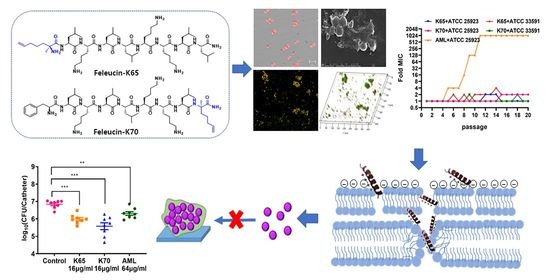
Potent Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities of Feleucin-K3 Analogs Modified by α-(4-Pentenyl)-Ala against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peptide Synthesis
2.2. Strains and Animals
2.3. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity and Salt Stability In Vitro
2.5. Hemolytic Activity
2.6. Serum Stability
2.7. In Vitro Antibiofilm Activity
2.8. Confocal Laser Scanning Fluorescence Microscopy (CLSM)
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.10. Time-Killing Assay
2.11. Resistance Development Assay
2.12. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/Lipoteichoic Acid (LTA) Competitive Inhibition Assay
2.13. Outer Membrane Permeabilization
2.14. Cytoplasmic Membrane Depolarization
2.15. PI Uptake Assay
2.16. DNA-Binding Affinity Assay
2.17. In Vivo Antibiofilm Activity
2.18. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Design and Characterization of the Peptides
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity In Vitro
3.3. Salt Stability
3.4. Hemolytic Activity
3.5. Serum Stability
3.6. Time-Kill Kinetic Curves
3.7. Resistance Development Assay
3.8. Biofilm Inhibition Activity In Vitro
3.8.1. CLSM
3.8.2. SEM
3.9. Membrane Mechanism of Action of Feleucin-K3 Analogs
3.10. DNA-Binding Affinity
3.11. Antibiofilm Activity In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aminov, R. History of antimicrobial drug discovery: Major classes and health impact. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 133, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J.V. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Dou, X.; Song, J.; Lyu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Shan, A. Antimicrobial peptides: Promising alternatives in the post feeding antibiotic era. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 831–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.D.; Green, H.T. Hospital Outbreak of Multiresistant Acinetobacter-Anitratus—An Airborne Mode of Spread. J. Hosp. Infect. 1987, 9, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.J.; Chotimah, I.N.H.; Bertani, P.; Bechinger, B. A spectroscopic study of the membrane interaction of the antimicrobial peptide pleurocidin. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2006, 23, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafee, T.M.A.; Lay, F.T.; Phan, T.K.; Anderson, M.A.; Hulett, M.D. Convergent evolution of defensin sequence, structure and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenson, J.; Stensen, W.; Brandsdal, B.-O.; Haug, B.E.; Monrad, J.; Svendsen, J.S. Antimicrobial Peptides with Stability toward Tryptic Degradation. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3777–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Yip, B.S.; Cheng, H.T.; Wang, A.H.; Chen, H.L.; Cheng, J.W.; Lo, H.J. Increased potency of a novel D-beta-naphthylalanine-substituted antimicrobial peptide against fluconazole-resistant fungal pathogens. FEMS Yeast Res. 2009, 9, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Mendive-Tapia, L.; Pastrian, M.B.; Albericio, F.; Lavilla, R.; Cascone, O.; Iannucci, N.B. Enhanced antimicrobial activity of a peptide derived from human lysozyme by arylation of its tryptophan residues. J. Pept. Sci. 2016, 22, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.J.; Du, Q.; Li, R.J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Chen, T.B.; Shaw, C. Feleucin-BO1: A Novel Antimicrobial Non-Apeptide Amide from the Skin Secretion of the Toad, Bombina orientalis, and Design of a Potent Broad-Spectrum Synthetic Analogue, Feleucin-K3. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 85, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, Z.; Wang, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Mou, L.; Yang, W.; et al. Potent effects of amino acid scanned antimicrobial peptide Feleucin-K3 analogs against both multidrug-resistant strains and biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Rao, J.; Yan, T.; Zhang, B.; Yang, W.; Sun, W.; Xie, J. Feleucin-K3 Analogue with an α-(4-Pentenyl)-Ala Substitution at the Key Site Has More Potent Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities in Vitro and in Vivo. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; He, S.