How Can Biomolecules Improve Mucoadhesion of Oral Insulin? A Comprehensive Insight using Ex-Vivo, In Silico, and In Vivo Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemicals
2.1.2. Animals
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of NPs
2.2.2. NPs Characterization
Mean Size, Polydispersity Index (PI), and Zeta Potential Analysis
Surface and Morphological Analysis
2.2.3. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency (EE)
2.2.4. Determination of Recovery Yield (RY)
2.2.5. Insulin Activity
Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.2.6. In Vitro Release Assay
2.2.7. Ex-Vivo Mucoadhesion Study
2.2.8. In Silico Mucoadhesion Analysis
2.2.9. Preliminary Safety Assessment
In Vitro Assessment
In Vivo Preliminary Safety Assessment
2.2.10. In Vivo Efficacy Assay
Diabetes Mellitus Induction
Study Design
2.2.11. Statistical Analysis
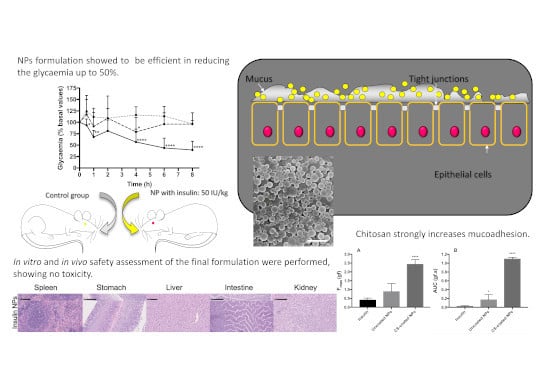
3. Results
3.1. NPs Characterization: Size, Surface Charge, PI, Morphology, EE, and RY
3.2. Insulin Secondary Structure
3.3. In Vitro Release Assay
3.4. Mucoadhesion Study
3.4.1. Ex-Vivo Mucoadhesion Study
3.4.2. In Silico Mucoadhesion Analysis
3.5. Preliminary Safety Assessment of Double-Coated Insulin-Loaded NPs
In Vitro Preliminary Safety Assessment (MTT)
3.6. In Vivo Preliminary Safety Assessment
3.7. In Vivo Efficacy Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 887. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, M.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Michels, A.W. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2014, 383, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeWitt, D.E.; Hirsch, I.B. Outpatient Insulin Therapy in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. JAMA 2003, 289, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conwell, L.S.; Pope, E.; Artiles, A.M.; Mohanta, A.; Daneman, A.; Daneman, D. Dermatological Complications of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, J.C.; Yemane, N.; Brackenridge, A.; Pender, S. Nonmetabolic Complications of Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion: A Patient Survey. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2014, 16, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsayed, A.M. Oral Delivery of Insulin: Novel Approaches. In Recent Advances in Novel Drug Carrier Systems; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.; Sharma, A.R.; Nam, J.-S.; Doss, G.P.C.; Lee, S.-S.; Chakraborty, C. Nanoparticle based insulin delivery system: The next generation efficient therapy for Type 1 diabetes. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elçioğlu, H.K.; Sezer, A.D. Nanoparticle Insulin Drug Delivery—Applications and New Aspects. In Application of Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery; InTech: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, C.P.; Veiga, F.J.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Neufeld, R.J.; Damgé, C. Nanoparticulate biopolymers deliver insulin orally eliciting pharmacological response. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 5290–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damgé, C.; Reis, C.P.; Maincent, P. Nanoparticle strategies for the oral delivery of insulin. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2008, 5, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgé, C.; Maincent, P.; Ubrich, N. Oral delivery of insulin associated to polymeric nanoparticles in diabetic rats. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, P.; Araújo, F.; Reis, S.; Sarmento, B. Oral Insulin Delivery: How Far are We? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.-W.; Sonaje, K.; Liao, Z.-X.; Hsu, L.-W.; Chuang, E.-Y. pH-Responsive Nanoparticles Shelled with Chitosan for Oral Delivery of Insulin: From Mechanism to Therapeutic Applications. Acc. Chem. Res 2012, 45, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-C.; Sonaje, K.; Chen, K.-J.; Sung, H.-W. A review of the prospects for polymeric nanoparticle platforms in oral insulin delivery. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9826–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carino, G.P.; Mathiowitz, E. Oral insulin delivery1Abbreviations: GI, gastrointestinal; IDDM, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus; IU, international units; NIDDM, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus; PIN, phase inversion nanoencapsulation; ZOT, zona occludens toxin.1. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 35, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, B.; Martins, S.; Ferreira, D.; Souto, E.B. Oral insulin delivery by means of solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 743. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, C.P.; Figueiredo, I.V.; Carvalho, R.A.; Jones, J.; Nunes, P.; Soares, A.F.; Silva, C.F.