Ensemble Kinetic Modeling of Metabolic Networks from Dynamic Metabolic Profiles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ensemble Kinetic Modeling


2.1. A Generic Branched Pathway


 = 0.130), and the upper 95% confidence bound of the error function value was determined using Monte Carlo approach (viable
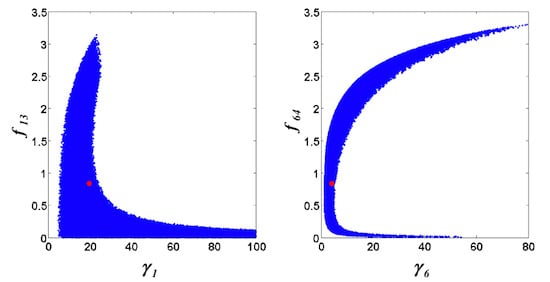
= 0.130), and the upper 95% confidence bound of the error function value was determined using Monte Carlo approach (viable  < 0.347). Table 1 summarizes the outcome of the ensemble modeling. The multiple ellipsoid-based sampling (MEBS) algorithm produces a model ensemble with 59,928 members within the viable parameter subspace. The corresponding volume of the viable subspace represented only 0.284% of the original parameter space (i.e. the space defined by the upper and lower parameter bounds). Figure 2 shows the projections of the viable regions onto the two-dimensional parameter axes of each independent flux. The true parameter values are contained in the viable subspace, and thus belong to the ensemble (red dot in Figure 2). The member models of the ensemble were able to predict the concentration and slope profiles reasonably well (see Table 1), even when the ensemble was constructed using a different error function. The comparison of data and model predictions in Figure 3 demonstrates the equivalence among five randomly selected models in the ensemble. Finally, Figure 4 shows the comparison of model simulations from the same five models and independent (simulated) experimental datasets, indicating that these models could predict the systems dynamics under different initial conditions reasonably well.
< 0.347). Table 1 summarizes the outcome of the ensemble modeling. The multiple ellipsoid-based sampling (MEBS) algorithm produces a model ensemble with 59,928 members within the viable parameter subspace. The corresponding volume of the viable subspace represented only 0.284% of the original parameter space (i.e. the space defined by the upper and lower parameter bounds). Figure 2 shows the projections of the viable regions onto the two-dimensional parameter axes of each independent flux. The true parameter values are contained in the viable subspace, and thus belong to the ensemble (red dot in Figure 2). The member models of the ensemble were able to predict the concentration and slope profiles reasonably well (see Table 1), even when the ensemble was constructed using a different error function. The comparison of data and model predictions in Figure 3 demonstrates the equivalence among five randomly selected models in the ensemble. Finally, Figure 4 shows the comparison of model simulations from the same five models and independent (simulated) experimental datasets, indicating that these models could predict the systems dynamics under different initial conditions reasonably well. | CPU time (sec) a | 1664 |
| Calculated volume of initial parameter space (Vci) b | 2.5 × 105 |
| Estimated volume of viable parameter space (Vev) c | 710.1 ± 5.1 |
| Ratio of Vev to Vci | (284.0 ± 2.0) × 10−3% |
Range of slope errors  | [1.370 × 10−1, 5.081 × 10−1] |
Range of concentration errors  | [3.554 × 10−2, 2.150 × 10−1] |

