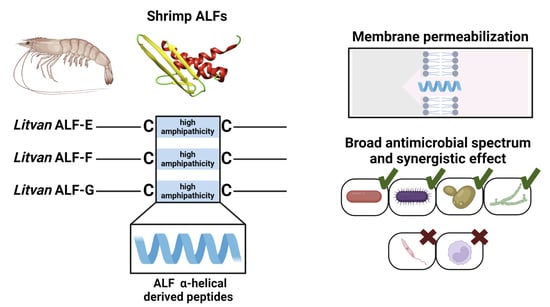
Antimicrobial Spectrum of Activity and Mechanism of Action of Linear Alpha-Helical Peptides Inspired by Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial and Fungal Strains
2.2. Chemical Synthesis of ALF-Derived Peptides
2.3. Circular Dichroism (CD) Measurement
2.4. Antibacterial Assays
2.5. Antifungal Assays
2.6. Determination of Fractional Inhibitory Concentrations (FICs)
2.7. Assays for Bacterial Membrane Permeability
2.8. Antiparasitic Activity
2.9. Cytotoxicity Assays
3. Results
3.1. Linear ALF-Derived Peptides Showed an α-Helical Secondary Structure
3.2. The Synthetic Litvan ALF-G35–54 Peptide Displays a Broad Spectrum of Antibacterial Activity
3.3. Antifungal Activity of Shrimp ALF-Derived Peptides Is Mainly Directed toward Yeasts
3.4. Shrimp ALF-Derived Peptides Can Act Synergically to Inhibit Microbial Growth
3.5. Shrimp ALF-Derived Peptides Permeabilize Bacterial Membranes
3.6. Shrimp ALF-Derived Peptides Display Low Cytotoxicity to Human THP-1 Cells
3.7. Shrimp ALF-Derived Peptides Showed No Trypanocidal or Leishmanicidal Activities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magana, M.; Pushpanathan, M.; Santos, A.L.; Leanse, L.; Fernandez, M.; Ioannidis, A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Apidianakis, Y.; Bradfute, S.; Ferguson, A.L.; et al. The Value of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Age of Resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e216–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijksteel, G.S.; Ulrich, M.M.W.; Middelkoop, E.; Boekema, B.K.H.L. Review: Lessons Learned From Clinical Trials Using Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 616979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, L.; Gross, S.P.; Siryaporn, A. Developing Antimicrobial Synergy With AMPs. Front. Med. Technol. 2021, 3, 640981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzaro, B.P.; Zasloff, M.; Rolff, J. Antimicrobial Peptides: Application Informed by Evolution. Science 2020, 368, eaau5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björn, C.; Noppa, L.; Näslund Salomonsson, E.; Johansson, A.-L.; Nilsson, E.; Mahlapuu, M.; Håkansson, J. Efficacy and Safety Profile of the Novel Antimicrobial Peptide PXL150 in a Mouse Model of Infected Burn Wounds. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Zhang, N.; Yang, J.; Meng, X.; Yang, R.; Li, J.; Sun, T. Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 and IDR-1 Ameliorate MRSA Pneumonia in Vivo. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segev-Zarko, L.; Saar-Dover, R.; Brumfeld, V.; Mangoni, M.L.; Shai, Y. Mechanisms of Biofilm Inhibition and Degradation by Antimicrobial Peptides. Biochem. J. 2015, 468, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greber, K.E.; Dawgul, M. Antimicrobial Peptides Under Clinical Trials. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, G.M.; Rosa, R.D. On the Silver Jubilee of Crustacean Antimicrobial Peptides. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 594–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Rosa, R.D.; Schmitt, P.; Barreto, C.; Vidal-Dupiol, J.; Mitta, G.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachère, E. Antimicrobial Peptides in Marine Invertebrate Health and Disease. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, G.M.; Schmitt, P.; Barreto, C.; Farias, N.D.; Toledo-Silva, G.; Guzmán, F.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Perazzolo, L.M.; Rosa, R.D. Massive Gene Expansion and Sequence Diversification Is Associated with Diverse Tissue Distribution, Regulation and Antimicrobial Properties of Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors in Shrimp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosa, R.D.; Vergnes, A.; de Lorgeril, J.; Goncalves, P.; Perazzolo, L.M.; Sauné, L.; Romestand, B.; Fievet, J.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachère, E.; et al. Functional Divergence in Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors (ALFs): From Recognition of Cell Wall Components to Antimicrobial Activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponprateep, S.; Tharntada, S.