Intracellular Fate of Universally Labelled 13C Isotopic Tracers of Glucose and Xylose in Central Metabolic Pathways of Xanthomonas oryzae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
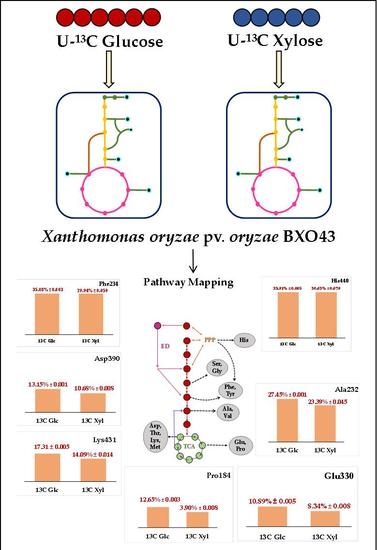
2.1. Central Metabolic Pathway Mapping of BXO43 Strain
2.2. Xoo Cells Dependency on Nutritional Substrates
2.3. Accurate Assessment of Mass Isotopomer Distribution in Amino Acids
2.4. 13C Label Incorporation in Amino Acids Highlights the Metabolic Pathway Activities in Xoo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. KEGG Mapper-Based Metabolic Pathway Reconstruction
4.2. Xanthomonas oryzae Strain Maintenance
4.3. Growth Experiments of Xoo
4.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) of Culture Filtrate
4.5. Cell Hydrolysis
4.6. GC-MS Analysis of TBDMS-Derivatised Amino Acids
4.6.1. Derivatisation of Proteinogenic Amino Acids
4.6.2. Processing of GC-MS Spectra
Data Acquisition
Mass Spectral Data Pre-Treatment
4.6.3. Isocorr-Based Natural Isotope (13C) Abundance Correction and Average 13C Calculation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, D.; Vishnupriya, M.R.; Anil, M.G.; Konda, K.; Raj, Y.; Sonti, R.V. Pathotype and Genetic Diversity amongst Indian Isolates of Xanthomonas Oryzae pv. Oryzae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, J.; Genin, S.; Magori, S.; Citovsky, V.; Sriariyanum, M.; Ronald, P.; Dow, M.; Verdier, V.; Beer, S.V.; Machado, M.A.; et al. Top 10 Plant Pathogenic Bacteria in Molecular Plant Pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midha, S.; Bansal, K.; Kumar, S.; Girija, A.M.; Mishra, D.; Brahma, K.; Laha, G.S.; Sundaram, R.M.; Sonti, R.V.; Patil, P.B. Population Genomic Insights into Variation and Evolution of Xanthomonas Oryzae pv. Oryzae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, B.-M.; Cho, J.-Y. Relationship between Glucose Catabolism and Xanthan Production in Xanthomonas Oryzae pv. Oryzae. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.H.; Cho, J.Y. Transcriptional Analysis of the Gum Gene Cluster from Xanthomonas Oryzae Pathovar Oryzae. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.F.; Degrassi, G.; Devescovi, G.; De Vleesschauwer, D.; Hofte, M.; Myers, M.P.; Venturi, V. A Proteomic Study of Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae in Rice Xylem Sap. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5911–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayi, L.; Maku, R.V.; Patel, H.K.; Sonti, R.V. Identification of Pectin Degrading Enzymes Secreted by Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae and Determination of Their Role in Virulence on Rice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Du, Z.; Huang, L.; Cruz, C.V.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z. Comparative Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Different Expression Patterns in Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae Strains with Putative Virulence-Relevant Genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G. Paper chromatography of inositol phosphates. Nature 1955, 175, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagallo, A.C.; Wang, C.H. Comparative Glucose Catabolism of Xanthomonas Species. J. Bacteriol. 1967, 93, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.F.; Jiang, B.L.; Yang, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Liang, X.X.; Bai, X.F.; Tang, D.J.; Lu, G.T.; He, Y.Q.; et al. Establishment of an Inducing Medium for Type III Effector Secretion in Xanthomonas Campestris Pv. Campestris. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuge, S.; Furutani, A.; Fukunaka, R.; Oku, T.; Tsuno, K.; Ochiai, H.; Inoue, Y.; Kaku, H.; Kubo, Y. Expression of Xanthomonas Oryzae Pv. Oryzae Hrp Genes in XOM2, a Novel Synthetic Medium. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2002, 68, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, U. Metabolic Networks in Motion: 13C-Based Flux Analysis. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiechert, W. 13C Metabolic Flux Analysis. Metab. Eng. 2001, 3, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masakapalli, S.K.; Bryant, F.M.; Kruger, N.J.; Ratcliffe, R.G. The metabolic flux phenotype of heterotrophic Arabidopsis cells reveals a flexible balance between the cytosolic and plastidic contributions to carbohydrate oxidation in response to phosphate limitation. Plant J. 2014, 78, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuge, S.; Ochiai, H.; Inoue, Y.; Oku, T.; Tsuno, K.; Kaku, H.; Kubo, Y. Involvement of Phosphoglucose Isomerase in Pathogenicity of Xanthomonas Oryzae pv. Oryzae. Phytopathology 2004, 94, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniewicz, M.R.; Kelleher, J.K.; Stephanopoulos, G. Accurate Assessment of Amino Acid Mass Isotopomer Distributions for Metabolic Flux Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7554–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatschneider, S.; Schneider, J.; Blom, J.; Letisse, F.; Niehaus, K.; Goesmann, A.; Vorholter, F.J. Systems and Synthetic Biology Perspective of the Versatile Plant-Pathogenic and Polysaccharide-Producing Bacterium Xanthomonas Campestris. Microbiology 2017, 163, 1117–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatschneider, S.; Huber, C.; Neuweger, H.; Watt, T.F.; Puhler, A.; Eisenreich, W.; Wittmann, C.; Niehaus, K.; Vorhölter, F.J. Metabolic Flux Pattern of Glucose Utilization by Xanthomonas Campestris Pv. Campestris: Prevalent Role of the Entner-Doudoroff Pathway and Minor Fluxes through the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Glycolysis. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 2663–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatschneider, S.; Vorholter, F.J.; Ruckert, C.; Becker, A.; Eisenreich, W.; Puhler, A.; Niehaus, K. Genome-Enabled Determination of Amino Acid Biosynthesis in Xanthomonas Campestris Pv. Campestris and Identification of Biosynthetic Pathways for Alanine, Glycine, and Isoleucine by 13C-Isotopologue Profiling. