The 40-Year Mystery of Insect Odorant-Binding Proteins
Abstract
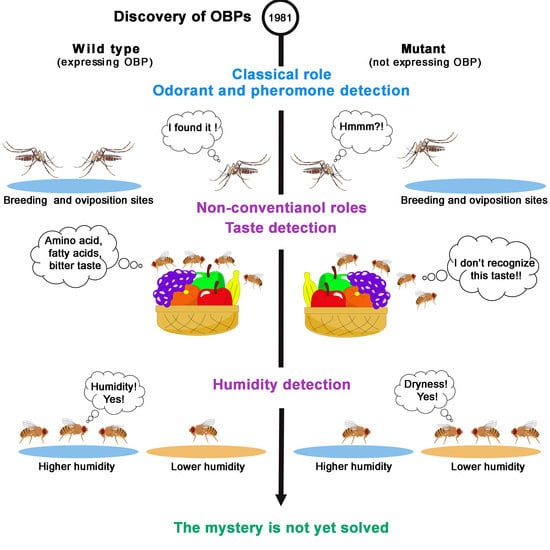
:1. Introduction
2. Expression Pattern of Insect OBPs
2.1. Number of OBP-Coding Genes in Insects
2.2. Evolution of OBP Genes
2.3. Tissue Expression and Cellular Localization of OBPs
3. Biochemical Properties of OBPs
3.1. Structure of Insect OBPs
3.2. Binding Properties of Insect OBPs
4. Diverse Chemosensory Functions of OBPs
4.1. Odorant and Pheromone Transport to Olfactory Receptors
4.2. Modulation of Mating Behaviour
4.3. Sensitivity Modulation
4.4. Humidity Detection
4.5. Haematopoiesis Modulator
4.6. Attraction and Aversion to Gustatory Cues
4.7. Perspectives on Genetic Analysis of OBPs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Getchell, T.V.; Margolis, F.L.; Getchell, M.L. Perireceptor and receptor events in vertebrate olfaction. Prog. Neurobiol. 1984, 23, 317–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant Reception in Insects: Roles of Receptors, Binding Proteins, and Degrading Enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Zhou, J.-J.; Ban, L.P.; Calvello, M. Soluble proteins in insect chemical communication. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Maida, R. Odorant-binding proteins in insects. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 111, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrecht, R.A. Odorant-Binding Proteins: Expression and Function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 855, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegonia, M.; Pelosi, P.; Vincenta, F.; Spinellia, S.; Campanacci, V.; Grollic, S.; Ramonic, R.; Cambillaua, C. Mammalian odorant binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 2000, 1482, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R. Molecular Basis of Pheromone Detection in Insects. Compr. Mol. Insect Sci. 2005, 3, 753–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Baldaccini, N.E.; Pisanelli, A.M. Identification of a specific olfactory receptor for 2-isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine. Biochem. J. 1982, 201, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelosi, P.; Pisanelli, A.M.; Baldaccini, N.E.; Gagliardo, A. Binding of [3H]-2-isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine to cow olfactory mucosa. Chem. Senses 1981, 6, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevsner, J.; Hou, V.; Snowman, A.M.; Snyder, S.H. Odorant-binding protein. Characterization of ligand binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 6118–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.G.; Riddiford, L.M. Pheromone binding and inactivation by moth antennae. Nat. Cell Biol. 1981, 293, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pevsner, J.; Sklar, P.B.; Snyder, S.H. Odorant-binding protein: Localization to nasal glands and secretions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4942–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, F.; Spinelli, S.; Ramoni, R.; Grolli, S.; Pelosi, P.; Cambillau, C.; Tegoni, M. Complexes of porcine odorant binding protein with odorant molecules belonging to different chemical classes. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 300, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, S.; Ramoni, R.; Grolli, S.; Bonicel, J.; Cambillau, C.; Tegoni, M. The Structure of the Monomeric Porcine Odorant Binding Protein Sheds Light on the Domain Swapping Mechanism. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 7913–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millery, J.; Briand, L.; Bézirard, V.; Blon, F.; Fenech, C.; Richard-Parpaillon, L.; Quennedey, B.; Gascuel, J.; Pernollet, J.-C. Specific expression of olfactory binding protein in the aerial olfactory cavity of adult and developing Xenopus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacazette, E.; Gachon, A.-M.; Pitiot, G. A novel human odorant-binding protein gene family resulting from genomic duplicons at 9q34: Differential expression in the oral and genital spheres. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Briand, L.; Eloit, C.; Nespoulous, C.; Bézirard, V.; Huet, J.-C.; Henry, C.; Blon, F.; Trotier, D.; Pernollet, J.-C. Evidence of an Odorant-Binding Protein in the Human Olfactory Mucus: Location, Structural Characterization, and Odorant-Binding Properties. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 7241–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maida, R.; Pelosi, P. Identification and partial purification of a pheromone-binding protein in Bombyx mori. Ital. J. Biochem. 1989, 38, 211A–213A. [Google Scholar]
- Shiota, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Daimon, T.; Mitsuno, H.; Fujii, T.; Matsuyama, S.; Sezutsu, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Kanzaki, R. In vivo functional characterisation of pheromone binding protein-1 in the silkmoth, Bombyx mori. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.; Kohne, A.; Dubnau, J.; Prestwich, G. Expression of pheromone binding proteins during antennal development in the gypsy moth Lymantria dispar. J. Neurosci. 1989, 9, 3332–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prestwich, G.D.; Du, G.; Laforest, S. How is Pheromone Specificity Encoded in Proteins? Chem. Senses 1995, 20, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandh, M.; Johansson, T.; Löfstedt, C. Global transcriptional analysis of pheromone biosynthesis-related genes in the female turnip moth, Agrotis segetum (Noctuidae) using a custom-made cDNA microarray. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, N.; Gallot, A.; Legeai, F.; Montagné, N.; Poivet, E.; Harry, M.; Calatayud, P.-A.; Jacquin-Joly, E. Candidate Chemosensory Genes in the Stemborer Sesamia nonagrioides. