Mice Mutated in the First Fibronectin Domain of Adhesion Molecule L1 Show Brain Malformations and Behavioral Abnormalities
Abstract
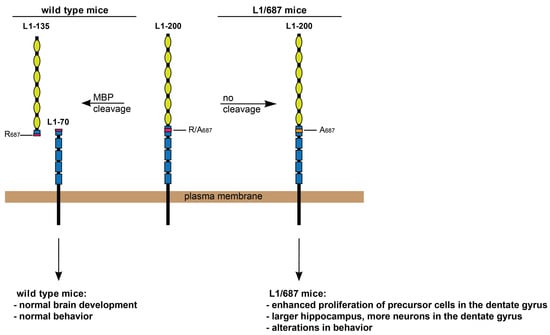
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Quantitative Morphological Analysis
2.5. Behavior
2.5.1. Open Field and Elevated Plus Maze
2.5.2. Social Interaction
2.5.3. Rotarod, Beam Walking and Pole Test
2.5.4. Circadian Activity
2.5.5. Marble Burying
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Analysis
3.1.1. Body Weight, Muscle Function and Motor Coordination
3.1.2. Exploratory Behavior in the Open Field and Elevated Plus Maze
3.1.3. Social Interaction
3.1.4. Marble Burying Test
3.1.5. Circadian Activity
3.1.6. Brain Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maness, P.F.; Schachner, M. Neural recognition molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily: Signaling transducers of axon guidance and neuronal migration. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sytnyk, V.; Leshchyns’ka, I.; Schachner, M. Neural cell adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily regulate synapse formation, maintenance, and function. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanova, I.I.; Lutz, D. Functional diversity of neuronal cell adhesion and recognition molecule L1CAM through proteolytic cleavage. Cells 2022, 11, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maretzky, T.; Schulte, M.; Ludwig, A.; Rose-John, S.; Blobel, C.; Hartmann, D.; Altevogt, P.; Saftig, P.; Reiss, K. L1 is sequentially processed by two differently activated metalloproteases and presenilin/gamma-secretase and regulates neural cell adhesion, cell migration, and neurite outgrowth. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 9040–9053. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pollerberg, G.E.; Thelen, K.; Theiss, M.O.; Hochlehnert, B.C. The role of cell adhesion molecules for navigating axons: Density matters. Mech. Dev. 2013, 130, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stallcup, W.B.; Beasley, L. Involvement of the nerve growth factor-inducible large external glycoprotein (NILE) in neurite fasciculation in primary cultures of rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagenaur, C.; Lemmon, V. An L1-like molecule, the 8D9 antigen, is a potent substrate for neurite extension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7753–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haspel, J.; Friedlander, D.R.; Ivgy-May, N.; Chickramane, S.; Roonprapunt, C.; Chen, S.; Schachner, M.; Grumet, M. Critical and optimal Ig domains for promotion of neurite outgrowth by L1/Ng-CAM. J. Neurobiol. 2000, 42, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheis, M.; Diestel, S.; Schmitz, B. The role of cytoplasmic serine residues of the cell adhesion molecule L1 in neurite outgrowth, endocytosis, and cell migration. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 27, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, Y.; Sung, M.; Chavez, E.; Wei, E.; Pak, K.K.; Housley, G.D.; Bodmer, D.; Ryan, A.F. Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 modulates type I but not type II inner ear spiral ganglion neurite outgrowth in an in vitro alternate choice assay. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 51, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronska-Peski, M.; Schachner, M.; Hebert, J.M. L1cam curbs the differentiation of adult-born hippocampal neurons. Stem Cell Res. 2020, 48, 101999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonosaki, M.; Itoh, K.; Umekage, M.; Kishimoto, T.; Yaoi, T.; Lemmon, V.P.; Fushiki, S. L1cam is crucial for cell locomotion and terminal translocation of the Soma in radial migration during murine corticogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidle, U.H.; Eggle, D.; Klostermann, S. L1-CAM as a target for treatment of cancer with monoclonal antibodies. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 4919–4931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valente, P.; Lignani, G.; Medrihan, L.; Bosco, F.; Contestabile, A.; Lippiello, P.; Ferrea, E.; Schachner, M.; Benfenati, F.; Giovedi, S.; et al. Cell adhesion molecule L1 contributes to neuronal excitability regulating the function of voltage-gated Na+ channels. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1878–1891. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Godenschwege, T.A.; Kristiansen, L.V.; Uthaman, S.B.; Hortsch, M.; Murphey, R.K. A conserved role for Drosophila Neuroglian and human L1-CAM in central-synapse formation. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silletti, S.; Mei, F.; Sheppard, D.; Montgomery, A.M. Plasmin-sensitive dibasic sequences in the third fibronectin-like domain of L1-cell adhesion molecule (CAM) facilitate homomultimerization and concomitant integrin recruitment. