Investigating the Protective Effect of Gross Saponins of Tribulus terrestris Fruit against Ischemic Stroke in Rat Using Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
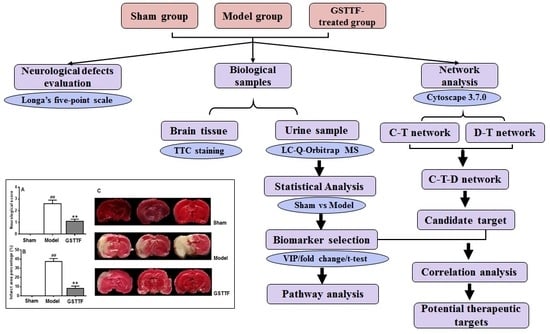
2. Results
2.1. The Effects of GSTTF on MCAO in Rats
2.2. Metabolic Profile in Urine
2.3. Biomarker Selection and Metabolic Pathway Analysis
2.4. Network Pharmacology Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals and Treatments
4.3. Infarct Volume Measurement
4.4. Evaluation of Neurological Defects
4.5. Urine Sample Preparation
4.6. LC-MS Analysis
4.7. Data Analysis and Biomarker Selection
4.8. Network Pharmacology Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Strong, K.; Mathers, C.; Bonita, R. Preventing stroke: Saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, A.; Iadecola, C. Cerebral vascular dysregulation in the ischemic brain. Handbook Clin. Neurol. 2008, 92, 283–305. [Google Scholar]
- Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.; Beumer, D.; van den Berg, L.A.; Lingsma, H.F.; Yoo, A.J.; Schonewille, W.J.; Vos, J.A.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Wermer, M.J. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonarow, G.C.; Smith, E.E.; Saver, J.L.; Reeves, M.J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Grau-Sepulveda, M.V.; Olson, D.M.; Hernandez, A.F.; Peterson, E.D.; Schwamm, L.H. Timeliness of tissue-type plasminogen activator therapy in acute ischemic stroke: Patient characteristics, hospital factors, and outcomes associated with door-to-needle times within 60 minutes. Circulation 2011, 125, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Venketasubramanian, N.; Gan, R.N.; Lambert, C.; Picard, D.; Chan, B.P.; Chan, E.; Bousser, M.G.; Xuemin, S. Danqi Piantang Jiaonang (DJ), a traditional Chinese medicine, in poststroke recovery. Stroke 2009, 40, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.L.; Aa, J.Y.; Feng, S.Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, B.C.; Wang, J.K.; Zhu, Y.J.; Huang, W.Z. Exploring the neuroprotective effects of ginkgolides injection in a rodent model of cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury by GC–MS based metabolomic profiling. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 142, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Xiao, H.; Jing, F.; Tang, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, H. Metabolomics study on the effects of Buchang Naoxintong capsules for treating cerebral ischemia in rats using UPLC-Q/TOF-MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 180, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.M.; Marquessilva, M.H.; Goncalves, E.; Mathias, A.C.; Aguiar, J.G.; Wolff, P. Effect of oral administration of Tribulus terrestris extract on semen quality and body fat index of infertile men. Andrologia 2017, 49, e12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaikan, P.G.; Gauthaman, K.; Prasad, R.N.V. History of herbal medicines with an insight on the pharmacological properties of Tribulus terrestris. Aging Male 2001, 4, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhatre, S.; Nesari, T.; Somani, G.; Kanchan, D.; Sathaye, S. Phytopharmacological overview of Tribulus terrestris. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2014, 8, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sucher, N.J. Insights from molecular investigations of traditional Chinese herbal stroke medicines: Implications for neuroprotective epilepsy therapy. Epilepsy Behav. 2006, 8, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, E.P.; Li, H.; Chen, J.G.; Yang, S.J. Protection by the gross saponins of Tribulus terrestris against cerebral ischemic injury in rats involves the NF-κB pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2011, 1, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, W.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, T.; Xie, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y. GC-MS-Based Metabolomics to Reveal the Protective Effect of Gross Saponins of Tribulus terrestris Fruit against Ischemic Stroke in Rat. Molecules 2019, 24, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Tang, D.-D.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Metabolomics highlights pharmacological bioactivity and biochemical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liang, Y.