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.-L.; Huang, L.-Q.; Pelosi, P.; Wang, C.-Z. Expression in Antennae and Reproductive Organs Suggests a Dual Role of an Odorant-Binding Protein in Two Sibling Helicoverpa Species. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, S.K.; Oxley, P.R.; Kronauer, D.J.C. Comparative genomics and transcriptomics in ants provide new insights into the evolution and function of odorant binding and chemosensory proteins. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manoharan, M.; Chong, M.N.F.; Vaïtinadapoulé, A.; Frumence, E.; Sowdhamini, R.; Offmann, B. Comparative Genomics of Odorant Binding Proteins in Anopheles gambiae, Aedes aegypti, and Culex quinquefasciatus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Gracia, A.; Vieira, F.G.; Rozas, J. Molecular evolution of the major chemosensory gene families in insects. Heredity 2009, 103, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.S.; Xiao, S.; Carlson, J.R. The diverse small proteins called odorant-binding proteins. R. Soc. Open Biol. 2018, 8, 180208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond chemoreception: Diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol. Rev. 2017, 93, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, F.G.; Rozas, J. Comparative Genomics of the Odorant-Binding and Chemosensory Protein Gene Families across the Arthropoda: Origin and Evolutionary History of the Chemosensory System. Genome Biol. Evol. 2011, 3, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyun, S.-I.; Soh, H.Y.; Posavi, M.; Munro, J.B.; Hughes, D.S.; Murali, S.C.; Qu, J.; Dugan, S.; Lee, S.L.; Chao, H.; et al. Evolutionary History of Chemosensory-Related Gene Families across the Arthropoda. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2017, 34, 1838–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epelosi, P.; Eiovinella, I.; Efelicioli, A.; Dani, F.R. Soluble proteins of chemical communication: An overview across arthropods. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinbrecht, R.A.; Ozaki, M.; Ziegelberger, G. Immunocytochemical localization of pheromone-binding protein in moth antennae. Cell Tissue Res. 1992, 270, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larter, N.K.; Sun, J.S.; Carlson, J.R. Organization and function of Drosophila odorant binding proteins. eLife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, J.; Tomioka, S.; Aigaki, T.; Matsuo, T. Evolution of expression patterns of two odorant-binding protein genes, Obp57d and Obp57e, in Drosophila. Gene 2010, 467, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.T.; Shim, J.; Oh, S.R.; Yoon, H.I.; Kim, C.H.; Moon, S.J.; Montell, C. An Odorant-Binding Protein Required for Suppression of Sweet Taste by Bitter Chemicals. Neuron 2013, 79, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rihani, K.; Fraichard, S.; Chauvel, I.; Poirier, N.; Delompré, T.; Neiers, F.; Tanimura, T.; Ferveur, J.-F.; Briand, L. A conserved odorant binding protein is required for essential amino acid detection in Drosophila. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pikielny, C.; Hasan, G.; Rouyer, F.; Rosbash, M. Members of a family of drosophila putative odorant-binding proteins are expressed in different subsets of olfactory hairs. Neuron 1994, 12, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, S.; Hekmat-Scafe, D.; Kim, M.-S.; Park, S.-K.; Carlson, J.; Pikielny, C.; Smith, D.; Steinbrecht, R. Expression mosaic of odorant-binding proteins inDrosophila olfactory organs. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 55, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Iovinella, I.; Dani, F.R.; Liu, Y.-L.; Huang, L.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.-Z.; Pelosi, P.; Wang, G. Conserved chemosensory proteins in the proboscis and eyes of Lepidoptera. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.-F.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Wei, D.; Wang, J.-J.; Jiang, H.-B. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of odorant-binding proteins in the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2019, 31, 100605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, J.; Leal, W.S. Genome Analysis and Expression Patterns of Odorant-Binding Proteins from the Southern House Mosquito Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sparks, J.T.; Bohbot, J.D.; Dickens, J.C. The genetics of chemoreception in the labella and tarsi of Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 48, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippel, S.; Oberhofer, G.; Kahnt, J.; Gerischer, L.; Opitz, L.; Schachtner, J.; Stanke, M.; Schütz, S.; Wimmer, E.A.; Angeli, S. Tissue-specific transcriptomics, chromosomal localization, and phylogeny of chemosensory and odorant binding proteins from the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum reveal subgroup specificities for olfaction or more general functions. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pregitzer, P.; Zielonka, M.; Eichhorn, A.-S.; Jiang, X.; Krieger, J.; Breer, H. Expression of odorant-binding proteins in mouthpart palps of the desert locustSchistocerca gregaria. Insect Mol. Biol. 2019, 28, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koganezawa, M.; Shimada, I. Novel odorant-binding proteins expressed in the taste tissue of the fly. Chem. Senses 2002, 27, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galindo, K.; Smith, D.P. A large family of divergent Drosophila odorant-binding proteins expressed in gustatory and olfactory sensilla. Genetics 2001, 159, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-X.; Pickett, J.A.; Field, L.M.; Zhou, J.-J. Identification and expression of odorant-binding proteins of the malaria-carrying mosquitoesAnopheles gambiae andAnopheles arabiensis. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 58, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitaka, H.; Matsuo, T.; Miura, N.; Ishikawa, Y. Identification of odorant-binding protein genes from antennal expressed sequence tags of the onion fly, Delia antiqua. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 38, 1787–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Peng, W.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Saccone, G.; Zhang, H. Identification and Expression Profile Analysis of Odorant Binding Proteins in the Oriental Fruit Fly Bactrocera dorsalis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14936–14949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, T.; Huang, K.; Tian, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Hao, D. Antennal transcriptome analysis and expression profiles of odorant binding proteins in Clostera restitura. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2019, 29, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.-H.; Wang, S.-P.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Wu, K.-M.; Guo, Y.-Y.; Zhou, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.-J. Identification and tissue distribution of odorant binding protein genes in the lucerne plant bug Adelphocoris lineolatus (Goeze). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvello, M.; Brandazza, A.; Navarrini, A.; Dani, F.; Turillazzi, S.; Felicioli, A.; Pelosi, P. Expression of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in some Hymenoptera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 35, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintapalli, V.R.; Wang, J.; Dow, J.A.T. Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemori, N.; Yamamoto, M.-T. Proteome mapping of the Drosophila melanogaster male reproductive system. Proteomics 2009, 9, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokupek, A.M.; Eyun, S.-I.; Ko, L.; Moriyama, E.N.; Harshman, L.G. Molecular evolutionary analysis of seminal receptacle sperm storage organ genes of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Evol. Biol. 2010, 23, 1386–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.S.; Larter, N.K.; Chahda, J.S.; Rioux, D.; Gumaste, A.; Carlson, J.R. Humidity response depends on the small soluble protein Obp59a in Drosophila. eLife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-K.; Shanbhag, S.; Dubin, A.; De Bruyne, M.; Wang, Q.; Yu, P.; Shimoni, N.; D’Mello, S.; Carlson, J.; Harris, G.; et al. Inactivation of olfactory sensilla of a single morphological type differentially affects the response ofDrosophila to odors. J. Neurobiol. 2002, 51, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchon, N.; Osman, D.; David, F.P.; Fang, H.Y.; Boquete, J.-P.; Deplancke, B.; Lemaitre, B. Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Adult Midgut Compartmentalization in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iovinella, I.; Dani, F.R.; Niccolini, A.; Sagona, S.; Michelucci, E.; Gazzano, A.; Turillazzi, S.; Felicioli, A.; Pelosi, P. Differential Expression of Odorant-Binding Proteins in the Mandibular Glands of the Honey Bee According to Caste and Age. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findlay, G.D.; Yi, X.; Maccoss, M.J.; Swanson, W.J. Proteomics reveals novel Drosophila seminal fluid proteins transferred at mating. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, T. The Soup in My Fly: Evolution, Form and Function of Seminal Fluid Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepil, I.; Hopkins, B.R.; Dean, R.; Thézénas, M.-L.; Charles, P.D.; Konietzny, R.; Fischer, R.; Kessler, B.M.; Wigby, S. Quantitative Proteomics Identification of Seminal Fluid Proteins in Male Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, S46–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Picimbon, J.-F.; Ji, S.; Kan, Y.; Chuanling, Q.; Zhou, J.-J.; Pelosi, P. Multiple functions of an odorant-binding protein in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 372, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirot, L.K.; Poulson, R.L.; McKenna, M.C.; Girnary, H.; Wolfner, M.F.; Harrington, L.C. Identity and transfer of male reproductive gland proteins of the dengue vector mosquito, Aedes aegypti: Potential tools for control of female feeding and reproduction. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baer, B.; Zareie, R.; Paynter, E.; Poland, V.; Millar, A.H. Seminal fluid proteins differ in abundance between genetic lineages of honeybees. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5646–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Baulding, J.; Palli, S.R. Proteomics of Tribolium castaneum seminal fluid proteins: Identification of an angiotensin-converting enzyme as a key player in regulation of reproduction. J. Proteom. 2013, 78, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Da-Silva, A.L.; Kojin, B.B.; Marinotti, O.; James, A.A.; Capurro, M.L. Expression and accumulation of the two-domain odorant-binding protein AaegOBP45 in the ovaries of blood-fed Aedes aegypti. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinotti, O.; Ngo, T.; Kojin, B.B.; Chou, S.-P.; Nguyen, B.; Juhn, J.; Carballar-Lejarazú, R.; Marinotti, P.N.; Jiang, X.; Walter, M.F.; et al. Integrated proteomic and transcriptomic analysis of the Aedes aegypti eggshell. BMC Dev. Biol. 2014, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amenya, D.A.; Chou, W.; Li, J.; Yan, G.; Gershon, P.D.; James, A.A.; Marinotti, O. Proteomics reveals novel components of the Anopheles gambiae eggshell. J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, M.N.; Videvall, E.; Walden, K.K.O.; Harris, M.O.; Robertson, H.M.; Löfstedt, C. Sex- and tissue-specific profiles of chemosensory gene expression in a herbivorous gall-inducing fly (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Cornel, A.J.; Leal, W.S. Odorant-Binding Proteins of the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles funestus sensu stricto. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heavner, M.E.; Gueguen, G.; Rajwani, R.; Pagan, P.E.; Small, C.; Govind, S. Partial venom gland transcriptome of a Drosophila parasitoid wasp, Leptopilina heterotoma, reveals novel and shared bioactive profiles with stinging Hymenoptera. Gene 2013, 526, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Qian, C.; Fang, Q.; Ye, G.-Y. VENOM OF THE PARASITOID WASPPteromalus puparumCONTAINS AN ODORANT BINDING PROTEIN. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 88, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Y.; Han, B.; Lu, X.; Zhou, T.; Feng, M.; Li, J. Proteome and phosphoproteome analysis of honeybee (Apis mellifera) venom collected from electrical stimulation and manual extraction of the venom gland. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishida, Y.; Ishibashi, J.; Leal, W.S. Fatty Acid Solubilizer from the Oral Disk of the Blowfly. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, S.P.; Genta, F.A.; Sorgine, M.H.F.; Logullo, R.; Mesquita, R.D.; Paiva-Silva, G.O.; Majerowicz, D.; Medeiros, M.; Koerich, L.; Terra, W.R.; et al. An Insight into the Transcriptome of the Digestive Tract of the Bloodsucking Bug, Rhodnius prolixus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smartt, C.T.; Erickson, J.S. Bloodmeal-induced differential gene expression in the disease vector culex nigripalpus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, C.T.; Erickson, J.S. Expression of a Novel Member of the Odorant-Binding Protein Gene Family in Culex nigripalpus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, E.D.; Geib, S.M.; Mason, C.J.; Carlson, J.E.; Tien, M.; Chen, H.-Y.; Harding, S.; Tsai, C.-J.; Hoover, K. Host-plant induced changes in microbial community structure and midgut gene expression in an invasive polyphage (Anoplophora glabripennis). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, J.B.; Vigneron, A.; Broderick, N.A.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.S.; Carlson, J.R.; Aksoy, S.; Weiss, B.L. Symbiont-induced odorant binding proteins mediate insect host hematopoiesis. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breer, H.; Boekhoff, I.; Tareilus, E. Rapid kinetics of second messenger formation in olfactory transduction. Nat. Cell Biol. 1990, 345, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raming, K.; Krieger, J.; Breer, H. Primary structure of a pheromone-binding protein from Antheraea pernyi: Homologies with other ligand-carrying proteins. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1990, 160, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorgyi, T.K.; Roby-Shemkovitz, A.J.; Lerner, M.R. Characterization and cDNA cloning of the pheromone-binding protein from the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta: A tissue-specific developmentally regulated protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 9851–9855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raming, K.; Krieger, J.; Breer, H. Molecular cloning of an insect pheromone-binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1989, 256, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogt, R.G.; Rybczynski, R.; Lerner, M.R. Molecular cloning and sequencing of general odorant-binding proteins GOBP1 and GOBP2 from the tobacco hawk moth Manduca sexta: Comparisons with other insect OBPs and their signal peptides. J. Neurosci. 1991, 11, 2972–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laue, M.; Steinbrecht, R.A.; Ziegelberger, G. Immunocytochemical Localization of General Odorant-Binding Protein in Olfactory Sensilla of the Silkmoth Antheraea polyphemus. Naturwissenschaften 1994, 81, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, J.; von Nickisch-Rosenegk, E.; Mameli, M.; Pelosi, P.; Breer, H. Binding proteins from the antennae of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 26, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.-P.; Zhang, H.-J.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q.-Y.; Xiang, Z.-H. The Odorant Binding Protein Gene Family from the Genome of Silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hekmat-Scafe, D.S.; Scafe, C.R.; McKinney, A.J.; Tanouye, M.A. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Odorant-Binding Protein Gene Family in Drosophila melanogaster. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.X.; Zwiebel, L.J.; Smith, D.P. Identification of a distinct family of genes encoding atypical odorant-binding proteins in the malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2003, 12, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, G.-A.; Pickett, J.A.; Field, L.M. “Plus-C” odorant-binding protein genes in two Drosophila species and the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Gene 2004, 327, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-J.; Zhang, G.-A.; Huang, W.; Birkett, M.A.; Field, L.M.; Pickett, J.A.; Pelosi, P. Revisiting the odorant-binding protein LUSH ofDrosophila melanogaster: Evidence for odour recognition and discrimination. FEBS Lett. 2004, 558, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, D.; Rihani, K.; Neiers, F.; Poirier, N.; Fraichard, S.; Gotthard, G.; Chertemps, T.; Maïbèche, M.; Ferveur, J.-F.; Briand, L. The Drosophila odorant-binding protein 28a is involved in the detection of the floral odour ß-ionone. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 77, 2565–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S.; Nikonova, L.; Peng, G. Disulfide structure of the pheromone binding protein from the silkworm moth, Bombyx mori. FEBS Lett. 1999, 464, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scaloni, A.; Montia, M.; Angelib, S.; Pelosib, P. Structural Analysis and Disulfide-Bridge Pairing of Two Odorant-Binding Proteins from Bombyx mori. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 266, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, L.; Nespoulous, C.; Huet, J.-C.; Takahashi, M.; Pernollet, J.-C. Ligand binding and physico-chemical properties of ASP2, a recombinant odorant-binding protein from honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, N.F.; Moreira, M.F.; Melo, A.C. A look inside odorant-binding proteins in insect chemoreception. J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 95, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigue, A.; Gruez, A.; Spinelli, S.; Rivière, S.; Brossut, R.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C. The Crystal Structure of a Cockroach Pheromone-binding Protein Suggests a New Ligand Binding and Release Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30213–30218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lartigue, A.; Gruez, A.; Briand, L.; Blon, F.; Bézirard, V.; Walsh, M.A.; Pernollet, J.-C.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C. Sulfur Single-wavelength Anomalous Diffraction Crystal Structure of a Pheromone-Binding Protein from the Honeybee Apis mellifera L. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4459–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lescop, E.; Briand, L.; Pernollet, J.-C.; Guittet, E. Structural Basis of the Broad Specificity of a General Odorant-Binding Protein from Honeybee. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 2431–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Zhu, J.; Knoll, W. Odorant-Binding Proteins as Sensing Elements for Odour Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pesenti, M.E.; Spinelli, S.; Bezirard, V.; Briand, L.; Pernollet, J.-C.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C. Structural Basis of the Honey Bee PBP Pheromone and pH-induced Conformational Change. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 380, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesenti, M.E.; Spinelli, S.; Bezirard, V.; Briand, L.; Pernollet, J.-C.; Campanacci, V.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C. Queen Bee Pheromone Binding Protein pH-Induced Domain Swapping Favors Pheromone Release. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 390, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinelli, S.; Lagarde, A.; Iovinella, I.; Legrand, P.; Tegoni, M.; Pelosi, P.; Cambillau, C. Crystal structure of Apis mellifera OBP14, a C-minus odorant-binding protein, and its complexes with odorant molecules. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, N.R.; Krogh, R.; Xu, W.; Ishida, Y.; Iulek, J.; Leal, W.S.; Oliva, G. Structure of an Odorant-Binding Protein from the Mosquito Aedes aegypti Suggests a Binding Pocket Covered by a pH-Sensitive “Lid”. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wogulis, M.; Morgan, T.; Ishida, Y.; Leal, W.S.; Wilson, D.K. The crystal structure of an odorant binding protein from Anopheles gambiae: Evidence for a common ligand release mechanism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 339, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanacci, V.; Krieger, J.; Bette, S.; Sturgis, J.N.; Lartigue, A.; Cambillau, C.; Breer, H.; Tegoni, M. Revisiting the Specificity of Mamestra brassicaeand Antheraea polyphemus Pheromone-binding Proteins with a Fluorescence Binding Assay. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20078–20084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drakou, C.E.; Tsitsanou, K.E.; Potamitis, C.; Fessas, D.; Zervou, M.; Zographos, S.E. The crystal structure of the AgamOBP1•Icaridin complex reveals alternative binding modes and stereo-selective repellent recognition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 74, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katti, S.; Lokhande, N.; González, D.; Cassill, A.; Renthal, R. Quantitative analysis of pheromone-binding protein specificity. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2013, 22, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laughlin, J.D.; Ha, T.S.; Jones, D.N.; Smith, D.P. Activation of Pheromone-Sensitive Neurons Is Mediated by Conformational Activation of Pheromone-Binding Protein. Cell 2008, 133, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tegoni, M.; Campanacci, V.; Cambillau, C. Structural aspects of sexual attraction and chemical communication in insects. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, B.H.; Nikonova, L.; Leal, W.S.; Clardy, J. Sexual attraction in the silkworm moth: Structure of the pheromone-binding-protein–bombykol complex. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivière, S.; Lartigue, A.; Quennedey, B.; Campanacci, V.; Farine, J.-P.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C.; Brossut, R. A pheromone-binding protein from the cockroach Leucophaea maderae: Cloning, expression and pheromone binding. Biochem. J. 2003, 371, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horst, R.; Damberger, F.; Luginbühl, P.; Güntert, P.; Peng, G.; Nikonova, L.; Leal, W.S.; Wüthrich, K. NMR structure reveals intramolecular regulation mechanism for pheromone binding and release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14374–14379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, W.S.; Chen, A.M.; Ishida, Y.; Chiang, V.P.; Erickson, M.L.; Morgan, T.I.; Tsuruda, J.M. Kinetics and molecular properties of pheromone binding and release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5386–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wojtasek, H.; Leal, W.S. Conformational Change in the Pheromone-binding Protein fromBombyx mori Induced by pH and by Interaction with Membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30950–30956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.S. Operating Mechanism and Molecular Dynamics of Pheromone-Binding Protein ASP1 as Influenced by pH. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Rayo, J.; Ishida, Y.; Leal, W.S.; Ames, J.B. NMR Structure of Navel Orangeworm Moth Pheromone-Binding Protein (AtraPBP1): Implications for pH-Sensitive Pheromone Detection. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zubkov, S.; Gronenborn, A.M.; Byeon, I.-J.L.; Mohanty, S. Structural Consequences of the pH-induced Conformational Switch in A.polyphemus Pheromone-binding Protein: Mechanisms of Ligand Release. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 354, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Ishida, Y.; Leal, W.S.; Ames, J.B.; Clardy, J. Crystal and solution structures of an odorant-binding protein from the southern house mosquito complexed with an oviposition pheromone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19102–19107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomez-Diaz, C.; Bargeton, B.; Abuin, L.; Bukar, N.; Reina, J.H.; Bartoi, T.; Graf, M.; Ong, H.; Ulbrich, M.H.; Masson, J.-F.; et al. A CD36 ectodomain mediates insect pheromone detection via a putative tunnelling mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvovskaya, S.; Smith, D.P. A spoonful of bitter helps the sugar response go down. Neuron 2013, 79, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, X.; Ha, T.S.; Smith, D.P. SNMP is a signaling component required for pheromone sensitivity in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10996–11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damberger, F.F.; Michel, E.; Ishida, Y.; Leal, W.S.; Wüthrich, K. Pheromone discrimination by a pH-tuned polymorphism of the Bombyx mori pheromone-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18680–18685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelosi, P. Odorant-Binding Proteins. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1994, 29, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessmann, H.; Andronopoulou, E.; Biessmann, M.R.; Douris, V.; Dimitratos, S.D.; Eliopoulos, E.; Guerin, P.M.; Iatrou, K.; Justice, R.W.; Kröber, T.; et al. The Anopheles gambiae Odorant Binding Protein 1 (AgamOBP1) Mediates Indole Recognition in the Antennae of Female Mosquitoes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelletier, J.; Guidolin, A.; Syed, Z.; Cornel, A.J.; Leal, W.S. Knockdown of a Mosquito Odorant-binding Protein Involved in the Sensitive Detection of Oviposition Attractants. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, H.; Gu, J.; Xu, J.; Wu, K.; Tu, Z.; James, A.A.; Chen, X. Molecular and Functional Characterization of Odorant-Binding Protein Genes in an Invasive Vector Mosquito, Aedes albopictus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Pelosi, P.; Dong, S.; Wang, G. Pheromone binding proteins enhance the sensitivity of olfactory receptors to sex pheromones in Chilo suppressalis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forstner, M.; Breer, H.; Krieger, J. A receptor and binding protein interplay in the detection of a distinct pheromone component in the silkmoth Antheraea polyphemus. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 5, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Walker, W.B.; Liu, C.; Lin, K.; Gu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Identification and Characterization of Pheromone Receptors and Interplay between Receptors and Pheromone Binding Proteins in the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xyllostella. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Große-Wilde, E.; Svatoš, A.; Krieger, J. A Pheromone-Binding Protein Mediates the Bombykol-Induced Activation of a Pheromone Receptor In Vitro. Chem. Senses 2006, 31, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Diaz, C.; Reina, J.H.; Cambillau, C.; Benton, R. Ligands for Pheromone-Sensing Neurons Are Not Conformationally Activated Odorant Binding Proteins. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benton, R.; Vannice, K.S.; Vosshall, L.B. An essential role for a CD36-related receptor in pheromone detection in Drosophila. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 450, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtovic, A.; Widmer, A.; Dickson, B.J. A single class of olfactory neurons mediates behavioural responses to a Drosophila sex pheromone. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 446, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naters, W.V.D.G.V.; Carlson, J.R. Receptors and Neurons for Fly Odors in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, T. Insect Sex-Pheromone Signals Mediated by Specific Combinations of Olfactory Receptors. Science 2005, 307, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, T.A.; Morinaga, S.; Ihara, S.; Touhara, K.; Marks, D.S.; Benton, R. Amino acid coevolution reveals three-dimensional structure and functional domains of insect odorant receptors. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentzur, A.; Shmueli, A.; Omesi, L.; Ryvkin, J.; Knapp, J.-M.; Parnas, M.; Davis, F.P.; Shohat-Ophir, G. Odorant binding protein 69a connects social interaction to modulation of social responsiveness in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swarup, S.; Williams, T.I.; Anholt, R.R.H. Functional dissection of Odorant binding protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes, Brain Behav. 