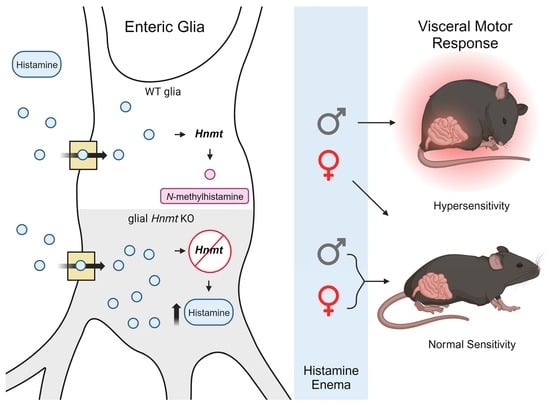
Sexually Dimorphic Effects of Histamine Degradation by Enteric Glial Histamine N-Methyltransferase (HNMT) on Visceral Hypersensitivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Generation of Hnmt Flox Mice
2.4. Whole-Mount Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Visceral Hypersensitivity Measurements
2.7. Ca2+ Imaging
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cellular Distribution of HNMT in the Myenteric Plexus
3.2. Generation of a Cell-Type Specific Hnmt Ablation Model
3.3. Effects of Glial Hnmt Ablation on Intracellular Histamine and ENS Structure
3.4. Glial Hnmt Regulates Visceral Sensitivity in Male Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drossman, D.A.; Hasler, W.L. Rome IV—Functional GI Disorders: Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palsson, O.S.; Sperber, A.D.; Bangdiwala, S.; Whitehead, W.E. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Disorders of Gut-brain Interaction in the United States: Comparison of Two Nationwide Internet Surveys. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palsson, O.S.; Whitehead, W.; Törnblom, H.; Sperber, A.D.; Simren, M. Prevalence of Rome IV Functional Bowel Disorders Among Adults in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1262–1273.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.M.; Poitras, P.; Day, A.G.; Sperber, A.D.; Palsson, O.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Vanner, S.J. The Epidemiology and Impact of Disorders of Gut–Brain Interaction in Canada: Results from the Rome Foundation Global Epidemiologic Study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, S.M.; Linden, D.R. Neuroplasticity and Dysfunction after Gastrointestinal Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Ryu, H.J.; Bhatt, R.R. The Neurobiology of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Wang, B.; Stanghellini, V.; de Giorgio, R.; Cremon, C.; Nardo, G.D.; Trevisani, M.; Campi, B.; Geppetti, P.; Tonini, M.; et al. Mast Cell-Dependent Excitation of Visceral-Nociceptive Sensory Neurons in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.C.; Fantozzi, R. Histamine and Neurogenic Inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, S.; Jutel, M.; Crameri, R.; O’Mahony, L. Histamine and Gut Mucosal Immune Regulation. Allergy 2014, 69, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabauskas, G.; Wu, X.; Gao, J.; Li, J.-Y.; Turgeon, D.K.; Owyang, C. Prostaglandin E2, Produced by Mast Cells in Colon Tissues from Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Contributes to Visceral Hypersensitivity in Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2195–2207.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, G.D.; Shimbori, C.; Reed, D.E.; Yu, Y.; Rabbia, V.; Lu, J.; Jimenez-Vargas, N.; Sessenwein, J.; Lopez-Lopez, C.; Pigrau, M.; et al. Histamine Production by the Gut Microbiota Induces Visceral Hyperalgesia through Histamine 4 Receptor Signaling in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabj1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balemans, D.; Aguilera-Lizarraga, J.; Florens, M.V.; Jain, P.; Denadai-Souza, A.; Viola, M.F.; Alpizar, Y.A.; Merwe, S.V.D.; Berghe, P.V.; Talavera, K.; et al. Histamine-Mediated Potentiation of Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Ankyrin 1 and TRP Vanilloid 4 Signaling in Submucosal Neurons in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 316, G338–G349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, M.M.; Balemans, D.; Wanrooy, S.V.; Dooley, J.; Cibert-Goton, V.; Alpizar, Y.A.; Valdez-Morales, E.E.; Nasser, Y.; Veldhoven, P.P.V.; Vanbrabant, W.; et al. Histamine Receptor H1–Mediated Sensitization of TRPV1 Mediates Visceral Hypersensitivity and Symptoms in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 875–887.