-Z.; Liu, H.-t. Chemometrics applied to quality control and metabolomics for traditional Chinese medicines. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1015, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; ZHANG, B. Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: Theory, methodology and application. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Fan, T.-P.; Jia, W.; Lu, A.; Zhang, W. Network pharmacology in traditional chinese medicine. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 138460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Tzur, D.; Knox, C.; Eisner, R.; Guo, A.C.; Young, N.; Cheng, D.; Jewell, K.; Arndt, D.; Sawhney, S. HMDB: The Human Metabolome Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijas, C.; Montenegroburke, J.R.; Domingoalmenara, X.; Palermo, A.; Warth, B.; Hermann, G.; Koellensperger, G.; Huan, T.; Uritboonthai, W.; Aisporna, A.E. METLIN: A Technology Platform for Identifying Knowns and Unknowns. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 3156–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamburov, A.; Cavill, R.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Herwig, R.; Keun, H.C. Integrated pathway-level analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics data with IMPaLA. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2917–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberly, W.T.; Wang, Y.; Pham, L.; Furie, K.L.; Gerszten, R.E. Metabolite Profiling Identifies a Branched Chain Amino Acid Signature in Acute Cardioembolic Stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Kong, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Lai, M. GC–MS-based metabolomics identifies an amino acid signature of acute ischemic stroke. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 642, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holecek, M. Branched-chain amino acids in health and disease: Metabolism, alterations in blood plasma, and as supplements. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arany, Z.; Neinast, M.D. Branched Chain Amino Acids in Metabolic Disease. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.J.; Newgard, C.B. Branched-chain amino acids in disease. Science 2019, 363, 582–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernstrom, J.D. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Brain Function. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zeng, X.; Ren, M.; Mao, X.; Qiao, S. Novel metabolic and physiological functions of branched chain amino acids: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, K.; Li, H.; Dong, X.; Tan, G.; Chai, Y.; Wang, W.; Bi, X. Potential of serum metabolites for diagnosing post-stroke cognitive impairment. Mol. BioSyst. 2015, 11, 3287–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, D.; Kim, N.S.; Cha, M.H.; Bang, O.; Ryu, D.H.; Hwang, G. 1H-NMR-based metabolomics study of cerebral infarction. Stroke 2011, 42, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Lou, Z.; Dong, X. UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS based serum metabonomics revealed the metabolic perturbations of ischemic stroke and the protective effect of RKIP in rat models. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorov, E.; Sanghera, D.K.; Vanamala, J.K.P. Biomarker for Ischemic Stroke Using Metabolome: A Clinician Perspective. J. Stroke 2019, 21, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, R.; Zauner, A.; Woodward, J.J.; Young, H.F. Massive Persistent Release of Excitatory Amino Acids Following Human Occlusive Stroke. Stroke 1995, 26, 2187–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoko, K.; Glushakov, A.V.; Colin, S.; Brandy, R.; Dennis, D.M.; Phillips, M.I.P.; Ozcan, M.S.; Seubert, C.N.; Martynyuk, A.E. Neuroprotective action of halogenated derivatives of L-phenylalanine. Stroke 2004, 35, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Corsani, L.; Bizzoco, E.; Pedata, F.; Gianfriddo, M.; Faussonepellegrini, M.S.; Vannucchi, M.G. Inducible nitric oxide synthase appears and is co-expressed with the neuronal isoform in interneurons of the rat hippocampus after transient ischemia induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 211, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirnagl, U.; Iadecola, C.; Moskowitz, M.A. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: An integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupitsyna, T.V.; Bondarenko, E.A.; Botsina, A.Y.; Shetova, I.M.; Limborskaya, S.A.; Skvortsova, V.I.; Slominskii, P.A. Role of polymorphic variants of gene of inducible NO synthase NOS2 in brain infarction in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Mol. Genet. Microbiol. Virol. 2010, 25, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Chuang, D. Regulation and Function of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Isoforms in Neuronal Survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 282, 3904–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jope, R.S.; Yuskaitis, C.J.; Beurel, E. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK3): Inflammation, Diseases, and Therapeutics. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, D.; Wang, Z.; Chiu, C. GSK-3 as a Target for Lithium-Induced Neuroprotection Against Excitotoxicity in Neuronal Cultures and Animal Models of Ischemic Stroke. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.; Messing, R.O.; Chou, W.-H. Mouse model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 13, e2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Want, E.J.; Wilson, I.D.; Gika, H.G.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.P.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling procedures for urine using UPLC–MS. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Annotated Metabolite | Ionization Mode | Retention Time (min) | Detected m/z | Adducts | KEGG ID | Model/Sham | GSTTF/Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leucine | P | 0.708 | 132.1017 | [M + H]+ | C00123 | ↑# | ↓ |
| Citric acid | P | 0.527 | 193.0339 | [M + H]+ | C00158 | ↓# | ↑ |
| Citric acid | N | 0.497 | 191.0190 | [M − H]− | C00158 | ↓# | ↑** |
| Isoleucine | P | 0.659 | 132.1016 | [M + H]+ | C00407 | ↓# | ↑ |
| d-Pantothenic acid | P | 2.928 | 220.1174 | [M + H]+ | C00864 | ↑# | ↓ |
| Hippuric acid | P | 4.044 | 180.0653 | [M + H]+ | C01586 | ↓## | ↑* |
| Hippuric acid | N | 3.999 | 178.0502 | [M − H]− | C01586 | ↓# | ↑ |
| l-Pyroglutamic acid | P | 0.571 | 130.0497 | [M + H]+ | C01879 | ↓### | ↑ |
| Citraconic acid | N | 0.416 | 129.0182 | [M − H]− | C02226 | ↓## | ↑ |
| trans-Aconitic acid | N | 0.591 | 173.0083 | [M − H]− | C02341 | ↓## | ↓ |
| N-Acetyl-l-leucine | P | 5.387 | 174.1122 | [M + H]+ | C02710 | ↑## | ↓ |
| N-Acetyl-l-leucine | N | 6.020 | 172.0972 | [M − H]− | C02710 | ↑## | ↓** |
| 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaric acid | N | 0.525 | 161.0447 | [M − H]− | C03761 | ↑## | ↓ |
| 6-Hydroxycaproic acid | N | 4.550 | 131.0704 | [M − H]− | C06103 | ↑### | ↓ |
| N-Acetyl-l-Citrulline | N | 0.531 | 216.0986 | [M − H]− | C15532 | ↑### | ↓** |
| 7-Aminomethyl-7-deazaguanine | P | 1.322 | 180.0876 | [M + H]+ | C16675 | ↑# | ↓ |
| Pentahomomethionine | P | 9.059 | 220.1361 | [M + H]+ | C17229 | ↑## | ↓ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Fan, M.; Zhao, H.; Xie, S.; Xu, Y. Investigating the Protective Effect of Gross Saponins of Tribulus terrestris Fruit against Ischemic Stroke in Rat Using Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology. Metabolites 2019, 9, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100240
Wang Y, Guo W, Liu Y, Wang J, Fan M, Zhao H, Xie S, Xu Y. Investigating the Protective Effect of Gross Saponins of Tribulus terrestris Fruit against Ischemic Stroke in Rat Using Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology. Metabolites. 2019; 9(10):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100240
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yang, Wenjun Guo, Yue Liu, Jifeng Wang, Meiling Fan, Hongyu Zhao, Shengxu Xie, and Yajuan Xu. 2019. "Investigating the Protective Effect of Gross Saponins of Tribulus terrestris Fruit against Ischemic Stroke in Rat Using Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology" Metabolites 9, no. 10: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100240
APA StyleWang, Y., Guo, W., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Fan, M., Zhao, H., Xie, S., & Xu, Y. (2019). Investigating the Protective Effect of Gross Saponins of Tribulus terrestris Fruit against Ischemic Stroke in Rat Using Metabolomics and Network Pharmacology. Metabolites, 9(10), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9100240