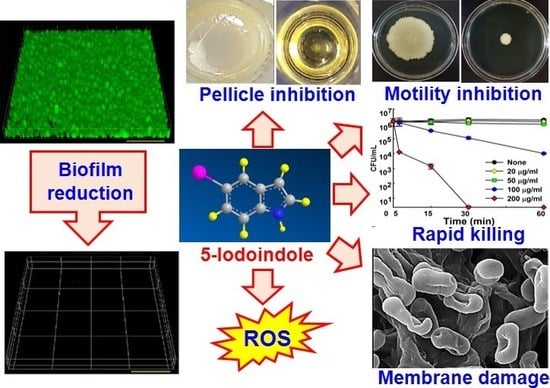
Rapid Killing and Biofilm Inhibition of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains and Other Microbes by Iodoindoles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Chemicals
2.3. Crystal Violet Biofilm Assay
2.4. Biofilm Dispersal Assay
2.5. Pellicle Formation and Motility Assays
2.6. Biofilm Examinations by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.7. Time-Kill Kinetics Assays
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of Cell Membrane Integrity
2.9. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assay
2.10. Analyses of Release of Reducing Sugars and Proteins
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antibiofilm and Antimicrobial Activities of Halogenated Indoles against A. baumannii
3.2. Effects of 5-Iodoindole on Biofilm Dispersal and Biofilm Formation
3.3. Effects of 5-Iodoindole on Pellicle Formation and Surface Motility
3.4. 5-Iodoindole Rapidly Induced A. baumannii Cell Death
3.5. 5-Iodoindole Killing of A. baumannii Was Mediated by Cell Membrane Damage
3.6. Effects of 5-Iodoindole on ROS Production and Release of Reducing Sugars and Proteins
3.7. Antimicrobial Activities of 5-Iodoindole against Other Bacteria and the Fungus C. albicans
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.; Edwards, J.E., Jr.; Gilbert, D.; Scheld, M.; Bartlett, J.G. Bad bugs need drugs: An update on the development pipeline from the antimicrobial availability task force of the infectious diseases society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Liang, B.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Du, X.; Liu, X.; Qiu, S.; Song, H. Relationship between antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation, and biofilm-specific resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergogne-Berezin, E. The increasing role of Acinetobacter species as nosocomial pathogens. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2001, 3, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergogne-Berezin, E.; Towner, K.J. Acinetobacter spp. as nosocomial pathogens: Microbiological, clinical, and epidemiological features. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, T.R.; Liu, X.; Schroeder, M.R.; Kraft, C.S.; Burd, E.M.; Weiss, D.S. Rapid killing of Acinetobacter baumannii by polymyxins is mediated by a hydroxyl radical death pathway. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 2012, 56, 5642–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villers, D.; Espaze, E.; Coste-Burel, M.; Giauffret, F.; Ninin, E.; Nicolas, F.; Richet, H. Nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii infections: Microbiological and clinical epidemiology. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 129, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, J.F.; Soubirou, J.F.; Voiriot, G.; Chemam, S.; Neuville, M.; Mourvillier, B.; Sonneville, R.; Mariotte, E.; Bouadma, L.; Wolff, M. Treatment of bloodstream infections in ICUs. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uwingabiye, J.; Lemnouer, A.; Baidoo, S.; Frikh, M.; Kasouati, J.; Maleb, A.; Benlahlou, Y.; Bssaibis, F.; Mbayo, A.; Doghmi, N.; et al. Intensive care unit-acquired Acinetobacter baumannii infections in a Moroccan teaching hospital: Epidemiology, risk factors and outcome. Germs 2017, 7, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wendt, C.; Dietze, B.; Dietz, E.; Ruden, H. Survival of Acinetobacter baumannii on dry surfaces. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapartegui-Gonzalez, I.; Lazaro-Diez, M.; Bravo, Z.; Navas, J.; Icardo, J.M.; Ramos-Vivas, J. Acinetobacter baumannii maintains its virulence after long-time starvation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Baxendale, I.R.; Ley, S.V.; Nikbin, N. An overview of the key routes to the best selling 5-membered ring heterocyclic pharmaceuticals. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2011, 7, 442–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Wood, T.K.; Lee, J. Roles of indole as an interspecies and interkingdom signaling molecule. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Attila, C.; Cirillo, S.L.; Cirillo, J.D.; Wood, T.K. Indole and 7-hydroxyindole diminish Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. 3-indolylacetonitrile decreases Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formation and Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. Indole and 3-indolylacetonitrile inhibit spore maturation in Paenibacillus alvei. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Cho, M.H.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, J. 7-fluoroindole as an antivirulence compound against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 329, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frei, R.; Breitbach, A.S.; Blackwell, H.E. 2-Aminobenzimidazole derivatives strongly inhibit and disperse Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Angew. Chem. 2012, 51, 5226–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.A.; Banskota, S.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. Indole and 7-benzyloxyindole attenuate the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 4543–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, R.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Efficacy of 7-benzyloxyindole and other halogenated indoles to inhibit Candida albicans biofilm and hyphal formation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 11, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Baek, K.H.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. The multifaceted roles of the interspecies signalling molecule indole in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Gwon, G.; Wood, T.K.; Lee, J. Halogenated indoles eradicate bacterial persister cells and biofilms. AMB Express 2016, 6, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Kim, M.; Kim, E.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J. Indole-associated predator-prey interactions between the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1776–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekharan, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Ravichandran, V.; Lee, J. Assessments of iodoindoles and abamectin as inducers of methuosis in pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajasekharan, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Ravichandran, V.; Kim, J.C.; Park, J.G.; Lee, J. Nematicidal and insecticidal activities of halogenated indoles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekharan, S.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, J. Nematicidal activity of 5-iodoindole against root-knot nematodes. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 163, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekharan, S.K.; Lee, J. Hydropic anthelmintics against parasitic nematodes. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz-Muniz, M.Y.; Lopez-Jacome, L.E.; Hernandez-Duran, M.; Franco-Cendejas, R.; Licona-Limon, P.; Ramos-Balderas, J.L.; Martinez-Vazquez, M.; Belmont-Diaz, J.A.; Wood, T.K.; Garcia-Contreras, R. Repurposing the anticancer drug mitomycin C for the treatment of persistent Acinetobacter baumannii infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikler, M.A. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically: Approved standard. CLSI (NCCLS) 2015, 26, M7–A7. [Google Scholar]