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2011, 286, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, E.; Eden, E.; Milo, R.; Alon, U. Central Carbon Metabolism as a Minimal Biochemical Walk between Precursors for Biomass and Energy. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfall, C.S.; Levin, P.A. Comprehensive Analysis of Central Carbon Metabolism Illuminates Connections between Nutrient Availability, Growth Rate, and Cell Morphology in Escherichia Coli. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagianni, M. Recent Advances in Engineering the Central Carbon Metabolism of Industrially Important Bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenreich, W.; Dandekar, T.; Heesemann, J.; Goebel, W. Carbon Metabolism of Intracellular Bacterial Pathogens and Possible Links to Virulence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.H.; Feng, X.; Tang, Y.J.; Blankenship, R.E. Carbohydrate Metabolism and Carbon Fixation in Roseobacter denitrificans OCh114. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodina, I.; Scho, C.; Eliasson, A.; Nielsen, J.; Schöller, C.; Eliasson, A.; Nielsen, J. Metabolic Network Analysis of Streptomyces Tenebrarius, a Streptomyces Species with an Active Entner-Duodoroff Pathway. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 2294–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnarsson, N.; Bruheim, P.; Nielsen, J. Glucose Metabolism in the Antibiotic Producing Actinomycete Nonomuraea Sp. ATCC 39727. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 88, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorholter, F.J.; Schneiker, S.; Goesmann, A.; Krause, L.; Bekel, T.; Kaiser, O.; Linke, B.; Patschkowski, T.; Ruckert, C.; Schmid, J.; et al. The genome of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris B100 and its use for the reconstruction of metabolic pathways involved in xanthan biosynthesis. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 134, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonien, J.; Schwender, J. Analysis of Metabolic Flux Phenotypes for Two Arabidopsis Mutants with Severe Impairment in Seed Storage Lipid Synthesis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwender, J.; Ohlrogge, J.B. Probing in Vivo Metabolism by Stable Isotope Labeling of Storage Lipids and Proteins in Developing Brassica napusEmbryos. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, B.W.; Carraro, F.; Wolfe, R.R. Measurement of 15 N Enrichment in Multiple Amino Acids and Urea in a Single Analysis by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Biol. Mass Spectrom. 1993, 22, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauner, M.; Sauer, U. GC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids Rapidly Provides Rich Information for Isotopomer Balancing. Biotechnol. Prog. 2000, 16, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapa, M.I.; Aon, J.C.; Stephanopoulos, G. Systematic Quantification of Complex Metabolic Flux Networks Using Stable Isotopes and Mass Spectrometry. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 3525–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crown, S.B.; Long, C.P.; Antoniewicz, M.R. Integrated 13C-Metabolic Flux Analysis of 14 Parallel Labeling Experiments in Escherichia Coli. Metab. Eng. 2015, 28, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, J.E.; Long, C.P.; Antoniewicz, M.R. Comprehensive Analysis of Glucose and Xylose Metabolism in Escherichia Coli under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions by 13C Metabolic Flux Analysis. Metab. Eng. 2017, 39, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommen, A.; Kools, H.J. MetAlign 3.0: Performance Enhancement by Efficient Use of Advances in Computer Hardware. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masakapalli, S.K.; Kruger, N.J.; Ratcliffe, R.G. The metabolic flux phenotype of heterotrophic Arabidopsis cells reveals a complex response to changes in nitrogen supply. Plant J. 2013, 74, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedenfuhr, S.; ten Pierick, A.; van Dam, P.T.N.; Suarez-Mendez, C.A.; Noh, K.; Wahl, S.A. Natural Isotope Correction of MS/MS Measurements for Metabolomics And 13C Fluxomics. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, H.N.B. Correcting for the Effects of Natural Abundance in Stable Isotope Resolved Metabolomics Experiments Involving Ultra-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, P.; Letisse, F.; Sokol, S.; Portais, J.C. IsoCor: Correcting MS Data in Isotope Labeling Experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shree, M.; K. Masakapalli, S. Intracellular Fate of Universally Labelled 13C Isotopic Tracers of Glucose and Xylose in Central Metabolic Pathways of Xanthomonas oryzae. Metabolites 2018, 8, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040066
Shree M, K. Masakapalli S. Intracellular Fate of Universally Labelled 13C Isotopic Tracers of Glucose and Xylose in Central Metabolic Pathways of Xanthomonas oryzae. Metabolites. 2018; 8(4):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040066
Chicago/Turabian StyleShree, Manu, and Shyam K. Masakapalli. 2018. "Intracellular Fate of Universally Labelled 13C Isotopic Tracers of Glucose and Xylose in Central Metabolic Pathways of Xanthomonas oryzae" Metabolites 8, no. 4: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040066
APA StyleShree, M., & K. Masakapalli, S. (2018). Intracellular Fate of Universally Labelled 13C Isotopic Tracers of Glucose and Xylose in Central Metabolic Pathways of Xanthomonas oryzae. Metabolites, 8(4), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040066