2011, 10, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorter, J.R.; Dembeck, L.M.; Everett, L.J.; Morozova, T.V.; Arya, G.H.; Turlapati, L.; Armour, G.E.S.; Schal, C.; Mackay, T.F.C.; Anholt, R.R.H. Obp56hModulates Mating Behavior inDrosophila melanogaster. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics 2016, 6, 3335–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howard, R.W.; Blomquist, G.J. ECOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS OF INSECT HYDROCARBONS. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferveur, J.-F.; Sureau, G. Simultaneous influence on male courtship of stimulatory and inhibitory pheromones produced by live sex-mosaic Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 1996, 263, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferveur, J. The pheromonal role of cuticular hydrocarbons inDrosophila melanogaster. BioEssays 1997, 19, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterbury, J.A.; Jackson, L.L.; Schedl, P. Analysis of the doublesex female protein in Drosophila melanogaster: Role on sexual differentiation and behavior and dependence on intersex. Genetics 1999, 152, 1653–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Sun, J.S.; Carlson, J.R. Robust olfactory responses in the absence of odorant binding proteins. eLife 2019, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegelberger, G. Redox-Shift of the Pheromone-Binding Protein in the Silkmoth Antheraea Polyphemus. Eur. J. Biochem. 2008, 232, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.P.; Hekmat-Scafe, D.S.; Gaines, P.; Carlson, J.R. Putative Drosophila pheromone-binding proteins expressed in a subregion of the olfactory system. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16340–16347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuermann, E.A.; Smith, D.P. Odor-Specific Deactivation Defects in aDrosophilaOdorant-Binding Protein Mutant. Genet. 2019, 213, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, E.; Haba, D.; Aigaki, T.; Matsuo, T. Behavioral analyses of mutants for two odorant-binding protein genes, Obp57d and Obp57e, in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Genet. Syst. 2008, 83, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, T.; Sugaya, S.; Yasukawa, J.; Aigaki, T.; Fuyama, Y. Odorant-Binding Proteins OBP57d and OBP57e Affect Taste Perception and Host-Plant Preference in Drosophila sechellia. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swarup, S.; Morozova, T.V.; Sridhar, S.; Nokes, M.; Anholt, R.R. Modulation of Feeding Behavior by Odorant-Binding Proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wei, Y.; Sun, L.; An, X.; Dhiloo, K.H.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Khashaveh, A.; Gu, S.; Zhang, Y. Mouthparts enriched odorant binding protein AfasOBP11 plays a role in the gustatory perception of Adelphocoris fasciaticollis. J. Insect Physiol. 2019, 117, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steck, K.; Walker, S.J.; Itskov, P.M.; Baltazar, C.; Moreira, J.-M.; Ribeiro, C. Internal amino acid state modulates yeast taste neurons to support protein homeostasis in Drosophila. eLife 2018, 7, e31625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tabuchi, M.; Liu, S.; Kodama, L.; Horiuchi, W.; Daniels, J.; Chiu, L.; Baldoni, D.; Wu, M.N. Branch-specific plasticity of a bifunctional dopamine circuit encodes protein hunger. Sci. 2017, 356, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Bai, X.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Y. Drosophila FIT is a protein-specific satiety hormone essential for feeding control. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Guo, P.-P.; Sun, Y.-L.; Huang, L.-Q.; Wang, C.-Z. Contribution of odorant binding proteins to olfactory detection of (Z)-11-hexadecenal in Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 131, 103554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grolli, S.; Merli, E.; Conti, V.; Scaltriti, E.; Ramoni, R. Odorant binding protein has the biochemical properties of a scavenger for 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal in mammalian nasal mucosa. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 5131–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo-Márquez, A.; Vázquez-Acevedo, M.; Ongay-Larios, L.; Miranda-Astudillo, H.; Hernández-Muñoz, R.; González-Halphen, D.; Grolli, S.; Ramoni, R. Overexpression of a monomeric form of the bovine odorant-binding protein protectsEscherichia colifrom chemical-induced oxidative stress. Free. Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Flisi, S.; Careri, M.; Riboni, N.; Resimini, S.; Sala, A.; Conti, V.; Mattarozzi, M.; Taddei, S.; Spadini, C.; et al. Vertebrate odorant binding proteins as antimicrobial humoral components of innate immunity for pathogenic microorganisms. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavaggioni, A.; Mucignat-Caretta, C. Major urinary proteins, α2U-globulins and aphrodisin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 2000, 1482, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.L.; Beynon, R.J. Scent wars: The chemobiology of competitive signalling in mice. BioEssays 2004, 26, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, R.; Karthikeyan, K.; Archunan, G.; Huang, P.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Ng, W.V.; Liao, C.C. Using mass spectrometry to detect buffalo salivary odorant-binding protein and its post-translational modifications. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 3248–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilayaraja, R.; Rajkumar, R.; Rajesh, D.; Muralidharan, A.R.; Padmanabhan, P.; Archunan, G. Evaluating the binding efficiency of pheromone binding protein with its natural ligand using molecular docking and fluorescence analysis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spinelli, S.; Vincent, F.; Pelosi, P.