2.2. The Trehalose Pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae






 = 7.64 × 10−2) and the upper 95% confidence bound was found using a Monte Carlo approach (viable
= 7.64 × 10−2) and the upper 95% confidence bound was found using a Monte Carlo approach (viable  < 0.186). Table 2 gives the summary of the model ensemble for the trehalose model. The model ensemble was represented by 3423 member models, and the volume of the corresponding viable subspace constitutes 2.59 × 10−3% of the original constrained parameter space. The slope errors were acceptable, but the concentration errors had a high upper bound. Upon a closer inspection, only a minority of the model (3 out of 3423) had concentration errors larger than 102, and removing these, the upper bound for the concentration error reduces to 35.92. This issue is not unexpected as the model ensemble was created based on the flux error function and not the concentration error. In particular, there is no guarantee that parameter values with a small flux error will also provide a low concentration error. However, we note that the divergence between the flux error and concentration error functions occurred only rarely (< 0.1%). Figure 6 shows the projections of the viable parameter subspace onto the two-dimensional parameter axes of each independent flux. Finally, Figure 7 shows a comparison between the concentration predictions of five randomly chosen models from the ensemble and the measured metabolite time profiles, again demonstrating that models in the ensemble can reproduce the data equally well.
< 0.186). Table 2 gives the summary of the model ensemble for the trehalose model. The model ensemble was represented by 3423 member models, and the volume of the corresponding viable subspace constitutes 2.59 × 10−3% of the original constrained parameter space. The slope errors were acceptable, but the concentration errors had a high upper bound. Upon a closer inspection, only a minority of the model (3 out of 3423) had concentration errors larger than 102, and removing these, the upper bound for the concentration error reduces to 35.92. This issue is not unexpected as the model ensemble was created based on the flux error function and not the concentration error. In particular, there is no guarantee that parameter values with a small flux error will also provide a low concentration error. However, we note that the divergence between the flux error and concentration error functions occurred only rarely (< 0.1%). Figure 6 shows the projections of the viable parameter subspace onto the two-dimensional parameter axes of each independent flux. Finally, Figure 7 shows a comparison between the concentration predictions of five randomly chosen models from the ensemble and the measured metabolite time profiles, again demonstrating that models in the ensemble can reproduce the data equally well.


| CPU time (sec) | 6489 |
| Calculated volume of initial parameter space (Vci) | 1.25 × 108 |
| Estimated volume of viable parameter space (Vev) | 3237 ± 125 |
| Ratio of Vev to Vci | (25.90 ± 1.00) × 10−4% |
Range of slope errors  | [5.825, 46.42] |
Range of concentration errors  | [1.125, 3.880 × 102] |
3. Discussion
4. Method
4.1. Problem Formulation