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhner, S.; Li, Q.; Vignali, S.; Barbara, G.; Giorgio, R.D.; Stanghellini, V.; Cremon, C.; Zeller, F.; Langer, R.; Daniel, H.; et al. Activation of Human Enteric Neurons by Supernatants of Colonic Biopsy Specimens from Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, S.; Cortes, O.; Thomas, R. Cyproheptadine Use in Children with Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, J.B.; Szabo, A.; Hsu, C.L.; Krier-Burris, R.A.; Schroeder, H.A.; Wang, M.Y.; Carter, R.G.; Velez, T.E.; Aguiniga, L.M.; Brown, J.B.; et al. Histamine Drives Severity of Innate Inflammation via Histamine 4 Receptor in Murine Experimental Colitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, B.; Rezniczek, T.; Seifert, R.; Neumann, D. Proinflammatory Role of the Histamine H4 Receptor in Dextrane Sodium Sulfate-Induced Acute Colitis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 98, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiteren, A.; Man, J.G.D.; Ruyssers, N.E.; Moreels, T.G.; Pelckmans, P.A.; Winter, B.Y.D. Histamine H4 and H1 Receptors Contribute to Postinflammatory Visceral Hypersensitivity. Gut 2014, 63, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, Y.; Nakano, K. Regulation of Histamine Synthesis in Mouse CD4+ and CD8+ T Lymphocytes. Inflamm. Res. 1999, 48, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeberényi, J.B.; Pállinger, É.; Zsinkó, M.; Pós, Z.; Rothe, G.; Orsó, E.; Szeberényi, S.; Schmitz, G.; Falus, A.; László, V. Inhibition of Effects of Endogenously Synthesized Histamine Disturbs In Vitro Human Dendritic Cell Differentiation. Immunol. Lett. 2001, 76, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslinski, C.; Kierska, D. Histamine in C3H/W Mice Carrying Spontaneous Tumors of the Mammary Gland. Agents Actions 1991, 33, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegaev, V.; Nies, A.T.; Porola, P.; Mieliauskaite, D.; Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Urdiales, J.L.; Sillat, T.; Schwelberger, H.G.; Chazot, P.L.; Katebe, M.; et al. Histamine Transport and Metabolism Are Deranged in Salivary Glands in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Finkelman, F.D. Molecular Regulation of Histamine Synthesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeun, D.; Davaatseren, M.; Chung, M.-S. Biogenic Amines in Foods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsenhans, B.; Hunder, G.; Strugala, G.; Schümann, K. Longitudinal Pattern of Enzymatic and Absorptive Functions in the Small Intestine of Rats after Short-Term Exposure to Dietary Cadmium Chloride. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 36, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnedl, W.J.; Enko, D. Histamine Intolerance Originates in the Gut. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas-Basté, O.; Sánchez-Pérez, S.; Veciana-Nogués, M.T.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.d.C. Histamine Intolerance: The Current State of the Art. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafałowska, U.; Waśkiewicz, J.; Albrecht, J. Is Neurotransmitter Histamine Predominantly Inactivated in Astrocytes? Neurosci. Lett. 1987, 80, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Naganuma, F.; Iida, T.; Nakamura, T.; Harada, R.; Mohsen, A.S.; Kasajima, A.; Sasano, H.; Yanai, K. Molecular Mechanism of Histamine Clearance by Primary Human Astrocytes. Glia 2013, 61, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, F.; Yoshikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Iida, T.; Harada, R.; Mohsen, A.S.; Miura, Y.; Yanai, K. Predominant Role of Plasma Membrane Monoamine Transporters in Monoamine Transport in 1321N1, a Human Astrocytoma-derived Cell Line. J. Neurochem. 2014, 129, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.R.; Sawada, K.; Nishibori, M.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X. Two Polymorphic Forms of Human Histamine Methyltransferase Structural, Thermal, and Kinetic Comparisons. Structure 2001, 9, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdan-Pirkmajer, K.; Mavri, J.; Kržan, M. Histamine (Re)Uptake by Astrocytes: An Experimental and Computational Study. J. Mol. Model. 2010, 16, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kržan, M.; Schwartz, J.P. Histamine Transport in Neonatal and Adult Astrocytes. Inflamm. Res. 2006, 55, S36–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClain, J.L.; Mazzotta, E.A.; Maradiaga, N.; Duque-Wilckens, N.; Grants, I.; Robison, A.J.; Christofi, F.L.; Moeser, A.J.; Gulbransen, B.D. Histamine-Dependent Interactions between Mast Cells, Glia, and Neurons Are Altered Following Early-Life Adversity in Mice and Humans. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G655–G668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjeira, C.; Sandgren, K.; Kessaris, N.; Richardson, W.; Potocnik, A.; Berghe, P.V.; Pachnis, V. Glial Cells in the Mouse Enteric Nervous System Can Undergo Neurogenesis in Response to Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3412–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenk, F.; Baron, U.; Rajewsky, K. A Cre—Transgenic Mouse Strain for the Ubiquitous Deletion of LoxP—Flanked Gene Segments Including Deletion in Germ Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 5080–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvalle, N.M.; Dharshika, C.; Morales-Soto, W.; Fried, D.E.; Gaudette, L.; Gulbransen, B.D. Communication between Enteric Neurons, Glia, and Nociceptors Underlies the Effects of Tachykinins on Neuroinflammation. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Dion, S.L.; Kutny, P.M.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, A.W.; Jillette, N.L.; Malhotra, A.; Geurts, A.M.; Chen, Y.-G.; Wang, H. Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Genome Editing in Mice by Zygote Electroporation of Nuclease. Genetics 2015, 200, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbransen, B.D.; Bashashati, M.; Hirota, S.A.; Gui, X.; Roberts, J.A.; MacDonald, J.A.; Muruve, D.A.; McKay, D.M.; Beck, P.L.; Mawe, G.M.; et al. Activation of Neuronal P2X7 Receptor—Pannexin-1 Mediates Death of Enteric Neurons during Colitis. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative CT Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larauche, M.; Gourcerol, G.; Wang, L.; Pambukchian, K.; Brunnhuber, S.; Adelson, D.W.; Rivier, J.; Million, M.; Taché, Y. Cortagine, a CRF1 Agonist, Induces Stresslike Alterations of Colonic Function and Visceral Hypersensitivity in Rodents Primarily through Peripheral Pathways. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G215–G227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubišić, V.; McClain, J.L.; Fried, D.E.; Grants, I.; Rajasekhar, P.; Csizmadia, E.; Ajijola, O.A.; Watson, R.E.; Poole, D.P.; Robson, S.C.; et al. Enteric Glia Modulate Macrophage Phenotype and Visceral Sensitivity Following Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenac, N.; Altier, C.; Motta, J.-P.; d’Aldebert, E.; Galeano, S.; Zamponi, G.W.; Vergnolle, N. Potentiation of TRPV4 Signalling by Histamine and Serotonin: An Important Mechanism for Visceral Hypersensitivity. Gut 2010, 59, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClain, J.L.; Gulbransen, B.D. The Acute Inhibition of Enteric Glial Metabolism with Fluoroacetate Alters Calcium Signaling, Hemichannel Function, and the Expression of Key Proteins. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, N.J.; Magnúsdóttir, E.I.; Jakobsson, J.E.T.; Kestell, G.; Chen, B.N.; Morris, D.; Brookes, S.J.; Lagerström, M.C. CGRPα within the Trpv1-Cre Population Contributes to Visceral Nociception. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 314, G188–G200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Camacho, P.; Lechleiter, J.D.; Herman, B. Measurement of Intracellular Calcium. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1089–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheis, F.; Muller, P.A.; Graves, C.L.; Gabanyi, I.; Kerner, Z.J.; Costa-Borges, D.; Ahrends, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; Mucida, D. Adrenergic Signaling in Muscularis Macrophages Limits Infection-Induced Neuronal Loss. Cell 2020, 180, 64–78.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drokhlyansky, E.; Smillie, C.S.; Wittenberghe, N.V.; Ericsson, M.; Griffin, G.K.; Eraslan, G.; Dionne, D.; Cuoco, M.S.; Goder-Reiser, M.N.; Sharova, T.; et al. The Human and Mouse Enteric Nervous System at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell 2020, 182, 1606–1622.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maquat, L.E. Nonsense-Mediated MRNA Decay in Mammals. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 1773–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.J.; Wood, J.D. Properties of Mechanosensitive Neurons within Auerbach’s Plexus of the Small Intestine of the Cat. Pflügers Arch. 1975, 357, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieling, T.; Cooke, H.J.; Wood, J.D. Histamine Receptors on Submucous Neurons in Guinea Pig Colon. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1993, 264, G74–G80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Wood, J.D. Effects of Prolonged Exposure to Histamine on Guinea Pig Intestinal Neurons. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1992, 37, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.D. Histamine Signals in Enteric Neuroimmune Interactionsa. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 664, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Palmer, J.M.; Wood, J.D. Presynaptic Inhibition Produced by Histamine at Nicotinic Synapses in Enteric Ganglia. Neuroscience 1988, 25, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbara, G.; Stanghellini, V.; Giorgio, R.D.; Cremon, C.; Cottrell, G.S.; Santini, D.; Pasquinelli, G.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Grady, E.F.; Bunnett, N.W.; et al. Activated Mast Cells in Proximity to Colonic Nerves Correlate with Abdominal Pain in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieling, T.; Palmer, J.M.; Cooke, H.J.; Wood, J.D. Neuroimmune Communication in the Submucous Plexus of Guinea Pig Colon after Infection with Trichinella Spiralis. Gastroenterology 1994, 107, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-D.; Wang, X.-Y.; Liu, S.; Qu, M.; Xia, Y.; Needleman, B.J.; Mikami, D.J.; Wood, J.D. Innervation of Enteric Mast Cells by Primary Spinal Afferents in Guinea Pig and Human Small Intestine. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G719–G731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klooker, T.K.; Braak, B.; Koopman, K.E.; Welting, O.; Wouters, M.M.; van der Heide, S.; Schemann, M.; Bischoff, S.C.; van den Wijngaard, R.M.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. The Mast Cell Stabiliser Ketotifen Decreases Visceral Hypersensitivity and Improves Intestinal Symptoms in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gut 2010, 59, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarakeh, J.I.; Torkaman-Boutorabi, A.; Rahimi, A.A.; Ghasri, S.; Nezhad, R.M.A.; Hamzely, A.; Sima, B.K.; Takahashi, K.; Nunoki, K.; Yanai, K. Interaction of Histamine and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in the Formalin Induced Pain Perception in Rats. Biomed. Res. 2011, 32, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.D. Histamine, Mast Cells, and the Enteric Nervous System in the Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Enteritis, and Food Allergies. Gut 2006, 55, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, R.; Naganuma, F.; Nakamura, T.; Miwa, H.; Nakayama-Naono, R.; Matsuzawa, T.; Komatsu, Y.; Sato, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Tatsuoka-Kitano, H.; et al. Contribution of Astrocytic Histamine N-Methyltransferase to Histamine Clearance and Brain Function in Mice. Neuropharmacology 2022, 212, 109065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naganuma, F.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Iida, T.; Miura, Y.; Kárpáti, A.; Matsuzawa, T.; Yanai, A.; Mogi, A.; Mochizuki, T.; et al. Histamine N-Methyltransferase Regulates Aggression and the Sleep-Wake Cycle. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palada, V.; Terzić, J.; Mazzulli, J.; Bwala, G.; Hagenah, J.; Peterlin, B.; Hung, A.Y.; Klein, C.; Krainc, D. Histamine N-Methyltransferase Thr105Ile Polymorphism Is Associated with Parkinson’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 836.e1–836.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Martín, E.; Martínez, C.; Benito-León, J.; Calleja, P.; Díaz-Sánchez, M.; Pisa, D.; Alonso-Navarro, H.; Ayuso-Peralta, L.; Torrecilla, D.; Agúndez, J.A.G.; et al. Histamine-N-methyl Transferase Polymorphism and Risk for Multiple Sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Han, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Association of Histamine N-Methyltransferase Thr105Ile Polymorphism with Parkinson’s Disease and Schizophrenia in Han Chinese: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitkemper, M.; Jarrett, M.; Bond, E.F.; Chang, L. Impact of Sex and Gender on Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2003, 5, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkley, K.J. Sex Differences in Pain. Behav. Brain Sci. 1997, 20, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, L.A.; Heitkemper, M.; Crowell, M.D.; Emmanuel, A.; Halpert, A.; McRoberts, J.A.; Toner, B. Age, Gender, and Women’s Health and the Patient. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1332–1343.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, E.; Ayyadurai, S.; Pohl, C.S.; Costa, S.D.; Li, Y.; Moeser, A.J. Sexual Dimorphism in the Mast Cell Transcriptome and the Pathophysiological Responses to Immunological and Psychological Stress. Biol. Sex Differ. 2016, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarakeh, J.I.; Sakurada, S.; Katsuyama, S.; Kutsuwa, M.; Kuramasu, A.; Lin, Z.Y.; Watanabe, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Yanai, K. Role of Histamine H1 Receptor in Pain Perception: A Study of the Receptor Gene Knockout Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 391, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg-Aiello, P.; Lamberti, C.; Ipponi, A.; Hänninen, J.; Ghelardini, C.; Bartolini, A. Effects of Two Histamine-N-Methyltransferase Inhibitors, SKF 91488 and BW 301 U, in Rodent Antinociception. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1997, 355, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gué, M.; Rio-Lacheze, C.D.; Eutamene, H.; Théodorou, V.; FIioramonti, J.; Buéno, L. Stress-induced Visceral Hypersensitivity to Rectal Distension in Rats: Role of CRF and Mast Cells. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 1997, 9, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado-Bedmar, M.; Keita, Å.V. Potential Neuro-Immune Therapeutic Targets in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820910630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabisiak, A.; Włodarczyk, J.; Fabisiak, N.; Storr, M.; Fichna, J. Targeting Histamine Receptors in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Critical Appraisal. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmeier, A.; Francke, K.; Chen, B.; Dunford, P.J.; Greenspan, A.J.; Xia, Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, B.; Thurmond, R.L. The Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonist, JNJ 39758979, Is Effective in Reducing Histamine-Induced Pruritus in a Randomized Clinical Study in Healthy Subjects. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.K.; Irvine, E.J. Ketotifen Treatment of Active Colitis in Patients with 5-Aminosalicylate Intolerance. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1998, 12, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, B.; Ramos, L.; Martínez, C.; Guilarte, M.; González-Castro, A.M.; Alonso-Cotoner, C.; Pigrau, M.; Torres, I.; Rodiño-Janeiro, B.K.; Salvo-Romero, E.; et al. Downregulation of Mucosal Mast Cell Activation and Immune Response in Diarrhoea-irritable Bowel Syndrome by Oral Disodium Cromoglycate: A Pilot Study. UEG J. 2017, 5, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, J. Ebastine in Allergic Rhinitis and Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria. Allergy 2008, 63, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmeier, A.P.; Barnathan, E.S.; O’Brien, C.; Chen, B.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, B.; Loza, M.J.; Silkoff, P.E.; Ge, M.; Thurmond, R.L. A Phase 2a Study of Toreforant, a Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonist, in Eosinophilic Asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 121, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurmond, R.L.; Greenspan, A.; Radziszewski, W.; Xu, X.L.; Miao, Y.; Chen, B.; Ge, T.; Zhou, B.; Baker, D.G.; Pavlova, D.; et al. Toreforant, A Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonist, in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Methotrexate Therapy: Results of 2 Phase II Studies. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, R.; Stanghellini, V.; Cremon, C.; Gargano, L.; Cogliandro, R.F.; Giorgio, R.D.; Bartesaghi, G.; Canovi, B.; Barbara, G. Effect of Mesalazine on Mucosal Immune Biomarkers in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Proof-of-concept Study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.-M.; Li, S.; Ding, L.; Xiang, S.-H.; Zhu, H.-T.; Yu, J.-H.; Xu, G.-Q. Effectiveness of Mesalazine to Treat Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Medicine 2019, 98, e16297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Primer Set | Sequence |