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Dou, X.; Shan, A. Antimicrobial Peptides with High Proteolytic Resistance for Combating Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2286–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.L.; Schneider, T.; Peoples, A.J.; Spoering, A.L.; Engels, I.; Conlon, B.P.; Mueller, A.; Schaberle, T.F.; Hughes, D.E.; Epstein, S.; et al. A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance. Nature 2015, 517, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Gou, S.; Xie, J.; Yao, J.; Ni, J. Antimicrobial peptides conjugated with fatty acids on the side chain of D-amino acid promises antimicrobial potency against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 141, 105123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Rao, J.; Yan, T.; Mou, L.; Wu, X.; Xie, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, B. CPF-C1 analog with effective antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities against Staphylococcus aureus including MRSA. Biochimie 2020, 176, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Li, W.; Lai, Z.; Akhtar, M.U.; Dong, N.; Shan, A.; Ma, D. Effect of terminal arrangement of tryptophan on biological activity of symmetric alpha-helix-forming peptides. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 94, 2051–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangalli-Leite, F.; Scorzoni, L.; Alves de Paula, E.S.A.C.; da Silva, J.F.; de Oliveira, H.C.; de Lacorte Singulani, J.; Gullo, F.P.; Moraes da Silva, R.; Regasini, L.O.; Siqueira da Silva, D.H.; et al. Synergistic effect of pedalitin and amphotericin B against Cryptococcus neoformans by in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, S.; Wang, J.; Shang, L.; Akhtar, M.U.; Wang, Z.; Shi, B.; Feng, X.; Shan, A. Short, symmetric-helical peptides have narrow-spectrum activity with low resistance potential and high selectivity. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2394–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lai, R. The antimicrobial peptide ZY4 combats multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Breij, A.; Riool, M.; Cordfunke, R.A.; Malanovic, N.; de Boer, L.; Koning, R.I.; Ravensbergen, E.; Franken, M.; van der Heijde, T.; Boekema, B.K.; et al. The antimicrobial peptide SAAP-148 combats drug-resistant bacteria and biofilms. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svendsen, J.S.M.; Grant, T.M.; Rennison, D.; Brimble, M.A.; Svenson, J. Very Short and Stable Lactoferricin-Derived Antimicrobial Peptides: Design Principles and Potential Uses. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilpert, K.; Elliott, M.R.; Volkmer-Engert, R.; Henklein, P.; Donini, O.; Zhou, Q.; Winkler, D.F.; Hancock, R.E. Sequence requirements and an optimization strategy for short antimicrobial peptides. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krokhin, O.V.; Spicer, V. Peptide Retention Standards and Hydrophobicity Indexes in Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography of Peptides. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9522–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Guarnieri, M.T.; Vasil, A.I.; Vasil, M.L.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Role of peptide hydrophobicity in the mechanism of action of alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.B.; Xia, Y.Q.; Li, D.; Du, Q.; Liang, D.H. Relationship between peptide structure and antimicrobial activity as studied by de novo designed peptides. BBA-Biomembranes 2014, 1838, 2985–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasupuleti, M.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Antimicrobial peptides: Key components of the innate immune system. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolcott, R.D.; Rhoads, D.D.; Bennett, M.E.; Wolcott, B.M.; Gogokhia, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Dowd, S.E. Chronic wounds and the medical biofilm paradigm. J. Wound Care 2010, 19, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, N.; Zhong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Gou, S.; Chang, L.; Bao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J. Effect of N-methylated and fatty acid conjugation on analogs of antimicrobial peptide Anoplin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, A.; Martínez, M.; Noguera, M.E.; Augusto, M.T.; Disalvo, A.; Santos, N.C.; Semorile, L.; Maffía, P.C. Role of amphipathicity and hydrophobicity in the balance between hemolysis and peptide-membrane interactions of three related antimicrobial peptides. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelezetsky, I.; Tossi, A. Alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides--using a sequence template to guide structure-activity relationship studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1436–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, M.D.T.; Sothiselvam, S.; Lu, T.K.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Peptide Design Principles for Antimicrobial Applications. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3547–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findlay, B.; Zhanel, G.G.; Schweizer, F. Cationic Amphiphiles, a New Generation of Antimicrobials Inspired by the Natural Antimicrobial Peptide Scaffold. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4049–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svenson, J.; Brandsdal, B.-O.; Stensen, W.; Svendsen, J.S. Albumin Binding of Short Cationic Antimicrobial Micropeptides and Its Influence on the in Vitro Bactericidal Effect. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3334–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Kang, N.; Ko, S.J.; Park, J.; Park, E.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.A.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity and Mode of Action of Magainin 2 against Drug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazzaro, B.P.; Zasloff, M.; Rolff, J. Antimicrobial peptides: Application informed by evolution. Science 2020, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamba, Y.; Yamazaki, M. Magainin 2-Induced Pore Formation in the Lipid Membranes Depends on Its Concentration in the Membrane Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 4846–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, M.; Saito, C.; Yokoo, H.; Goto, C.; Kawano, R.; Misawa, T.; Demizu, Y. Development of Antimicrobial Stapled Peptides Based on Magainin 2 Sequence. Molecules 2021, 26, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Speziale, P.; Montanaro, L.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilm formation in Staphylococcus implant infections. A review of molecular mechanisms and implications for biofilm-resistant materials. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5967–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K. Gram-positive bacterial cell envelopes: The impact on the activity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, C.X.; Gao, N.; Lyu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.C.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, J.J.; Shan, A.S. A Novel Dual-Targeted alpha-Helical Peptide With Potent Antifungal Activity Against Fluconazole-Resistant Candida albicans Clinical Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, J.L.; Gillies, E.R. Amphipathic beta-Strand Mimics as Potential Membrane Disruptive Antibiotics. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5953–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Dong, N.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.C.; Ma, Q.Q.; Shan, A.S. Design of imperfectly amphipathic alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides with enhanced cell selectivity. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Peptides. | Sequence a | Mass (Da) b | Number of Amino Acids | Net Charge | TR (Min) c | α-Helix (%) PBS d | α-Helix (%) TFE d | Purity (%) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feleucin-K63 | LKLLKKLL-NH2 | 967.7 | 8 | +4 | 23.738 | 4.600 | 14.970 | 96.070 |
| Feleucin-K64 | LKα-(4-pentenyl)-AlaLKKLL-NH2 | 993.8 | 8 | +4 | 17.768 | 3.330 | 2.900 | 100.000 |
| Feleucin-K65 | α-(4-pentenyl)-AlaLKLLKKLL-NH2 | 1106.8 | 9 | +4 | 17.762 | 2.920 | 5.120 | 98.900 |
| Feleucin-K66 | α-(4-pentenyl)-AlaLKAKKLL-NH2 | 951.7 | 8 | +4 | 14.450 | 3.140 | 5.050 | 96.250 |
| Feleucin-K67 | Fα-(4-pentenyl)-AlaKLLKKLL-NH2 | 1140.8 | 9 | +4 | 18.086 | 3.620 | 18.610 | 98.450 |
| Feleucin-K68 | FLKLα-(4-pentenyl)-AlaKKLL-NH2 | 1140.8 | 9 | +4 | 18.466 | 2.930 | 19.640 | 100.000 |
| Feleucin-K69 | FLKLLKKα-(4-pentenyl)-AlaL-NH2 | 1140.8 | 9 | +4 | 18.635 | 2.990 | 7.140 | 100.000 |
| Feleucin-K70 | FLKLLKKLα-(4-pentenyl)-Ala-NH2 | 1140.8 | 9 | +4 | 17.942 | 3.070 | 15.620 | 100.000 |
| Feleucin-K71 | FLKLLα-(4-pentenyl)-AlaKLL-NH2 | 1125.8 | 9 | +3 | 20.493 | 1.870 | 5.240 | 100.000 |
| Peptides | MIC (μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | S. aureus ATCC 25923 | P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | A. baumannii ATCC 19606 | |
| Feleucin-K63 | >128 | >128 | 64 | >128 |
| Feleucin-K64 | 16 | 16 | 4 | 64 |
| Feleucin-K65 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 |
| Feleucin-K66 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| Feleucin-K67 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| Feleucin-K68 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| Feleucin-K69 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 8 |
| Feleucin-K70 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Feleucin-K71 Magainin 2 | 16 64 | 4 >256 | 8 256 | 4 16 |
| MIC (μg/mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA | K3 | K65 | K67 | K68 | K69 | K70 | K71 |