4.2. HYPERSPACE Toolbox


4.3. Model Viability Criteria

4.4. Ensemble Modeling Procedure




5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Stephanopoulos, G.; Aristidou, A.A.; Nielsen, J.H. Metabolic Engineering: Principles and Methodologies; Academic Press: San Diego, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Palsson, B. Systems Biology : Properties of Reconstructed Networks; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, A.; Palsson, B.O. Metabolic flux balancing - basic concepts, scientific and practical use. Nat. Biotech. 1994, 12, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombert, A.K.; Nielsen, J. Mathematical modelling of metabolism. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadkar, K.G.; Gunawan, R.; Doyle, F.J. Iterative approach to model identification of biological networks. BMC Bioinf. 2005, 6, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, I.C.; Voit, E.O. Recent developments in parameter estimation and structure identification of biochemical and genomic systems. Math Biosci. 2009, 219, 57–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chis, O.T.; Banga, J.R.; Balsa-Canto, E. Structural identifiability of systems biology models: A critical comparison of methods. Plos One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikerel, I.E.; van Winden, W.A.; Verheijen, P.J.; Heijnen, J.J. Model reduction and a priori kinetic parameter identifiability analysis using metabolome time series for metabolic reaction networks with linlog kinetics. Metab. Eng. 2009, 11, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, A.; Kreutz, C.; Maiwald, T.; Bachmann, J.; Schilling, M.; Klingmuller, U.; Timmer, J. Structural and practical identifiability analysis of partially observed dynamical models by exploiting the profile likelihood. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinath, S.; Gunawan, R. Parameter identifiability of power-law biochemical system models. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 149, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Vilela, M.; Vinga, S.; Maia, M.A.; Voit, E.O.; Almeida, J.S. Identification of neutral biochemical network models from time series data. BMC Syst. Biol. 2009, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, P.; Kell, D. Non-linear optimization of biochemical pathways: Applications to metabolic engineering and parameter estimation. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles, C.G.; Mendes, P.; Banga, J.R. Parameter estimation in biochemical pathways: A comparison of global optimization methods. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.O.; Chakrabarti, A.; Varner, J.D. Ensembles of signal transduction models using pareto optimal ensemble techniques (poets). Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 768–780. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, C.S.; Broadbelt, L.J.; Hatzimanikatis, V. Thermodynamics-based metabolic flux analysis. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 1792–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskovic, L.; Hatzimanikatis, V. Modeling of uncertainties in biochemical reactions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.M.; Rizk, M.L.; Liao, J.C. Ensemble modeling of metabolic networks. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 5606–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Birol, I.; Hatzimanikatis, V. Metabolic control analysis under uncertainty: Framework development and case studies. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 3750–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuepfer, L.; Peter, M.; Sauer, U.; Stelling, J. Ensemble modeling for analysis of cell signaling dynamics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, J.; Flottmann, M.; Li, J.; Tiger, C.F.; Hohmann, S.; Klipp, E. Automated ensemble modeling with modelmage: Analyzing feedback mechanisms in the sho1 branch of the hog pathway. PLOS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanese, M.; Vicino, A. Optimal estimation theory for dynamic systems with set membership uncertainty : An overview. Automatica 1991, 27, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battogtokh, D.; Asch, D.K.; Case, M.E.; Arnold, J.; Schuttler, H.B. An ensemble method for identifying regulatory circuits with special reference to the qa gene cluster of neurospora crassa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16904–16909. [Google Scholar]
- Bardow, A.; Marquardt, W. Incremental and simultaneous identification of reaction kinetics: Methods and comparison. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 2673–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, G.; Chou, I.C.; Voit, E.O. System estimation from metabolic time-series data. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2505–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Sillero, E.; Hafner, M.; Ibig, A.; Stelling, J.; Wagner, A. Efficient characterization of high-dimensional parameter spaces for systems biology. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voit, E.O.; Almeida, J. Decoupling dynamical systems for pathway identification from metabolic profiles. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.L.; Sanchez, C.; Santos, H.; Voit, E.O. Complex coordination of multi-scale cellular responses to environmental stress. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, I.C.; Voit, E.O. Estimation of dynamic flux profiles from metabolic time series data. BMC Syst. Biol. 2012, 6, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, E.O. Computational Analysis of Biochemical Systems : A Practical Guide for Biochemists and Molecular Biologists; Cambridge University Press: New York, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Savageau, M.A. Biochemical systems analysis. I. Some mathematical properties of the rate law for the component enzymatic reactions. J. Theor. Biol. 1969a, 25, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savageau, M.A. Biochemical systems analysis: II. The steady-state solutions for an n-pool system using a power-law approximation. J. Theor. Biol. 1969b, 25, 370–379. [Google Scholar]
- Sorribas, A.; Cascante, M. Structure identifiability in metabolic pathways: Parameter estimation in models based on the power-law formalism. Biochem. J. 1994, 298, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt, W.; Brendel, M.; Bonvin, D. Incremental identification of kinetic models for homogeneous reaction systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 5404–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Runger, G.C. Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, 4th ed; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. New look at statistical-model identification. Ieee T. Automat. Contr. 1974, Ac19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassagnole, C.; Noisommit-Rizzi, N.; Schmid, J.W.; Mauch, K.; Reuss, M. Dynamic modeling of the central carbon metabolism of escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 79, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, W.; Kutalik, Z.; Moulton, V. Estimating parameters for generalized mass action models using constraint propagation. Math. Biosci. 2007, 208, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, E.O.; Goel, G.; Chou, I.C.; Fonseca, L.L. Estimation of metabolic pathway systems from different data sources. IET Syst. Biol. 2009, 3, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J.; Barkema, G.T. Monte carlo methods in statistical physics; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Gelatt, C.D.; Vecchi, M.P. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 1983, 220, 671–680. [Google Scholar]
- Khachiyan, L.G. Rounding of polytopes in the real number model of computation. Math. Oper. Res. 1996, 21, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.V.; Arnold, K.J. Parameter Estimation in Engineering and Science; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, Y. Nonlinear Parameter Estimation; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
Supplementary Files
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, G.; Stephanopoulos, G.; Gunawan, R. Ensemble Kinetic Modeling of Metabolic Networks from Dynamic Metabolic Profiles. Metabolites 2012, 2, 891-912. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo2040891
Jia G, Stephanopoulos G, Gunawan R. Ensemble Kinetic Modeling of Metabolic Networks from Dynamic Metabolic Profiles. Metabolites. 2012; 2(4):891-912. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo2040891
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Gengjie, Gregory Stephanopoulos, and Rudiyanto Gunawan. 2012. "Ensemble Kinetic Modeling of Metabolic Networks from Dynamic Metabolic Profiles" Metabolites 2, no. 4: 891-912. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo2040891
APA StyleJia, G., Stephanopoulos, G., & Gunawan, R. (2012). Ensemble Kinetic Modeling of Metabolic Networks from Dynamic Metabolic Profiles. Metabolites, 2(4), 891-912. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo2040891