|---|---|
| 5′gRNA (−) [5′-(N)20 NGG-3′] | crRNA79: 5′-AAGAGGCCAACATGAAAGTG AGG-3′ |
| 5′ loxP ssODN donor template | O613: 5′-CTTCGCCTGTGTTTTCAGGCACTCTAATAAGAGAAACAGAAAT AAATAAAGAAGAGCCACAGACATGACCTCACGGATCCATAACTTCGTATA GCATACATTATACGAAGTTATGAATTCTTTCATGTTGGCCTCTTGTCCATTCATC CATTCTCTTTTGCTTATCAATAGACTTGATAGGAAGAATTGGC-3′ |
| 5′ LoxP genotyping primers | O716 Fwd: 5′-GCCTGTGTTTTCAGGCACTC-3′ O714 Rev: 5′-CACCTCCGCCTACACTCAGA-3′ |
| 3′ gRNA (−) [5′-(N)20 NGG-3′] | crRNA80: 5′-TAGTGAAGGCTAAAGTCCCAAGG-3′ |
| 3′ loxP ssODN donor template | O614: 5′-GCCACTTTACTTTTGTAAAATATCAAGTTATAAATACTAGCAAC ATCATTCAACTCAAATTCATTGCTCTCAATATATGTATAGGCCTTGGGAATTCA TAACTTCGTATAGCATACATTATACGAAGTTATAAGCTTGACTTTAGCCTTC ACTATAATTTGTAGGATAGGTAGAACTGAGAA-3′ |
| 3′ LoxP genotyping primers | O779 Fwd: 5′-AGATTCTGAGTGTAGGCGGA-3′ O577 Rev: 5′-TTTCCTTCCCTCACATGGGC-3′ |
| Antibody | Source | Catalog No. | Resource ID | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Antibodies | ||||
| chicken anti-GFAP | Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA | ab4674 | AB_304558 | 1:1000 |
| chicken anti-S100b | Synaptic Systems, Göttingen, Germany | 287 006 | AB_2713986 | 1:1000 |
| rabbit anti-H1R | Alomone, Jerusalem, Israel | AHR-001 | AB_2039915 | 1:200 |
| rabbit anti-Histamine | Millipore Sigma, Burlington, MA, USA | H7403 | AB_260077 | 1:200 |
| rabbit anti-HNMT | Atlas Antibodies, Bromma, Sweden | HPA035481 | AB_10672094 | 1:400 |
| biotin mouse anti-HuC/D | Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA | A21272 | AB_2535822 | 1:200 |
| mouse anti-Peripherin | Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX, USA | sc-377093 | AB_2923264 | 1:100 |
| Secondary Antibodies | ||||
| goat anti-chicken Dylight 405 | Jackson Labs, West Grove, PA, USA | 103-475-155 | AB_2337389 | 1:400 |
| donkey anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 488 | Jackson Labs, West Grove, PA, USA | 711-545-152 | AB_2313584 | 1:400 |
| goat anti-mouse IgG2a Alexa Fluor 488 | Jackson Labs, West Grove, PA, USA | 115-545-206 | AB_2338855 | 1:400 |
| goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 594 | Jackson Labs, West Grove, PA, USA | 115-585-207 | AB_2338887 | 1:400 |
| donkey anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 647 | Jackson Labs, West Grove, PA, USA | 711-605-152 | AB_2492288 | 1:400 |
| Primer Set | Forward 3′-5′ | Reverse 5′-3′ |
|---|---|---|
| mRPS6 | GAAGCGCAAGTCTGTTCGTG | GTCCTGGGCTTCTTACCTTCT |
| mDao | ATCTGCTGTGACGACTCCTC | TGGCCAAAGTCAGATTCTTGG |
| mHnmt Ex1 | AGCTGCTGAGAACCCAATATG | CACTGGTGTTCCGTGGAATTA |
| mHnmt Ex2–4 | AGCTTCCGGGCATAATAGCAA | CAGCACTTGGCTCAACAACT |
| mHnmt Ex3 | AGATTCTGAGTGTAGGCGGAG | ACTTCGGTGGCTCTTCTTCT |
| mNat2 | GGATGGTGTCTCCAGGTTAAT | CATGCCACTGCTGTACTTATT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McClain, J.L.; Morales-Soto, W.; Gonzales, J.; Parmar, V.; Demireva, E.Y.; Gulbransen, B.D. Sexually Dimorphic Effects of Histamine Degradation by Enteric Glial Histamine N-Methyltransferase (HNMT) on Visceral Hypersensitivity. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111651
McClain JL, Morales-Soto W, Gonzales J, Parmar V, Demireva EY, Gulbransen BD. Sexually Dimorphic Effects of Histamine Degradation by Enteric Glial Histamine N-Methyltransferase (HNMT) on Visceral Hypersensitivity. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(11):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111651
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcClain, Jonathon L., Wilmarie Morales-Soto, Jacques Gonzales, Visha Parmar, Elena Y. Demireva, and Brian D. Gulbransen. 2023. "Sexually Dimorphic Effects of Histamine Degradation by Enteric Glial Histamine N-Methyltransferase (HNMT) on Visceral Hypersensitivity" Biomolecules 13, no. 11: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111651
APA StyleMcClain, J. L., Morales-Soto, W., Gonzales, J., Parmar, V., Demireva, E. Y., & Gulbransen, B. D. (2023). Sexually Dimorphic Effects of Histamine Degradation by Enteric Glial Histamine N-Methyltransferase (HNMT) on Visceral Hypersensitivity. Biomolecules, 13(11), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13111651