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F.J.; Damgé, C.; et al. Toxicological assessment of orally delivered nanoparticulate insulin. Nanotoxicology 2008, 2, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Shi, K.; Zhang, L.; Tao, A.; Kawashima, Y. Biodegradable nanoparticles loaded with insulin–phospholipid complex for oral delivery: Preparation, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation’. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alai, M.S.; Lin, W.J.; Pingale, S.S. Application of polymeric nanoparticles and micelles in insulin oral delivery. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseininasab, S.; Pashaei-asl, R. Synthesis, Characterization, and In vitro Studies of PLGA-PEG Nanoparticles for Oral Insulin Delivery Synthesis, Characterization, and In vitro Studies of PLGA—PEG Nanoparticles for Oral Insulin Delivery. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 84, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Shrestha, N.; Correia, A.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Sarmento, B.; Hirvonen, J.; Veiga, F.; Seiça, R.; Ribeiro, A.; Santos, H.A. Dual chitosan/albumin-coated alginate/dextran sulfate nanoparticles for enhanced oral delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2016, 232, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.P.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Veiga, F.; Neufeld, R.J.; Damgé, C. Polyelectrolyte Biomaterial Interactions Provide Nanoparticulate Carrier for Oral Insulin Delivery. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.T.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-nemrawi, N.K. Surface modification of PLGA nanoparticles using chitosan: Effect of molecular weight, concentration, and degree of deacetylation. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 3066–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogias, I.A.; Williams, A.C.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Chitosan-based mucoadhesive tablets for oral delivery of ibuprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogias, I.A.; Williams, A.C.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Why is Chitosan Mucoadhesive? Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indest, T.; Laine, J.; Johansson, L.S.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Strnad, S.; Dworczak, R.; Ribitsch, V. Adsorption of Fucoidan and Chitosan Sulfate on Chitosan Modified PET Films Monitored by QCM-D. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, S.; Holmäng, A.; Björntorp, P. The effects of oestrogen and progesterone on insulin sensitivity in female rats. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1993, 149, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.P.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Houng, S.; Veiga, F.; Neufeld, R.J. Nanoparticulate delivery system for insulin: Design, characterization and in vitro/in vivo bioactivity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correia, C.; Nicolai, M.; Matias, D.; Reis, C.P. Optimization of the encapsulation efficiency of a novel oral insulin delivery nanosystem. Biomed. Biopharm. Res. 2014, 11, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrow, C.J.; Yasuda, A.; Kenny, P.T.M.; Zagorski, M.G. Solution conformations and aggregational properties of synthetic amyloid β-peptides of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 225, 1075–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, N.J.; Fasman, G.D. Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry 1969, 8, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.C.B.P. Encapsulação de Fármacos Peptídicos pelo Método de Emulsificação/gelificação Interna; Universidade de Coimbra: Coimbra, Portugal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Prusty, A.K.; Sahu, S.K. Development and Evaluation of Insulin Incorporated Nanoparticles for Oral Administration. ISRN Nanotechnol. 2013, 2013, 591751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagesaether, E.; Hiorth, M.; Sande, S.A. Mucoadhesion and drug permeability of free mixed films of pectin and chitosan : An in vitro and ex vivo study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeleke, O.A.; Choonara, Y.E.; Toit, L.C.; Kumar, P.; Pillay, V. In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Silico Mechanistic Elucidation of the Performance of an Optimized Porosity-Controlled Multi-Elemental Transbuccal System. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 2384–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; Pillay, V. In silico analytico-mathematical interpretation of biopolymeric assemblies: Quantification of energy surfaces and molecular attributes via atomistic simulations. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2018, 3, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malathi, S.; Nandhakumar, P.; Pandiyan, V.; Webster, T.J.; Balasubramanian, S. Novel PLGA-based nanoparticles for the oral delivery of insulin Novel PLGA-based nanoparticles for the oral delivery of insulin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 10, 2207. [Google Scholar]