- Raorane, C.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Rajasekharan, S.K.; Garcia-Contreras, R.; Lee, J. Antibiofilm and antivirulence efficacies of flavonoids and curcumin against Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, M.; Nanda, S.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Construction of alizarin conjugated graphene oxide composites for inhibition of Candida albicans biofilms. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mai, J.; Tian, X.L.; Gallant, J.W.; Merkley, N.; Biswas, Z.; Syvitski, R.; Douglas, S.E.; Ling, J.; Li, Y.H. A novel target-specific, salt-resistant antimicrobial peptide against the cariogenic pathogen Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemoth. 2011, 55, 5205–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marti, S.; Rodriguez-Bano, J.; Catel-Ferreira, M.; Jouenne, T.; Vila, J.; Seifert, H.; De, E. Biofilm formation at the solid-liquid and air-liquid interfaces by Acinetobacter species. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mussi, M.A.; Gaddy, J.A.; Cabruja, M.; Arivett, B.A.; Viale, A.M.; Rasia, R.; Actis, L.A. The opportunistic human pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii senses and responds to light. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 6336–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemmer, K.M.; Bonomo, R.A.; Rather, P.N. Genetic analysis of surface motility in Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiology 2011, 157, 2534–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Runci, F.; Bonchi, C.; Frangipani, E.; Visaggio, D.; Visca, P. Acinetobacter baumannii biofilm formation in human serum and disruption by gallium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemoth. 2017, 61, e01563-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Shi, D.; Zhong, R.; Ye, Z.; Ma, C.; Zhou, M.; Xi, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, T.; Kwok, H.F. Bioevaluation of ranatuerin-2Pb from the frog skin secretion of Rana pipiens and its truncated analogues. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golding, C.G.; Lamboo, L.L.; Beniac, D.R.; Booth, T.F. The scanning electron microscope in microbiology and diagnosis of infectious disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, A.; Sharma, P.; Capalash, N. Curcumin alleviates persistence of Acinetobacter baumannii against colistin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, T.K. Combatting bacterial persister cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kentache, T.; Ben Abdelkrim, A.; Jouenne, T.; De, E.; Hardouin, J. Global dynamic proteome study of a pellicle-forming Acinetobacter baumannii strain. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khadke, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Woo, J.T.; Lee, J. Inhibitory effects of honokiol and magnolol on biofilm formation by Acinetobacter baumannii. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2019, 24, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.L.; Chou, C.C.; Hung, D.J.; Lin, S.H.; Pao, I.C.; Lin, J.H.; Huang, F.L.; Dong, R.X.; Lin, J.J. The disruption of bacterial membrane integrity through ROS generation induced by nanohybrids of silver and clay. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5979–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, G.W. The diversity of naturally produced organohalogens. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ke, Z.H.; Yeung, Y.Y. Environmentally benign indole-catalyzed position-selective halogenation of thioarenes and other aromatics. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4448–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boman, H.G. Peptide antibiotics and their role in innate immunity. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 1995, 13, 61–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.; Tiwari, M.; Tiwari, V. Molecular mechanism of antimicrobial activity of chlorhexidine against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Sakr, W.A.; Rahman, K.W. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cell death induction by indole compounds. Cancers 2011, 3, 2955–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, M.R.; Bajaksouzian, S.; Good, C.E.; Butler, M.M.; Williams, J.D.; Peet, N.P.; Bowlin, T.L.; Endimiani, A.; Bonomo, R.A. Novel bis-indole agents active against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 69, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsson, P.; Kihlberg, J. How big is too big for cell permeability? J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1662–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, W.; Yu, Z.; Song, W.; Li, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Hong, W.; Sun, N. Indole-core-based novel antibacterial agent targeting FtsZ. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terraneo, G.; Giuseppe Resnati, G.; Metrangolo, P. Iodine and halogen bonding. In Iodine Chemistry and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 159–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunders, C.A.; Minvielle, M.J.; Worthington, R.J.; Ortiz, M.; Cavanagh, J.; Melander, C. Intercepting bacterial indole signaling with flustramine derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20160–20163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raorane, C.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Rapid Killing and Biofilm Inhibition of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains and Other Microbes by Iodoindoles. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081186
Raorane CJ, Lee J-H, Lee J. Rapid Killing and Biofilm Inhibition of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains and Other Microbes by Iodoindoles. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(8):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081186
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaorane, Chaitany Jayprakash, Jin-Hyung Lee, and Jintae Lee. 2020. "Rapid Killing and Biofilm Inhibition of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains and Other Microbes by Iodoindoles" Biomolecules 10, no. 8: 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081186
APA StyleRaorane, C. J., Lee, J.-H., & Lee, J. (2020). Rapid Killing and Biofilm Inhibition of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains and Other Microbes by Iodoindoles. Biomolecules, 10(8), 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081186