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 1485–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Luiselli, G.; Ogagan, C.; Dai, H.; Chiu, L.; Carroll, R.S.; Johnson, M.D. Increased plasmin-mediated proteolysis of L1CAM in a mouse model of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2010528118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, D.; Loers, G.; Kleene, R.; Oezen, I.; Kataria, H.; Katagihallimath, N.; Braren, I.; Harauz, G.; Schachner, M. Myelin basic protein cleaves cell adhesion molecule L1 and promotes neuritogenesis and cell survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13503–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedle, S.; Kiefel, H.; Gast, D.; Bondong, S.; Wolterink, S.; Gutwein, P.; Altevogt, P. Nuclear translocation and signalling of L1-CAM in human carcinoma cells requires ADAM10 and presenilin/gamma-secretase activity. Biochem. J. 2009, 420, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, M.; Altevogt, P. L1CAM malfunction in the nervous system and human carcinomas. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Barao, S.; Laga, M.; Bockstael, K.; Borgers, M.; Gijsen, H.; Annaert, W.; Moechars, D.; Mercken, M.; Gevaert, K.; et al. The neural cell adhesion molecules L1 and CHL1 are cleaved by BACE1 protease in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 25927–25940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Watanabe, H.; Lomoio, S.; Tesco, G. Spatiotemporal processing of neural cell adhesion molecules 1 and 2 by BACE1 in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linneberg, C.; Toft, C.L.F.; Kjaer-Sorensen, K.; Laursen, L.S. L1cam-mediated developmental processes of the nervous system are differentially regulated by proteolytic processing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechtersheimer, S.; Gutwein, P.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Stoeck, A.; Oleszewski, M.; Riedle, S.; Postina, R.; Fahrenholz, F.; Fogel, M.; Lemmon, V.; et al. Ectodomain shedding of L1 adhesion molecule promotes cell migration by autocrine binding to integrins. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto-Miyai, K.; Ninomiya, A.; Yamasaki, H.; Tamura, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Shiosaka, S. NMDA-dependent proteolysis of presynaptic adhesion molecule L1 in the hippocampus by neuropsin. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7727–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barman, B.; Thakur, M.K. Neuropsin promotes hippocampal synaptogenesis by regulating the expression and cleavage of L1CAM. J. Cell Sci. 2024, 137, jcs261422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loers, G.; Kleene, R.; Bork, U.; Schachner, M. The interactions of the 70 kDa fragment of cell adhesion molecule L1 with topoisomerase 1, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) flavoprotein 2 are involved in gene expression and neuronal L1-dependent functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2097. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kleene, R.; Loers, G.; Schachner, M. The KDET Motif in the intracellular domain of the cell adhesion molecule L1 interacts with several nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitochondrial proteins essential for neuronal functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, K.; Kleene, R.; Henis, M.; Braren, I.; Kataria, H.; Sharaf, A.; Loers, G.; Schachner, M.; Lutz, D. A fragment of adhesion molecule L1 binds to nuclear receptors to regulate synaptic plasticity and motor coordination. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 7164–7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, K.; Kleene, R.; Braren, I.; Loers, G.; Lutz, D.; Schachner, M. A fragment of adhesion molecule L1 is imported into mitochondria, and regulates mitochondrial metabolism and trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs210500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, D.; Kataria, H.; Kleene, R.; Loers, G.; Chaudhary, H.; Guseva, D.; Wu, B.; Jakovcevski, I.; Schachner, M. Myelin basic protein cleaves cell adhesion molecule L1 and improves regeneration after injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3360–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, V.; De Angelis, E.; Kenwrick, S.; Rougon, G. Cis and trans interactions of L1 with neuropilin-1 control axonal responses to semaphorin 3A. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6348–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loers, G.; Kleene, R.; Girbes Minguez, M.; Schachner, M. The cell adhesion molecule L1 interacts with methyl CpG binding protein 2 via its intracellular domain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duczmal, A.; Schollhammer, S.; Katich, S.; Ebeling, O.; Schwartz-Albiez, R.; Altevogt, P. The L1 adhesion molecule supports alpha v beta 3-mediated migration of human tumor cells and activated T lymphocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 232, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, T.C.; Mintz, C.D.; Benson, D.L.; Salton, S.R. Functional binding interaction identified between the axonal CAM L1 and members of the ERM family. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 157, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.Q.; Bennett, V. Ankyrin binding activity shared by the neurofascin/L1/NrCAM family of nervous system cell adhesion molecules. J. Biol Chem. 1994, 269, 27163–27166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Maness, P.F. Perisomatic GABAergic innervation in prefrontal cortex is regulated by ankyrin interaction with the L1 cell adhesion molecule. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 2684–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Baba, K.; Huang, L.; Wei, K.T.; Okano, K.; Hosokawa, Y.; Inagaki, N. Mechanosensitive axon outgrowth mediated by L1-laminin clutch interface. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 3566–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.; Gallo, N.B.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.R.; Van Aelst, L. Axo-axonic innervation of neocortical pyramidal neurons by GABAergic chandelier cells requires ankyrinG-associated L1CAM. Neuron 2019, 102, 358–372.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortsch, M.; Nagaraj, K.; Mualla, R. The L1 family of cell adhesion molecules: A sickening number of mutations and protein functions. Adv. Neurobiol. 2014, 8, 195–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stumpel, C.; Vos, Y.J. L1 Syndrome. In GeneReviews((R)); Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Varagur, K.; Sanka, S.A.; Strahle, J.M. Syndromic hydrocephalus. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 33, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahme, M.; Bartsch, U.; Martini, R.; Anliker, B.; Schachner, M.; Mantei, N. Disruption of the mouse L1 gene leads to malformations of the nervous system. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loers, G.; Appel, D.; Lutz, D.; Congiu, L.; Kleene, R.; Hermans-Borgmeyer, I.; Schafer, M.K.E.; Schachner, M. Amelioration of the abnormal phenotype of a new L1 syndrome mouse mutation with L1 mimetics. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolf, B.; Kutsche, M.; Bartsch, U. Severe hydrocephalus in L1-deficient mice. Brain Res. 2001, 891, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rünker, A.E.; Bartsch, U.; Nave, K.A.; Schachner, M. The C264Y missense mutation in the extracellular domain of L1 impairs protein trafficking in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyanenko, G.P.; Tsai, A.Y.; Maness, P.F. Abnormalities in neuronal process extension, hippocampal development, and the ventricular system of L1 knockout mice. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 4907–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.R.; Taylor, J.S.; Scott, L.B.; Guillery, R.W.; Soriano, P.; Furley, A.J. Errors in corticospinal axon guidance in mice lacking the neural cell adhesion molecule L1. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransen, E.; D’Hooge, R.; Van Camp, G.; Verhoye, M.; Sijbers, J.; Reyniers, E.; Soriano, P.; Kamiguchi, H.; Willemsen, R.; Koekkoek, S.K.; et al. L1 knockout mice show dilated ventricles, vermis hypoplasia and impaired exploration patterns. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1998, 7, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Sun, X.Z.; Cui, C.; Sakata-Haga, H.; Sawada, K.; Ye, C.; Fukui, Y. Spatial learning and expression of neural cell adhesion molecule L1 in rats X-irradiated prenatally. J. Med. Investig. 2007, 54, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauce, B.; Wass, C.; Netrakanti, M.; Saylor, J.; Schachner, M.; Matzel, L.D. Heterozygous L1-deficient mice express an autism-like phenotype. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 292, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfer, D.P.; Mohajeri, H.M.; Lipp, H.P.; Schachner, M. Increased flexibility and selectivity in spatial learning of transgenic mice ectopically expressing the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 in astrocytes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleene, R.; Lutz, D.; Loers, G.; Bork, U.; Borgmeyer, U.; Hermans-Borgmeyer, I.; Schachner, M. Revisiting the proteolytic processing of cell adhesion molecule L1. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 1102–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congiu, L.; Granato, V.; Loers, G.; Kleene, R.; Schachner, M. Mitochondrial and neuronal dysfunctions in L1 mutant mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loers, G.; Kleene, R.; Granato, V.; Bork, U.; Schachner, M. Interaction of L1CAM with LC3 is required for L1-dependent neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. J. Gene Med. 2010, 12, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congiu, L.; Granato, V.; Jakovcevski, I.; Kleene, R.; Fernandes, L.; Freitag, S.; Kneussel, M.; Schachner, M.; Loers, G. Mice mutated in the third fibronectin domain of L1 show enhanced hippocampal neuronal cell death, astrogliosis and alterations in behavior. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitag, S.; Schachner, M.; Morellini, F. Behavioral alterations in mice deficient for the extracellular matrix glycoprotein tenascin-R. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 145, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koitmae, A.; Karsten, Y.; Li, X.; Morellini, F.; Rune, G.M.; Bender, R.A. GPER1 deficiency causes sex-specific dysregulation of hippocampal plasticity and cognitive function. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 258, e220204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carola, V.; D’Olimpio, F.; Brunamonti, E.; Mangia, F.; Renzi, P. Evaluation of the elevated plus-maze and open-field tests for the assessment of anxiety-related behaviour in inbred mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 134, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, N.W.; Miya, T.S. A note on a simple apparatus for detecting neurological deficit in rats and mice. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 1957, 46, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.J.; Roberts, D.J. The quantiative measurement of motor inco-ordination in naive mice using an acelerating rotarod. J. Pharm Pharmacol. 1968, 20, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, A.; Mishra, B.; Kurschat, N.; Schulze, C.; Bian, S.; Loers, G.; Irintchev, A.; Schachner, M. Polysialic acid glycomimetics promote myelination and functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury in mice. Brain 2009, 132, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angoa-Perez, M.; Kane, M.J.; Briggs, D.I.; Francescutti, D.M.; Kuhn, D.M. Marble burying and nestlet shredding as tests of repetitive, compulsive-like behaviors in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 24, e50978. [Google Scholar]
- De Boer, S.F.; Koolhaas, J.M. Defensive burying in rodents: Ethology, neurobiology and psychopharmacology. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 463, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, E.; Onay, H.; Atik, T.; Akgun, B.; Cogulu, O.; Ozkinay, F. Clinical and genetic features of L1 syndrome patients: Definition of two novel mutations. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 172, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolin, C.; Boaretto, F.; Barbon, G.; Salviati, L.; Lapi, E.; Divizia, M.T.; Garavelli, L.; Occhi, G.; Vazza, G.; Mostacciuolo, M.L. Novel mutations in the L1CAM gene support the complexity of L1 syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2010, 294, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, R.; Ley-Martos, M.; Gutierrez, G.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, F.; Arroyo, D.; Mora-Lopez, F. Three cases with L1 syndrome and two novel mutations in the L1CAM gene. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, G.; Huang, T.T.; Giffard, R.G. Age-related defects in sensorimotor activity, spatial learning, and memory in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2010, 22, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graber, T.G.; Ferguson-Stegall, L.; Kim, J.H.; Thompson, L.V. C57BL/6 neuromuscular healthspan scoring system. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, M.; Wevers, M.; Pisters, M.; Pfundt, R.; Vos, Y.; Nievelstein, R.J.; Stumpel, C. A novel mutation in L1CAM causes a mild form of L1 syndrome: A case report. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.; Yap, T.Y.; Henden, L.; Bahlo, M.; Gardner, A.; Kalscheuer, V.M.; Haan, E.; Christie, L.; Hackett, A.; Gecz, J. Identical by descent L1CAM mutation in two apparently unrelated families with intellectual disability without L1 syndrome. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 58, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, M.; Carromeu, C.; Kwon, O.; Muotri, A.; Schachner, M. The L1 adhesion molecule normalizes neuritogenesis in Rett syndrome-derived neural precursor cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cai, S.; Guo, B.; Wu, F.