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C. Boar salivary lipocalin. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Arena, S.; Spinelli, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Wei, R.; Cambillau, C.; Scaloni, A.; Wang, G.; Pelosi, P. Reverse chemical ecology: Olfactory proteins from the giant panda and their interactions with putative pheromones and bamboo volatiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9802–E9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthukumar, S.; Rajesh, D.; Selvam, R.M.; Saibaba, G.; Suvaithenamudhan, S.; Akbarsha, M.A.; Padmanabhan, P.; Gulyas, B.; Archunan, G. Buffalo nasal odorant-binding protein (bunOBP) and its structural evaluation with putative pheromones. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loebel, D.; Scaloni, A.; Paolini, S.; Fini, C.; Ferrara, L.; Breer, H.; Pelosi, P. Cloning, post-translational modifications, heterologous expression and ligand-binding of boar salivary lipocalin. Biochem. J. 2000, 350, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikkaraja, C.; Bhavika, M.; Singh, R.; Nagarathnam, B.; George, G.; Gulyani, A.; Archunan, G.; Sowdhamini, R. Molecular and functional characterization of buffalo nasal epithelial odorant binding proteins and their structural insights by in silico and biochemical approaches. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, M.A.; Hellinga, H.W. Periplasmic binding proteins: A versatile superfamily for protein engineering. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004, 14, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellinga, H.W.; Marvin, J.S. Protein engineering and the development of generic biosensors. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, C.J. Engineering periplasmic ligand binding proteins as glucose nanosensors. Nano Rev. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Jo, K.; Lee, H.S. Genetically encoded FRET sensors using a fluorescent unnatural amino acid as a FRET donor. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 78661–78668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.S. Engineering a periplasmic binding protein for amino acid sensors with improved binding properties. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 8761–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Wegberg, A.M.J.; Macdonald, A.; Ahring, K.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Blau, N.; Bosch, A.M.; Burlina, A.; Campistol, J.; Feillet, F.; Giżewska, M.; et al. The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: Diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, F.; Ribeiro, A.; Silva, C.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Biotechnological applications of mammalian odorant-binding proteins. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Basini, G.; Grolli, S.; Conti, V.; Bianchi, F.; Grasselli, F.; Careri, M.; Ramoni, R. An innovative bovine odorant binding protein-based filtering cartridge for the removal of triazine herbicides from water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 405, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, C.M.P.M.; Matamá, M.T.; Azoia, N.G.; Mansilha, C.; Casal, M.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Odorant binding proteins: A biotechnological tool for odour control. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 98, 3629–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Species | OBP Gene Number | |
|---|---|---|
 | D. melanogaster | 52 |
| D. simulans | 52 | |
| D. sechellia | 51 | |
| D. yakuba | 55 | |
| D. erecta | 50 | |
| D. ananassae | 50 | |
| D. pseudoobscura | 45 | |
| D. persimilis | 45 | |
| D. willistoni | 62 | |
| D. mojavensis | 43 | |
| D. virilis | 41 | |
| D. grimshaw | 46 | |
 | Anophele gambiae | 69 |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | 109 | |
| Aedes aegypti | 111 | |
 | Tribolium castaneum | 49 |
 | Apis mellifera | 21 |
 | Blatella germanica | 109 |
 | Solenopsis invicta | 18 |
 | Bombyx mori | 44 |
| OBP | Role | Publication |
|---|---|---|
| OBP76a (LUSH) | Solubilization, transport and interaction with SNMP1 | [111,122,134] |
| OBP69a | Implication in cVA response, role remains unclear | [139] |
| OBP28a | Modulation of olfactory sensitivity | [34,94] |
| OBP59a | Humidity detection | [57] |
| OBP57d and OBP57e | Modulation of oviposition site preference to C6-C9 acids in D. melanogaster and D. sechellia Specialization of D. sechellia to its host plant (Tahitian Noni) | [149] [150] |
| OBP49a | Suppression of the appetence for sweet compounds through the perception of bitter chemicals | [36] |
| OBP56h | Modulation of mating behaviour by alteration of cuticular hydrocarbon profiles in males | [141] |
| OBP19b | Detection of peculiar amino acids | [37] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rihani, K.; Ferveur, J.-F.; Briand, L. The 40-Year Mystery of Insect Odorant-Binding Proteins. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040509
Rihani K, Ferveur J-F, Briand L. The 40-Year Mystery of Insect Odorant-Binding Proteins. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(4):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040509
Chicago/Turabian StyleRihani, Karen, Jean-François Ferveur, and Loïc Briand. 2021. "The 40-Year Mystery of Insect Odorant-Binding Proteins" Biomolecules 11, no. 4: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040509
APA StyleRihani, K., Ferveur, J.-F., & Briand, L. (2021). The 40-Year Mystery of Insect Odorant-Binding Proteins. Biomolecules, 11(4), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040509