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Tassanakajon, A. Gene Silencing Reveals a Crucial Role for Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors from Penaeus Monodon in the Protection against Microbial Infections. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2012, 32, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Boze, H.; Chemardin, P.; Padilla, A.; Moulin, G.; Tassanakajon, A.; Pugnière, M.; Roquet, F.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Gueguen, Y.; et al. NMR Structure of RALF-Pm3, an Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor from Shrimp: Model of the Possible Lipid A-Binding Site. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, P.; Rosa, R.D.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D. An Intimate Link between Antimicrobial Peptide Sequence Diversity and Binding to Essential Components of Bacterial Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somboonwiwat, K.; Marcos, M.; Tassanakajon, A.; Klinbunga, S.; Aumelas, A.; Romestand, B.; Gueguen, Y.; Boze, H.; Moulin, G.; Bachère, E. Recombinant Expression and Anti-Microbial Activity of Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor (ALF) from the Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus Monodon. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Structure and Bioactivity of a Modified Peptide Derived from the LPS-Binding Domain of an Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor (ALF) of Shrimp. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Li, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, J. Modification of a Synthetic LPS-Binding Domain of Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor from Shrimp Reveals Strong Structure-Activity Relationship in Their Antimicrobial Characteristics. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharntada, S.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Rimphanitchayakit, V.; Tassanakajon, A. Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors from the Black Tiger Shrimp, Penaeus Monodon, Are Encoded by Two Genomic Loci. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2008, 24, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Vega, E.; O’Leary, N.A.; Shockey, J.E.; Robalino, J.; Payne, C.; Browdy, C.L.; Warr, G.W.; Gross, P.S. Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor in Litopenaeus Vannamei (LvALF): A Broad Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide Essential for Shrimp Immunity against Bacterial and Fungal Infection. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetru, C.; Bulet, P. Strategies for the Isolation and Characterization of Antimicrobial Peptides of Invertebrates. Methods Mol. Biol. 1997, 78, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, P.; de Lorgeril, J.; Gueguen, Y.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Bachère, E. Expression, Tissue Localization and Synergy of Antimicrobial Peptides and Proteins in the Immune Response of the Oyster Crassostrea Gigas. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 37, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löfgren, S.E.; Miletti, L.C.; Steindel, M.; Bachère, E.; Barracco, M.A. Trypanocidal and Leishmanicidal Activities of Different Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) Isolated from Aquatic Animals. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 118, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, S.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Functional Diversity of Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor Isoforms in Shrimp and Their Characters Related to Antiviral Activity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2602–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial Peptides: Pore Formers or Metabolic Inhibitors in Bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Vasil, A.I.; Hale, J.D.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Vasil, M.L.; Hodges, R.S. Effects of Net Charge and the Number of Positively Charged Residues on the Biological Activity of Amphipathic Alpha-Helical Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides. Biopolymers 2008, 90, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leptihn, S.; Har, J.Y.; Wohland, T.; Ding, J.L. Correlation of Charge, Hydrophobicity, and Structure with Antimicrobial Activity of S1 and MIRIAM Peptides. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9161–9170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jin, S.; Wang, M.; Pang, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y. The Critical Role of Tryptophan in the Antimicrobial Activity and Cell Toxicity of the Duck Antimicrobial Peptide DCATH. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.F.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Seleem, M.N. Evaluation of Short Synthetic Antimicrobial Peptides for Treatment of Drug-Resistant and Intracellular Staphylococcus Aureus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyashree, M.; Mani, M.K.; Reddy, D.; Kumavath, R.; Ghosh, P.; Azevedo, V.; Barh, D. Clinical Applications of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): Where Do We Stand Now? Protein Pept. Lett. 2020, 27, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullberg, B.J.; Arendrup, M.C. Invasive Candidiasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoppo, M.; Poma, N.; Di Luca, M.; Bottai, D.; Tavanti, A. Genetic Manipulation as a Tool to Unravel Candida Parapsilosis Species Complex Virulence and Drug Resistance: State of the Art. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trofa, D.; Gácser, A.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Candida Parapsilosis, an Emerging Fungal Pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H.; Yi, H. Antimicrobial Peptides: Classification, Design, Application and Research Progress in Multiple Fields. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 582779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Covarrubias, M.S.; Cuéllar-Anjel, J.; Varela-Mejías, A.; Elizondo-Ovares, C. Shrimp Bacterial Infections in Latin America: A Review. Asian Fish. Sci. 2018, 31S, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-S.E.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ni, I.-H.; Sheen, J.-F.; Pan, Y.-L.; Kuo, C.-M. Gene Expression and Localization of the Epinecidin-1 Antimicrobial Peptide in the Grouper (Epinephelus Coioides), and Its Role in Protecting Fish against Pathogenic Infection. DNA Cell Biol. 2007, 26, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Patrzykat, A.; Devlin, R.H.; Ackerman, P.A.; Iwama, G.K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Antimicrobial Peptides Protect Coho Salmon FromVibrio Anguillarum Infections. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, A.-C.; Lin, H.-L.; Shiu, Y.-L.; Tyan, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-H. Isolation and Characterization of Antimicrobial Peptides Derived from Bacillus Subtilis E20-Fermented Soybean Meal and Its Use for Preventing Vibrio Infection in Shrimp Aquaculture. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 67, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strøm, M.B.; Rekdal, O.; Svendsen, J.S. Antimicrobial Activity of Short Arginine- and Tryptophan-Rich Peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 2002, 8, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Duperthuy, M.; Vanhove, A.S.; Schmitt, P.; Wai, S.N. Resistance to Antimicrobial Peptides in Vibrios. Antibiotics 2014, 3, 540–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Strain | Litvan ALF-E33–52 | Litvan ALF-F31–50 | Litvan ALF-G35–54 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | |
| Actinobacteria | ||||||
| Corynebacterium stationis CIP 101282 | na | na | 10–20 | 20–40 | 1.25–2.5 | 2.5–5 |
| Microbacterium maritypicum CIP 105733 | 20–40 | 20–40 | 5–10 | 5–10 | 1.25–2.5 | 1.25–2.5 |
| Micrococcus luteus CIP 5345 | na | na | 10–20 | 10–20 | 1.25–2.5 | 2.5–5 |
| Firmicutes | ||||||
| Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 | na | na | na | na | 2.5–5 | 2.5–5 |
| Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25932 | na | na | na | na | 2.5–5 | 2.5–5 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29737 | na | na | na | na | 10–20 | na |
| Staphylococcus aureus SG511 | na | na | na | na | 10–20 | 20–40 |
| Staphylococcus aureus 16003 (MRSA) | na | na | na | na | 20–40 | na |
| Staphylococcus aureus 16006 (MRSA) | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Staphylococcus aureus 17018 (MRSA) | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Staphylococcus aureus 17022 (MRSA) | na | na | na | na | 20–40 | na |
