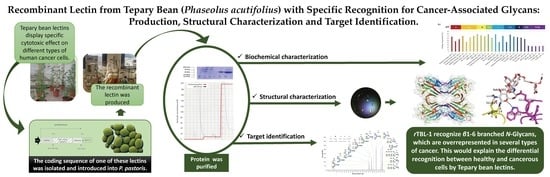
Recombinant Lectin from Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) with Specific Recognition for Cancer-Associated Glycans: Production, Structural Characterization, and Target Identification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Strains
2.3. Plasmids
2.4. Tepary Bean Lectin Fraction (TBLF)
2.5. Vector Construction
2.6. Transformation of Pichia pastoris
2.7. Production
2.8. Heterologus Expression and Purification of rTBL-1
2.9. Molecular Size Exclusion Chromatography
2.10. Thermal Shift Assay (TSA)
2.11. Determination of the Polypeptidic Sequence
2.12. Identification of the Glycosylations Present in the Recombinant Lectin
2.13. Crystallization and Data Collection
2.14. Structure Determination
2.15. Glycan Array
2.16. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
3. Results
3.1. Production of Recombinant TBL1 (rTBL-1)
3.2. rTBL-1 Characterization
3.3. Comparison of rTBL-1 with Native TBL-1
3.4. Structure Determination
3.5. rTBL-1 Binding Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferriz-Martínez, R.A.; Torres-Arteaga, I.C.; Blanco-Labra, A.; García-Gasca, T. The role of plant lectins in cancer treatment. In New Approaches in the Treatment of Cancer; Mejia-Vazquez, M.C., Navarro, S., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 71–89. ISBN 978-1-61728-304-8. [Google Scholar]
- De Mejía, E.G.; Prisecaru, V.I. Lectins as bioactive plant proteins: A potential in cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabelsteen, E. Cell surface carbohydrates as prognostic markers in human carcinomas. J. Pathol. 1996, 179, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.S.; Reis, C.A. Glycosylation in cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A.; Kannagi, R.; Toole, B.; Stanley, P. Glycosylation Changes in Cancer. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Darvill, A.G., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, O.M.T.; Läubli, H. Sialic acids in cancer biology and immunity. Glycobiology 2015, 26, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muinelo-romay, L.; Villar-portela, S.; Cuevas, E.; Gil-martín, E.; Fernández-briera, A. Identification of a (1, 6) fucosylated proteins differentially expressed in human colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriwaki, K.; Miyoshi, E. Fucosylation and gastrointestinal cancer. World J. Hepatol. 2010, 2, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, S.; Gnanapragassam, V.S.; Jain, M.; Rachagani, S.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Batra, S.K. Pathobiological implications of mucin glycans in cancer: Sweet poison and novel targets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2015, 1856, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannagi, R.; Sakuma, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Lim, K.T.; Yusa, A.; Yin, J.; Izawa, M. Altered expression of glycan genes in cancers induced by epigenetic silencing and tumor hypoxia: Clues in the ongoing search for new tumor markers. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, N.; Kizuka, Y. Glycans and cancer: Role of N-Glycans in cancer biomarker, progression and metastasis, and therapeutics. In Advances in Cancer Research; Kenneth, D.T., Fisher, P.B., Eds.; Academic Press Inc.: California, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 126, pp. 11–51. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Qin, C.D.; Yao, R.R.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Ren, Z.G. Over expression of hyaluronan promotes progression of HCC via CD44-mediated pyruvate kinase M2 nuclear translocation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 509–521. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Xiang, T.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Tan, J.; Ren, G. Hyaluronan synthase 2 overexpression is correlated with the tumorigenesis and metastasis of human breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 12101–12114. [Google Scholar]