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Ni, L.; et al. Whole-transcriptome analysis of serum L1CAM-captured extracellular vesicles reveals neural and glycosylation changes in autism spectrum disorder. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 1274–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, T.P.; Zhou, F.; Sai, L.Y.; Chen, H.; Lin, S.L.; Schachner, M. Duloxetine ameliorates valproic acid-induced hyperactivity, anxiety-like behavior, and social interaction deficits in zebrafish. Autism. Res. 2022, 15, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.S.; Kyriakopoulos, M.; James, A.; Marwedel, S.; Borsay, C.; Gutierrez, A.A.; Blakemore, A.I.; Need, A.C. Hemizygous mutations in L1CAM in two unrelated male probands with childhood onset psychosis. Psychiatr. Genet. 2020, 30, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Academic Press: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, J.; Das, G.D. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1965, 124, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G.; Wiskott, L.; Gage, F.H. Functional significance of adult neurogenesis. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, L.J.; Fusi, S.; Hen, R. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian hippocampus: Why the dentate gyrus? Learn Mem. 2013, 20, 710–729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.S.; Ferrante, S.C.; Cameron, H.A. Late maturation of adult-born neurons in the temporal dentate gyrus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.S.; Soumier, A.; Brewer, M.; Pickel, J.; Cameron, H.A. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis buffers stress responses and depressive behaviour. Nature 2011, 476, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, G.; Dai, P.; Kong, X. Analysis of L1CAM gene mutation and imaging appearance in three Chinese families with L1 syndrome: Three case reports. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2022, 10, e2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Yao, Q.; Xu, B.; Yang, M.; Jiang, J.; Xiang, Q.; Xiao, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. A novel splicing variation in L1CAM is responsible for recurrent fetal hydrocephalus. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2023, 11, e2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liao, H.; Wang, Q.; Xie, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, S. L1 syndrome prenatal diagnosis supplemented by functional analysis of one L1CAM gene missense variant. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidsey, B.A.; Baldwin, E.E.; Toydemir, R.; Ahles, L.; Hanson, H.; Stevenson, D.A. L1CAM whole gene deletion in a child with L1 syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164a, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulding, H.D.; Martuza, R.L.; Rabkin, S.D. Clinical mutations in the L1 neural cell adhesion molecule affect cell-surface expression. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 5696–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christaller, W.A.; Vos, Y.; Gebre-Medhin, S.; Hofstra, R.M.; Schäfer, M.K. L1 syndrome diagnosis complemented with functional analysis of L1CAM variants located to the two N-terminal Ig-like domains. Clin. Genet. 2017, 91, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, M.; Diestel, S.; Bozon, M.; Keglowich, L.; Drouot, N.; Bouche, E.; Frebourg, T.; Minz, M.; Saugier-Veber, P.; Castellani, V.; et al. Pathomechanistic characterization of two exonic L1CAM variants located in trans in an obligate carrier of X-linked hydrocephalus. Neurogenetics 2012, 13, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, M.K.E.; Nam, Y.C.; Moumen, A.; Keglowich, L.; Bouche, E.; Kuffner, M.; Bock, H.H.; Rathjen, F.G.; Raoul, C.; Frotscher, M. L1 syndrome mutations impair neuronal L1 function at different levels by divergent mechanisms. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 40, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, E.; Watkins, A.; Schäfer, M.; Brümmendorf, T.; Kenwrick, S. Disease-associated mutations in L1 CAM interfere with ligand interactions and cell-surface expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, E.; MacFarlane, J.; Du, J.S.; Yeo, G.; Hicks, R.; Rathjen, F.G.; Kenwrick, S.; Brummendorf, T. Pathological missense mutations of neural cell adhesion molecule L1 affect homophilic and heterophilic binding activities. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4744–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakeman, L.B.; Chen, Y.; Lucin, K.M.; McTigue, D.M. Mice lacking L1 cell adhesion molecule have deficits in locomotion and exhibit enhanced corticospinal tract sprouting following mild contusion injury to the spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 1997–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Dolado, M.; Cuadrado, A.; Navarro-Yubero, C.; Sonderegger, P.; Furley, A.J.; Bernal, J.; Munoz, A. Regulation of the L1 cell adhesion molecule by thyroid hormone in the developing brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 16, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, K.; Brackenbury, R.; Akeson, R.A. Induction of L1 mRNA in PC12 cells by NGF is modulated by cell-cell contact and does not require the high-affinity NGF receptor. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 2504–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, B.W.; Murphy, K.E.; Maness, P.F. Molecular mechanisms of L1 and NCAM adhesion molecules in synaptic pruning, plasticity, and stabilization. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 625340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, P.; Lisman, J. Structure, function, and plasticity of hippocampal dentate gyrus microcircuits. Front. Neural Circuits 2014, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, L.; Comijs, H.C.; van der Graaf, Y.; Knoops, A.J.; Penninx, B.W.; Geerlings, M.I. Depression, hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis, and hippocampal and entorhinal cortex volumes--the SMART Medea study. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Neylan, T.C.; Mueller, S.G.; Lenoci, M.; Truran, D.; Marmar, C.R.; Weiner, M.W.; Schuff, N. Magnetic resonance imaging of hippocampal subfields in posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.S.; Sahay, A.; Hen, R. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to reduce anxiety and depression-like behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacol 2015, 40, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.B.; Park, S.C. The entorhinal cortex and adult neurogenesis in major depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzello, M.; Ramirez, S.; Treves, A.; Lee, I.; Scharfman, H.; Stark, C.; Knierim, J.J.; Rangel, L.M. Assessments of dentate gyrus function: Discoveries and debates. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 24, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.D.; Doan, N.B.; Imura, T.; Bush, T.G.; Sofroniew, M.V. GFAP-expressing progenitors are the principal source of constitutive neurogenesis in adult mouse forebrain. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overall, R.W.; Walker, T.L.; Fischer, T.J.; Brandt, M.D.; Kempermann, G. Different mechanisms must be considered to explain the increase in hippocampal neural precursor cell proliferation by physical activity. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saaltink, D.J.; Vreugdenhil, E. Stress, glucocorticoid receptors, and adult neurogenesis: A balance between excitation and inhibition? Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2499–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.; Cao, F.; Nguyen, R.; Joshi, K.; Aqrabawi, A.J.; Xia, S.; Cortez, M.A.; Snead, O.C., 3rd; Kim, J.C.; Jia, Z. Activation of entorhinal cortical projections to the dentate gyrus underlies social memory retrieval. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2379–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Jiang, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, L.; Yang, Q.; Bai, Z. Neural circuits for social interactions: From microcircuits to input-output circuits. Front. Neural Circuits 2021, 15, 768294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Granato, V.; Congiu, L.; Jakovcevski, I.; Kleene, R.; Schwindenhammer, B.; Fernandes, L.; Freitag, S.; Schachner, M.; Loers, G. Mice Mutated in the First Fibronectin Domain of Adhesion Molecule L1 Show Brain Malformations and Behavioral Abnormalities. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040468
Granato V, Congiu L, Jakovcevski I, Kleene R, Schwindenhammer B, Fernandes L, Freitag S, Schachner M, Loers G. Mice Mutated in the First Fibronectin Domain of Adhesion Molecule L1 Show Brain Malformations and Behavioral Abnormalities. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(4):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040468
Chicago/Turabian StyleGranato, Viviana, Ludovica Congiu, Igor Jakovcevski, Ralf Kleene, Benjamin Schwindenhammer, Luciana Fernandes, Sandra Freitag, Melitta Schachner, and Gabriele Loers. 2024. "Mice Mutated in the First Fibronectin Domain of Adhesion Molecule L1 Show Brain Malformations and Behavioral Abnormalities" Biomolecules 14, no. 4: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040468
APA StyleGranato, V., Congiu, L., Jakovcevski, I., Kleene, R., Schwindenhammer, B., Fernandes, L., Freitag, S., Schachner, M., & Loers, G. (2024). Mice Mutated in the First Fibronectin Domain of Adhesion Molecule L1 Show Brain Malformations and Behavioral Abnormalities. Biomolecules, 14(4), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14040468