- Rescignano, N.; Pérez, A.; Kenny, J.; Hernández, R.; Mijangos, C. Preparation and characterization of nickel chelating functionalized poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 468, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffazick, S.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Freitas, L.d.; Pohlmann, A.R. Caracterização e estabilidade físico-química de sistemas poliméricos nanoparticulados para administração de fármacos. Quim. Nova 2003, 26, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Cloos, J. Cell Sensitivity Assays: The MTT Assay; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, O.; Zur, B.; Koch, A.; Tran, N.; Freyenhagen, R.; Hartmann, M.; Zacharowski, K. Clinical chemistry reference database for Wistar rats and C57/BL6 mice. Biol. Chem. 2007, 388, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.; Smyth, H.D.C.; Ghosh, D. Physicochemical properties of mucus and their impact on transmucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.J.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.M.; Ling, Y.; Dong, J.; Xia, R.D.; Sun, X.H. Nanoparticles: Oral Delivery for Protein and Peptide Drugs. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mishra, R.; Kundu, P.P. pH-sensitive chitosan/alginate core-shell nanoparticles for efficient and safe oral insulin delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brange, J.; Langkjœr, L. Insulin Structure and Stability; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 315–350. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, S.; Price, N. The Use of Circular Dichroism in the Investigation of Protein Structure and Function. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2000, 1, 349–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.-G.; Choi, K.-D.; Jang, S.-H.; Shin, H.-C. Role of disulfide bonds in the structure and activity of human insulin. Mol. Cells 2003, 16, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qi, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wu, W. Nanoemulsions coated with alginate/chitosan as oral insulin delivery systems: Preparation, characterization, and hypoglycemic effect in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cózar-Bernal, M.J.; Holgado, M.A.; Arias, J.L.; Muñoz-Rubio, I.; Martín-Banderas, L.; Alvarez-Fuentes, J.; Fernández-Arévalo, M. Insulin-loaded PLGA microparticles: Flow focusing versus double emulsion/solvent evaporation. J. Microencapsul. 2011, 28, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, K.; Sakai, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Hirashima, N.; Kawashima, Y. Improved cellular uptake of chitosan-modified PLGA nanospheres by A549 cell. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 382, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanao, R.P.F.; Jonker, A.M.; Wolke, J.G.C.; Jansen, J.A.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Leeuwenburgh, S.C.G. Physicochemical Properties and Applications of Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) for Use in Bone Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Zheng, A.; Cao, D.; Bi, Y.; Sun, J. Preparation and characterization of insulin-loaded bioadhesive PLGA nanoparticles for oral administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.O.; Rijo, P.; Molpeceres, J.; Figueiredo, I.V.; Ascensao, L.; Fernandes, A.S.; Reis, C.P. Polymeric nanoparticles modified with fatty acids encapsulating betamethasone for anti-inflammatory treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 493, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, S.; Kidron, M.; Wohlgelernter, J.; Modi, P.; Raz, I. Comparison of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of single-dose oral insulin spray and subcutaneous insulin injection in healthy subjects using the euglycemic clamp technique. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidron, M.; Raz, I.; Wolfensberger, M.; Schwob, H.; Schruefer, C. Pharmacokinetics (PK) and Pharmacodynamics (PD) of Oral Insulin in Healthy Subjects. In Proceedings of the ADA 68th Annual Scientific Sessions, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–10 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, F.; Qian, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yin, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Preparation, Characterization, and Oral Delivery of Insulin Loaded Carboxylated Chitosan Grafted Poly(methyl methacrylate) Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreani, T.; de Souza, A.L.; Kiill, C.P.; Lorenzón, E.N.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Calpena, A.C.; Chaud, M.V.; Garcia, M.L.; Gremião, M.P.; Silva, A.M.; et al. Preparation and characterization of PEG-coated silica nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Meng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, R.; Qi, N.; He, H.; Xu, H.; Tang, X. Thiolated Eudragit nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonte, P.; Andrade, F.; Araújo, F.; Andrade, C.; Neves, J.D.; Sarmento, B. Chitosan-Coated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Insulin Delivery; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 295–314. [Google Scholar]