- Mereiter, S.; Balmaña, M.; Campos, D.; Gomes, J.; Reis, C.A. Glycosylation in the era of cancer-targeted therapy: Where are we heading? Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszuba, K.; Grzybek, M.; Orłowski, A.; Danne, R.; Róg, T.; Simons, K.; Coskun, Ü.; Vattulainen, I. N-Glycosylation as determinant of epidermal growth factor receptor conformation in membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4334–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pucci, M.; Venturi, G.; Malagolini, N.; Chiricolo, M. Glycosylation as a main regulator of growth and death factor receptors signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 580. [Google Scholar]
- García-Gasca, T.; Hernandez-rivera, E.; Lopez-Martínez, J.; Casta, A.L.; Yllescas-gasca, L.; Rodriguez, A.J.; Mendiola-olaya, E.; Castro-guillen, L.; Blanco-labra, A. Effects of tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) protease inhibitor and semipure lectin fractions on cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Celis, U.; López-Martínez, F.J.; Cervantes-Jiménez, R.; Ferríz-Martínez, R.A.; Blanco-Labra, A.; García-Gasca, T. Tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) lectins induce apoptosis and cell arrest in G0/G1 by p53(ser46) phosphorylation in colon cancer cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferriz-Martinez, R.; Garcia-Gasca, K.; Torres-Arteaga, I.; Rodriguez-Mendez, A.J.; Guerrero-Carrillo, M. de J.; Moreno-Celis, U.; Ángeles-Zaragoza, M.V.; Blanco-Labra, A.; Gallegos-Corona, M.A.; Robles-Álvarez, J.P.; et al. Tolerability assessment of a lectin fraction from Tepary bean seeds (Phaseolus acutifolius) orally administered to rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Celis, U.; López-Martínez, J.; Blanco-Labra, A.; Cervantes-Jiménez, R.; Estrada-Martínez, L.E.; García-Pascalin, A.E.; De Jesús Guerrero-Carrillo, M.; Rodríguez-Méndez, A.J.; Mejía, C.; Ferríz-Martínez, R.A.; et al. Phaseolus acutifolius lectin fractions exhibit apoptotic effects on colon cancer: Preclinical studies using dimethilhydrazine or azoxi-methane as cancer induction agents. Molecules 2017, 22, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alatorre-Cruz, J.M.; Pita-López, W.; López-Reyes, R.G.; Ferriz-Martínez, R.A.; Cervantes-Jiménez, R.; de Jesús Guerrero Carrillo, M.; Vargas, P.J.A.; López-Herrera, G.; Rodríguez-Méndez, A.J.; Zamora-Arroyo, A.; et al. Effects of intragastrically-administered Tepary bean lectins on digestive and immune organs: Preclinical evaluation. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alarcón, D.; Mora-Avilés, A.; Espinoza-Núñez, A.; Serrano Jamaica, L.M.; Cruz-Hernández, A.; Rodríguez-Torres, A.; Castro-Guillen, J.L.; Blanco-Labra, A.; García-Gasca, T. Rhizosecretion of a cisgenic lectin by genetic manipulation of Tepary bean plants (Phaseolus acutifolius). J. Biotechnol. X 2019, 3, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.L.; Vaishnav, P. Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alarcón, D.; Blanco-Labra, A.; García-Gasca, T. Expression of lectins in heterologous systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cereghino, J.L.; Cregg, J.M. Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretthauer, R.K.; Castellino, F.J. Glycosylation of Pichia pastoris-derived proteins. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 1999, 30, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Raemaekers, J.M.; De Muro, L.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Fordham-Skelton, A.P. Functional phytohemagglutinin (PHA) and Galanthus nivalis agglutinin (GNA) expressed in Pichia pastoris. Correct N-terminal processing and secretion of heterologous proteins expressed using the PHA-E signal peptide. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 265, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitches, E.C.; Pyati, P.; King, G.F.; Gatehouse, J.A. Fusion to snowdrop lectin magnifies the oral activity of insecticidal ω-hexatoxin-Hv1a peptide by enabling its delivery to the central nervous system. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Pyati, P.; Fitches, E.; Gatehouse, J.A. A recombinant fusion protein containing a spider toxin specific for the insect voltage-gated sodium ion channel shows oral toxicity towards insects of different orders. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winn, M.D.; Ballard, C.C.; Cowtan, K.D.; Dodson, E.J.; Emsley, P.; Evans, P.R.; Keegan, R.M.; Krissinel, E.B.; Leslie, A.G.W.; McCoy, A.; et al. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2011, 67, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamelryck, T.W.; Poortmans, F.; Chrispeels, M.J.; Wyns, L.; Loris, R. The Crystallographic structure of phytohemagglutinin-L. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20479–20485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Nicholls, R.A. REFMAC 5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cummings, R.D.; Darvill, A.G.; Etzler, M.E.; Hahn, M.G. Glycan-recognizing probes as tools. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Har, G.W., Aebi, M., Darvil, A.G., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., Eds.; Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor NY, USA, 2015; pp. 611–625. [Google Scholar]
- Hammarstrom, S.; Hammarstrom, M.L.; Sundblad, G.; Arnarp, J.; Lönngren, J. Mitogenic leukoagglutinin from Phaseolus vulgaris binds to a pentasaccharide unit in N-acetyllactosamine-type glycoprotein glycans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loris, R.; Hamelryck, T.; Bouckaert, J.; Wyns, L. Legume lectin structure. BBA 1998, 1383, 9–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Data Collection | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beamline | PX1, SOLEIL | ||||
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.97918 | ||||
| Space group | P1 | ||||
| a, b, c (Å) | 57.57, 64.47, 67.59 | ||||
| α, β, γ (°) | 96.35, 101.95, 97.27 | ||||
| No. of monomers in asymmetric unit | 4 | ||||
| Resolution (Å) | 32.73–1.9 (1.94–1.9) | ||||
| Total no. of reflections | 451,693 (25,605) | ||||
| No. of unique reflections | 73,400 (4491) | ||||
| Completeness (%) | 99.7 (98.8) | ||||
| Multiplicity | 6.2 (5.7) | ||||
| Mean I/σ (I) | 11 (2.8) | ||||
| Rmerge | 0.073 (0.529) | ||||
| Rmeas | 0.088 (0.649) | ||||
| CC1/2 | 0.997 (0.902) | ||||
| Wilson B factor (A°2) | 23.8 | ||||
| Refinement | |||||
| Resolution (Å) | 32.73–1.90 | ||||
| No. of reflections | 73,390 | ||||
| No. of reflections in test set | 3643 | ||||
| Rwork/Rfree | 0.169/0.213 | ||||
| Rmsd bonds (Å) | 0.014 | ||||
| Rmsd angles (°) | 1.846 | ||||
| Rmsd Chiral (Å3) | 0.091 | ||||
| No. Atoms/Bfac (Å2) | Chain A | Chain B | Chain C | Chain D | |
| Protein | 1805/30.1 | 1779/30.7 | 1805/30.7 | 1747/31.7 | |
| Glycan | 94/40.7 | 28/51.8 | 28/58.0 | 72/47.9 | |
| Metal ions | 2/22.7 | 2/23.0 | 2/22.4 | 2/23.0 | |
| Water | 129/37.1 | 131/36.5 | 136/37.0 | 124/36.5 | |
| Ramachandran Favored (%) Allowed (%) Outliers (%) | 97 3 0 | ||||
| PDB Code | 6TT9 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Alarcón, D.; Varrot, A.; Fitches, E.; Gatehouse, J.A.; Cao, M.; Pyati, P.; Blanco-Labra, A.; Garcia-Gasca, T. Recombinant Lectin from Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) with Specific Recognition for Cancer-Associated Glycans: Production, Structural Characterization, and Target Identification. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040654
Martínez-Alarcón D, Varrot A, Fitches E, Gatehouse JA, Cao M, Pyati P, Blanco-Labra A, Garcia-Gasca T. Recombinant Lectin from Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) with Specific Recognition for Cancer-Associated Glycans: Production, Structural Characterization, and Target Identification. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040654
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Alarcón, Dania, Annabelle Varrot, Elaine Fitches, John A. Gatehouse, Min Cao, Prashant Pyati, Alejandro Blanco-Labra, and Teresa Garcia-Gasca. 2020. "Recombinant Lectin from Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) with Specific Recognition for Cancer-Associated Glycans: Production, Structural Characterization, and Target Identification" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040654
APA StyleMartínez-Alarcón, D., Varrot, A., Fitches, E., Gatehouse, J. A., Cao, M., Pyati, P., Blanco-Labra, A., & Garcia-Gasca, T. (2020). Recombinant Lectin from Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) with Specific Recognition for Cancer-Associated Glycans: Production, Structural Characterization, and Target Identification. Biomolecules, 10(4), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040654