| Proteobacteria | ||||||
| Escherichia coli SBS 363 | na | na | 5–10 | 5–10 | 5–10 | 5–10 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 | na | na | na | na | 10–20 | na |
| Vibrio alginolyticus ATCC 17749 | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Vibrio anguillarum ATCC 19264 | na | na | na | na | 5–10 | na |
| Vibrio fluvialis ENBRAPA-SE | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Vibrio harveyi ATCC 14126 | na | na | na | na | 2.5–5 | 5–10 |
| Vibrio nigripulchritudo CIP 103195 | na | na | 2.5–5 | 5–10 | 2.5–5 | 2.5–5 |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus ENBRAPA-SE | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus IOC 18950 | na | na | na | na | 10–20 | 20–40 |
| Strain | Litvan ALF-E33–52 | Litvan ALF-F31–50 | Litvan ALF-G35–54 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | MFC | MIC | MFC | MIC | MFC | |
| Filamentous fungi | ||||||
| Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 16404 | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Aspergillus niger LAMPB-UFSC DR02 | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Colletotrichum chrysophilum MANE 147 | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Colletotrichum higginsianum MANE 166 | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Fusarium oxysporum MUCL 909 | na | na | na | na | 10–20 | 10–20 |
| Penicillium sp. LIAA-UFSC | na | na | na | na | 20–40 | na |
| Rhizopus sp. LAMPB-UFSC | na | na | na | na | 20–40 | na |
| Trichoderma virens ATCC 9645 | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Yeast | ||||||
| Candida albicans 12A (MDM8) | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Candida krusei ATCC 6258 | na | na | na | na | 5–10 | 5–10 |
| Candida glabrata CCT 0728 | na | na | na | na | na | na |
| Candida parapsilosis ATCC 22019 | na | na | na | na | 20–40 | na |
| Candida tropicalis LMC-UFSC | 10–20 | na | 10–20 | 10–20 | 5–10 | 10–20 |
| Rhodotorula sp. LIAA-UFSC | 5–10 | na | 10–20 | na | 1.25–2.5 | 5–10 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae CAT1 | 20–40 | 20–40 | 20–40 | na | 10–20 | 20–40 |
| Peptide Combination | M. maritypicum | E. coli | Rhodotorula sp. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALF-E33–52 + ALF-F31–50 | 2 | 2 | 0.75 |
| ALF-E33–52 + ALF-G35–54 | 0.63 | 2 | 2 |
| ALF-F31–50 + ALF-G35–54 | 1 | 0.63 | 2 |
| Peptide | IC50 THP-1 | T. cruzi | L. (L.) infantum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Litvan ALF-E33–52 | >80 | na | na |
| Litvan ALF-F31–50 | >80 | na | na |
| Litvan ALF-G35–54 | >80 | na | na |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matos, G.M.; Garcia-Teodoro, B.; Martins, C.P.; Schmitt, P.; Guzmán, F.; de Freitas, A.C.O.; Stoco, P.H.; Ferreira, F.A.; Stadnik, M.J.; Robl, D.; et al. Antimicrobial Spectrum of Activity and Mechanism of Action of Linear Alpha-Helical Peptides Inspired by Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010150
Matos GM, Garcia-Teodoro B, Martins CP, Schmitt P, Guzmán F, de Freitas ACO, Stoco PH, Ferreira FA, Stadnik MJ, Robl D, et al. Antimicrobial Spectrum of Activity and Mechanism of Action of Linear Alpha-Helical Peptides Inspired by Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(1):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010150
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatos, Gabriel Machado, Beatriz Garcia-Teodoro, Camila Pimentel Martins, Paulina Schmitt, Fanny Guzmán, Ana Claudia Oliveira de Freitas, Patricia Hermes Stoco, Fabienne Antunes Ferreira, Marciel João Stadnik, Diogo Robl, and et al. 2023. "Antimicrobial Spectrum of Activity and Mechanism of Action of Linear Alpha-Helical Peptides Inspired by Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors" Biomolecules 13, no. 1: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010150
APA StyleMatos, G. M., Garcia-Teodoro, B., Martins, C. P., Schmitt, P., Guzmán, F., de Freitas, A. C. O., Stoco, P. H., Ferreira, F. A., Stadnik, M. J., Robl, D., Perazzolo, L. M., & Rosa, R. D. (2023). Antimicrobial Spectrum of Activity and Mechanism of Action of Linear Alpha-Helical Peptides Inspired by Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors. Biomolecules, 13(1), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010150