| MRSA ATCC 33591 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 48 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 54 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 936 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 52 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 74 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 23 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 75 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 113 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 51 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MRSA 71 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| S. aureus 794 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| S. aureus 725 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 |
| MIC (μg/mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. baumannii | K3 | K65 | K67 | K68 | K69 | K70 | K71 |
| A. baumannii 9828 | 16 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 9840 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 9896 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 91152 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 98110 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 92359 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 97830 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 32 |
| A. baumannii 9234 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 5444 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 9236 | 16 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 91869 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 91199 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 9336 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 91810 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 822144 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 91944 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| A. baumannii 91105 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 51243 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 32 |
| A. baumannii 8309 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 9331 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 64 |
| Peptides | E. coli ATCC 25922 | S. aureus ATCC 25923 | P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | A. baumannii ATCC 19606 | MRSA ATCC 33591 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150-mM NaCl | Fold Change | 150-mM NaCl | Fold Change | 150-mM NaCl | Fold Change | 150-mM NaCl | Fold Change | 150-mM NaCl | Fold Change | |
| K65 | 32 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 32 | 4 | 16 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| K67 | 16 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| K68 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| K69 | 16 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 8 | 2 |
| K70 | 32 | 4 | 16 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 16 | 2 | 8 | 1 |
| K71 | 16 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 16 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| Strains | K65 (μg/mL) | K70 (μg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | MBIC50 | MBIC90 | MIC | MBIC50 | MBIC90 | |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| MRSA ATCC 33591 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 8 | 8 | 32 |
| A. baumannii ATCC 19606 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| P.aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Yan, T.; Rao, J.; Yue, X.; Pei, X.; Deng, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, W.; Zhang, B.; Xie, J. Potent Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities of Feleucin-K3 Analogs Modified by α-(4-Pentenyl)-Ala against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050761
Guo X, Yan T, Rao J, Yue X, Pei X, Deng J, Sun W, Yang W, Zhang B, Xie J. Potent Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities of Feleucin-K3 Analogs Modified by α-(4-Pentenyl)-Ala against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(5):761. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050761
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaomin, Tiantian Yan, Jing Rao, Xin Yue, Xiong Pei, Jiahui Deng, Wangsheng Sun, Wenle Yang, Bangzhi Zhang, and Junqiu Xie. 2021. "Potent Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities of Feleucin-K3 Analogs Modified by α-(4-Pentenyl)-Ala against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria" Biomolecules 11, no. 5: 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050761
APA StyleGuo, X., Yan, T., Rao, J., Yue, X., Pei, X., Deng, J., Sun, W., Yang, W., Zhang, B., & Xie, J. (2021). Potent Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities of Feleucin-K3 Analogs Modified by α-(4-Pentenyl)-Ala against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Biomolecules, 11(5), 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050761