, A.A. Protective Effect of [Pyr1]-Apelin-13 on Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Hair Cell-like Cells Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 853, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, A.; O’Connor, L.; Dixit, V.M. Apoptosis signaling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 217–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ali Shah, S.W.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, X.; Teng, X. The Contributions of MiR-25-3p, Oxidative Stress, and Heat Shock Protein in a Complex Mechanism of Autophagy Caused by Pollutant Cadmium in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Hepatopancreas. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.A.; Baganizi, D.R.; Sahu, R.; Singh, S.R.; Dennis, V.A. SOCS Proteins as Regulators of Inflammatory Responses Induced by Bacterial Infections: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, R.R.; Wolfe, S.A.; Bajo, M.; Abeynaike, S.; Pahng, A.; Borgonetti, V.; D’Ambrosio, S.; Nikzad, R.; Edwards, S.; Paust, S.; et al. IL-10 Normalizes Aberrant Amygdala GABA Transmission and Reverses Anxiety-like Behavior and Dependence-Induced Escalation of Alcohol Intake. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 199, 101952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayanan, A.; Carter, J.M.; Landin, J.D.; Morrow, A.L.; Werner, D.F.; Spigelman, I. Role of Interleukin-10 (IL-10) in Regulation of GABAergic Transmission and Acute Response to Ethanol. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, G.; Feng, X.-X.; Ru, Y.-X.; Xiong, T.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, Z.-L.; Mo, R.; Guo, F.; He, Y.-P.; et al. TLR2/4 Ligand-Amplified Liver Inflammation Promotes Initiation of Autoimmune Hepatitis Due to Sustained IL-6/IL-12/IL-4/IL-25 Expression. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 99, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e Habiba, U.; Rafiq, M.; Khawar, M.B.; Nazir, B.; Haider, G.; Nazir, N. The Multifaceted Role of IL-12 in Cancer. Adv. Cancer Biol. Metastasis 2022, 5, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portielje, J.E.; Gratama, J.; van Ojik, H.H.; Stoter, G.; Kruit, W.H. IL-12: A Promising Adjuvant for Cancer Vaccination. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2003, 52, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Behavior | Definition | |
|---|---|---|
| State behavior | Standing | The body is supported on the ground and the piglets stay in a state of arousal |
| Lying | Lying on side or belly | |
| Event behavior | Positive emotion-related behavior | Piglets wagging their tails or playing with penmates, usually including play behavior and tail wagging |
| Rooting | Sniffing, touching, or rooting (substrate on floor) | |
| Pen interaction | Sniffing or biting the trough and grooves with nose or mouth | |
| Belly nosing | Touching or sniffing any part of the body of a penmate except the head | |
| Manipulating ears | Nibbling, sucking, or chewing the tail of a penmate | |
| Manipulating tails | Nibbling, sucking, or chewing the tail of a penmate | |
| Aggressive behavior | Mutual pushing, biting, ramming, or lifting of penmate | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nian, H.; Ding, S.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Bao, J. Effect of Noise and Music on Neurotransmitters in the Amygdala: The Role Auditory Stimuli Play in Emotion Regulation. Metabolites 2023, 13, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080928
Nian H, Ding S, Feng Y, Liu H, Li J, Li X, Zhang R, Bao J. Effect of Noise and Music on Neurotransmitters in the Amygdala: The Role Auditory Stimuli Play in Emotion Regulation. Metabolites. 2023; 13(8):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080928
Chicago/Turabian StyleNian, Haoyang, Susu Ding, Yanru Feng, Honggui Liu, Jianhong Li, Xiang Li, Runxiang Zhang, and Jun Bao. 2023. "Effect of Noise and Music on Neurotransmitters in the Amygdala: The Role Auditory Stimuli Play in Emotion Regulation" Metabolites 13, no. 8: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080928
APA StyleNian, H., Ding, S., Feng, Y., Liu, H., Li, J., Li, X., Zhang, R., & Bao, J. (2023). Effect of Noise and Music on Neurotransmitters in the Amygdala: The Role Auditory Stimuli Play in Emotion Regulation. Metabolites, 13(8), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080928