- Makhlof, A.; Tozuka, Y.; Takeuchi, H. Design and evaluation of novel pH-sensitive chitosan nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 42, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonte, P.; Nogueira, T.; Gehm, C.; Ferreira, D.; Sarmento, B. Chitosan-coated solid lipid nanoparticles enhance the oral absorption of insulin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Lv, P.; Wang, L.; Ma, G. Preparation and evaluation of alginate–chitosan microspheres for oral delivery of insulin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample | Mean Size (nm) | PdI | Mean Zeta Potential (mV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empty NPs | Uncoated NPs | 240 ± 2 | 0.110 ± 0.016 | −39 ± 6 |
| Chitosan-coated NPs | 328 ± 2 | 0.231 ± 0.015 | +48 ± 8 | |
| Double-coated NPs | 233 ± 2 | 0.184 ± 0.016 | +34 ± 8 | |
| Insulin-loaded NPs | Uncoated NPs | 936 ± 4 | 0.449 ± 0.023 | −49 ± 5 |
| Chitosan-coated NPs | 819 ± 7 | 0.527 ± 0.028 | +41 ± 13 | |
| Double-coated NPs | 560 ± 9 | 0.546 ± 0.030 | +31 ± 3 | |
| Energy | MUC | PLGA | PLGA–MUC | ΔE a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure Stabilizing | Structure Destabilizing | ||||
| Total b | −166.812 | 2.638 | −171.699 | −7.53 | |
| Bond c | 5.474 | 0.288 | 6.149 | 0.39 | |
| Angle d | 70.351 | 2.534 | 90.682 | 17.80 | |
| Dihed e | 55.173 | 0.885 | 59.13 | 3.07 | |
| vdW f | −29.066 | −1.062 | −62.948 | −32.82 | |
| H-bond g | −7.096 | −0.007 | −6.724 | 0.38 | |
| Elec h | −261.649 | 0.000 | −257.987 | 3.66 | |
| Energy | MUC | Chitosan | PEG | Chitosan/PEG-MUC | ΔE a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure Stabilizing | Structure Destabilizing | |||||
| Total b | −166.812 | 8.822 | 10.127 | −201.742 | −53.879 | |
| Bond c | 5.474 | 1.077 | 0.158 | 6.706 | −0.003 | |
| Angle d | 70.351 | 6.058 | 0.703 | 82.729 | 5.617 | |
| Dihed e | 55.173 | 8.755 | 6.001 | 66.450 | −3.479 | |
| vdW f | −29.066 | 5.920 | 3.264 | −43.716 | −23.834 | |
| H-bond g | −7.096 | 0.000 | 0.000 | −6.774 | 0.322 | |
| Elec h | −261.649 | −12.988 | 0.000 | −307.137 | −32.5 | |
| Insulin-Loaded NPs (n = 5) | Empty NPs (n = 5) | Non-Encapsulated insulin, p.o. (n = 3) | PBS (n = 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leucocytes | - | - | - | - |
| Urobilinogen | N | N | N | N |
| Bilirubin | - | - | - | - |
| Hematuria | +/- | +/- | - | +/- |
| Nitrite | - | - | - | - |
| pH | 5.4 | 5.9 | 5.3 | 5.5 |
| Density | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.03 |
| Proteinuria | +/- | +/- | +/- | +/- |
| Glycosuria | - | - | - | - |
| Ketonic bodies | - | - | +/- | +/- |
| Formulation and Number of Animals | ALT (U/L) | Creatinine (mg/dL) | Urea (mg/dL) | IL-6 (ng/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS (n = 2) | 30.5 ± 12.0 | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 37.0 ± 9.9 | < 1.5 |
| Oral non-encapsulated Insulin (n = 3) | 34. 7 ± 3.8 | 0.38 ± 0.02 | 37. 7 ± 6.5 | < 1.5 |
| SC non-encapsulated Insulin (n = 2) | 21.0± 4.2 | 0.37± 0.01 | 41.0± 1. 8 | < 1.5 |
| Double-coated Insulin-loaded NPs (n = 5) | 34.6 ± 12.1 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 37.4 ± 2.8 | < 1.5 |
| Empty NPs (n = 5) | 35.6 ± 14.2 | 0.35 ± 0.06 | 37.2 ± 1.9 | < 1.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, M.; Martins, A.S.; Catarino, J.; Faísca, P.; Kumar, P.; Pinto, J.F.; Pinto, R.; Correia, I.; Ascensão, L.; Afonso, R.A.; et al. How Can Biomolecules Improve Mucoadhesion of Oral Insulin? A Comprehensive Insight using Ex-Vivo, In Silico, and In Vivo Models. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050675
Amaral M, Martins AS, Catarino J, Faísca P, Kumar P, Pinto JF, Pinto R, Correia I, Ascensão L, Afonso RA, et al. How Can Biomolecules Improve Mucoadhesion of Oral Insulin? A Comprehensive Insight using Ex-Vivo, In Silico, and In Vivo Models. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(5):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050675
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Mariana, Ana Sofia Martins, José Catarino, Pedro Faísca, Pradeep Kumar, João F. Pinto, Rui Pinto, Isabel Correia, Lia Ascensão, Ricardo A. Afonso, and et al. 2020. "How Can Biomolecules Improve Mucoadhesion of Oral Insulin? A Comprehensive Insight using Ex-Vivo, In Silico, and In Vivo Models" Biomolecules 10, no. 5: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050675
APA StyleAmaral, M., Martins, A. S., Catarino, J., Faísca, P., Kumar, P., Pinto, J. F., Pinto, R., Correia, I., Ascensão, L., Afonso, R. A., Gaspar, M. M., Charmier, A. J., Figueiredo, I. V., & Reis, C. P. (2020). How Can Biomolecules Improve Mucoadhesion of Oral Insulin? A Comprehensive Insight using Ex-Vivo, In Silico, and In Vivo Models. Biomolecules, 10(5), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050675