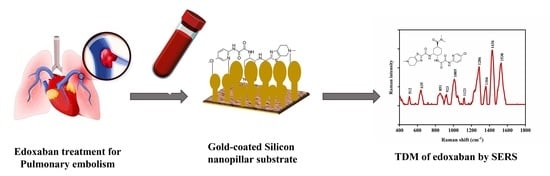
Rapid Assay for the Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Edoxaban
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Preparation of Edoxaban Standard Solutions
2.4. SERS Quantification of Edoxaban
2.5. Reproducibility of SERS Measurements
2.6. Positive and Negative Control Tests
2.7. Cross Validation by HPLC-UV Method
2.8. Determination of Edoxaban in Spiked Blood Plasma
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SERS Measurement of Edoxaban
3.2. SERS Quantification of Edoxaban and Cross-Validation against HPLC-UV Method
3.3. Selectivity of the SERS Method
3.4. Reproducibility of the SERS Measurements
3.5. HPLC-SERS Detection of Edoxaban in Spiked Human Blood Plasma
3.6. Detection of Edoxaban Using Low-Cost SERS Substrate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Horani, R.A. Potential Therapeutic Roles for Direct Factor Xa Inhibitors in Coronavirus Infections. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2020, 20, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langella, V.; Bottino, R.; Asti, A.; Maresca, G.; Di Palma, G.; Pomponi, D.; Sassone, C.; Imbalzano, E.; Russo, V. Edoxaban for the treatment of pulmonary embolism in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, H.A.B.d.; Faria, S.S.; Nascimento, G.P.d.; Santos, I.d.O.; Kobinger, G.P.; Magalhães, K.G. The use of the anticoagulant heparin and corticosteroid dexamethasone as prominent treatments for COVID-19. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 615333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenger-Eriksen, C.; Münster, A.-M.B.; Grove, E. New oral anticoagulants: Clinical indications, monitoring and treatment of acute bleeding complications. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2014, 58, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanuri, S.H.; Kreutz, R.P. Pharmacogenomics of Novel Direct Oral Anticoagulants: Newly Identified Genes and Genetic Variants. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunois, C. Laboratory Monitoring of Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs). Biomed. 2021, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, E.; Shipkova, M. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Drug Monitoring of Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants: Where Do We Stand? Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scridon, A.; Serban, R.C. Laboratory monitoring: A turning point in the use of new oral anticoagulants. Ther. Drug Monit. 2016, 38, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-L.; Lou, D.; Zhang, D.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.-J. Determination of rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban in rat plasma by UPLC–MS/MS method. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 42, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, F.; Bicker, J.; Santos, J.; Rocha, M.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A.; Fortuna, A. Development, validation and application of a new HPLC-DAD method for simultaneous quantification of apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2020, 181, 113109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Couchman, L.; Kipper, K.; Arya, R.; Patel, J.P. A UHPLC-MS/MS method to simultaneously quantify apixaban, edoxaban and rivaroxaban in human plasma and breast milk: For emerging lactation studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1144, 122095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesen, M.H.; Blaich, C.; Streichert, T.; Michels, G.; Müller, C. Paramagnetic micro-particles as a tool for rapid quantification of apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban in human plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2017, 55, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Kochan, J.; Lin, M.; Vandell, A.; Brown, K.; Depasse, F. Determination of edoxaban equivalent concentrations in human plasma by an automated anti-factor Xa chromogenic assay. Thromb. Res. 2017, 155, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanada, K.; Matsumoto, S.-I.; Shibata, S.; Matsubara, H.; Tsukimura, Y.; Takahashi, H. A quantitative LC/MSMS method for determination of edoxaban, a Xa inhibitor and its pharmacokinetic application in patients after total knee arthroplasty. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, e4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, S.; Dyrkorn, R.; Spigset, O.; Hegstad, S. Quantification of apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban in human serum by UHPLC-MS/MS—Method development, validation, and application. Ther. Drug Monit. 2018, 40, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylda, C.; Thiele, R.; Kobold, U.; Volmer, D.A. Recent advances in sample preparation techniques to overcome difficulties encountered during quantitative analysis of small molecules from biofluids using LC-MS/MS. Analyst 2014, 139, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, A.G.; Restaino, S.M.; White, I.M. Vertical-flow paper SERS system for therapeutic drug monitoring of flucytosine in serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 949, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashbee, H.R.; Barnes, R.A.; Johnson, E.M.; Richardson, M.D.; Gorton, R.; Hope, W.W. Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of antifungal agents: Guidelines from the British Society for Medical Mycology. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 69, 1162–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turzhitsky, V.; Zhang, L.; Horowitz, G.L.; Vitkin, E.; Khan, U.; Zakharov, Y.; Qiu, L.; Itzkan, I.; Perelman, L.T. Picoanalysis of Drugs in Biofluids with Quantitative Label-Free Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Small 2018, 14, e1802392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaniawska, A.; Kudelski, A. Applications of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering in Biochemical and Medical Analysis. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.A.; El-Alamin, M.M.A.; Wark, A.W.; Azab, M.M. Detection and quantification of warfarin in pharmaceutical dosage form and in spiked human plasma using surface enhanced Raman scattering. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 228, 117533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muneer, S.; Sarfo, D.K.; Ayoko, G.A.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. Gold-Deposited Nickel Foam as Recyclable Plasmonic Sensor for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Blood by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gushiken, N.K.; Paganoto, G.T.; Temperini, M.L.A.; Teixeira, F.S.; Salvadori, M.C. Substrate for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Formed by Gold Nanoparticles Buried in Poly(methyl methacrylate). ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10366–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.; Muneer, S.; Mendhi, J.; Sabuj, M.Z.R.; Alhamhoom, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, T.; Izake, E.L.; Islam, N. Inhaled Edoxaban dry powder inhaler formulations: Development, characterization and their effects on the coagulopathy associated with COVID-19 infection. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 608, 121122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, P.R.; Eswarudu, M.; Krishna, P.S.; Srikanth, D.; Babu, P.S.; Rohith, N. Novel validated RP-HPLC method for determination of edoxaban tosylate monohydrate in bulk and its pharmaceutical dosage form. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 13, 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Subaihi, A.; Trivedi, D.K.; Hollywood, K.A.; Bluett, J.; Xu, Y.; Muhamadali, H.; Ellis, D.I.; Goodacre, R. Quantitative Online Liquid Chromatography–Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (LC-SERS) of Methotrexate and its Major Metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6702–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, D.; Du, X.; Lo, K.H.; Wang, S.; Zhou, B.; Pan, H. 2D materials: Excellent substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) in chemical sensing and biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Hong, S.-W.; Wu, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.-F. Rapid Formation of Nanoclusters for Detection of Drugs in Urine Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Wu, K.; Hansen, M.F.; Schmidt, M.S.; Boisen, A.; Sun, Y. Quantitative Detection of Trace Level Cloxacillin in Food Samples Using Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Extraction and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Nanopillars. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11484–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Häkkinen, H. The gold–sulfur interface at the nanoscale. Nat. Chem. 2021, 4, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, S.I.; Khan, I. Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) sensors for gas analysis. Analyst 2010, 135, 1365–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.; Mecarini, F.; Gentile, F.; De Angelis, F.; Kumar, H.M.; Candeloro, P.; Liberale, C.; Cuda, G.; Di Fabrizio, E. Nano-patterned SERS substrate: Application for protein analysis vs. temperature. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göksel, Y.; Zor, K.; Rindzevicius, T.; Als-Nielsen, B.E.T.; Schmiegelow, K.; Boisen, A. Quantification of Methotrexate in Human Serum Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering—Toward Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2664–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muneer, S.; Ayoko, G.A.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. Utilizing the thiol chemistry of biomolecules for the rapid determination of anti-TNF-α drug in blood. Talanta 2020, 208, 120411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balčytis, A.; Ryu, M.; Seniutinas, G.; Juodkazytė, J.; Cowie, B.C.; Stoddart, P.R.; Zamengo, M.; Morikawa, J.; Juodkazis, S. Black-CuO: Surface-enhanced Raman scattering and infrared properties. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 18299–18304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muneer, S.; Ayoko, G.A.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. Preconcentration and SERS-based determination of infliximab in blood by using a TNF-α-modified gold-coated copper oxide nanomaterial. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rashid, M.A.; Muneer, S.; Alhamhoom, Y.; Islam, N. Rapid Assay for the Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Edoxaban. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040590
Rashid MA, Muneer S, Alhamhoom Y, Islam N. Rapid Assay for the Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Edoxaban. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(4):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040590
Chicago/Turabian StyleRashid, Md Abdur, Saiqa Muneer, Yahya Alhamhoom, and Nazrul Islam. 2022. "Rapid Assay for the Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Edoxaban" Biomolecules 12, no. 4: 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040590
APA StyleRashid, M. A., Muneer, S., Alhamhoom, Y., & Islam, N. (2022). Rapid Assay for the Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Edoxaban. Biomolecules, 12(4), 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040590